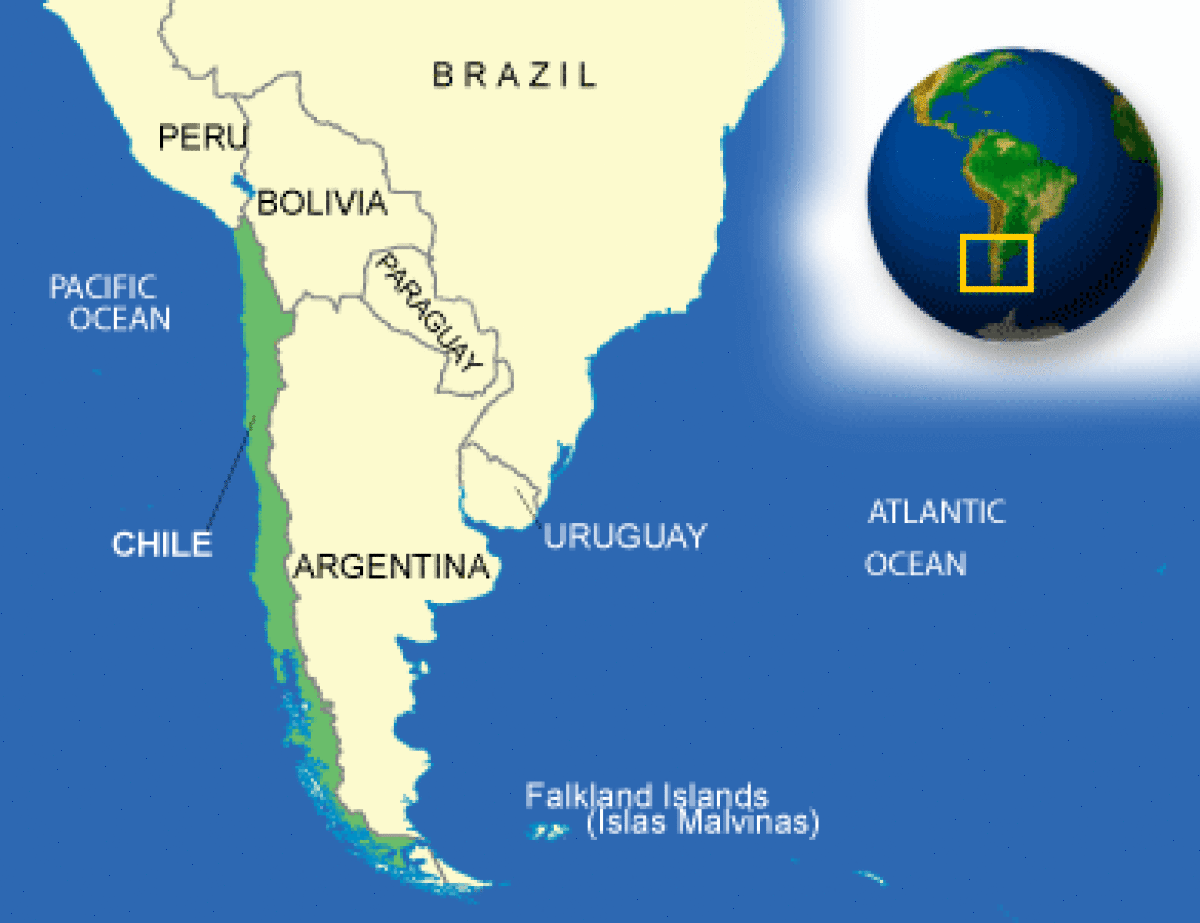
Where is Chile located?
What countries border Chile?
Chile Weather
What is the current weather in Chile?
Chile Facts and Culture
What is Chile famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Chilean people are friendly, both among themselves and with strangers. The people are known for having a witty sense... More
- Family: The family is important in Chile, including the extended family. While men have tended to dominate private and public life... More
- Personal Apperance: Fashions follow European styles. Appearance is quite important to individuals; even in rural areas, it is important to be neatly... More
- Recreation: The most popular spectator sport in Chile is fútbol, or soccer. Many consider it Chile's national sport. Major soccer events... More
- Diet: Many national dishes are prepared with fish, seafood, chicken, beef, beans, eggs, and corn. A common meal is a soup... More
- Food and Recipes: Hands are kept above the table at all times. It is impolite to ask for second helpings. Even if they... More
- Visiting: Contrary to some areas in South America, guests wait outside the door of a home until invited inside by the... More
- Dating: Young people begin dating by the time they are 16. Group dating is emphasized early on. Men marry from age... More
Chile Facts
What is the capital of Chile?
| Capital | Santiago; note - Valparaiso is the seat of the national legislature |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Chilean pesos (CLP) |
| Total Area |
291,931 Square Miles 756,102 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru |
| Language | Spanish (official), Mapudungun, German, English |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.7% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $24,000.00 (USD) |
Chile Demographics
What is the population of Chile?
| Ethnic Groups | White and non-Indigenous 88.9%, Mapuche 9.1%, Aymara 0.7%, other Indigenous groups 1% (includes Rapa Nui, Likan Antai, Quechua, Colla, Diaguita, Kawesqar, Yagan or Yamana), unspecified 0.3% |
| Languages | Spanish 99.5% (official), English 10.2%, Indigenous 1% (includes Mapudungun, Aymara, Quechua, Rapa Nui), other 2.3%, unspecified 0.2%; note - shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Chilean(s) adjective: Chilean |
| Population | 18,664,652 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.61% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 6.903 million SANTIAGO (capital), 1.009 million Valparaiso, 912,000 Concepcion |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 88% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.78% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 9,169,736 female: 9,494,916 |
Chile Government
What type of government does Chile have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Gabriel BORIC (since 11 March 2022); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Gabriel BORIC (since 11 March 2022) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a single 4-year term; election last held on 21 November 2021 with a runoff held on 19 December 2021 (next to be held on 23 November 2025 with runoff if needed on 20 December) election results: 2021: Gabriel BORIC elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Jose Antonio KAST (FSC) 27.9%; Gabriel BORIC (AD) 25.8%; Franco PARISI (PDG) 12.8%; Sebastian SICHEL (ChP+) 12.8%; Yasna PROVOSTE (New Social Pact) 11.6%; other 9.1%; percent of vote in second round - Gabriel BORIC 55.9%; Jose Antonio KAST 44.1% 2017: Sebastian PINERA Echenique elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Sebastian PINERA Echenique (independent) 36.6%; Alejandro GUILLIER (independent) 22.7%; Beatriz SANCHEZ (independent) 20.3%; Jose Antonio KAST (independent) 7.9%; Carolina GOIC (PDC) 5.9%; Marco ENRIQUEZ-OMINAMI (PRO) 5.7%; other 0.9%; percent of vote in second round - Sebastian PINERA Echenique 54.6%, Alejandro GUILLIER 45.4% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 18 September (1810) |
| Constitution |
history: many previous; latest adopted 11 September 1980, effective 11 March 1981; a referendum held on 4 September 2022 to implement a new constitution was defeated by nearly 62% of voters; a second 50-member constitutional council elected in early May 2023 is charged with producing another draft constitution for submission to a national referendum by 17 December 2023 amendments: proposed by members of either house of the National Congress or by the president of the republic; passage requires at least three-fifths majority vote of the membership in both houses and approval by the president; passage of amendments to constitutional articles, such as the republican form of government, basic rights and freedoms, the Constitutional Tribunal, electoral justice, the Council of National Security, or the constitutional amendment process, requires at least two-third majority vote by both houses of Congress and approval by the president; the president can opt to hold a referendum when Congress and the president disagree on an amendment; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 18 September 1810 (from Spain) |
Chile Video
YouTube: Expoza Travel Chile Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Chile Geography
What environmental issues does Chile have?
| Overview |
Chile is a narrow ribbon of land stretching almost 2,700 miles along the southwest coast of South America. Although it is one of the world’s longest countries, its average width is only 110 miles. It is only 250 miles at its widest point. Larger than any European country except Russia, Chile covers an area of 292,257 square miles. If you stretched Chile east to west across the United States, it would reach from Maine to California. Geographically, Chile offers diversity unmatched by most other countries. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; to the east, it is separated from Bolivia and Argentina by the towering Andes range (La Cordillera de los Andes), with peaks in Chile that rise to 22,600 feet. Peru shares a short border to the north. Within its borders, Chile has four distinct geographic zones: the dry northern desert, the fertile Central Valley, the forests and lakes of south-central Chile, and the archipelagos, fiords, and channels of the far south. The great northern desert or "Norte Grande," which covers one-fourth of the country, is one of the earth’s driest, most barren areas. Some parts have never recorded rainfall. Nonetheless, this desolate, inhospitable area produces rich mineral deposits of copper and nitrates that are vital to Chile’s economy. The Central Valley, where most Chileans live, begins with the Aconcagua River Basin north of Santiago and ends with the Bio-Bio River at Concepcion. The nation’s major industrial and agricultural production is located in this region. South of the Bio-Bio the landscape becomes increasingly forested. Especially striking is the area from southeast of Temuco south to Puerto Montt. Here the mountains are dotted with picturesque lakes, hot springs, and snow-capped volcanoes. This area, known as the Chilean Lake District (Región de los Lagos), is a favorite destination for Chilean and foreign tourists. South of Puerto Montt is an archipelago characterized by high rainfall, with forested fiords, glaciers, and sea channels. Still farther south are the windy steppes and sheep country of Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego. Chile also claims a wedge-shaped piece of Antarctica. Several Pacific islands are Chilean territory as well. The Juan Fernandez Islands are 360 miles southwest of Valparaiso. The marooned sailor, Alexander Selkirk, lived on one of these islands for 5 years; his adventures inspired Daniel Defoe’s novel, Robinson Crusoe. About 2,300 miles west of Chile is Easter Island, locally referred to as "Rapa-Nui," which is inhabited by ethnic Polynesians whose ancestors carved the gigantic stone monuments (Moai) for which the island is famous. |
| Climate | Chile's climate is as varied as its geography. Despite lying in the tropics, northern Chile is characterized by warm summers and mild winters, due to the moderating influence of the cool Humboldt Current. In the central region, where Santiago is located, summers (December to March) are dry, with warm days reaching into the high 80s or low 90s, but cooler nights. Winter (June to September) is generally cold, foggy, and rainy (rainfall averages 14 inches a year); temperatures climb into the 50s and 60s during the day and usually drop to the 40s at night, with occasional frost. The southern Lake District has cooler average temperatures and is wetter than the central region, with annual rainfall reaching 100 inches. In the far south, the climate is colder still, with gale force winds much of the year. Rainfall in this region also averages 100 inches annually, except in the Patagonian steppes, where it drops to an average of 20 inches a year. |
| Border Countries | Argentina 5,308 km, Bolivia 860 km, Peru 171 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Widespread deforestation and mining threaten natural resources; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Low coastal mountains; a fertile central valley; the rugged Andes in the east |
Chile Economy
How big is the Chile economy?
| Economic Overview |
Chile has a market-oriented economy characterized by a high level of foreign trade and a reputation for strong financial institutions and sound policy that have given it the strongest sovereign bond rating in South America. Exports of goods and services account for approximately one-third of GDP, with commodities making up some 60% of total exports. Copper is Chile’s top export and provides 20% of government revenue. From 2003 through 2013, real growth averaged almost 5% per year, despite a slight contraction in 2009 that resulted from the global financial crisis. Growth slowed to an estimated 1.4% in 2017. A continued drop in copper prices prompted Chile to experience its third consecutive year of slow growth. Chile deepened its longstanding commitment to trade liberalization with the signing of a free trade agreement with the US, effective 1 January 2004. Chile has 26 trade agreements covering 60 countries including agreements with the EU, Mercosur, China, India, South Korea, and Mexico. In May 2010, Chile signed the OECD Convention, becoming the first South American country to join the OECD. In October 2015, Chile signed the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade agreement, which was finalized as the Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and signed at a ceremony in Chile in March 2018. The Chilean Government has generally followed a countercyclical fiscal policy, under which it accumulates surpluses in sovereign wealth funds during periods of high copper prices and economic growth, and generally allows deficit spending only during periods of low copper prices and growth. As of 31 October 2016, those sovereign wealth funds - kept mostly outside the country and separate from Central Bank reserves - amounted to more than $23.5 billion. Chile used these funds to finance fiscal stimulus packages during the 2009 economic downturn. In 2014, then-President Michelle BACHELET introduced tax reforms aimed at delivering her campaign promise to fight inequality and to provide access to education and health care. The reforms are expected to generate additional tax revenues equal to 3% of Chile’s GDP, mostly by increasing corporate tax rates to OECD averages. |
| Industries | Copper, lithium, other minerals, foodstuffs, fish processing, iron and steel, wood and wood products, transport equipment, cement, textiles |
| Currency Name and Code | Chilean pesos (CLP) |
| Export Partners | China 26.3%, United States 13.2%, Japan 8.5%, South Korea 6.5%, Brazil 4.9% |
| Import Partners | China 23.4%, United States 18.8%, Brazil 7.8%, Argentina 4% |
Chile News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Chile?
Source: Google News
Chile Travel Information
What makes Chile a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
In addition to its stunning natural beauty, the Republic of Chile has a large, educated middle class and a robust free-market economy. Santiago and other large cities have well-developed tourist facilities and services, although the quality of tourist facilities may vary outside major populated areas. Spanish is the national language. English is frequently understood in major tourist hotels and resorts but is not widely used outside those areas.
Crime
Most foreigners visit Chile without incident. Nevertheless, street crime is a problem, especially in Santiago and Valparaiso. As in any large city, be cautious and aware of your surroundings. Be alert for pick-pocketing, purse and camera snatching, and thefts from backpacks and rental cars. Petty crime is common in major tourist destinations, in hotel lobbies and restaurants, internet cafes, at bus and subway stations, and in cruise ship ports. Exercise caution when touring Cerro Santa Lucia, Cerro San Cristobal, and Mercado Central as pick-pocketing and muggings occur frequently in these areas. Criminals usually work in groups and employ a variety of ruses to distract and victimize unsuspecting visitors. A few taxi drivers engage in currency switching and overcharge with altered taxi meters. Incidents of individuals smashing car windows of occupied vehicles stopped in traffic and taking items of value on seats have occurred. Drivers should keep car doors locked at all times and valuables out of sight while driving and while the vehicle is parked. Your passport is a valuable document. Report the loss or theft of a U.S. passport to the police and to the U.S. Embassy immediately. Secure your passport and other valuables in a hotel safe, and carry a photocopy of your passport for identification purposes. Leave copies of your passport and important documents with family members in case of emergency.Counterfeit and pirated goods may sometimes be available in Chile, and transactions involving such products are generally illegal under local law. In addition, bringing such goods back to the United States may result in forfeitures and/or fines.
The local equivalents to the “911” emergency lines in Chile follow an ABC-123 plan:
131 - Ambulancia/Ambulance
132 - Bomberos/Fire Department
133 - Carabineros/Police Department
Criminal Penalties
While in Chile, you are subject to Chile's laws and regulations. Chilean laws may differ significantly from those in the United States. You may not have the same protections available to you as under U.S. law, and penalties for breaking the law can also be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Chile's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Chile are strict, and convicted offenders can expect lengthy jail sentences and fines. Persons engaging in sexual conduct with children and using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country may be prosecuted in the United States.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Chile, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy in Santiago of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Languages
Spanish 99.5% (official), English 10.2%, Indigenous 1% (includes Mapudungun, Aymara, Quechua, Rapa Nui), other 2.3%, unspecified 0.2%; note - shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Santiago has two main private hospitals that are accredited by The American Hospital Association and meet U.S. standards: Clinica Alemana and Clinica Las Condes. Both have international patient departments and experience with some international insurance companies. Medical care in Chile is generally good, though it may not meet U.S. standards in remote areas. Major hospitals accept credit cards, but many doctors and hospitals in Chile expect immediate payment in cash. Prescriptions written by local doctors and over-the-counter medicines are widely available.Air pollution is a major health concern in Santiago, resulting in severe bronchial ailments affecting infants, small children, and the elderly. The most severe air pollution occurs during the winter (May through August).
The ozone layer is especially thin over parts of Chile. Take precautions to protect yourself from ultraviolet radiation.
Safety and Security
Demonstrations occur frequently. Although most are peaceful and have pre-approved routes, they sometimes become violent or change course with little warning. Demonstrations are common on March 29, the Day of the Young Combatant, and September 11, the anniversary of the 1973 coup against the government of President Salvador Allende. Even demonstrations that are meant to be peaceful can become violent and unpredictable. Avoid them if possible. Be alert and aware of your surroundings and pay attention to the local news media.Protest and anarchist groups are known to place small explosive devices at ATMs and other Chilean government/business locations, which have thus far resulted in few injuries. Several incidents occurred this year involving the fabrication of homemade explosive devices set in the lobbies of national and international banks, and at cash dispensing machines, normally between the hours of 2400 and 0400. Most of these incidents were planned to cause damage to buildings and make a political statement while minimizing the possibility of injury or death, but some have occurred in high-traffic pedestrian areas. The devices are usually comprised of black powder placed inside a fire extinguisher. Be aware of your surroundings and report anything unusual to the local police. U.S. citizens have not been targeted in these attacks.
Araucanía Conflict: The Mapuches, an indigenous group, make up a small percentage of the Chilean population and are concentrated in Araucanía and Santiago. Elements within some Mapuche communities are engaged in a conflict over land and indigenous rights in Chile. Violent individuals and activist groups seeking redress for grievances sometimes utilize protest tactics, including the burning of structures and pastures, attacks on trucks and other equipment, and death threats. There have been several attacks, allegedly perpetrated by Mapuche members, in the region of Araucanía (Region IX, in south-central Chile) since 2012 which have resulted in deaths. Other attacks on property have taken place in the same area. These attacks have targeted multinational forestry corporations and private Chilean landowners, rather than U.S. citizens or other foreigners. Nevertheless, U.S. citizens are advised to exercise caution when traveling in the Araucanía region.
Visitors to Easter Island may occasionally encounter non-violent demonstrations. Such demonstrations have caused minor disruption at the airport and closure of some government facilities. Demonstrations may result in minor inconveniences and occasional delays.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Chile, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States:Right-hand turns are prohibited at red lights unless otherwise posted.
Major highways in and around Santiago collect tolls through the use of an electronic transmitter (available at www.concesiones.cl ).
Secondary and mountain roads may be poorly maintained, poorly lit, and may lack guardrails.
Many drivers do not signal lane changes and rarely yield to merging traffic.
Many drivers exceed posted speed limits, do not maintain safe distances, and do not observe posted road signs.
Major arteries in Santiago may switch directions during morning and evening rush hours.
Drivers must carry sufficient Chilean pesos to pay frequent highway tolls.
Chile has modern infrastructure. Taxis and public transportation are plentiful and relatively inexpensive. Avoid using unmetered taxis; if you do use an unmetered taxi, agree to a fare before embarking. To use the public bus system in Santiago you need to obtain the prepaid “Bip” card. This card can also be used when traveling on the Santiago subway.
Driving under the influence of alcohol in Chile is severely punished (“Zero Tolerance” policy) and can result in incarceration.
Visitors for fewer than 90 days can rent a car and drive with a valid U.S. license, though insurance may not be available in some forms for drivers without a Chilean or international driver’s license. Visitors to Chile for more than 90 days must have an international driver's permit and their U.S. driver's license to legally drive in Chile. An international driver's license must be obtained in the United States before traveling to Chile. The police may fine foreigners for driving without a valid international permit.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
