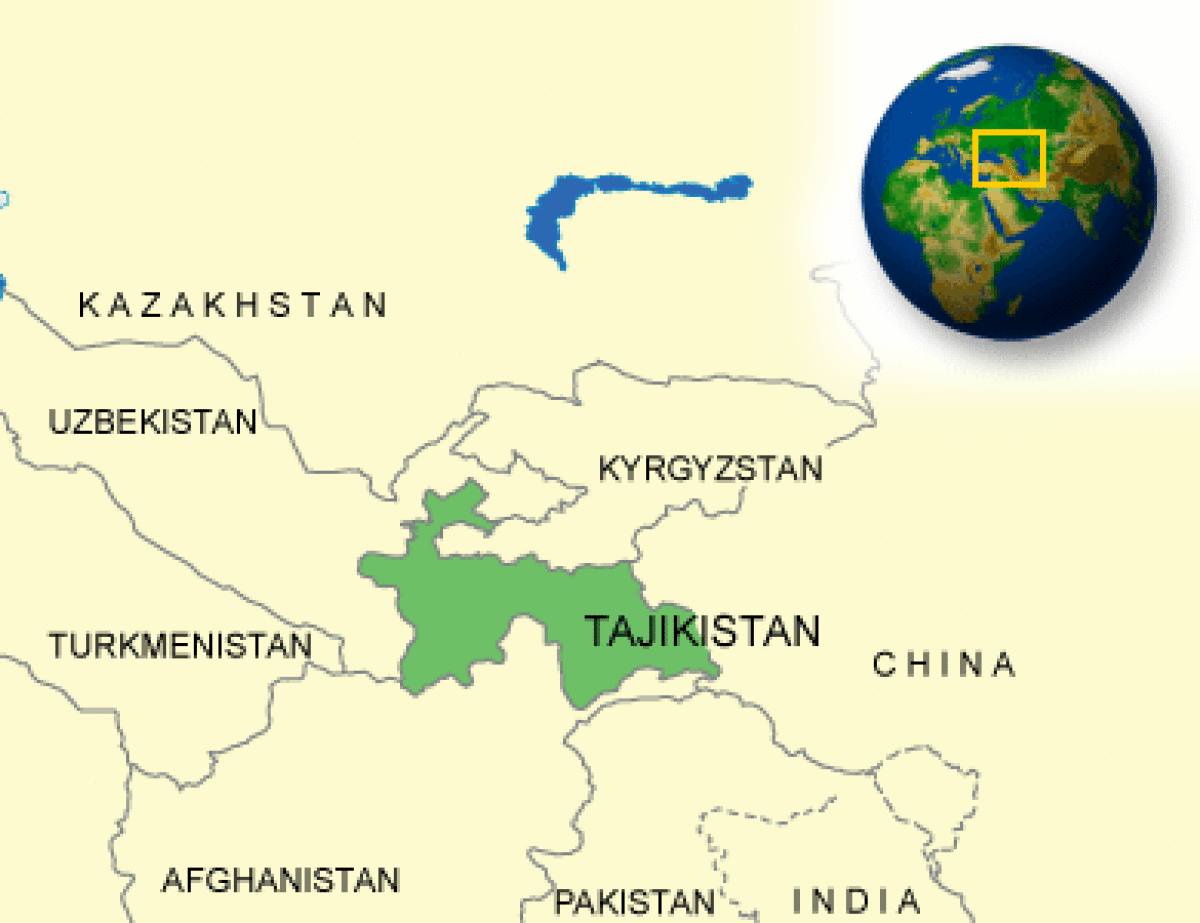
Where is Tajikistan located?
What countries border Tajikistan?
Tajikistan Weather
What is the current weather in Tajikistan?
Tajikistan Facts and Culture
What is Tajikistan famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Tajikistan is a country with a rich and diverse cultural heritage that reflects its location at the crossroads of different... More
- Family: Women's roles vary depending upon if they are Muslim or Soviet influenced. Soviet influenced women participate in all aspects of... More
- Personal Apperance: The traditional clothing in Tajikistan is known as the "Atlas" and is made of silk, cotton or wool. It is... More
- Recreation: Tajikistan offers a wide range of recreational activities for both locals and tourists to enjoy. The country's diverse geography and... More
- Diet: Tajikistan's traditional cuisine is based on the country's agricultural heritage and the availability of local ingredients. The diet is generally... More
- Food and Recipes: Tajikistan has several eating customs that reflect the country's cultural heritage and traditions. Here are some examples: Hosting Guests: In Tajik culture,... More
- Visiting: In Tajikistan, visiting is an important social activity, and there are several social norms related to visiting that reflect the... More
- Dating: Dating customs in Tajikistan are shaped by the country's traditional values and Islamic heritage. Here are some examples: Arranged Marriages: In Tajik... More
Tajikistan Facts
What is the capital of Tajikistan?
| Capital | Dushanbe |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Somoni (TJS)somon |
| Total Area |
55,251 Square Miles 143,100 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Asia, west of China, south of Kyrgyzstan |
| Language | Tajik (official), Russian widely used in government and business |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $2,800.00 (USD) |
Tajikistan Demographics
What is the population of Tajikistan?
| Ethnic Groups | Tajik 64.9%, Uzbek 25%, Russian 3.5% (declining because of emigration), other 6.6% |
| Nationality Noun | Tajikistani(s) |
| Population | 8,873,669 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.79% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | DUSHANBE (capital) 739,000 |
| Urban Population | 26.500000 |
Tajikistan Government
What type of government does Tajikistan have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Emomali RAHMON (since 6 November 1994; head of state and Supreme Assembly Chairman since 19 November 1992) head of government: Prime Minister Qohir RASULZODA (since 23 November 2013) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the Supreme Assembly elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 7-year term (two-term limit); however, as the "Leader of the Nation" President RAHMON can run an unlimited number of times; election last held on 11 October 2020 (next to be held in 2027); prime minister appointed by the president election results: 2020: Emomali RAHMON reelected president; percent of vote - Emomali RAHMON (PDPT) 92.1%, Rustam LATIFZODA (APT) 3.1%, and other 4.8% 2013: Emomali RAHMOND reelected president; percent of vote - Emomali RAHMOND (PDPT) 84%, Ismoil TALBAKOV CPT) 5%, other 11% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Tajikistan dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years or 3 years of continuous residence prior to application |
| National Holiday | Independence Day (or National Day), 9 September (1991) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 6 November 1994 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by at least one third of the total membership of both houses of the Supreme Assembly; adoption of any amendment requires a referendum, which includes approval of the president or approval by at least two-thirds majority of the Assembly of Representatives; passage in a referendum requires participation of an absolute majority of eligible voters and an absolute majority of votes; constitutional articles, including Tajikistan’s form of government, its territory, and its democratic nature, cannot be amended; amended 1999, 2003, 2016 |
| Independence | 9 September 1991 (from the Soviet Union) |
Tajikistan Video
YouTube: FTD Facts 10 Surprising Facts About Tajikistan
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Tajikistan Geography
What environmental issues does Tajikistan have?
| Overview |
The Republic of Tajikistan gained its independence during the breakup of the USSR and is part of former Soviet Central Asia nestled between Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan to the north and west, Afghanistan to the south, and China to the east. Tajikistan is home to some of the highest mountains in the world, including parts of the Kunlun, Himalayan, Tienshan, and Pamir Ranges. Ninety-three percent of the country is mountainous with altitudes ranging from 1,000 feet to 25,000 feet, with fully 50% of Tajikistan's territory at elevations above 10,000 feet. Earthquakes of varying degrees are frequent. The massive mountain ranges are cut by hundreds of scenic canyons and gorges through which streams finger their way into the larger river valleys where the majority of the country's population lives and works. The principal rivers of central Asia, the Amu-Darya and the Syr-Darya, both flow through Tajikistan, fed by melting snow in the mountains of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. |
| Climate |
There are four distinct seasons in Tajikistan gorgeous springs, with soft breezes and flowers blooming everywhere; hot, dry summers; pleasant autumns with warm days and cool evenings, and in the low altitude city of Dushanbe, relatively mild winters. Snowfall rapidly increases with altitude. The climate of the mountainous Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (GBAO), which occupies the eastern half of Tajikistan, is more extreme. The mountainous east receives 90% of Tajikistan's yearly precipitation, and its average annual temperature is 49°F; in Dushanbe it's 65 °F. |
| Border Countries | Afghanistan 1,206 km, China 414 km, Kyrgyzstan 870 km, Uzbekistan 1,161 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | inadequate sanitation facilities; increasing levels of soil salinity; industrial pollution; excessive pesticides |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Environmental Modification, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Pamir and Alay Mountains dominate landscape; western Fergana Valley in north, Kofarnihon and Vakhsh Valleys in southwest |
Tajikistan Economy
How big is the Tajikistan economy?
| Economic Overview |
Tajikistan is one of the poorest countries in the region, with an economy heavily reliant on agriculture and remittances from migrant workers. Agriculture accounts for around 23% of Tajikistan's GDP, with cotton, fruits, and vegetables being the main crops. However, the sector faces challenges such as water scarcity and limited access to modern technology and equipment. The industry sector, which includes mining, manufacturing, and construction, accounts for around 20% of GDP, but it is relatively underdeveloped. Remittances from Tajik migrant workers, primarily in Russia, make up around 30% of the country's GDP. The reliance on remittances leaves the country vulnerable to economic shocks, as seen during the global financial crisis in 2008-2009 and the COVID-19 pandemic. Tajikistan's natural resources, such as aluminum, gold, and silver, present opportunities for economic growth. The country has attracted foreign investment in mining, with Chinese and Russian companies being the major players in the sector. However, the government's control of the economy and weak legal and regulatory frameworks create barriers to foreign investment. Tajikistan's infrastructure is underdeveloped, with limited access to electricity and poor road networks. The government has made efforts to improve infrastructure, including the construction of hydropower plants and the rehabilitation of roads. However, funding constraints and corruption continue to hinder progress. The Tajikistan economy faces several challenges, including high levels of poverty, limited economic diversification, weak governance, and security risks. The country's economic growth has been slow, averaging around 7% over the past decade. Despite these challenges, Tajikistan has the potential to diversify its economy and reduce its reliance on remittances by developing its natural resources, improving infrastructure, and attracting foreign investment. |
| Industries | aluminum, zinc, lead, chemicals and fertilizers, cement, vegetable oil, metal-cutting machine tools, refrigerators and freezers |
| Currency Name and Code | Somoni (TJS)somon |
| Export Partners | Netherlands 29.4%, Turkey 16.1%, Russia 11.9%, Uzbekistan 9.9%, Switzerland 9.4%, Hungary 5.4%, Latvia 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Russia 23.1%, Uzbekistan 18.6%, Ukraine 11.4%, Kazakhstan 10.1%, Turkmenistan 6.6%, Azerbaijan 5.8%, India 4.5% |
Tajikistan News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Tajikistan?
Source: Google News
Tajikistan Travel Information
What makes Tajikistan a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Tajikistan is a small land-locked country that borders Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, China, and Afghanistan and is home to some of the highest mountains in the world. Tajikistan is the poorest of the former Soviet republics in Central Asia. It is a nominally constitutional, democratic, and secular republic, dominated by President Emomali Rahmon who has been in power since 1992. Tourist facilities are undeveloped and many goods and services usually available in other countries are unavailable.
Crime
The level of criminal activity in Dushanbe is moderate to high. Of significant concern is the inability of Tajikistan’s law enforcement entities to provide adequate and immediate assistance. Lack of manpower, low salaries, and inadequate training all contribute to a lack of professionalism among law enforcement entities. Tajikistan’s struggling economy and high unemployment have resulted in incidents of street crime, including pick-pocketing, muggings, and armed robberies. Alcohol-related incidents such as drunk driving are common. Criminals are not deterred by the risk of confrontation and tend to operate in groups of two or more to decrease their chances of arrest. When crimes do occur, they can be violent in nature. Additionally, the lack of a free media and infrequent government outreach through the media do not provide the average citizen with current and accurate information to make informed decisions about safety. Government statistics are typically inaccurate because many crimes are not reported to law enforcement organizations. Often police refuse to open minor or routine cases that seem too difficult to resolve.Crimes of opportunity can occur against anyone, and you are reminded to be careful and cautious in your own personal security, whether within the city limits of Dushanbe or in the more remote areas of the country. You should be aware that danger increases after dark, and to use caution when traveling alone or on foot after dark. The U.S. Embassy encourages visitors to travel in pairs and to notify colleagues of their whereabouts when not working, especially during evening hours. It is wise to refrain from wearing expensive jewelry or anything that may indicate that you have any amount of wealth. Travelers are also encouraged to carry a copy of their passport (separate from their wallets) to speed up issuance of a new passport in case of theft.
Don't buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Tajikistan, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don't have your passport with you. In some places it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Tajikistan, your passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It's very important to know what's legal and what's not in the countries where you are going.Persons violating Tajik laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Tajikistan are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
The Government of Tajikistan may enforce strict customs regulations. Customs authorities may subject all items, including travel souvenirs, imported into or exported from Tajikistan to a high level of scrutiny. The export of antiques, precious stones and metals, and cultural valuables requires special permission. The number of items that can be exported may be limited. It is illegal to export or possess unprocessed stones and metals and jewelry without a hallmark (mark of authenticity). Even if travelers have a receipt confirming legal purchase of such items at a store in Tajikistan, the items must be declared upon departure. Failure to abide by Tajik customs laws and regulations may result in heavy fines, arrest, or imprisonment.
There are also currency restrictions. You must fill out a Customs Declaration Form upon arrival in Tajikistan, have it stamped by Tajik customs officials at the port of entry and retain the form until your departure to demonstrate that you are not leaving Tajikistan with more money than you brought into the country. Please contact the Embassy of the Republic of Tajikistan in the United States for specific information about customs requirements.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
The quality of Tajikistan’s medical infrastructure is significantly below Western standards, with severe shortages of basic medical supplies, including disposable needles, anesthetics, prescription drugs, and antibiotics. Many trained medical personnel left the country during or after the civil war. Elderly travelers and those with pre-existing health problems may be at particular risk due to inadequate medical facilities.Significant disease outbreaks are possible due to population shifts and a decline in some immunization coverage among the general population. There have been outbreaks of polio in the southwest areas of the country near the borders with Afghanistan and Uzbekistan, including the capital city Dushanbe; typhoid outbreaks in the Dushanbe area and in the south of the country; an outbreak of Congo Crimea hemorrhagic fever to the west of Dushanbe; and the risk of contracting malaria, cholera, and water-borne illnesses is high. Throughout Central Asia, infection rates of various forms of hepatitis and tuberculosis (including drug-resistant strains) are on the rise. Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Tajikistan.
It is advisable to drink only bottled or thoroughly boiled water while in Tajikistan.
The government of Tajikistan requires all foreign citizens who remain in the country for more than 90 days to present a medical certificate from a medical facility or to submit to an HIV test in Tajikistan if they are already in Tajikistan without such a certificate (with the exception of persons applying for diplomatic, official, investor, and humanitarian types of visas).
Safety and Security
Supporters of terrorist groups such as the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan (IMU), the Islamic Jihad Union (IJU), al-Qaida, and the Eastern Turkistan Islamic Movement as well as anti-Western, anti-Semitic extremist organizations such as Hizb’ut-Tahrir have expressed anti-U.S. sentiments and may attempt to target U.S. government or private interests in the region, including in Tajikistan.Terrorist attacks involving the use of suicide bombers have occurred in Tajikistan and in neighboring Uzbekistan. Minor explosions occasionally occur in Dushanbe and rarely cause serious injuries or damage. From time to time, the Tajik government conducts counter-terrorist operations in areas outside Dushanbe. In July 2012, Tajik military forces conducted operations in Khorog, the capital of the Gorno-Badakshan region in eastern Tajikistan, causing instability and disruptions for visitors and the local population. Although there have been rare instances of criminal or terrorist groups specifically targeting U.S. citizens or foreigners, you should take care to abide by government-imposed restricted areas. Additionally, insurgent activity in neighboring Afghanistan could also affect the security situation along the border and in Tajikistan. You should exercise extra caution if traveling in border provinces.
Because of increased security at official U.S. facilities, terrorists may seek softer civilian targets such as residential areas, clubs and restaurants, places of worship, hotels, outdoor recreation events, and other venues. The limited number of facilities catering to Westerners in Tajikistan presents a heightened risk. You should also avoid demonstrations and large crowds. Demonstrations and mobs are rare in Tajikistan since the 1992–1997 civil war, and police reaction to such behavior is unpredictable.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Tajikistan, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Tajikistan is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in any particular location or circumstance.Travel to, from, and within Tajikistan is difficult and unreliable. Neighboring countries may unilaterally close borders and some borders are poorly delineated. Armed police or military checkpoints can make road travel outside Dushanbe more difficult. Crossing the Tajik-Uzbek border, in particular, has been known to present difficulties for drivers operating vehicles with non-Tajik government-issued plates. Road travel should be undertaken only in daylight hours and on routes known to the traveler or a reliable escort. Those traveling to Gorno-Badakhshan by car should do so only during daylight hours. The roads traverse mountainous terrain along the Afghan border that is difficult to navigate, even in daylight hours. If you are driving, be vigilant because pedestrians often tend to cross the street at inappropriate places or walk along the highway without paying attention to vehicular traffic. Also, erratic driving and car accidents are common. Traffic police are posted at stationary positions and checkpoints and along major roads. They are notorious for paying little if any attention to traffic safety issues, but rather for randomly pulling over cars and exacting bribes. In Dushanbe, expensive cars and those with government license plates routinely speed past police, sometimes on the wrong side of the road and through stoplights, while other cars are flagged down for “document checks.”
Public transportation vehicles in the city are often overcrowded and not always safe. Bus services between major cities have been severely disrupted by border closures and should not be relied upon. The State Traffic Inspectorate (GAI, or in Tajiki, BDA), which has checkpoints in many cities and at regular intervals along all highways outside the city, frequently stops vehicles for inspection of both the vehicle and the driver’s documents. The government will not register vehicles with darkly tinted windows. During the winter months, the potential dangers when traveling outside Dushanbe in the mountainous areas of the country are heightened. Every year, accidents and casualties occur on Tajikistan’s mountain roads and passes, often when drivers ignore warnings not to travel over a closed mountain pass. Avalanches are a common occurrence in Tajikistan’s mountains during the winter months. The tunnel bypassing the Anzob Pass is still not complete and you should try to obtain information regarding tunnel conditions before traveling via this route. The alternate Anzob Pass road is not maintained. Please exercise caution and limit winter travel to Tajikistan’s mountain regions.
In certain parts of the country, including the Vakhsh and Rasht valleys and along the Afghan-Tajik border, land mines and cluster munitions form an additional hazard. If an area has land mine warning signs, or is marked off with red and white plastic tape, heed the warning and do not venture off the road. In all cases, do not pick up or handle anything that looks like unexploded munitions.
Emergency phone numbers in Tajikistan include: fire – 01, police – 02, ambulance – 03, state traffic control (GAI) duty officer – 235-4545.
