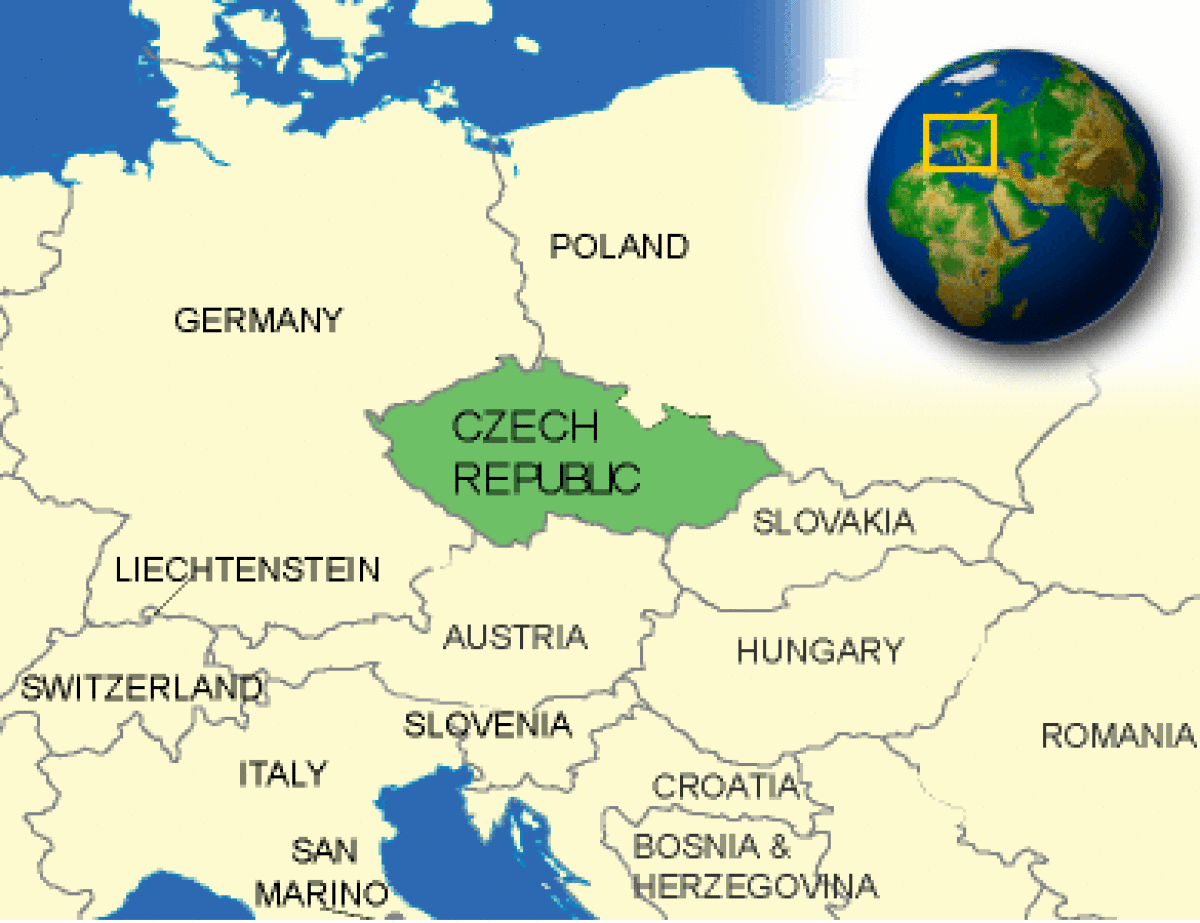
Where is Czech Republic located?
What countries border Czech Republic?
Czech Republic Weather
What is the current weather in Czech Republic?
Czech Republic Facts and Culture
What is Czech Republic famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Professionals are respected. The long tradition of highly industrialized nation formed a skilled nation of manual workers. This brought a... More
- Family: Parents generally work outside the home, but women are also responsible for the household and children. Grandparents often help with... More
- Personal Apperance: European fashions and formal dress is common on the streets, at work and in shops, Two-piece suit for women and... More
- Recreation: The country's most popular sport is soccer. Huge crowds go to watch the games at the Letná stadium in Prague.... More
- Diet: Unfortunately the high fat eating culture survived into the modern low physical activity way of life. Tasty meals close to... More
- Food and Recipes: Dinner is the main Czechs meal. About 70 percent of the population eat meals while watching TV, reading a... More
- Visiting: Friends visit quite frequently for small talk with coffee and drinks. Most first-time visitors are invited for a more formal... More
- Dating: Young people usually socialize in their sphere of interest. Following European trends, most men are married by the age of... More
Czech Republic Facts
What is the capital of Czech Republic?
| Capital | Prague |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | koruny (CZK) |
| Total Area |
30,451 Square Miles 78,867 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Europe, between Germany, Poland, Slovakia, and Austria |
| Language | Czech |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $33,200.00 (USD) |
Czech Republic Demographics
What is the population of Czech Republic?
| Ethnic Groups | Czech 81.2%, Moravian 13.2%, Slovak 3.1%, Polish 0.6%, German 0.5%, Silesian 0.4%, Roma 0.3%, Hungarian 0.2%, other 0.5% |
| Languages | Czech belongs to the Slavic group of languages. The central European nation is ethnically quite homogeneous. The only noticeable minority is Roms (Gypsies), who are bilingual. Many Czechs speak German, French, Russian or English as a second language, depending on their generation. Younger Czechs generally use English as a second language. The Czech Republic came into existence first in 1918, and then on 1 January 1993 the division of the Czech and Slovak Republics. In their language days, months, season and lots of other words are wrote with non-capitalized first letters. |
| Nationality Noun | Czech(s) |
| Population | 10,702,498 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.15% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | PRAGUE (capital) 1.276 million |
| Urban Population | 73.400000 |
Czech Republic Government
What type of government does Czech Republic have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Petr PAVEL (since 9 March 2023) head of government: Prime Minister Petr FIALA (since 17 December 2021); First Deputy Prime Minister Vit RAKUSAN (since 17 December 2021), Deputy Prime Ministers Marian JURECKA, Ivan BARTOS, Vlastimil VALEK (all since 17 December 2021) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (limited to 2 consecutive terms); elections last held on 13 to 14 January 2023 with a second round held from 27 to 28 January 2023; next election to be by January 2028; prime minister appointed by the president for a 4-year term election results: 2023: Petr PAVEL elected in the second round; percent of vote in the first round - Petr PAVEL (independent) 35.4%, Andrej BABIS (ANO) 35%, Danuse NERUDOVA (Mayors and Independents) 13.9%, Pavel FISCHER (independent) 6.8%; percent of vote in the second round - Petr PAVEL 58.3%, Andrej BABIS 41.6% 2018: Milos ZEMAN reelected president in the second round; percent of vote - Milos ZEMAN (SPO) 51.4%, Jiri DRAHOS (independent) 48.6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Czechia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Czechoslovak Founding Day, 28 October (1918) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1960; latest ratified 16 December 1992, effective 1 January 1993 amendments: passage requires at least three-fifths concurrence of members present in both houses of Parliament; amended several times, last in 2021 |
| Independence | 1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia); note - although 1 January is the day the Czech Republic came into being, the Czechs commemorate 28 October 1918, the day the former Czechoslovakia declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, as their independence day |
Czech Republic Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Prague Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Czech Republic Geography
What environmental issues does Czech Republic have?
| Overview |
The Czech Republic lies in the heartland of Central Europe. The Czech Republic is almost entirely surrounded by mountains. To the north and northeast are the Sudetes Mountains, which include the Krkonose Mountains and Mt. Snazka, the highest point in the country. To the southeast along the Czech-Slovak border are the Carpathian Mountains. The Sumava Mountains in the southwest form the border with Germany. These mountain ranges protect the country from the extremes of western and northern European winters. The main geographic subdivisions are the Czech lands of Bohemia to the west and Moravia to the east. In addition, a section of what was once Silesia occupies the north-central part of the country. The Czech Republic covers a total area of 30,332 square miles (78,864 square kilometers). The terrain is typically hilly with wide, rolling plains. Bohemia has more low mountains and plateaus than Moravia, which tends to be flatter. At 20,368 square miles (52,764 square kilometers), Bohemia is twice the size of Moravia and includes the capital city of Prague. Prague lies on the Vltava River (Moldau in German), which flows northward and joins the Labe (Elbe) north of Prague. Prague, with an altitude of 800 feet, lies at the center of the gently rolling Bohemian Plain. |
| Climate | Prague has a humid, continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. Temperatures range from January's average daily high of 32°F (0°C) and low of 22°F (-4°C) to July's average daily high of 76°F (24.5°C) and low of 56°F (14°) Average annual rainfall is about 30 inches, distributed throughout the year. Humidity averages about 80 percent. During the winter months, high humidity makes the winter cold penetrating. Light to moderately heavy snow can be expected during January and February. Pollution can be severe during the winter months because of soft-burning coal and frequent temperature inversions. Reduced hours of daylight from November through March combined with smog and raw weather create a gloomy atmosphere. In fact, from mid-October when Daylight Savings Time ends until early April when it begins again, Czech law requires drivers to drive with their headlights on at all times. |
| Border Countries | Austria 362 km, Germany 646 km, Poland 658 km, Slovakia 215 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air and water pollution in areas of northwest Bohemia and in northern Moravia around Ostrava present health risks; acid rain damaging forests; efforts to bring industry up to EU code should improve domestic pollution |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Bohemia in the west consists of rolling plains, hills, and plateaus surrounded by low mountains; Moravia in the east consists of very hilly country |
Czech Republic Economy
How big is the Czech Republic economy?
| Economic Overview |
Czechia is a prosperous market economy that boasts one of the highest GDP growth rates and lowest unemployment levels in the EU, but its dependence on exports makes economic growth vulnerable to contractions in external demand. Czechia’s exports comprise some 80% of GDP and largely consist of automobiles, the country’s single largest industry. Czechia acceded to the EU in 2004 but has yet to join the euro-zone. While the flexible koruna helps Czechia weather external shocks, it was one of the world’s strongest performing currencies in 2017, appreciating approximately 16% relative to the US dollar after the central bank (Czech National Bank - CNB) ended its cap on the currency’s value in early April 2017, which it had maintained since November 2013. The CNB hiked rates in August and November 2017 - the first rate changes in nine years - to address rising inflationary pressures brought by strong economic growth and a tight labor market. Since coming to power in 2014, the new government has undertaken some reforms to try to reduce corruption, attract investment, and improve social welfare programs, which could help increase the government’s revenues and improve living conditions for Czechs. The government introduced in December 2016 an online tax reporting system intended to reduce tax evasion and increase revenues. The government also plans to remove labor market rigidities to improve the business climate, bring procurement procedures in line with EU best practices, and boost wages. The country's low unemployment rate has led to steady increases in salaries, and the government is facing pressure from businesses to allow greater migration of qualified workers, at least from Ukraine and neighboring Central European countries. Long-term challenges include dealing with a rapidly aging population, a shortage of skilled workers, a lagging education system, funding an unsustainable pension and health care system, and diversifying away from manufacturing and toward a more high-tech, services-based, knowledge economy. |
| Industries | motor vehicles, metallurgy, machinery and equipment, glass, armaments |
| Currency Name and Code | koruny (CZK) |
| Export Partners | Germany 32.4%, Slovakia 9%, Poland 5.8%, UK 5.3%, France 5.1%, Austria 4.1% |
| Import Partners | Germany 30%, Poland 9%, China 8.3%, Slovakia 6.6%, Netherlands 5%, Austria 4.1% |
Czech Republic News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Czech Republic?
Source: Google News
Czech Republic Travel Information
What makes Czech Republic a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Czech Republic is centrally located in the heart of Europe. It has a democratic parliamentary system of government and a well-developed economy. The Czech Republic is a member of NATO and the European Union. Tourist facilities in the capital city of Prague are at the level of those found in most European capitals, although travelers can expect varying standards outside of Prague.
Crime
The Czech Republic generally has a low crime rate. However, pick-pocketing is a problem, especially in major tourist areas in Prague. Travelers are at a particularly high risk when:On public transportation (trains, trams or the Prague metro);
In the city center;
In crowded areas; and
Eating at outdoor cafes.
As criminals may operate in groups, and could conceivably be armed with simple weapons, victims should avoid direct confrontation with potential criminals. Pick-pocketing rings in the Czech Republic tend to be professional and highly organized.
Keep a copy of your passport biodata page (and any pages with valid visas) in a safe place separate from the passport itself; this can help you to apply for a new passport if yours is lost or stolen. Under Czech law, you must verify your identity by presenting a travel document, a residence permit card, or an identity card issued by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, if asked by Czech police. If you are a tourist, this means that you are expected to carry your passport with you. Please ensure the security of your passport while traveling to prevent incidents of pick-pocketing or theft. If you cannot produce your passport upon request, an immediate on-the-spot fine may be levied. Laws against traffic violations by pedestrians, such as jaywalking, are also frequently enforced in the Prague city center, and a fine will also be applied.
Incidents of violent crime, while still relatively infrequent, are possible. U.S. citizens have reported incidents of sexual assault in recent years. You should be aware of the reported use of rohypnol and other “date rape” drugs in the Czech Republic. Use caution when accepting open drinks at bars or clubs, and don’t leave your drinks unattended.
You should only change money at banks or legitimate money kiosks. An offer to change money by an unknown person on the street is most likely a scam. Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) are widely available throughout major cities in the Czech Republic. Most Czech ATMs offer instructions in multiple languages and allow access to U.S. bank accounts.
The press has reported that criminal organizations are illegally obtaining users’ ATM card numbers and PIN codes by electronically “skimming” the information from victims’ cards at ATMs. This activity has reportedly occurred at ATMs in public areas--even bank lobbies covered by security cameras. Visitors requiring ATM services should attempt to use machines at more secure or heavily traveled and monitored locations, such as commercial banks, large hotels, and the airport.
U.S. citizens have reported being overcharged by merchants on credit card transactions. While visiting the Czech Republic, you should carefully verify that charges are correct before signing for purchases, keep all receipts, and check your credit card accounts online to ensure that you are billed properly for credit card payments.
Auto thefts and break-ins are common in the Czech Republic, especially in major cities. To avoid vehicle-related crimes, you should use parking garages and anti-theft devices. You should also not leave valuables in plain sight inside vehicles, as this increases the possibility of theft.
Czech bars and dance clubs are generally safe. However, as with many cities, you may be approached to purchase illicit drugs; this is against the law in the Czech Republic. Be mindful that security at nightclubs could respond more forcefully than at similar venues in the United States. Be aware that casinos and gaming establishments are government-regulated, but some have been affiliated with, or attracted the interest of, organized crime.
Taxis: You should be alert to the potential for substantial overcharging by taxis, particularly in areas frequented by tourists. Some taxi drivers charge unsuspecting foreigners two or three times the standard rate. To minimize the possibility of being overcharged, you should obtain a price estimate in advance and ensure that the driver is using the meter.
The Embassy has also received limited reports of passengers being assaulted or robbed by taxi drivers after hailing a random cab on the street. We strongly recommend that you call for a taxi, rather than hail one on the street. If calling is not possible, visitors should obtain a taxi at one of the clearly marked “Fair Place” taxi stands, which are regulated by the Prague city government. All taxis should be clearly marked.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in the Czech Republic, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. The Czech Republic has a zero-tolerance policy for drinking and driving, and this is strictly enforced. Criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States; for instance, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, by purchasing them you may also be breaking local law. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in the Czech Republic, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are traveling.If you are arrested in the Czech Republic, authorities are required to notify the U.S. Embassy in Prague of your arrest. If you are concerned the Embassy may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy.
Languages
Czech belongs to the Slavic group of languages. The central European nation is ethnically quite homogeneous. The only noticeable minority is Roms (Gypsies), who are bilingual. Many Czechs speak German, French, Russian or English as a second language, depending on their generation. Younger Czechs generally use English as a second language. The Czech Republic came into existence first in 1918, and then on 1 January 1993 the division of the Czech and Slovak Republics. In their language days, months, season and lots of other words are wrote with non-capitalized first letters.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Prague has adequate Western-style medical clinics with English-speaking doctors and dentists. However, the Czech medical system is organized differently from the medical system in the United States. Even though central emergency rooms exist in most hospitals, patients are often sent to the facility that treats their specific medical condition (i.e., broken noses are sent to the Ear, Nose, and Throat specialist rather than to the General Practitioner). There are family practices in the Czech Republic that function like those in the United States, but they are located mostly in larger cities.All major hospitals accept credit cards or cash as a method of payment. Private specialists usually expect cash payment for health services, though some private facilities accept credit cards as well. Administrative staff at the majority of Czech medical facilities may not speak English. Hospitalization in the Czech Republic is much more liberal than in the United States; conditions that would be treated on an outpatient basis in the United States are often treated on an inpatient basis in the Czech Republic. Ambulance services are on par with U.S. standards. Response time is generally less than 15 minutes. Ambulance companies generally expect payment at the time of service. Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost thousands of dollars or more. Please note that because euthanasia is not permitted under Czech law, U.S. living wills stipulating no exceptional interventions to prolong life cannot be honored in the Czech Republic.
Tick-Borne Illness: If you plan to camp or hike in long grass or woodlands from March through October, you run the risk of both tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease. You should take precautions to prevent tick bites. While there is no vaccine for Lyme disease, you may obtain a vaccine for tick-borne encephalitis in a three-shot series. The first two shots are given 2-4 weeks apart, and the last shot 6 -12 months after the second.
Safety and Security
The Czech Republic remains largely free of terrorist incidents. However, like other countries in the Schengen Zone, the Czech Republic’s open borders with its neighbors allow for the possibility of terrorist groups entering/exiting the country undetected.Civil disorder is rare in the Czech Republic, although strikes and demonstrations may occur. You should be vigilant in protecting your security, bearing in mind that even demonstrations intended to be peaceful may turn violent. Avoid street demonstrations whenever possible.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in the Czech Republic, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning the Czech Republic is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Road fatalities in the Czech Republic in 2011 were at their lowest level since 1947, according to Czech safety experts, but caution should be exercised while driving. Driving speeds on European highways are higher than in the United States, and drivers are expected to stay in the right lane except when passing. Highways in the Czech Republic generally meet European standards; however, on two-lane roads, drivers should be prepared to encounter uneven surfaces, irregular lane markings, and sign placements that are not clear. Streets in towns are not always in good condition. You should pay special attention to driving on cobblestone and among streetcars in historic city centers, especially in wet or icy conditions. Traffic lights are placed before the intersection, so be aware of where you stop at signaled intersections. Speed limits are 50 km/h in towns, 90 km/h outside of towns, and 130 km/h on highways, but drivers routinely flout the limits. An International Driving Permit (IDP), available from AAA (in the United States only), must accompany a U.S. driver’s license; failure to have the IDP with a valid license may result in denial of an insurance claim after an accident.
Persons driving into the Czech Republic should be aware that a toll sticker is required to drive legally on major highways. Signs stating this requirement are posted near the border, but are easy to miss. The stickers are available at most gas stations. The fine for failing to display a toll sticker is assessed on the spot.
Czech law requires that drivers have their headlights on at all times when driving in the Czech Republic. The law also requires that all private cars, including those of foreign visitors, carry each of the following items: fluorescent green high visibility safety jacket, first aid kit, spare pair of prescription glasses kept in the glove compartment (if necessary), warning triangle, and complete set of spare bulbs.
Czech law allows for breathalyzer testing of drivers stopped by local law enforcement officials for any reason. There is a zero-tolerance policy for alcohol and driving; driving with any trace of detected alcohol, however slight, is illegal and those caught usually face immediate fines and possible criminal proceedings.
U.S. citizens have reported instances of motorists stopped on the shoulders of highways waving at drivers as if they needed assistance. Some drivers have reported being pressured into giving money to the person who has purportedly broken down, and it was unclear in those situations if the motorist was truly in need or trying to scam those who stopped to offer assistance.
For specific information concerning Czech requirements for driver’s permits, vehicle inspection, road tax and mandatory insurance, please contact the Czech Tourist Authority offices in New York by telephone at (212) 288-0830 or by email. Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Also, we suggest that you visit the website of the Czech Republic’s national tourist office and the Ministry of Transport.
