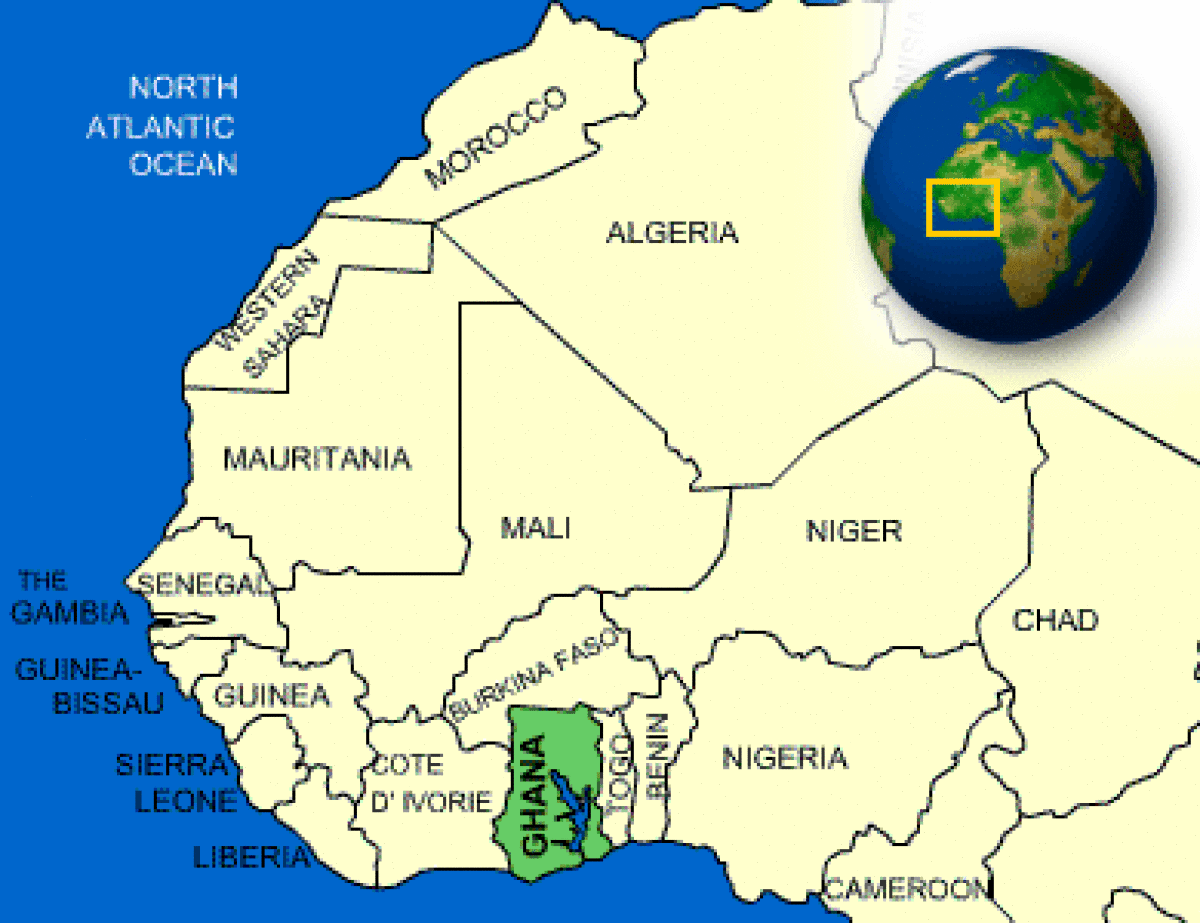
Where is Ghana located?
What countries border Ghana?
Ghana Weather
What is the current weather in Ghana?
Ghana Facts and Culture
What is Ghana famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Ghanaian's are a polite and open people. They live life at a relaxed pace. People are more important than... More
- Family: Family structures vary from one ethnic group to another. Some family groups have the chief responsibilities for the family... More
- Personal Apperance: Ghanaian dress is modest, neat, and generally conservative. Casual dress is the rule for most occasions, although a suit and... More
- Recreation: The most popular sport is football (soccer). Basketball and tennis are the popular sports of the wealthy. More
- Diet: Popular foods are yams, cassava (a starchy root), rice, plantain and maize. Eating fish is most common due to... More
- Food and Recipes: A bowl of water is provided at the beginning of the meal, in which each person washes the hands. Food... More
- Visiting: Friends and relatives frequently visit and typically do not need an appointment to do so. Ghananian's work hard to... More
- Dating: Many marriages are arranged by families, although the children have the right to reject the arrangement. Marriage in rural... More
Ghana Facts
What is the capital of Ghana?
| Capital | Accra |
| Government Type | Presidential republic |
| Currency | Cedi (GHC) |
| Total Area |
92,098 Square Miles 238,533 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Africa, bordering the Gulf of Guinea, between Cote d'Ivoire and Togo |
| Language | English (official), African languages (including Akan, Moshi-Dagomba, Ewe, and Ga) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $4,300.00 (USD) |
Ghana Demographics
What is the population of Ghana?
| Ethnic Groups | Black African 98.5% (major tribes - Akan 44%, Moshi-Dagomba 16%, Ewe 13%, Ga 8%, Gurma 3%, Yoruba 1%), European and other 1.5% |
| Languages | The official language of Ghana is English. There are movements to make several local languages official as well. The Twi dialect of Akan is the language most commonly used on a daily basis to communicate between ethnic groups. Most Ghanaians are at least bilingual. |
| Nationality Noun | Ghanaian(s) |
| Population | 29,340,248 |
| Population - note | Note: Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.19% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | ACCRA (capital) 2.573 million; Kumasi 2.019 million |
| Urban Population | 51.900000 |
Ghana Government
What type of government does Ghana have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (since 7 January 2017); Vice President Mahamudu BAWUMIA (since 7 January 2017); the president is both chief of state and head of government Head of Government: President Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (since 7 January 2017); Vice President Mahamudu BAWUMIA (since 7 January 2017) Cabinet: Council of Ministers; nominated by the president, approved by Parliament Elections/Appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 December 2020 (next to be held on 7 December 2024) Election results: 2020: Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (NPP) 51.3%, John Dramani MAHAMA (NDC) 47.4%, other 1.3% (2020) |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: At least one parent or grandparent must be a citizen of Ghana Dual citizenship recognized: Yes Residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 6 March (1957) |
| Constitution |
History: Several previous; latest drafted 31 March 1992, approved and promulgated 28 April 1992, entered into force 7 January 1993 Amendments: Proposed by Parliament; consideration requires prior referral to the Council of State, a body of prominent citizens who advise the president of the republic; passage of amendments to "entrenched" constitutional articles (including those on national sovereignty, fundamental rights and freedoms, the structure and authorities of the branches of government, and amendment procedures) requires approval in a referendum by at least 40% participation of eligible voters and at least 75% of votes cast, followed by at least two-thirds majority vote in Parliament, and assent of the president; amendments to non-entrenched articles do not require referenda; amended 1996 |
| Independence | 6 March 1957 (from the UK) |
Ghana Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Ghana Geography
What environmental issues does Ghana have?
| Overview |
Ghana is situated on West Africa’s Gulf of Guinea, and its capital, Accra, is 4 degrees north of the Equator. Ghana covers 238,540 square kilometers and is about the size of Oregon. Half of the country lies less than 152 meters above sea level and the highest point is 883 meters. The 537-kilometer coastline is mostly a low, sandy shore backed by a narrow coastal plain with scrub brush, and intersected by rivers and streams, navigable only by canoe. A tropical rain forest belt, broken by heavily forested hills and many streams and rivers, extends northward from the shore near the border with Côte d’Ivoire. This area, traditionally known as Ashanti, but now divided into several administrative regions, produces most of Ghana’s cocoa, minerals, and timber. North of this belt the country varies from 91 to 396 meters above sea level and is covered by low bush, savanna, and grassy plains. A major feature of the country’s geography is the Volta Lake, the world’s largest manmade lake (8,900 square kilometers), which extends from the Akosombo Dam (completed in 1966) in southeastern Ghana to the town of Yapei, 520 kilometers to the north. The dam generates electricity for all of Ghana as well as some exports to neighboring countries. The lake also serves as an inland waterway and is a potentially valuable resource for irrigation and fish farming. |
| Climate |
Ghana's climate is tropical with temperatures between 21°C and 32°C (70°F and 90°F). Rainy seasons extend from April to July (heavy rains) and from September to November (light rains). Annual rainfall exceeds 200 centimeters on the coast, decreasing inland. Accra’s annual rainfall averages about 76 centimeters, low for coastal West Africa. The southern part of the country is humid most of the year, but the north can be very dry. It is coolest from May until October. In December the harmattan, a dry dusty wind from the Sahara, covers the country, and lasts through February. The desert wind reduces humidity, and early mornings and nights are relatively cool. Visibility during the harmattan can be poor, as the air is filled with fine dust. |
| Border Countries | Burkina Faso 549 km, Cote d'Ivoire 668 km, Togo 877 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Recurrent drought in the north severely affects agricultural activities; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; poaching and habitat destruction threatens wildlife populations; water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable water |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | Mostly low plains with dissected plateau in south-central area |
Ghana Economy
How big is the Ghana economy?
| Economic Overview |
Ghana has a market-based economy with relatively few policy barriers to trade and investment in comparison with other countries in the region, and Ghana is endowed with natural resources. Ghana's economy was strengthened by a quarter century of relatively sound management, a competitive business environment, and sustained reductions in poverty levels, but in recent years has suffered the consequences of loose fiscal policy, high budget and current account deficits, and a depreciating currency. Agriculture accounts for about 20% of GDP and employs more than half of the workforce, mainly small landholders. Gold, oil, and cocoa exports, and individual remittances, are major sources of foreign exchange. Expansion of Ghana’s nascent oil industry has boosted economic growth, but the fall in oil prices since 2015 reduced by half Ghana’s oil revenue. Production at Jubilee, Ghana's first commercial offshore oilfield, began in mid-December 2010. Production from two more fields, TEN and Sankofa, started in 2016 and 2017 respectively. The country’s first gas processing plant at Atuabo is also producing natural gas from the Jubilee field, providing power to several of Ghana’s thermal power plants. As of 2018, key economic concerns facing the government include the lack of affordable electricity, lack of a solid domestic revenue base, and the high debt burden. The AKUFO-ADDO administration has made some progress by committing to fiscal consolidation, but much work is still to be done. Ghana signed a $920 million extended credit facility with the IMF in April 2015 to help it address its growing economic crisis. The IMF fiscal targets require Ghana to reduce the deficit by cutting subsidies, decreasing the bloated public sector wage bill, strengthening revenue administration, boosting tax revenues, and improving the health of Ghana’s banking sector. Priorities for the new administration include rescheduling some of Ghana’s $31 billion debt, stimulating economic growth, reducing inflation, and stabilizing the currency. Prospects for new oil and gas production and follow through on tighter fiscal management are likely to help Ghana’s economy in 2018. |
| Industries | Mining, lumbering, light manufacturing, aluminum smelting, food processing |
| Currency Name and Code | Cedi (GHC) |
| Export Partners | Netherlands 14.6%, UK 9.7%, US 6.9%, Germany 6.4%, France 5.7%, Nigeria 4.7%, Belgium 4.4%, Italy 4.1% |
| Import Partners | Nigeria 20.8%, UK 7%, US 6.4%, China 6%, Italy 6%, Cote d'Ivoire 6%, Germany 4.6% |
Ghana News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Ghana?
Source: Google News
Ghana Travel Information
What makes Ghana a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Ghana is a developing country on the west coast of Africa. The capital is Accra. Tourist facilities are available in the population centers of the greater Accra region, Kumasi in the Ashanti region, and in the Cape Coast area of the Central region. They are limited in the more remote areas of the country. English is the official language.
Crime
Pick-pocketing, purse-snatching, and various types of scams are the most common forms of crime confronting visitors. Travelers have reported these types of theft at crowded markets, beaches, parks, and tourist attractions. Incidences of violent crime, such as armed robbery, are on the rise, including reports of armed robberies in expatriate residential and shopping areas, specifically the Osu and Ablekuma/Dzorwulu neighborhoods after 10 p.m. Victims who resist attackers run a high risk of serious physical injury. Take security measures, such as traveling in groups and avoiding travel at night. Avoid travel in communal taxis. Travelers who limit their display of jewelry and handle their cash discreetly reduce their vulnerability to crime. Pay close attention to those around you or following you, particularly after exchanging money, making a purchase, or withdrawing money from an ATM. Travelers should carry limited amounts of cash and only photocopies of key documents.Thefts of both luggage and travel documents occur at Kotoka International Airport in Accra and in hotels across Ghana. All U.S. citizens should ensure that documents are kept secure at all times (including when leaving the airport) and that baggage is never left unattended. Travelers should be wary of all offers of unsolicited assistance at the airport unless from uniformed porters or officials. All permanent staff at the airport are issued current ID cards bearing their name and photograph. ID cards without a photograph are not valid. Travelers who are met at the airport should confirm the identity of their driver, either by requesting proper identification or otherwise verifying that the driver is an official from an organization or a hotel. There have been increasing incidences of impostors who approach travelers before the main arrivals area claiming to be the traveler's driver or contact. The impostor will have obtained the traveler's name from the board displayed by the official driver in the arrivals area outside the airport. The impostor then attempts to extort money from the traveler once the traveler is in the impostor's vehicle.
Use of credit cards in Ghana should be avoided if possible, as a growing number of travelers have been victims of credit card fraud.
In recent years, U.S. citizens have reported substantial financial losses from questionable transactions involving gold and other precious metals. The Government of Ghana maintains strict regulations on these natural resources. All agents must be licensed and all transactions must be certified. (See Special Circumstances below.)
Perpetrators of business fraud often target foreigners, including U.S. citizens. Such fraud schemes are now prevalent throughout West Africa, including Ghana.
U.S. citizens frequently consult the Embassy regarding questionable business offers sent from Ghana. These are scams and typically begin with an unsolicited communication (usually by e-mail) from an unknown individual who describes a situation that promises quick financial gain, often by assisting in the transfer of a large sum of money or valuables out of the country. A series of "advance fees" must be paid in order to conclude the transaction, such as fees to open a bank account or to pay certain taxes. In fact, the final payoff does not exist; the purpose of the scam is simply to collect money from the victim. The Embassy has also received reports of fraudulent charities soliciting contributions through the Internet or direct mail. If you receive such business offers or charity requests, carefully check them out before you commit any funds, provide any goods or services, or undertake any travel. Check with the U.S. Embassy in Ghana at telephone (233)-(030)-274-1443/1449 for an assessment of the offer's credibility.
Another type of fraud is committed by persons claiming to live in Ghana or traveling to Ghana on business, and who profess friendship or romantic interest over the Internet. Once a relationship has been established, the correspondent typically asks the U.S. citizen to send money for living expenses, travel expenses, or visa costs. Sometimes a "hospital"or "doctor" telephones to say that the friend has suffered an "accident" and needs immediate financial assistance to cover medical bills. There are other variations of this scam, but the common goal is to fraudulently obtain as much money as possible from the victim. U.S. citizens have reported losing thousands of dollars through such scams. The anonymity of the Internet means that the victim cannot be sure of the real name, age, marital status, nationality, or even gender of the correspondent. In most cases reported to the Embassy, the correspondent turned out to be a fictitious persona created to lure U.S. citizens into sending money.
Visitors to Ghana should also be wary of overly-friendly locals offering tours, discounted lodging, or other services that seem too good to be true. Tourists are often targeted by touts and scam artists. Some U.S. citizens have been victims of false criminal accusations and have lost time and money as they seek to resolve these difficult situations.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Ghana, you are subject to its laws. Foreign laws and legal systems can be significantly different than our own and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don't have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Ghana, your U.S. passport won't help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It's very important to know what's legal and what's not wherever you go.Persons violating Ghanaian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Ghana are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. The use of illegal drugs procured in Ghana may have life-threatening consequences. There have been several deaths of U.S. citizens resulting from the use of narcotics procured locally.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Languages
The official language of Ghana is English. There are movements to make several local languages official as well. The Twi dialect of Akan is the language most commonly used on a daily basis to communicate between ethnic groups. Most Ghanaians are at least bilingual.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Ghana are limited, particularly outside Accra, the capital. Travelers should carry adequate supplies of any needed prescription medicines, along with copies of their prescriptions, the generic name of the drugs, and a supply of preferred over-the-counter medications.Documentation of Yellow fever vaccination is required upon arrival from all countries.
Motor vehicle accidents, drownings, and water-related accidents due to Ghana's rough surf have been reported by U.S. citizens. Muggings, and other violent attacks, as well as the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases - including HIV - are health and safety concerns that have been reported by U.S. citizens and can be at least partially mitigated by using common-sense safety precautions.
Safety and Security
Due to the potential for violence, U.S. citizens should avoid political rallies and street demonstrations and stay aware of their safety at all times.There are a number of ongoing chieftaincy disputes in Ghana that generally involve competition over limited resources. Several of these disputes have erupted into violence and unrest during recent years, most notably in Yendi in the Northern Region and Bawku in the Upper East Region. Visitors should exercise caution when traveling in these areas and remain alert to outbreaks of unrest.
Travelers should also be aware that the standards of construction are often lower than those found in the United States. These lower standards have contributed to building collapses, fires, and reports of electrical shock, including the death of a Westerner from electrocution at the Stellar Lodge in Takoradi (Ghana's Western Region).
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Ghana is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Primary roads are generally paved and well maintained. However, some side roads within major cities and many roads outside of major cities are in poor condition. The road from Accra to the central region tourist area of Cape Coast continues to be the site of many accidents. Travel in darkness, particularly outside the major cities, is extremely hazardous due to poor street lighting and the unpredictable behavior of pedestrians, bicyclists and farm animals, particularly goats and sheep. Aggressive drivers, poorly maintained vehicles, and overloaded vehicles pose serious threats to road safety.
Another hazard is pedestrians who intentionally bump vehicles and pretend to be hit. They then attempt to extort money from the vehicle occupants. Scams of this nature most commonly occur in congested urban areas.
The safety standards of the small private buses that transit roads and highways are uncertain. Travelers are encouraged to consider this when making travel arrangements.
Armed robbers have targeted travelers following their arrival at Kotoka airport. An increasingly used tactic is to deliberately cause a minor road traffic accident to make a car stop, and to then rob the occupants. If your car is hit by another car it is best to drive to the nearest police station to sort out the incident. Otherwise, all drivers, particularly at night, should remain vigilant, and drive with doors locked.
There has been an increase in incidents of highway robbery on the road from Kintampo to Tamale in the Brong Ahafo and Northern regions. Travelers along this route should exercise due caution.
Travelers are routinely stopped at police checkpoints throughout Ghana, and vehicles and passengers may be searched. Drivers must possess an international driver's license (available from AAA and the American Automobile Touring Alliance). Foreign nationals should carry documentation of their status, such as a passport and a visa.
