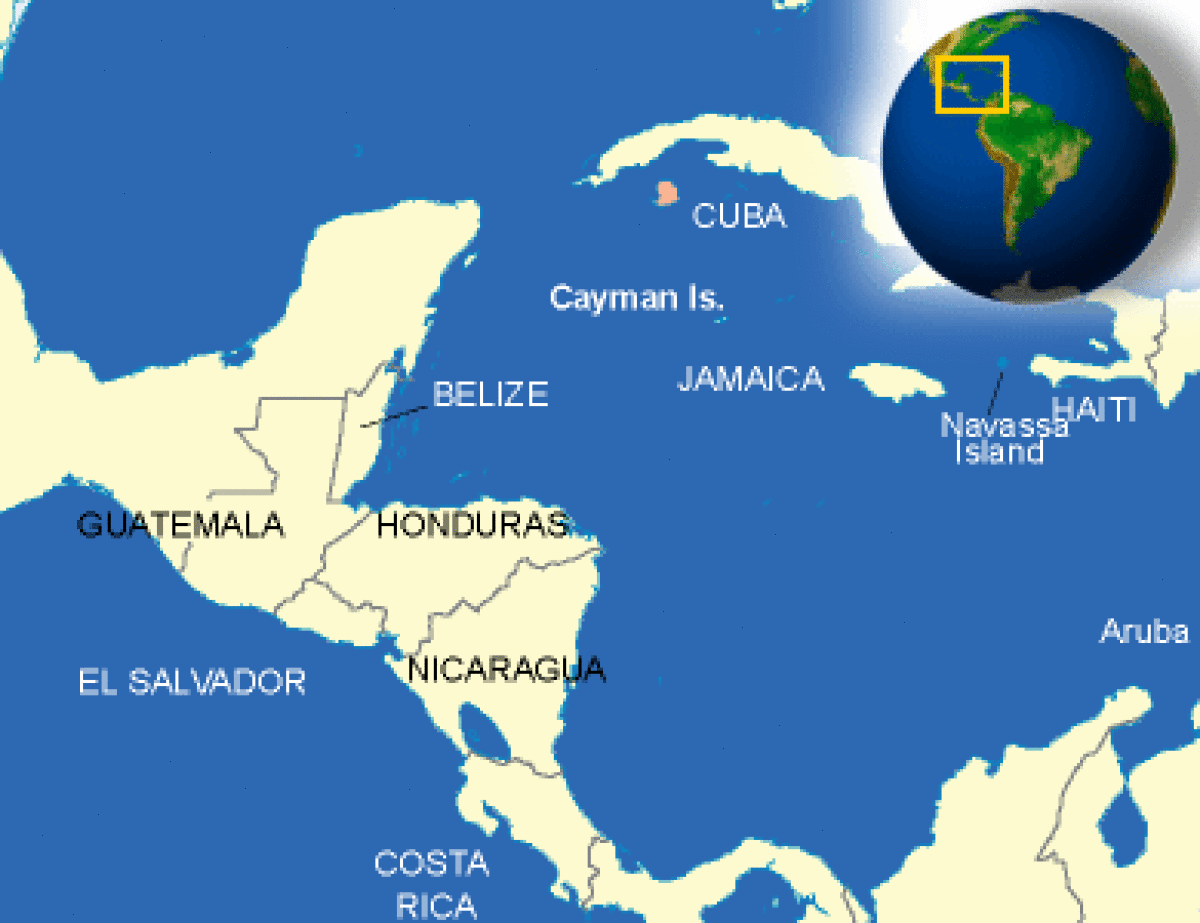
Where is Cayman Islands located?
What countries border Cayman Islands?
Cayman Islands Weather
What is the current weather in Cayman Islands?
Click for weather forecast
Cayman Islands Facts and Culture
What is Cayman Islands famous for?
- Recreation: Residents of the Cayman Islands keep active! Some of the most popular competition sports are soccer, cricket, basketball, sailing, rugby,... More
Cayman Islands Facts
What is the capital of Cayman Islands?
| Capital | George Town (on Grand Cayman) |
| Government Type | parliamentary democracy; self-governing overseas territory of the UK |
| Currency | Caymanian dollars (KYD) |
| Total Area |
102 Square Miles 264 Square Kilometers |
| Location | The Caribbean, three-island group (Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, Little Cayman) in the Caribbean Sea, 240 km south of Cuba and 268 km northwest of Jamaica |
| Language | English |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.7% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $43,800.00 (USD) |
Cayman Islands Demographics
What is the population of Cayman Islands?
| Ethnic Groups | Mixed 40%, white 20%, black 20%, expatriates of various ethnic groups 20% |
| Nationality Noun | Caymanian(s) |
| Population | 61,994 |
| Population - note | Note: most of the population lives on Grand Cayman |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.19% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | GEORGE TOWN (capital) 28,000 |
| Urban Population | 100.000000 |
Cayman Islands Government
What type of government does Cayman Islands have?
| Executive Branch |
King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022); represented by Governor Jane OWEN (since 21 April 2023) previous Queen ELIZABETH II (6 February 1952 - 8 September 2022) head of government: Premier Juliana O'CONNOR-CONNOLLY (since 15 November 2023) cabinet: Cabinet selected from the Parliament and appointed by the governor on the advice of the premier elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition appointed premier by the governor |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship | see United Kingdom |
| National Holiday | Constitution Day, the first Monday in July (1959) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest approved 10 June 2009, entered into force 6 November 2009 (The Cayman Islands Constitution Order 2009) amendments: amended 2016, 2020 |
| Independence | none (overseas territory of the UK) |
Cayman Islands Video
YouTube: Unravel Travel TV Cayman Islands Department of Tourism - Unravel Travel TV
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Cayman Islands Geography
What environmental issues does Cayman Islands have?
| Climate | Tropical marine; warm, rainy summers (May to October) and cool, relatively dry winters (November to April) |
| Environment - Current Issues | No natural fresh water resources; drinking water supplies must be met by rainwater catchments |
| Terrain | Low-lying limestone base surrounded by coral reefs |
Cayman Islands Economy
How big is the Cayman Islands economy?
| Economic Overview |
With no direct taxation, the islands are a thriving offshore financial center. More than 65,000 companies were registered in the Cayman Islands as of 2017, including more than 280 banks, 700 insurers, and 10,500 mutual funds. A stock exchange was opened in 1997. Nearly 90% of the islands' food and consumer goods must be imported. The Caymanians enjoy a standard of living comparable to that of Switzerland. Tourism is also a mainstay, accounting for about 70% of GDP and 75% of foreign currency earnings. The tourist industry is aimed at the luxury market and caters mainly to visitors from North America. Total tourist arrivals exceeded 2.1 million in 2016, with more than three-quarters from the US. |
| Industries | Tourism, banking, insurance and finance, construction, construction materials, furniture |
| Currency Name and Code | Caymanian dollars (KYD) |
Cayman Islands News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Cayman Islands?
Source: Google News
Cayman Islands Travel Information
What makes Cayman Islands a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Cayman Islands are a British overseas territory consisting of three main islands with a total area of approximately 100 square miles and located about 500 miles west of Jamaica. There is an international airport located in Grand Cayman, and facilities for tourists are widely available. The U.S. Embassy in Kingston, Jamaica, has consular responsibility for the Cayman Islands.
Crime
The crime threat in the Cayman Islands is generally considered low, although travelers should always take normal precautions when in unfamiliar surroundings. Petty theft, pick-pocketing, and purse snatchings occur. A few cases involving sexual assault have been reported to the Embassy. Police in the Cayman Islands rigorously enforce laws against illegal drugs. U.S. citizens should avoid buying, selling, holding, or taking illegal drugs under any circumstances.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in the Cayman Islands, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail for the night. In most cases, the passport is confiscated until you appear before a Magistrate Judge and a fine is imposed. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in the Cayman Islands, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Persons violating Caymanian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in the Cayman Islands are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
The quality of medical care in the Cayman Islands is generally comparable to that available in the United States; however, some procedures and cases requiring critical care may require medical evacuation to the United States. Several American citizens each year drown or suffer cardiac arrest while snorkeling or SCUBA diving in the Cayman Islands. These deaths may be attributed in part to tourists attempting to do more than they are trained to do or to poor physical conditioning or preexisting medical conditions that are exacerbated when snorkeling or diving. A hyperbaric chamber is available for the treatment of decompression illness. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate payment for health services.Emergency response services in the Cayman Islands are on par with those generally available in the United States.
Safety and Security
Since a surge of gang-related criminal activity in 2011, the Royal Cayman Island Police have aggressively addressed gang activity and murders are down dramatically. Guns remain a problem, however, and sentencing for people found with guns or ammunition is strict.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in the Cayman Islands, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning the Cayman Islands is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.As in Great Britain and its other territories, vehicles in the Cayman Islands travel on the left-hand side of the road (the opposite side compared with driving in the United States). Due to their size, the Caymans have little highway infrastructure to maintain. Local driving standards, the risk of accidents, the availability of emergency roadside service, quality and frequency of signage, and enforcement of traffic laws, generally meet the standards of the United States. Visitors must obtain a temporary driver's license, easily granted upon presentation of a valid state driver's license and payment of a small fee, at a car rental agency or a police station. Laws against driving while intoxicated are strictly enforced, with a legal maximum blood alcohol level set at 100 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood (equivalent to a .10 blood/alcohol level in the United States). Seatbelt laws are also enforced and require the driver and all passengers to wear seatbelts while in motion.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
