Where is Antigua and Barbuda located?
What countries border Antigua and Barbuda?
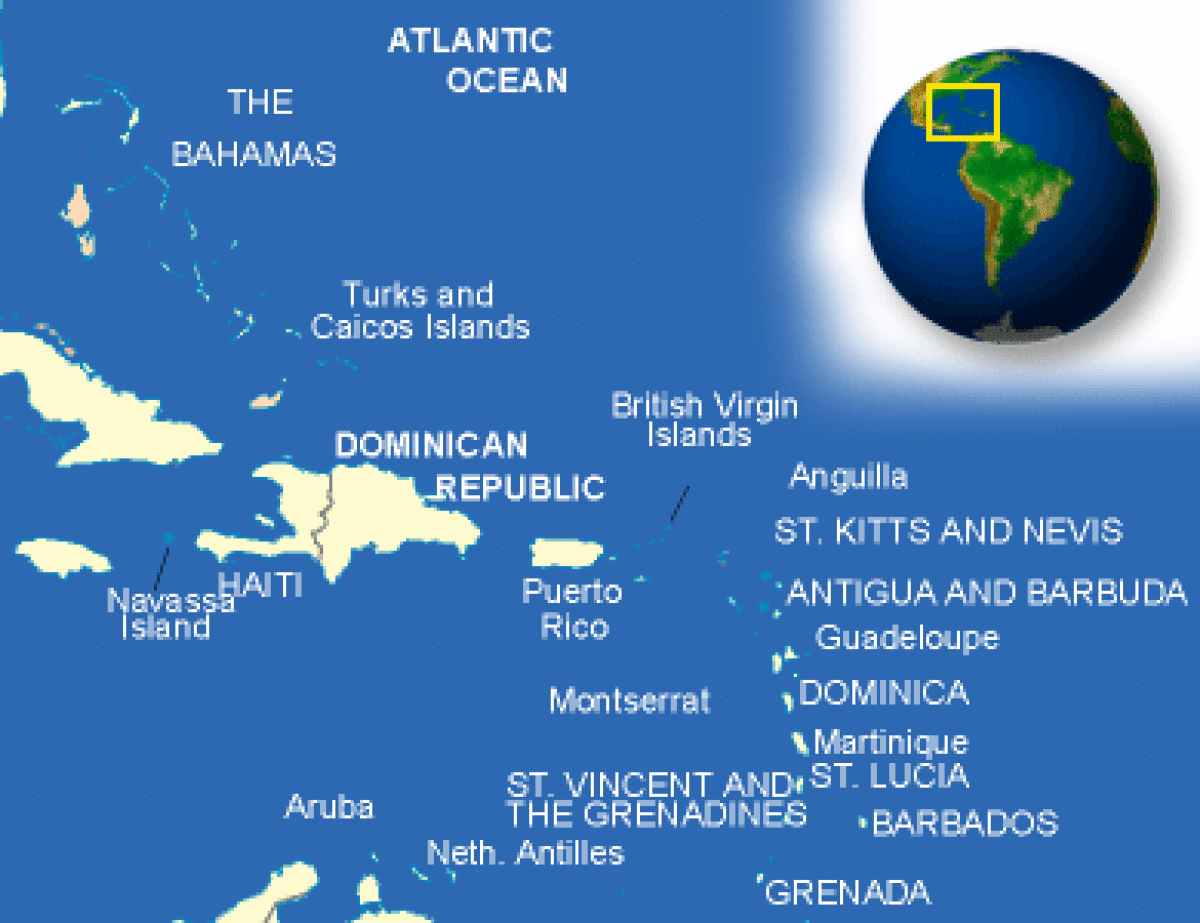
Antigua and Barbuda Facts and Culture
What is Antigua and Barbuda famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Antiguans are warm and friendly. They take a casual approach to life. People are more important than schedules. Antiguans are... More
- Family: Bearing or fathering children is highly valued. The traditional two-parent family is the norm. More
- Personal Apperance: The people wear Western-style clothing. At work, men do not wear shorts, colorful designs on shirts and light pants are... More
- Recreation: Cricket is very popular from November to May. Soccer is also popular. Draughts (a form of checkers) is played... More
- Diet: Most food is imported to the islands Tropical fruits include Coconuts, Mangos, pumpkins, yams, and potatoes. The basic food... More
- Food and Recipes: The Creole food is similar to that of other West Indian nations. Fungi is a cornmeal pudding made with boiled... More
- Visiting: Antiguans enjoy socializing; the term lime or liming is used to describe time spent relaxing. When... More
- Dating: Couples are affectionate but not in public. Parents and churches encourage marriage over other types of relationships. Weddings are lavish... More
Antigua and Barbuda Facts
What is the capital of Antigua and Barbuda?
| Capital | Saint John's |
| Government Type | parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollars (XCD) |
| Total Area |
171 Square Miles 442 Square Kilometers |
| Location | The Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico |
| Language | English (official), local dialects |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $24,100.00 (USD) |
Antigua and Barbuda Demographics
What is the population of Antigua and Barbuda?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent population by ethnic group |
| Ethnic Groups | African descent 87.3%, mixed 4.7%, Hispanic 2.7%, White 1.6%, other 2.7%, unspecified 0.9% |
| Languages | English (official), Antiguan Creole (an English-based creole) |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Antiguan(s), Barbudan(s) adjective: Antiguan, Barbudan |
| Population | 102,634 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.11% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 21,000 SAINT JOHN'S (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 24.3% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.87% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 48,311 female: 54,323 |
Antigua and Barbuda Government
What type of government does Antigua and Barbuda have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022); represented by Governor General Rodney WILLIAMS (since 14 August 2014) previous chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (6 February 1952 - 8 September 2022) head of government: Prime Minister Gaston BROWNE (since 13 June 2014) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor general |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 1 November (1981) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest presented 31 July 1981, effective 31 October 1981 (The Antigua and Barbuda Constitution Order 1981) amendments: proposed by either house of Parliament; passage of amendments to constitutional sections such as citizenship, fundamental rights and freedoms, the establishment, power, and authority of the executive and legislative branches, the Supreme Court Order, and the procedure for amending the constitution requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of the membership of both houses, approval by at least two-thirds majority in a referendum, and assent to by the governor general; passage of other amendments requires only two-thirds majority vote by both houses; amended 2009, 2011, 2018 |
| Independence | 1 November 1981 (from the UK) |
Antigua and Barbuda Video
YouTube: Expedia Antigua Vacation Travel Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Antigua and Barbuda Geography
What environmental issues does Antigua and Barbuda have?
| Climate | Tropical; little seasonal temperature variation |
| Environment - Current Issues | Water management - a major concern because of limited natural fresh water resources - is further hampered by the clearing of trees to increase crop production, causing rainfall to run off quickly |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Mostly low-lying limestone and coral islands, with some higher volcanic areas |
Antigua and Barbuda Economy
How big is the Antigua and Barbuda economy?
| Economic Overview |
Tourism continues to dominate Antigua and Barbuda's economy, accounting for nearly 60% of GDP and 40% of investment. The dual-island nation's agricultural production is focused on the domestic market and constrained by a limited water supply and a labor shortage stemming from the lure of higher wages in tourism and construction. Manufacturing comprises an enclave-type assembly for export with major products being bedding, handicrafts, and electronic components. Like other countries in the region, Antigua's economy was severely hit by the effects of the global economic recession in 2009. The country suffered from the collapse of its largest private-sector employer, a steep decline in tourism, a rise in debt, and a sharp economic contraction between 2009 and 2011. Antigua has not yet returned to its pre-crisis growth levels. Barbuda suffered significant damages after hurricanes Irma and Maria passed through the Caribbean in 2017. Prospects for economic growth in the medium term will continue to depend on tourist arrivals from the US, Canada, and Europe and could be disrupted by potential damage from natural disasters. The new government, elected in 2014 and led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne, continues to face significant fiscal challenges. The government places some hope in a new Citizenship by Investment Program, to both reduce public debt levels and spur growth and a resolution of a WTO dispute with the US. |
| Industries | Tourism, construction, light manufacturing (clothing, alcohol, household appliances) |
| Currency Name and Code | East Caribbean dollars (XCD) |
Antigua and Barbuda News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Antigua and Barbuda?
Source: Google News
Antigua and Barbuda Travel Information
What makes Antigua and Barbuda a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Antigua and Barbuda is a two-island nation known for its beaches and is a favorite destination for yachtsmen. Tourist facilities are widely available, and English is the primary language. Banking facilities and ATMs are available throughout the island.
Crime
Violent crimes, including rape and murder, do occur, and reported cases appear to be rising in Antigua. Robberies and assaults have affected visitors as well as students studying in Antigua. Take precautions to ensure your safety when traveling around the island as well as in your residence or hotel. In November 2012, there were at least 10 tourists robbed within a week by armed men. Always avoid visiting isolated beaches alone and leaving valuables unattended. Be alert and maintain the same level of personal security used when visiting major U.S. cities.Be especially vigilant when taking taxis in Antigua and Barbuda. Make certain that the taxi driver is licensed and is a member of the official taxi association. Unlicensed taxi operators have been known to extort money from passengers, despite having agreed to a fare beforehand. This can sometimes amount to double or triple the agreed-upon fare.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but you may also be breaking local law too.
Languages
English (official), Antiguan Creole (an English-based creole)
Medical Facilities and Health Information
There are qualified doctors in Antigua and Barbuda, but medical facilities are limited to one public hospital and two private clinics. They do not meet U.S. standards. The principal medical facility in Antigua is Mount St. John, on Hospital Road, St. John's (telephone (268) 462-0251). There is no hyperbaric chamber; divers requiring treatment for decompression illness must be evacuated from the island to either Saba or Guadeloupe. Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost thousands of dollars. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services, and U.S. medical insurance is not always valid outside the United States. U.S. Medicare and Medicaid programs do NOT provide payment for medical services outside the United States.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Antigua and Barbuda is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Traffic in Antigua and Barbuda moves on the left. Major roads are in average to poor condition, and drivers may encounter wandering animals and slow-moving heavy equipment. Drivers often stop in the middle of the roadway without warning, so you should always maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front of you and watch for signs of sudden braking. There is relatively little police enforcement of traffic regulations. Buses and vans are frequently crowded and may travel at excessive speeds. Automobiles may lack working safety and signaling devices, such as brake lights.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
