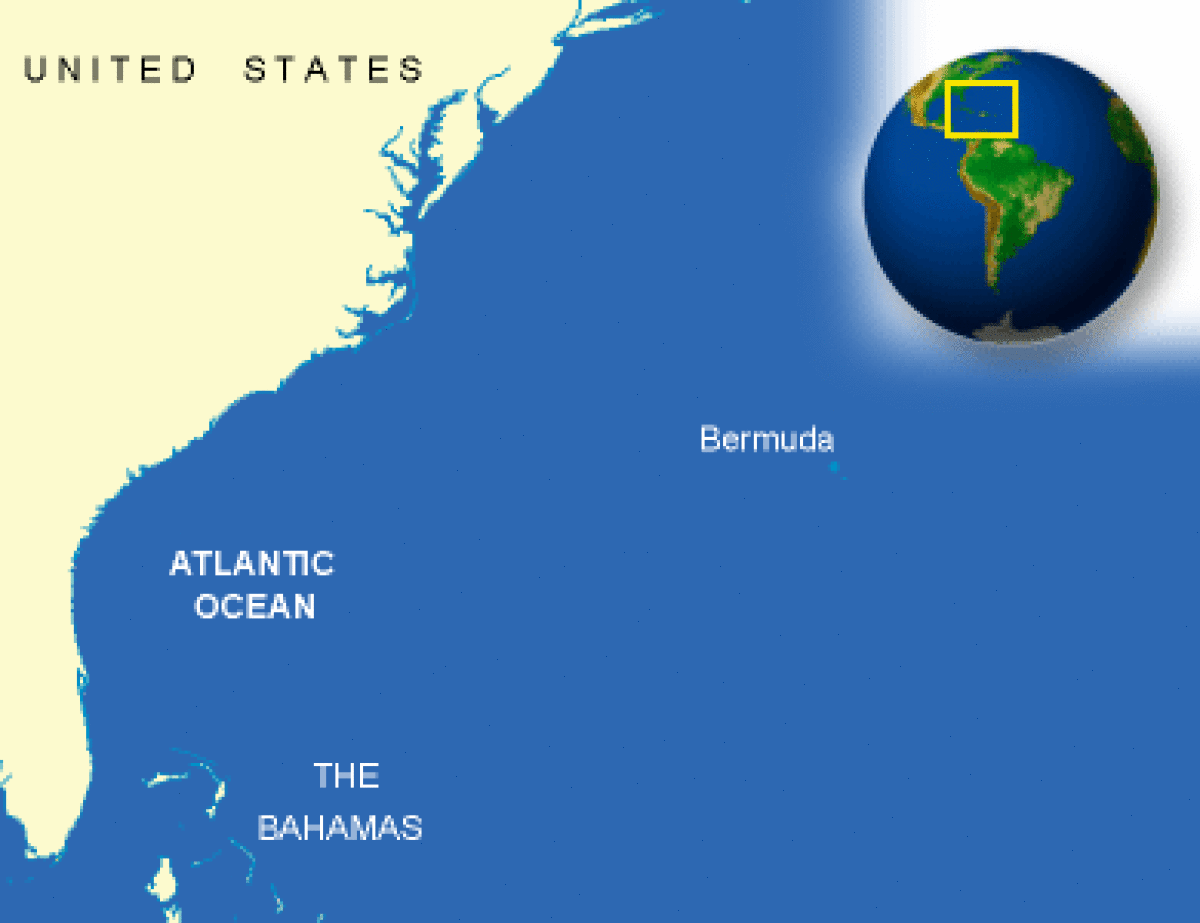
Where is Bermuda located?
What countries border Bermuda?
Bermuda Weather
What is the current weather in Bermuda?
Bermuda Facts and Culture
What is Bermuda famous for?
- Food and Recipes: The European style of eating is used. Dinner is the main meal of the day usually starting with soup, followed... More
Bermuda Facts
What is the capital of Bermuda?
| Capital | Hamilton |
| Government Type | Overseas Territory of the UK with limited self-government; parliamentary democracy |
| Currency | Bermudian Dollar (BMD) |
| Total Area |
21 Square Miles 54 Square Kilometers |
| Location | North America, a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, east of South Carolina (US) |
| Language | English (official), Portuguese |
| GDP - real growth rate | -2.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $85,700.00 (USD) |
Bermuda Demographics
What is the population of Bermuda?
| Ethnic Groups | Black 58%, white 36%, other 6% |
| Nationality Noun | Bermudian(s) |
| Population | 71,750 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.55% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | HAMILTON (capital) 11,000 |
| Urban Population | 100.000000 |
Bermuda Government
What type of government does Bermuda have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022); represented by Governor Rena LALGIE (since 14 December 2020) previous Queen ELIZABETH II (6 February 1952 - 8 September 2022) head of government: Premier David BURT (since 19 July 2017) cabinet: Cabinet nominated by the premier, appointed by the governor elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed premier by the governor |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the UK dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Bermuda Day, 24 May; note - formerly known as Victoria Day, Empire Day, and Commonwealth Day |
| Constitution |
history: several previous (dating to 1684); latest entered into force 8 June 1968 (Bermuda Constitution Order 1968) amendments: proposal procedure - NA; passage by an Order in Council in the UK; amended several times, last in 2012 |
| Independence | none (overseas territory of the UK) |
Bermuda Video
YouTube: Cherly Echevarria Bermuda General & Culture
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Bermuda Geography
What environmental issues does Bermuda have?
| Overview |
Bermuda is an archipelago of seven main islands and some 150 other islands and islets. The main islands, joined by bridges or causeways, stretch from northeast to southwest in a long, narrow formation that hooks northward at the western end. On the map, the shape is much like that of a fishhook. The main islands are in close proximity and, since being joined, the Bermuda Islands (or Somers Isles, their other name) are generally called the island of Bermuda. Bermuda’s total land area is about 20 square miles — some 22 miles in length and an average of less than a mile in width — making the country smaller than the city of Manhattan. During World War II, the U.S. military created 1.25 square miles of the present land mass by uniting and enlarging some of the islands with material dredged from the sea bottom, now the site of the Bermuda International Airport. The archipelago is the summit of a submerged volcanic mountain range, 14,000–15,000 feet high, which has been extinct since before the first ice age. Between the volcanic foundation and the inches-thin layer of soil capping it lies a 200-foot thick layer of limestone formed by deposits of mollusks, coral polyps, and other sea creatures. The coral content in the limestone substructure justifies Bermuda’s classification as a “coral island,” though it is more fully described as a mixed superstructure of Aeolian petrified sand hills and limestone upon an eroded volcanic base. The surrounding reefs are true coral growths, making Bermuda the most northerly point on the globe where reef-building coral exists. Bermuda lies at latitude 32’18” north and longitude 65’46” west. Geographically, it is remote and does not lie within or near the West Indies or the Caribbean, with which it is often erroneously identified. The terrain is hilly, with the highest — Gibb’s Hill — 260 feet above sea level. A fertile valley extends along the length of the main island. Wind-carved cliffs cascade into the sea along the rocky northern shore. Similar rock formations form a dramatic backdrop for the long beaches and small coves along the south shore. The enclosing reef, a few yards offshore on the south coast and up to several miles offshore on the north, emerges from the sea each day at low tide, framing the islands and completing the topographical picture. Except for a few small ponds, there are no rivers, streams, lakes, or other surface freshwater formations. For most of its history, Bermuda was thought to have no groundwater, but freshwater lens formations lying above underground saltwater were discovered in the 1920s and 30s. These have subsequently been exploited to supplement the island’s main source of drinking water, which is rainwater collected on roofs and paved catchments. |
| Climate |
Though far north from tropical latitudes, Bermuda has a mild, humid, frost-free climate. The annual mean temperature is 70.2°F. Highs in summer rarely top 90°F, and lows in winter rarely drop under the 50s. The lowest temperature ever officially recorded was 44°F. The Gulf Stream, running west and north of the island, is the main reason for the good climate. The average annual rainfall is 57.6 inches, spread evenly throughout the year. The year-round high humidity, averaging more than 75%, makes some days uncomfortably sticky in summer and damp and cold in winter. January through March tends to be overcast and squally, although when the sun shines it can be like a breezy spring day. April and May are very pleasant. June through August are very hot and very humid. The heat factor (temperature plus humidity) during the hottest summer months can exceed 110°F degrees Fahrenheit. September is the stormy season, although hurricane season officially extends from June through November. Barring hurricanes, October through December are calm, mild, and usually sunny, and are considered by many to be the most pleasant part of the year. The climate, well-distributed rainfall, and heavy dew promote the luxuriant growth of vegetation of every description, despite the dearth of soil. Palms, Australian and Norfolk Island pines, mangroves, poincianas, casuarinas, ficus trees, citrus, and some tropical fruit trees grow well in Bermuda. Prolific oleander and hibiscus brighten gardens and lanes everywhere. Sadly, the famous Bermuda cedar trees that for centuries dominated the landscape and were the islands' pride, were nearly all destroyed by blight in the 1940s. The few remaining native cedars are protected, and some reforestation with blight-resistant stock is underway. |
| Environment - Current Issues | Asbestos disposal; water pollution; preservation of open space; sustainable development |
| Terrain | Low hills separated by fertile depressions |
Bermuda Economy
How big is the Bermuda economy?
| Economic Overview |
International business, which consists primarily of insurance and other financial services, is the real bedrock of Bermuda's economy, consistently accounting for about 85% of the island's GDP. Tourism is the country’s second-largest industry, accounting for about 5% of Bermuda's GDP but a much larger share of employment. Over 80% of visitors come from the US and the sector struggled in the wake of the global recession of 2008-09. Even the financial sector has lost roughly 5,000 high-paying expatriate jobs since 2008, weighing heavily on household consumption and retail sales. Bermuda must import almost everything. Agriculture and industry are limited due to the small size of the island. Bermuda's economy returned to negative growth in 2016, reporting a contraction of 0.1% GDP, after growing by 0.6% in 2015. Unemployment reached 7% in 2016 and 2017, public debt is growing and exceeds $2.4 billion, and the government continues to work on attracting foreign investment. Still, Bermuda enjoys one of the highest per capita incomes in the world. |
| Industries | International business, tourism, light manufacturing |
| Currency Name and Code | Bermudian Dollar (BMD) |
| Export Partners | United States 14.4%, Iceland 13.7%, Spain 6.8%, United Kingdom 5.8%, Mauritius 5.6% |
| Import Partners | South Korea 49.5%, United States 14.6%, Germany 11.4%, China 9%, Turkmenistan 5.2% |
Bermuda News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Bermuda?
Source: Google News
Bermuda Travel Information
What makes Bermuda a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Bermuda is a British overseas territory with a stable democracy and developed economy. Tourist facilities are widely available.
Crime
By comparison to the United States, Bermuda has a low to moderate crime rate. Recent crime statistics are available on the official website of the Bermuda Police Service. Valuables left unattended in public areas, in unsecured hotel rooms, or on rental motorbikes are vulnerable to theft. Criminals have been known to target visitors on motorbikes and at popular tourist attractions, and purse snatchings (perpetrated by thieves riding motorbikes) and muggings have occurred in the past. The back streets of the City of Hamilton have been the setting for nighttime assaults, particularly at night after the bars close. Travelers should exercise caution when walking after dark or visiting out-of-the-way places on the island as they can be vulnerable to theft and assault, and because narrow and dark roadways can contribute to accidents.Travelers should note an increase in gang presence and illegal drug activity in Bermuda. There have been no reports of gang violence targeted toward visitors to Bermuda, although gunfire between gang members has occurred throughout the island.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Bermuda, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Bermuda, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Persons violating Bermuda’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Having a prescription for an illegal drug in Bermuda, such as marijuana, will not protect you from prosecution for possession of that illegal drug. Bermuda Customs routinely boards visiting cruise ships with drug-sniffing dogs and will arrest persons found to have any illegal drugs in their cabin. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Bermuda are severe, and convicted offenders can expect jail sentences and/or heavy fines.
If you are arrested in Bermuda, authorities of Bermuda are required to notify the U.S. Consulate of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Consulate of your arrest.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical care is available for routine procedures, though extremely expensive. The hospital performs general surgery and has an emergency room and intensive care unit. Serious or complex medical programs will likely require medical evacuation to the United States. Most Bermudian health care providers including the local hospital do not accept overseas insurance and will expect payment at the time of service.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Bermuda you will encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Traffic in Bermuda moves on the left side and the roads are very narrow, often with no defined shoulder. The maximum speed in the city of Hamilton is 25 kph (15 mph) and 35 kph (21 mph) on the rest of the island. Under Bermudian law, non-residents are not allowed to own, rent or drive four-wheeled vehicles. Non-residents must rely on taxis, the local bus system, or rented motorbikes. Traffic is moderate. Road accidents – particularly involving motorbikes – are common and can result in serious injuries or death.Rental motorbikes are readily available, and the required helmet is provided. However, visitors should carefully consider the significant risks of riding a motorbike. Motorbikes provide the greatest road peril in Bermuda; local operators tend to abuse the speed limit and will often pass on the left or right side with no warning. Those unfamiliar with driving on the left side are likely to find the roundabouts and regulations for yielding at junctions confusing and dangerous. In addition, vehicles often stop on the side of the road, blocking one lane of traffic. Main roads, while generally in good condition, are extremely narrow and tend to be bordered by heavy vegetation or stone walls. Taxis are readily available. The local bus system serves the length of the island and stops close to most beaches, hotels, the downtown shopping area, and other points of interest. In addition, water ferry service to a variety of stops around the island is available seven days a week and is a very safe and enjoyable mode of transportation.
For specific information concerning Bermuda’s drivers' permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, and mandatory insurance, please contact the Bermuda Department of Tourism offices at 675 Third Avenue, 20th Floor, New York, NY 10017 Tel: (800)_223-6106.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
