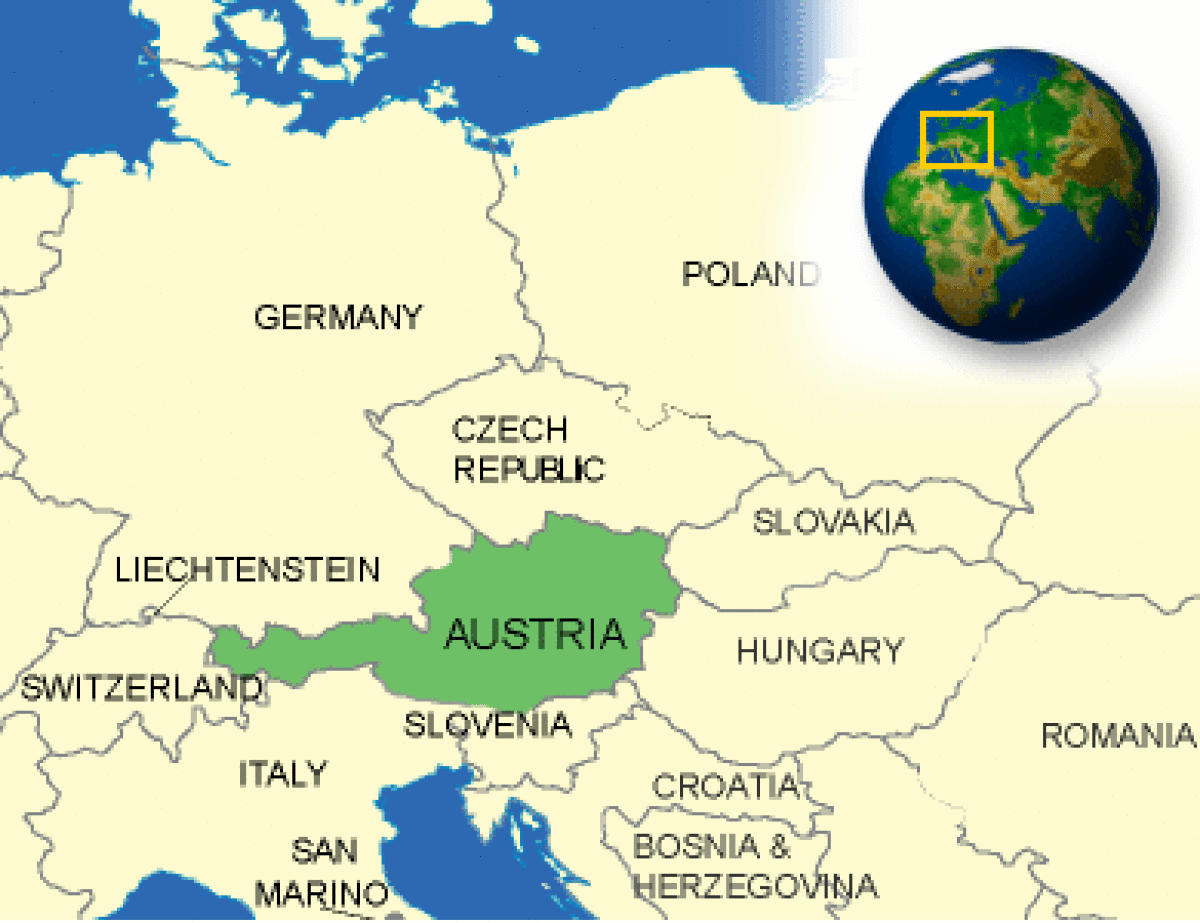
Where is Austria located?
What countries border Austria?
Austria Weather
What is the current weather in Austria?
Austria Facts and Culture
What is Austria famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Austrians are not Germans and should not be referred to as such; it can be considered an insult. A good-natured sense... More
- Family: Austrian families are usually small, having one or two children. However, rural families are often a bit larger. Most Austrians... More
- Personal Apperance: It is important to dress properly for all events. European clothing is usually worn by both men and women. For... More
- Recreation: Skiing is Austria's leading winter sport followed by ice skating and tobogganing. Summer sports include bicycling, mountain climbing, sailing,... More
- Diet: Austrians love good food and have a large variety of recipes derived from the various cultures that exist in Austria.... More
- Food and Recipes: One should keep hands above the table while eating and elbows should not be on the table. The main... More
- Visiting: Men stand when a woman enters the room or when talking to a woman who is standing. One should... More
Austria Facts
What is the capital of Austria?
| Capital | Vienna |
| Government Type | federal parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
32,383 Square Miles 83,871 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Europe, north of Italy and Slovenia |
| Language | German (official nationwide), Slovene (official in Carinthia), Croatian (official in Burgenland), Hungarian (official in Burgenland) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $47,900.00 (USD) |
Austria Demographics
What is the population of Austria?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent population by country of birth |
| Ethnic Groups | Austrian 80.8%, German 2.6%, Bosnian and Herzegovinian 1.9%, Turkish 1.8%, Serbian 1.6%, Romanian 1.3%, other 10% |
| Languages | German (official nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in southern Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3% |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Austrian(s) adjective: Austrian |
| Population | 8,967,982 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.3% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 1.975 million VIENNA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 59.5% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.68% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 4,392,898 female: 4,575,084 |
Austria Government
What type of government does Austria have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Alexander VAN DER BELLEN (since 26 January 2017); note - President Alexander VAN DER BELLEN reelected to a second six-year term on 9 October 2022 head of government: Chancellor Karl NEHAMMER (since 6 December 2021) cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the chancellor and appointed by the president elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 9 October 2022; (next election to be held in 2028); chancellor appointed by the president but determined by the majority coalition parties in the Federal Assembly; vice chancellor appointed by the president on the advice of the chancellor election results: 2022: Alexander VAN DER BELLEN elected in first round; percent of vote - Alexander VAN DER BELLEN (the Greens) 56.7%, Walter ROSENKRANZ (FPO) 17.7%, Dominik WLAZNY (Beer) 8.3%, Tassilo WALLENTIN (independent) 8.1%, Gerald GROSZ (independent) 5.6% 2016: Alexander VAN DER BELLEN elected in second round; percent of vote in first round - Norbert HOFER (FPOe) 35.1%, Alexander VAN DER BELLEN (independent, allied with the Greens) 21.3%, Irmgard GRISS (independent) 18.9%, Rudolf HUNDSTORFER (SPOe) 11.3%, Andreas KHOL (OeVP) 11.1%, Richard LUGNER (independent) 2.3%; percent of vote in second round - Alexander VAN DER BELLEN 53.8%, Norbert HOFER 46.2% |
| Suffrage | 16 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Austria dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | National Day (commemorates passage of the law on permanent neutrality), 26 October (1955) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 1 October 1920, revised 1929, replaced May 1934, replaced by German Weimar constitution in 1938 following German annexation, reinstated 1 May 1945 amendments: proposed through laws designated "constitutional laws" or through the constitutional process if the amendment is part of another law; approval required by at least a two-thirds majority vote by the National Assembly and the presence of one-half of the members; a referendum is required only if requested by one-third of the National Council or Federal Council membership; passage by referendum requires absolute majority vote; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | no official date of independence: 976 (Margravate of Austria established); 17 September 1156 (Duchy of Austria founded); 6 January 1453 (Archduchy of Austria acknowledged); 11 August 1804 (Austrian Empire proclaimed); 30 March 1867 (Austro-Hungarian dual monarchy established); 12 November 1918 (First Republic proclaimed); 27 April 1945 (Second Republic proclaimed) |
Austria Video
YouTube: Expoza Travel Austria Travel Video Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Austria Geography
What environmental issues does Austria have?
| Climate |
Temperature extremes in Vienna vary between summer highs of 95°F and - 4°F in winter. October may be damp and rainy, and light snowfalls occur in November and December. Snow, sometimes heavy, and frost can occur from January until mid-March. April, May, and early June offer pleasant spring weather, and summers are often delightful. Vienna sometimes becomes uncomfortably hot in July and August, especially in the city's center, but the suburbs, particularly those which are elevated, are pleasant. The city is subject to rapid and marked changes in atmospheric pressures with accompanying winds. One such wind, the foehn, carries warm air from the south. It has a special meaning for the Viennese since many people blame it for peculiar human behavior. The average annual precipitation in Vienna is 21.02 inches. The mountainous regions have long, cold winters with heavy snowfall and bright, crisp days. The Danube Basin usually has less snow, is damper, and therefore has more gray and overcast days than the higher altitudes. |
| Border Countries | The Czech Republic 362 km, Germany 784 km, Hungary 366 km, Italy 430 km, Liechtenstein 35 km, Slovakia 91 km, Slovenia 330 km, Switzerland 164 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Some forest degradation is caused by air and soil pollution; soil pollution results from the use of agricultural chemicals; air pollution results from emissions by coal- and oil-fired power stations and industrial plants and from trucks transiting Austria between northern and southern Europe |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | In the west and south mostly mountains (Alps); along the eastern and northern margins mostly flat or gently sloping |
Austria Economy
How big is the Austria economy?
| Economic Overview |
Austria is a well-developed market economy with a skilled labor force and a high standard of living. It is closely tied to other EU economies, especially Germany's, but also to the United States, its third-largest trade partner. Its economy features a large service sector, a sound industrial sector, and a small, but highly developed agricultural sector. Austrian economic growth strengthen in 2017, with a 2.9% increase in GDP. Austrian exports, accounting for around 60% of the GDP, were up 8.2% in 2017. Austria’s unemployment rate fell by 0.3% to 5.5%, which is low by European standards, but still at its second-highest rate since the end of World War II, driven by an increased number of refugees and EU migrants entering the labor market. Austria's fiscal position compares favorably with other euro-zone countries. The budget deficit stood at a low 0.7% of GDP in 2017 and public debt declined again to 78.4% of GDP in 2017, after reaching a post-war high of 84.6% in 2015. The Austrian government has announced its plans to balance the fiscal budget in 2019. Several external risks, such as Austrian banks' exposure to Central and Eastern Europe, the refugee crisis, and continued unrest in Russia/Ukraine, eased in 2017, but are still a factor for the Austrian economy. Exposure to the Russian banking sector and a deep energy relationship with Russia present additional risks. Austria elected a new pro-business government in October 2017 that campaigned on promises to reduce bureaucracy, improve public sector efficiency, reduce labor market protections, and provide positive investment incentives. |
| Industries | Construction, machinery, vehicles and parts, food, metals, chemicals, lumber, paper and paperboard, communications equipment, tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 29.4%, United States 6.4%, Italy 6.1%, Switzerland 5.7%, France 4.4%, Slovakia 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Germany 41.5%, Italy 6.3%, Switzerland 6%, Czech Republic 4.2% |
Austria News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Austria?
Source: Google News
Austria Travel Information
What makes Austria a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Austria is a highly developed, stable democracy with a modern economy. Tourism is an important pillar of the Austrian economy and facilities are widely available.
Crime
Austria has one of the lowest crime rates in Europe, and violent crime is rare. However, crimes involving the theft of personal property do occur. As such, most crimes involving U.S. citizens are crimes of opportunity, involving theft of personal belongings. Travelers are also targets of pick-pockets who operate where tourists tend to gather. Some of the spots where such crimes are most frequently reported include Vienna’s two largest train stations, the plaza around St. Stephen’s Cathedral, and the nearby pedestrian shopping areas (in Vienna’s First District).The U.S. Embassy receives reports of theft and pick-pocketing on public transportation lines, especially on those lines coming into and out of the city center. Secure your personal belongings and always take precautions while on public transportation and in public places such as cafes and tourist areas.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, but by buying them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While traveling in Austria, you are subject to its laws. While you are overseas you do not enjoy the same rights and privileges that you have in the U.S. If you do something illegal in your host country, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not, since foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. Criminal penalties also vary from country to country. There are also some things that may be legal where you are traveling but illegal in the United States. If you engage in sexual conduct with children or use or disseminate child pornography in a foreign country, you can be prosecuted in the United States.Persons violating Austrian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Austria are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Arrest Notifications: Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Austria, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the Embassy.
Languages
German (official nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in southern Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3%
Medical Facilities and Health Information
There are an adequate number of hospitals available in Austria. Local hospitals will not settle their accounts directly with American insurance companies. You must pay the bill to the local hospital and later claim a refund from the insurance carrier in the United States. Medicare payments are not available outside the United States.The Austrian Medicine Import Act generally prohibits the import of prescription drugs into Austria, with two exceptions:
Travelers residing outside the European Union are allowed to carry with them (as part of their personal luggage) drugs and medicines, but only a quantity the individual requires during the course of the stay; and,
Travelers, while staying in Austria, may receive drugs and medicines for their personal use by mail. The quantity is limited to the length of their stay in Austria and must never exceed three packages.
We recommend you have either a prescription or written statement from your personal physician that you are under a doctor’s care and that the medicine is necessary for your physical well-being while traveling.
Public health in Austria is excellent. Community sanitation in Vienna meets or exceeds that of most U.S. cities. Disease incidence and type are similar to the rest of Europe and the United States. At the present time, air pollution is not a major health problem in Vienna.
Safety and Security
Austria remains largely free of terrorist incidents; however, like other countries in the Schengen area, Austria’s open borders with its Western European neighbors allow the possibility of terrorist groups entering and exiting the country with anonymity. U.S. citizens are reminded to remain vigilant with regard to their personal security and to exercise caution.Austrian intelligence experts have registered increased radicalization of immigrant Muslim individuals and of small conspiratorial groups, as well as intensified use of the Internet as a propaganda and communications platform.
Every year, a number of avalanche deaths occur in Austria's alpine regions. Many occur when skiers/snowboarders stray from designated ski slopes. Leaving designated slopes to ski off-piste may pose serious risks and may delay rescue attempts in case of emergency. Skiers and snowboarders should monitor weather and terrain conditions, and use available avalanche rescue equipment. Avalanche beepers (transceivers) are the most common rescue devices and, when properly used, provide the fastest way of locating an avalanche victim, usually enabling authorities to begin rescue operations within minutes. Climbing, hill walking, and mountaineering involve a level of risk with a danger of personal injury or death. While the number of people requiring rescue in Austria remains steady each year, there has been a marked increase in air evacuations since July 2013. Alpine rescuers are increasingly concerned about the growing number of people participating in mountaineering activities without proper preparation and planning; people participating in these activities should closely monitor weather and terrain conditions and contact local tourism offices or mountain guide associations for information on trails that are tailored to individual skill levels. Also, it is recommended to buy special leisure insurance. More information, including safety tips, is available on the Austrian Alpine Club website http://www.alpenverein.at/portal/service/mitgliedschaft/index.php To call for an emergency, dial 144 (Austrian Red Cross) or the European emergency number 112.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Austria, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Road conditions in Austria are generally excellent. During the winter, however, roads in alpine areas may become dangerous due to snowfall, ice, or avalanches. Some mountain roads may be closed for extended periods and tire chains are often required. Be extra careful during the heavily traveled vacation periods (i.e., December-February, Easter, and July-August). Be alert when you drive through autobahn construction zones, particularly on the A-1 East/West Autobahn. Reduced lanes and two-way traffic in these zones have resulted in several deadly accidents in recent years. Traffic information and road conditions are broadcast on the English-language channel, fm4, located between 91 and 105 FM depending on the locale.A U.S. driver’s license alone is not sufficient to drive in Austria. You must also get an international driver’s permit (obtainable in the U.S. from the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance) or by an official translation of the U.S. driver’s license, which can be obtained at one of the Austrian automobile clubs (OEAMTC or ARBOE). This arrangement is only acceptable for the first six months of driving in Austria, after which all drivers must obtain an Austrian license.
Austria requires all vehicles using the autobahn to display an “Autobahn Vignette” highway-tax sticker on the inside of the vehicle’s windshield. The sticker may be purchased at border crossings, gas stations in Austria, and small “Tabak” shops located in Austrian towns. The fine for failing to display a valid autobahn vignette on the windshield of your car is EUR 120 (approx. $ 150 08/2013 exchange rate) if paid in cash and “on the spot”. For more information, please see http://www.asfinag.at/maut/vignette
Austrian autobahns have a maximum speed limit of 130 km/hr, although drivers often drive much faster and pass aggressively. The use of hand-held cell phones while driving is prohibited. Turning right on red is also prohibited throughout Austria. The legal limit for blood alcohol content in Austria is .05 percent and penalties for driving under the influence tend to be stricter than in many U.S. states.
It is mandatory for cars on Austrian motorways and highways to leave an emergency corridor, even when no emergency vehicle is approaching. When traffic stops, create an emergency corridor in between the far-left lane and all others to the right; vehicles should also be using the shoulder. For more information, please click here. Failure to comply carries a fine of EUR 2,180 (approx.$ 2,700)
Between November 1 and April 15, the use of winter tires is mandated by law. All-season tires comply if they carry the “M S” mark and have at least 4 mm of tread. In addition, local police may require snow chains in heavy snow. Failure to comply with the law results in a substantial fine and the suspension of the cited vehicle's use. Insurance is deemed void if a vehicle that is involved in an accident between November 1 and April 15 is not fitted with winter tires.
Tourists driving rented vehicles must ensure that the vehicle is equipped with the proper tires and pay close attention to the provisions of their rental contract. Many contracts prohibit drivers from taking rented vehicles into eastern European countries. Drivers attempting to enter countries listed as “prohibited” on the car rental contract may be arrested, fined, and/or charged with attempted auto theft. Austrian police are authorized to hold the rented vehicle for the car rental company.
Emergency roadside help and information may be reached by dialing 123 or 120 for vehicle assistance and towing services (Austrian automobile clubs), 122 for the fire department, 133 for police, and 144 for an ambulance. The European emergency line is 112.
Austrian Federal Railroads (Österreichische Bundesbahnen) offer excellent railroad service to all major towns of the country and also direct connections with all major cities in Europe. Trains are well maintained and fares are reasonable. There is also an extensive network of bus lines operated by the Austrian Postal Service (Österreichische Post). All major cities also offer excellent public transportation services.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
