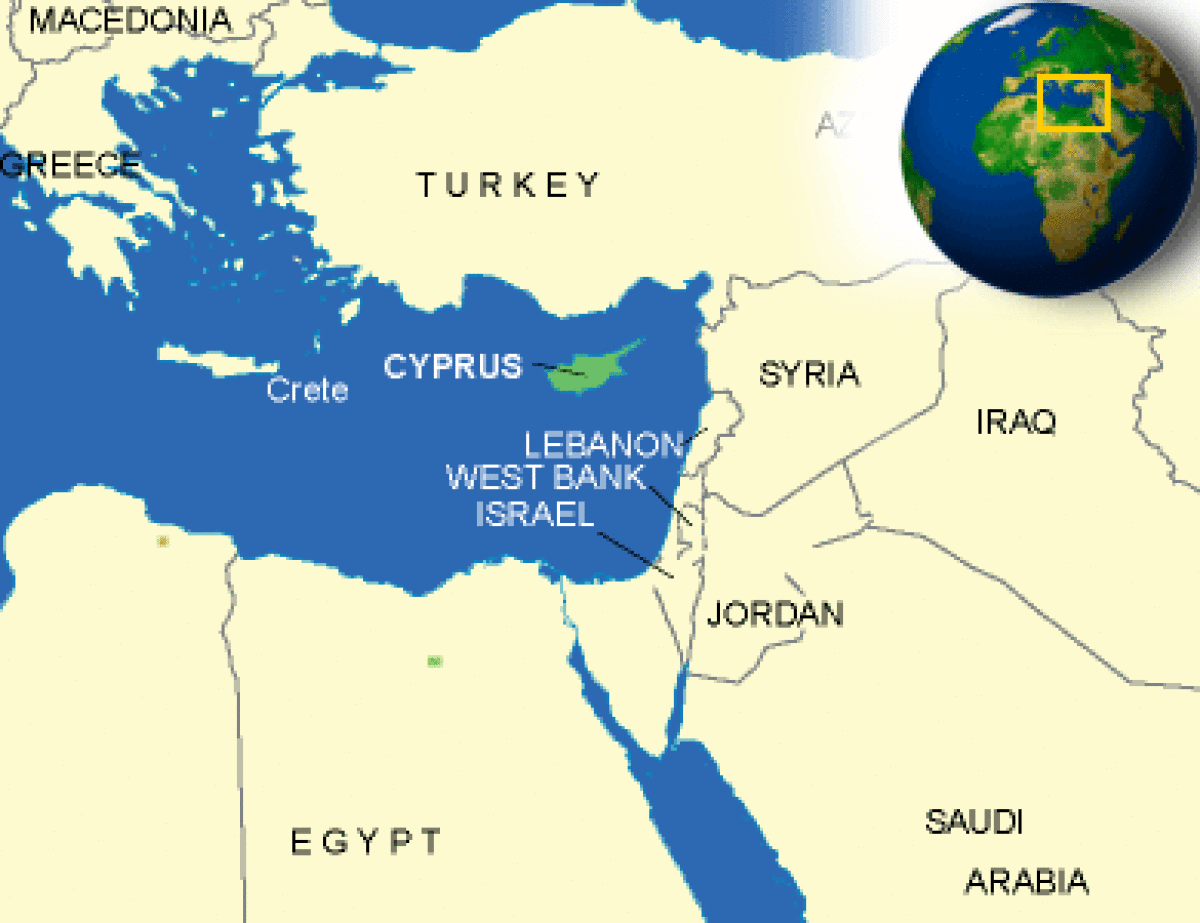
Where is Cyprus located?
What countries border Cyprus?
Cyprus Weather
What is the current weather in Cyprus?
Click for weather forecast
Cyprus Facts and Culture
What is Cyprus famous for?
- Family: One should not bring dishonor on the family. Parents strive to provide the young couple with a home, and perhaps... More
- Personal Apperance: Traditional costumes are worn at folk festivals and special events, including formal visits. Generally, people dress according to occupation, ranging... More
- Recreation: Futból (Soccer) is popular for both players and spectators. Three ski runs on Mount Olympus draw skiers from January... More
- Food and Recipes: Cyprus cuisine is closely related to that of Greece, but the island's unique position at the crossroads of Europe, Africa,... More
- Visiting: Visitors from outside Cyprus often note that Cyprus seems to be a place where 'everyone knows everyone else, or is... More
- Dating: Arranged marriages have largely disappeared, but some parents still exert a strong influence on the choice of spouse. Marriage is... More
Cyprus Facts
What is the capital of Cyprus?
| Capital | Nicosia (Lefkosia/Lefkosa) |
| Government Type |
Republic of Cyprus - presidential republic; self-declared "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus" (TRNC) - a parliamentary republic with an enhanced presidency Note: a separation of the two main ethnic communities inhabiting the island began following the outbreak of communal strife in 1963; this separation was further solidified when a Greek military-junta-supported coup attempt prompted the Turkish military intervention in July 1974 that gave the Turkish Cypriots de facto control in the north; Greek Cypriots control the only internationally recognized government on the island; on 15 November 1983, then Turkish Cypriot "President" Rauf DENKTAS declared independence and the formation of the "TRNC,” which is recognized only by Turkey |
| Currency | Greek Cypriot area: euros (EUR); Turkish Cypriot area: Turkish new lira (YTL) |
| Total Area |
3,572 Square Miles 9,251 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Middle East, island in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Turkey |
| Language | Greek, Turkish, English |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $34,400.00 (USD) |
Cyprus Demographics
What is the population of Cyprus?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent only the Greek-Cypriot citizens in the Republic of Cyprus |
| Ethnic Groups | Greek 98.8%, other 1% (includes Maronite, Armenian, Turkish-Cypriot), unspecified 0.2% |
| Languages | Greek (official) 80.9%, Turkish (official) 0.2%, English 4.1%, Romanian 2.9%, Russian 2.5%, Bulgarian 2.2%, Arabic 1.2%, Filipino 1.1%, other 4.3%, unspecified 0.6%; note - data represent only the Republic of Cyprus |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Cypriot(s) adjective: Cypriot |
| Population | 1,320,525 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.95% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 269,000 NICOSIA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 67% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.76% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 675,196 female: 645,329 |
Cyprus Government
What type of government does Cyprus have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Nikos CHRISTODOULIDIS (since 28 February 2023); the president is both chief of state and head of government; note - vice presidency reserved for a Turkish Cypriot but vacant since 1974 because Turkish Cypriots do not participate in the Republic of Cyprus Government head of government: President Nikos CHRISTODOULIDIS (since 28 February 2023) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president; note - under the 1960 constitution, 3 of the ministerial posts reserved for Turkish Cypriots, appointed by the vice president; positions currently filled by Greek Cypriots elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (limited to 2 consecutive terms); election last held on held 5 February 2023 with a runoff on 12 February 2023 (next to be held in 2028) election results: 2023: Nikos CHRISTODOULIDIS elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Nikos CHRISTODOULIDIS (independent) 32%, Andreas MAVROGIIANNIS (independent) 29.6%, Averof NEOFYTOU (DISY) 26.1%, Christos CHRISTOU (ELAM) 6%, other 6.3%; percent of vote in second round - Nikos CHRISTODOULIDS 52%, Andreas MAVROGIANNIS 48% 2018: Nikos ANASTASIADIS reelected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Nikos ANASTASIADIS (DISY) 35.5%, Stavros MALAS (AKEL) 30.2%, Nicolas PAPADOPOULOS (DIKO) 25.7%, other 8.6%; percent of vote in second round - Nikos ANASTASIADIS 56%, Stavros MALAS 44% note: the first round of the TRNC presidential election, originally scheduled for 26 April 2020, was postponed to 11 October 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic; the second round was held on 18 October 2020; percent of vote in the first round - Ersin TATAR (UBP) 32.4%, Mustafa AKINCI (independent) 29.8%, Tufan ERHURMAN (RTP) 21.7%, Kudret OZERSAY (independent) 5.7%, Erhan ARIKLI (YDP) 5.4%, Serdar DENKTAS (independent) 4.2%, other 0.8%; percent of vote in the second round - Ersin TATAR 51.7%, Mustafa AKINCI 48.3% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Cyprus dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 1 October (1960); note - Turkish Cypriots celebrate 15 November (1983) as "Republic Day" |
| Constitution |
history: ratified 16 August 1960; note - in 1963, the constitution was partly suspended as Turkish Cypriots withdrew from the government; Turkish-held territory in 1983 was declared the "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus" ("TRNC"); in 1985, the "TRNC" approved its own constitution amendments: constitution of the Republic of Cyprus - proposed by the House of Representatives; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority vote of the total membership of the "Greek Community" and the "Turkish Community"; however, all seats of Turkish Cypriot members have remained vacant since 1964; amended many times, last in 2020; constitution of the “Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus” - proposed by at least 10 members of the "Assembly of the Republic"; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority vote of the total Assembly membership and approval by referendum; amended 2014 |
| Independence | 16 August 1960 (from the UK); note - Turkish Cypriots proclaimed self-rule on 13 February 1975 and independence in 1983, but these proclamations are recognized only by Turkey |
Cyprus Video
Cyprus Urban Guide A Day in Nicosia - UrbanTV
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Cyprus Geography
What environmental issues does Cyprus have?
| Overview | Cyprus is in the eastern Mediterranean Basin, 44 miles south of Turkey, 64 miles west of Syria, and 150 miles north of the Nile Delta. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, makes visits to those regions quite easy. The island has a maximum length of 142 miles from northeast to southwest and a maximum width of 60 miles from north to south. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia, with an area of 3,572 square miles. Two mountain ranges dominate the landscape. The narrow and largely barren Kyrenia Range in the north (maximum elevation 3,360 feet) rises almost directly up from the northern coastline and follows it from east to west for some 80 miles. The forest‑covered Troodos Range rises in the southwestern sector of the island, culminating in Mount Olympus at an altitude of 6,400 feet. Between the two ranges, extending from Morphou Bay in the west to Famagusta Bay in the east lies the Mesaoria, meaning "between the mountains," a broad, fertile, coastal plain which produces most of the island’s cereal grains and other crops. Nicosia, the capital of Cyprus, is on the Mesaoria. Throughout the long summer, the plain is arid and parched, but in the winter and spring, it is carpeted with a lush growth of young wheat and barley. Cyprus supports a varied flora with some 1,800 different species of flowering plants, including over 120 endemic plants. Additionally, Cyprus is host to a diverse group of bird and insect fauna, as well as a surprising range of reptiles and amphibians. |
| Climate | Cyprus has hot, dry, dusty summers and moderately cool, damp winters. Nicosia's maximum mean temperature is about 80°F, while the minimum mean temperature is 50°F. From mid-June to mid-September, the temperature sometimes exceeds 100°F. After sunset, it usually falls to between 60°F and 70°F. The summer heat is tolerable because humidity is usually low and high temperatures are often tempered by westerly winds. Nicosia's summer weather is generally more comfortable than in the seaside towns, where humidity is higher though temperatures are lower. Rain falls almost exclusively from December through March. Winters are usually cool and damp. On the whole, Cyprus has an enjoyable Mediterranean climate. |
| Environment - Current Issues | Water resource problems (no natural reservoir catchments, seasonal disparity in rainfall, sea water intrusion to the island's largest aquifer, increased salination in the north); water pollution from sewage and industrial wastes; coastal degradation; loss of wildlife habitats from urbanization |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Central plain with mountains to the north and south; scattered but significant plains along the southern coast |
Cyprus Economy
How big is the Cyprus economy?
| Economic Overview |
The area of the Republic of Cyprus under government control has a market economy dominated by a services sector that accounts for more than four-fifths of GDP. Tourism, finance, shipping, and real estate have traditionally been the most important services. Cyprus has been a member of the EU since May 2004 and adopted the euro as its national currency in January 2008. During the first five years of EU membership, the Cyprus economy grew at an average rate of about 4%, with unemployment between 2004 and 2008 averaging about 4%. However, the economy tipped into recession in 2009 as the ongoing global financial crisis and resulting low demand hit the tourism and construction sectors. An overextended banking sector with excessive exposure to Greek debt added to the contraction. Cyprus’ biggest two banks were among the largest holders of Greek bonds in Europe and had a substantial presence in Greece through bank branches and subsidiaries. Following numerous downgrades of its credit rating, Cyprus lost access to international capital markets in May 2011. In July 2012, Cyprus became the fifth euro-zone government to request an economic bailout program from the European Commission, European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund - known collectively as the "Troika." Shortly after the election of President Nikos ANASTASIADES in February 2013, Cyprus reached an agreement with the Troika on a $13 billion bailout that triggered a two-week bank closure and the imposition of capital controls that remained partially in place until April 2015. Cyprus' two largest banks merged and the combined entity was recapitalized through conversion of some large bank deposits to shares and imposition of losses on bank bondholders. As with other EU countries, the Troika conditioned the bailout on passing financial and structural reforms and privatizing state-owned enterprises. Despite downsizing and restructuring, the Cypriot financial sector remains burdened by the largest stock of non-performing loans in the euro zone, equal to nearly half of all loans. Since the bailout, Cyprus has received positive appraisals by the Troika and outperformed fiscal targets but has struggled to overcome political opposition to bailout-mandated legislation, particularly regarding privatizations. The rate of non-performing loans (NPLs) is still very high at around 49%, and growth would accelerate if Cypriot banks could increase the pace of resolution of the NPLs. In October 2013, a US-Israeli consortium completed preliminary appraisals of hydrocarbon deposits in Cyprus’ exclusive economic zone (EEZ), which estimated gross mean reserves of about 130 billion cubic meters. Though exploration continues in Cyprus’ EEZ, no additional commercially exploitable reserves have been identified. Developing offshore hydrocarbon resources remains a critical component of the government’s economic recovery efforts, but development has been delayed as a result of regional developments and disagreements about exploitation methods. |
| Industries |
Greek Cypriot area: tourism, food and beverage processing, cement and gypsum, ship repair and refurbishment, textiles, light chemicals, metal products, wood, paper, stone and clay products Turkish Cypriot area: foodstuffs, textiles, clothing, ship repair, clay, gypsum, copper, furniture |
| Currency Name and Code | Greek Cypriot area: euros (EUR); Turkish Cypriot area: Turkish new lira (YTL) |
| Export Partners | Greece 10.9%, Ireland 10.2%, UK 7.2%, Israel 6% |
| Import Partners | Greece 25.7%, UK 9.1%, Italy 8%, Germany 7.5%, Israel 5.5%, China 4.8%, Netherlands 4.1% |
Cyprus News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Cyprus?
Source: Google News
Cyprus Travel Information
What makes Cyprus a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Cyprus is an island nation in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Since 1974, Cyprus has been divided between a government-controlled area, comprising the southern two-thirds of the island, and a northern third administered by Turkish Cypriots. The United States does not recognize the “Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus,” nor does any country other than Turkey. Facilities for tourism in Cyprus are highly developed. Cyprus joined the European Union in 2004.
Crime
Although the crime rate in Cyprus is low, visitors in any urban area should take the normal precautions they would take in any large city. Be alert and always vigilant of your surroundings and of your personal belongings. Criminals often target persons who are distracted, alone in an isolated area, or impaired. There has been a reported increase in the rate of home break-ins, particularly in Nicosia. Although most home break-ins take place overnight, this type of crime can take place at any time of day or night, as perpetrators seek targets of opportunity whenever available. As in any major metropolitan area, all travelers and residents should exercise care by locking all doors and windows to their homes, offices, and cars, and not leaving any valuables unattended or out in public view.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are these items illegal to bring back into the United States, by purchasing them you may also be breaking local law.
Avoid so-called “cabarets” or topless bars, as they reportedly employ women brought to Cyprus for sexual exploitation. These establishments can also present foreign patrons with grossly inflated bar tabs, and customers who refuse to pay may be threatened.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Cyprus, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States; for instance, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods while traveling overseas. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Cyprus, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.If you are arrested in Cyprus, authorities of Cyprus are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should ask the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. You also have the option to request communications from you be forwarded to the U.S. Embassy.
Languages
Greek (official) 80.9%, Turkish (official) 0.2%, English 4.1%, Romanian 2.9%, Russian 2.5%, Bulgarian 2.2%, Arabic 1.2%, Filipino 1.1%, other 4.3%, unspecified 0.6%; note - data represent only the Republic of Cyprus
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care is available both at government hospitals and private clinics. Emergency rooms offer adequate care to stabilize patients, most of who are then transferred to private hospitals. Many of the private-sector doctors have been trained in the United Kingdom or the United States. While fees are generally lower than those in the United States, medical supplies are often more expensive. Paramedics do not staff ambulances. The standard of medical care in the area administered by Turkish Cypriots is improving but still falls below that found in the government-controlled area. The World Health Organization considers Cyprus to be one of the healthiest areas of the Mediterranean. Water supplies are potable, and the refuse collection/sewage disposal system is adequate. Communicable diseases such as typhoid are rare. Respiratory ailments and allergies are sometimes exacerbated by the dry and dusty climate.
Safety and Security
Do not, under any circumstances, attempt to enter the U.N. buffer zone at any place other than a designated crossing point. This area is mined and militarized. Never photograph military installations or anything that could be perceived as being of security interest (especially in the areas not under the effective control of the Government of the Republic of Cyprus). Pay particular attention to areas marked with “no photography” signs. Police on both sides strictly enforce these restrictions.The Embassy has received reports of instances of discrimination and sexual harassment against U.S. citizens of Eastern European or non-European descent, particularly against U.S. citizens of Asian descent.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Cyprus, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.Driving conventions and practices in Cyprus differ from those you may be used to in the United States. Speeding, tailgating, overtaking, and the running of caution lights are commonplace and major causes of accidents. Emergency assistance is available in the Republic of Cyprus by calling 112 or 199. Emergency assistance is available in the area administered by Turkish Cypriots by calling 155.
There are few public buses and no rail lines in Cyprus. Taxis are widely available. Traffic moves on the left side of the road, British style, and modern motorways link the major cities. Secondary roads, especially in mountainous areas, tend to be narrow and winding, and not as well maintained as major highways. Traffic laws, signs, and speed limits are consistent with the standards used throughout Europe. Traffic circles (roundabouts) are often utilized at major intersections.
The use of seat belts (in front seats) and child car seats is required. Motorcyclists are required to wear helmets and the use of cellular phones while driving is prohibited unless used with some form of hands-free kit. Liability insurance is mandatory.
Road safety conditions in the area administered by Turkish Cypriots are similar to conditions in the south, except that the road network is less developed. Insurance purchased in the government-controlled area is not valid in the area administered by Turkish Cypriots, but insurance for that area may be purchased near the U.N. buffer zone checkpoints.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
