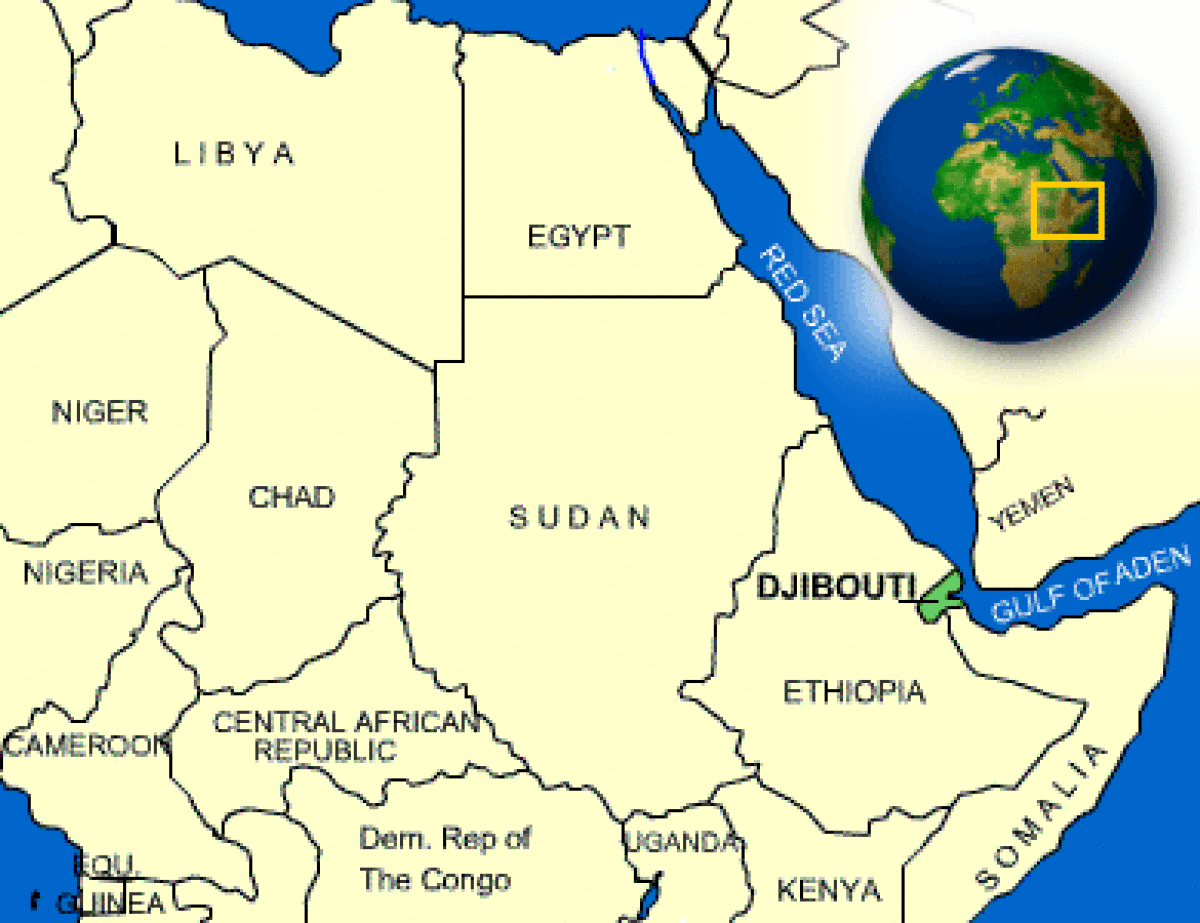
Where is Djibouti located?
What countries border Djibouti?
Djibouti Weather
What is the current weather in Djibouti?
Djibouti Facts and Culture
What is Djibouti famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Djiboutians respect traditional especially oral poetry and song. The visual arts are influenced by Islam which does not allow humans... More
- Family: Djiboutians show great respect for their elders. Family relationships are strong among the nomads because they do not have a... More
- Personal Apperance: Women in Djibouti do not wear veils although Afar women wear a black headscarf. In the cities people wear Western... More
- Recreation: In rural areas women enjoy visiting and doing crafts such as weaving or needlework while talking. Men enjoy drinking coffee... More
- Food and Recipes: Islamic dietary laws are observed by many which include not eating pork or drinking alcohol. Goats, sheep, camels and cattle... More
Djibouti Facts
What is the capital of Djibouti?
| Capital | Djibouti |
| Government Type | Presidential republic |
| Currency | Djiboutian francs (DJF) |
| Total Area |
8,958 Square Miles 23,200 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, between Eritrea and Somalia |
| Language | French (official), Arabic (official), Somali, Afar |
| GDP - real growth rate | 6.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $3,400.00 (USD) |
Djibouti Demographics
What is the population of Djibouti?
| Ethnic Groups | Somali 60%, Afar 35%, French, Arab, Ethiopian, and Italian 5% |
| Nationality Noun | Djiboutian(s) |
| Population | 921,804 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.26% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | DJIBOUTI (capital) 496,000 |
| Urban Population | 77.100000 |
Djibouti Government
What type of government does Djibouti have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President Ismail Omar GUELLEH (since 8 May 1999) Head of Government: Prime Minister Abdoulkader Kamil MOHAMED (since 1 April 2013) Cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister Elections/Appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term; election last held on 9 April 2021 (next to be held in April 2026); prime minister appointed by the president Election results: 2021: Ismail Omar GUELLEH reelected president for a fifth term; percent of vote - Ismail Omar GUELLEH (RPP) 97.4%, Zakaria Ismael FARAH (MDEND) 2.7% 2016: Ismail Omar GUELLEH reelected president for a fourth term; percent of vote - Ismail Omar GUELLEH (RPP) 87%, Omar Elmi KHAIREH (CDU) 7.3%, other 5.6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: The mother must be a citizen of Djibouti Dual citizenship recognized: No Residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 27 June (1977) |
| Constitution |
History: Approved by referendum 4 September 1992 Amendments: Proposed by the president of the republic or by the National Assembly; Assembly consideration of proposals requires assent of at least one third of the membership; passage requires a simple majority vote by the Assembly and approval by simple majority vote in a referendum; the president can opt to bypass a referendum if adopted by at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly; constitutional articles on the sovereignty of Djibouti, its republican form of government, and its pluralist form of democracy cannot be amended; amended 2006, 2008, 2010 |
| Independence | 27 June 1977 (from France) |
Djibouti Video
Geography Now- YouTube Geography Now! Djibouti
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Djibouti Geography
What environmental issues does Djibouti have?
| Overview |
The Republic of Djibouti is situated in the Horn of Africa on Africa’s east coast. Djibouti covers 8,400 square miles (21,883 square kilometers). The country is shaped like a "C" surrounding the Gulf of Tadjoura, an inlet off the Gulf of Aden. Along with Eritrea and Yemen, Djibouti shares direct access to the strategic Bab el Mandeb, the "Gate of Tears," which controls southern access to the Red Sea. Djibouti’s capital, also called Djibouti, is a verdant oasis in an area of dry watersheds composed of harsh, stony desert and low, barren hills. The capital is at sea level and mostly surrounded by water, affording sea views from much of the city. In addition to Djibouti City, Djibouti has four provincial capitals: Ali Sabieh and Dikhil in the interior to the south and west, and Tadjoura and Obock on the north coast of the Gulf of Tadjoura. The landscape beyond the capital, though largely barren, is quite strange and impressive. Beyond the Gulf of Tadjoura via a narrow strait is the Ghoubet, a deep body of blue water with two striking volcanic islands. The coastline north of the Gulf of Tadjoura juxtaposes palm-lined beaches with jagged hills. In the north a large high desert region rises to Mount Moussa Ali, the highest point in Djibouti (3,600 feet). Also to the north is the Forêt du Dai, a national park on Mount Goda. In this last vestige of a forest that once covered the area are several rare plants and animals, including monkeys and antelope. Lake Assal, a unique natural phenomenon over 500 feet below sea level, is 80 miles west of Djibouti City. A lake ten times saltier than the ocean, Lake Assal is an ethereal blue and surrounded by picturesque volcanic hills. It is the lowest body of water in Africa and the second lowest on Earth. Farther into the countryside to the southwest lies Lake Abbe, a large salt lake bisected by the Djibouti-Ethiopia border. Djibouti’s location astride the East Africa, Red Sea, and Gulf of Aden rift systems provides a unique environment for studying volcanic, geothermal, and earthquake activity arising from the meeting of three tectonic plates. Over 600 tremors occur every year, virtually none of which are felt. |
| Climate |
Djibouti has two seasons. During the May-to-September hot season, daytime temperatures average over 100°F and often exceed 120°F. The high temperatures are sometimes accompanied by hot, sandy winds called the "Kahm Sin." The beginning and ending months of the hot season are also marked by high humidity. The cooler season, from October through April, has clear skies, refreshingly cool breezes, somewhat lower humidity, and temperatures in the 80s. Because of its geographic location between the Ethiopian and Yemeni escarpments, Djibouti gets little precipitation. Occasional rains occur mostly in the hills in the interior, but the average annual rainfall is only 5 to 10 inches. Rains most often come to Djibouti City in the fall and spring; some years are rainless. Because of a high water table and lack of drainage, the rare heavy rain can cause flooding in and around the capital. |
| Border Countries | Eritrea 109 km, Ethiopia 349 km, Somalia 58 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Inadequate supplies of potable water; limited arable land; desertification; endangered species |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | coastal plain and plateau separated by central mountains |
Djibouti Economy
How big is the Djibouti economy?
| Economic Overview |
Djibouti's economy is based on service activities connected with the country's strategic location as a deepwater port on the Red Sea. Three-fourths of Djibouti's inhabitants live in the capital city; the remainder are mostly nomadic herders. Scant rainfall and less than 4% arable land limits crop production to small quantities of fruits and vegetables, and most food must be imported. Djibouti provides services as both a transit port for the region and an international transshipment and refueling center. Imports, exports, and reexports represent 70% of port activity at Djibouti's container terminal. Reexports consist primarily of coffee from landlocked neighbor Ethiopia. Djibouti has few natural resources and little industry. The nation is, therefore, heavily dependent on foreign assistance to support its balance of payments and to finance development projects. An official unemployment rate of nearly 40% - with youth unemployment near 80% - continues to be a major problem. Inflation was a modest 3% in 2014-2017, due to low international food prices and a decline in electricity tariffs. Djibouti’s reliance on diesel-generated electricity and imported food and water leave average consumers vulnerable to global price shocks, though in mid-2015 Djibouti passed new legislation to liberalize the energy sector. The government has emphasized infrastructure development for transportation and energy and Djibouti – with the help of foreign partners, particularly China – has begun to increase and modernize its port capacity. In 2017, Djibouti opened two of the largest projects in its history, the Doraleh Port and Djibouti-Addis Ababa Railway, funded by China as part of the "Belt and Road Initiative," which will increase the country’s ability to capitalize on its strategic location. |
| Industries | Construction, agricultural processing, shipping |
| Currency Name and Code | Djiboutian francs (DJF) |
| Export Partners | Somalia 79.8%, US 5.4%, Yemen 4.6%, UAE 4% |
| Import Partners | China 42.1%, Saudi Arabia 14.3%, Indonesia 5.9%, India 4.4% |
Djibouti News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Djibouti?
Source: Google News
Djibouti Travel Information
What makes Djibouti a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Djibouti is a developing country located at the juncture of the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean that gained independence from France in 1977. It is a multi-party democracy with a legal system based on French civil law, though modified by traditional practices and Islamic (Sharia) law. Although exact numbers are unavailable, unemployment is estimated to be in excess of 60% of the working-age population. Over two-thirds of the country’s estimated 850,000 residents live in the capital, also called Djibouti. Modern tourist facilities and communications infrastructure exist in the city of Djibouti but are limited outside the capital.
Crime
Accurate Djiboutian crime statistics are not available, but the majority of crimes are petty theft and crimes of opportunity. Anecdotal evidence suggests an increasing frequency of violent crimes against Djiboutian citizens and burglaries of residences in established neighborhoods. Violent crimes against foreigners are rare in Djibouti. However, foreigners are frequent victims of snatch-and-grab robberies and price gouging by unscrupulous taxi drivers.Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Djibouti, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in Djibouti, but still illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Djibouti, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what is legal and what is not wherever you go.If you are arrested in Djibouti, you have the right to request authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. The U.S. does not have an agreement with Djibouti requiring notification of the U.S. Embassy upon your arrest. If you are arrested in Djibouti you should use whatever means of communication available to alert the U.S. Embassy of your situation.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical facilities in the capital of Djibouti are limited and trauma services are only for stabilization and air ambulance transfer. Medical services in many outlying areas are nonexistent. Even in the capital, hospitals are unable to treat many ailments and frequently recommend medical evacuation. Visitors to Djibouti should purchase medical evacuation insurance. Hospitals in Djibouti require up-front cash payment for services and do not have service agreements with U.S. insurance companies. Cash payment will be requested in full before the patient is allowed to depart the hospital – reimbursement may then be requested by the U.S. Citizen through their insurance company in the United States.U.S. Motorists should be especially aware that, in case of an accident outside the capital, emergency medical treatment would depend on assistance from passersby. In addition, cell phone coverage in outlying areas is often unavailable, making it impossible to summon help. Ambulance service in Djibouti is limited in effectiveness, must be scheduled and paid for in advance and is only a means of transportation. U.S. Citizen visitors to Djibouti are not permitted to access Embassy or U.S. Military medical facilities and must depend entirely on local medical facilities.
Malaria and dengue fever are endemic to Djibouti. Travelers who become ill with a fever or flu-like illness while traveling in a malaria-risk area and even up to one year after returning home should seek prompt medical attention, tell their medical provider about their travel history and what anti-malarial drugs they have been taking.
In 2013, polio was found in Djibouti’s neighbors (Somalia and Ethiopia), and health professionals strongly suspect it is present in Djibouti. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that all infants and children in the United States should receive four doses of inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) at 2, 4, 6–18 months and 4–6 years of age. Adults traveling to polio-endemic and epidemic areas and who have received a primary series with either IPV or oral polio vaccine should receive another dose of IPV. For adults, available data does not indicate the need for more than a single lifetime booster dose with IPV.
Tuberculosis is a serious health concern in Djibouti, including multi-drug resistant strains. For further information, please consult the CDC's information on TB.
In May 2006, avian influenza was confirmed in three chickens and one human in Djibouti.
Safety and Security
Djibouti’s historically stable political climate tends to become more fluid following national elections. In 2011 following a Presidential election and in February 2013 following parliamentary elections, sporadic protesting marked by rock throwing and tire burning disrupted travel around the city. If you see a demonstration, do not try to walk or drive through it. Remember the importance of maintaining a low profile. Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence. You should avoid areas of demonstrations, and exercise caution near any large gatherings, protests, or demonstrations.Djibouti’s international borders are porous. Terrorism poses a threat in east Africa and in particular, al-Shabaab (which merged with al-Qaeda in February 2012) poses a threat to U.S. citizens in Djibouti. After Djibouti announced it would join the AMISOM peacekeeping mission to Somalia, al Shabaab threatened to retaliate by launching attacks inside Djibouti. On July 11, 2010, al-Shabaab launched simultaneous suicide attacks at two popular venues in Kampala, Uganda where people had gathered to watch the World Cup. Dozens of people were killed and injured, including Americans. U.S. citizens traveling in east Africa should be aware of the potential for indiscriminate attacks on civilian targets in public places, including hotels, and tourist sites where Westerners are known to congregate. Kidnapping of Westerners for ransom is a growing concern in the region. Read our Worldwide Caution for more information on terrorism in Africa.
Tensions exist between neighboring Ethiopia and Eritrea due to their long-running border dispute. Relations were further aggravated in January 2012 when ethnic Afar gunmen attacked a Western tourist convoy travelling in Ethiopia's northeastern region that borders Djibouti. In March and May 2012, Ethiopia staged raids across the Eritrean border - bringing tensions to their highest point since the 1998-2000 war between the two countries.
Since April 2008, there has been tension on Djibouti’s border with Eritrea after the Eritrean military occupied disputed territory, killing several Djiboutian soldiers and wounding dozens more. Americans in Djibouti should not attempt to cross the land border with Eritrea nor travel north of the town of Obock. Civil unrest or armed conflict in neighboring countries could disrupt air travel to and from Djibouti or otherwise negatively affect its security. Travelers should exercise caution when traveling to any remote area of Djibouti, especially near the borders with Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
Pirates and other criminals have specifically targeted and kidnapped foreigners working in Somalia. In October 2011, a U.S. citizen aid worker living in Somalia was kidnapped, and in January 2012, another U.S. citizen was kidnapped while on work-related travel in Somalia. In both cases, as well as in recent kidnappings of other Westerners, the victims took precautionary measures by hiring local security personnel, but those hired to protect them appear to have played a key role in the abductions. A strong familiarity with Somalia and/or extensive prior travel to the region does not reduce travel risk. Any U.S. citizens travelling to Somalia, including Somaliland and Puntland, are advised to obtain Kidnap and Recovery Insurance, as well as Medical Evacuation Insurance, prior to travel and register with the U.S. Embassy in Nairobi, which covers Somalia.
Seaborne travel near Djibouti is extremely dangerous. There have been hundreds of incidents of armed attacks and robberies at sea by pirate groups on ships transiting around the Horn of Africa. On February 21, 2011, pirates hijacked a yacht in the Gulf of Aden carrying four Americans, who were subsequently killed. Additionally, after the April 2009 hijacking of a U.S. cargo vessel and subsequent rescue of the vessel’s captain by U.S. forces, Somali pirates threatened to retaliate against U.S. citizens transiting the region. See our International Maritime Piracy Fact Sheet. Also, please see the Somalia Travel Warning and the U.S. Department of Transportation Maritime Administration Maritime Advisory
In the event that seaborne travel is unavoidable, vessels should convoy in groups and maintain good communications contact at all times. Marine channels 12, 13 and 16 VHF-FM are international call-up and emergency channels and are commonly monitored by ships at sea. 2182 MHz is the HF international call-up and emergency channel. In the Gulf of Aden, use of transit routes farther offshore appears to reduce, but does not eliminate, the risk of contact with assailants. Wherever possible, travel in trafficked sea-lanes. Avoid loitering in or transiting isolated or remote areas. In the event of an attack, activate the Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon. Due to distances involved, there may be a considerable delay before assistance arrives. Vessels may also contact the Yemeni Coast Guard 24-hour Operations Center at 967-1-562-402. Operations Center staff members speak English.
The United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) has advised that elevated regional tensions have increased the risk of maritime attacks being conducted by extremist to vessels operating in the Gulf of Oman, North Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden, and the Bab el Mandeb regions.
MARAD recommends vessels at anchor, operating in restricted maneuvering environments, or at slow speeds should be especially vigilant, and report suspicious activity. U.S. flag vessels that observe suspicious activity in the area are advised to report such suspicious activity or any hostile or potentially hostile action to Commander, U.S. Naval Forces Central Command (COMUSNAVCENT) battlewatch captain at phone number 011-973-1785-3879. All suspicious activities and events are also to be reported to the U.S. Coast Guard National Response Center at the following toll free telephone: 1-800-424-8802, direct telephone 202-267-2675, or TDD 202-267-4477. The complete advisory is available on the MARAD website at www.MARAD.DOT.gov.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Djibouti, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Djibouti is provided for general reference only, and may not be accurate in a particular location or circumstance.The only means of public inter-city travel is by bus. Buses are poorly maintained and their operators often drive erratically with little regard for passenger safety. Taxis should be avoided at all costs.
Driving on Djiboutian roads can be hazardous. Since most roads do not have shoulders or sidewalks, pedestrians and livestock use the roadways both day and night. Driving at night is extremely dangerous and strongly discouraged on all roads outside Djibouti City. While some main roads in Djibouti are well maintained, roads are often narrow, poorly lit, or rutted. Many secondary roads are in poor repair. Drivers and pedestrians should exercise extreme caution. Minibuses and cars often break down; when breakdowns occur, local drivers usually place branches or rocks behind the vehicle to indicate trouble, but these warning signals are barely visible and hazardous in and of themselves. Excessive speed, unpredictable local driving habits, pedestrians, and livestock in the roadway, and the lack of basic safety equipment on many vehicles are daily hazards. Speed limits are posted occasionally but are not enforced. The leafy narcotic – khat, is widely used, particularly in the afternoons, creating other traffic hazards.
The Djiboutian Gendarmerie and the National Police Force share responsibility for road safety in Djibouti. In March 2012, a “Road Police” was created, though its role has yet to be clearly defined. Djiboutian authorities recently erected traffic lights to help regulate the flow of traffic. Be very cautious approaching these lights, as many other drivers continue to disregard them. It is illegal to turn right on a red light. Travelers should be aware that police use large obstacles as roadblocks on some of the major roads, and these may be difficult to see at night.
There are two main international highways to the capital city, via Dire Dawa, Ethiopia, and Obock, Djibouti, and both demand that drivers remain vigilant. The route toward Dire Dawa is in very poor condition. Both have a high volume of Ethiopian trucks transporting large cargo. Railroad crossings are not clearly marked. Drivers who do not have a four-wheel drive vehicle will encounter problems driving on rural roads. While the quality of roads is improving, drivers should make sure their vehicle is in good mechanical condition before leaving major population centers. Once a driver has left Djibouti city there are limited services to aid broken-down vehicles. The Embassy recommends that U.S. Citizens travel in two-vehicle caravans outside the city. In addition, gasoline is not readily available outside of Djibouti City so drivers utilizing a gasoline-powered vehicle should plan accordingly. Diesel fuel is available in other areas of Djibouti.
There are no emergency services in Djibouti. It will be difficult to coordinate medical assistance in the event of an accident. It is always advisable to carry a cell phone or satellite phone when undertaking a trip outside of the capital; however, many parts of the country do not have cell phone coverage.
While Djibouti has been declared a “mine-safe” country, this indicates that landmines have been identified and marked, not that they have been removed. Landmines are known to be present in northern Tadjourah and Obock districts. In addition, there may be mines in the Ali Sabieh area of the south. In March 2012, a 12-year-old boy was seriously injured by a land mine near Lac Assal and Ghoubet, two popular tourist destinations. The incident occurred in the area known as Dabaleh Gahar, east of where National Route 10 splits off from National Route 9. This location is approximately 20 km southeast of where most people visit Lac Assal, about one kilometer from the paved road. This area was home to a Djiboutian military encampment during the civil war (1991-1994) and the mine likely remained in place after that conflict. Travelers should stay on paved roads and should check with local authorities before using unpaved roads.
