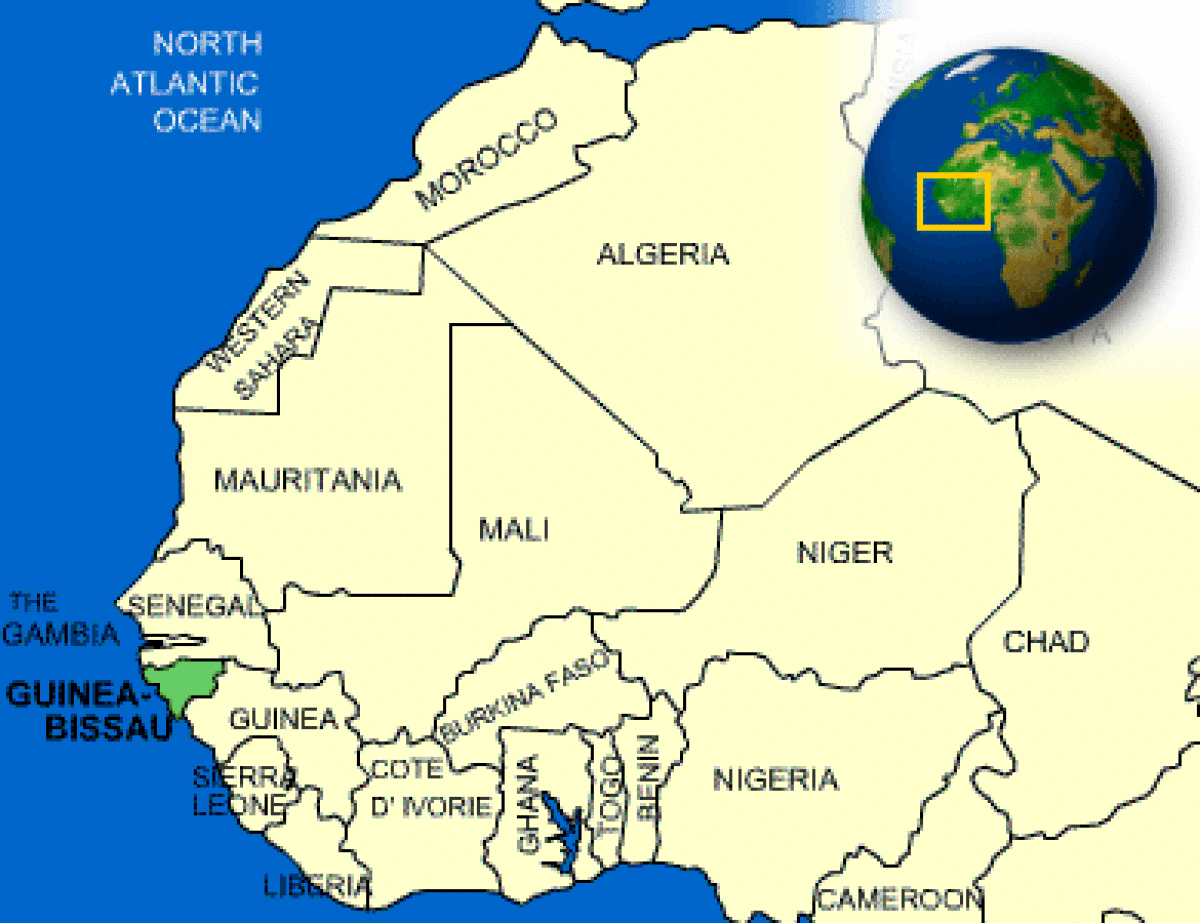
Where is Guinea-Bissau located?
What countries border Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau Weather
What is the current weather in Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau Facts
What is the capital of Guinea-Bissau?
| Capital | Bissau |
| Government Type | Semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Guinea-Bissau Peso (GWP) and CFA Franc BCEAO (XOF) |
| Total Area |
13,948 Square Miles 36,125 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Senegal |
| Language | Portuguese (official), Crioulo, African languages |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.7% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $1,500.00 (USD) |
Guinea-Bissau Demographics
What is the population of Guinea-Bissau?
| Ethnic Groups | African 99% (Balanta 30%, Fula 20%, Manjaca 14%, Mandinga 13%, Papel 7%), European and mulatto less than 1% |
| Nationality Noun | Guinean(s) |
| Population | 1,927,104 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.95% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | BISSAU (capital) 423,000 |
| Urban Population | 43.900000 |
Guinea-Bissau Government
What type of government does Guinea-Bissau have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President Umaro Sissoco EMBALO (since 27 February 2020); note - President EMBALO was declared winner of the 29 December 2019 runoff presidential election by the electoral commission; in late February 2020, EMBALO inaugurated himself with only military leadership present, even though the Supreme Court of Justice had yet to rule on an electoral litigation appeal lodged by his political rival Domingos Simoes PEREIRA Head of Government: Prime Minister Rui Duarte DE BARROS (since 27 December 2023); note - on 4 December 2023 the president dissolved the parliament Cabinet: Cabinet nominated by the prime minister, appointed by the president Elections/Appointments: President directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for up to 2 consecutive 5-year terms; the election last held on 24 November 2019 with a runoff on 29 December 2019 (next to be held in 2024); prime minister appointed by the president after consultation with party leaders in the National People's Assembly; note - the president cannot apply for a third consecutive term Election results: 2019: Umaro Sissoco EMBALO elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Domingos Simoes PEREIRA (PAIGC) 40.1%, Umaro Sissoco EMBALO (Madem G15) 27.7%, Nuno Gomez NABIAM (APU-PDGB) 13.2%, Jose Mario VAZ (independent) 12.4%, other 6.6%; percent of vote in second round - Umaro Sissoco EMBALO 53.6%, Domingos Simoes PEREIRA 46.5% (2019) |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: Yes Citizenship by descent only: Yes Dual citizenship recognized: No Residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 24 September (1973) |
| Constitution |
History: Promulgated 16 May 1984; note - constitution suspended following military coup April 2012, restored 2014; note - in May 2020, President EMBALO established a commission to draft a revised constitution Amendments: Proposed by the National People’s Assembly if supported by at least one-third of its members, by the Council of State (a presidential consultant body), or by the government; passage requires approval by at least a two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly; constitutional articles on the republican and secular form of government and national sovereignty cannot be amended; amended 1991, 1993, 1996 |
| Independence | 24 September 1973 (declared); 10 September 1974 (from Portugal) |
Guinea-Bissau Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Guinea-Bissau Geography
What environmental issues does Guinea-Bissau have?
| Climate | Tropical; generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds |
| Border Countries | Guinea 386 km, Senegal 338 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; overfishing |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified: None of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east |
Guinea-Bissau Economy
How big is the Guinea-Bissau economy?
| Economic Overview |
Guinea-Bissau is highly dependent on subsistence agriculture, cashew nut exports, and foreign assistance. Two out of three Bissau-Guineans remain below the absolute poverty line. The legal economy is based on cashews and fishing. Illegal logging and trafficking in narcotics also play significant roles. The combination of limited economic prospects, weak institutions, and favorable geography have made this West African country a way station for drugs bound for Europe. Guinea-Bissau has substantial potential for development of mineral resources, including phosphates, bauxite, and mineral sands. Offshore oil and gas exploration has begun. The country’s climate and soil make it feasible to grow a wide range of cash crops, fruit, vegetables, and tubers; however, cashews generate more than 80% of export receipts and are the main source of income for many rural communities. The government was deposed in August 2015, and since then, a political stalemate has resulted in weak governance and reduced donor support. The country is participating in a three-year, IMF extended credit facility program that was suspended because of a planned bank bailout. The program was renewed in 2017, but the major donors of direct budget support (the EU, World Bank, and African Development Bank) have halted their programs indefinitely. Diversification of the economy remains a key policy goal, but Guinea-Bissau’s poor infrastructure and business climate will constrain this effort. |
| Industries | Agricultural products processing, beer, soft drinks |
| Currency Name and Code | Guinea-Bissau Peso (GWP) and CFA Franc BCEAO (XOF) |
| Export Partners | India 50%, Thailand 19.2%, Uruguay 19.2% |
| Import Partners | Senegal 19.6%, Portugal 18.8%, India 15.2% |
Guinea-Bissau News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Guinea-Bissau?
Source: Google News
Guinea-Bissau Travel Information
What makes Guinea-Bissau a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The U.S. Liaison Office in Bissau suspended its operations on April 4, 2013, and therefore cannot provide consular services to U.S. citizens in Guinea-Bissau. Guinea-Bissau currently falls under the consular jurisdiction of the U.S. Embassy in Dakar, Senegal.The Republic of Guinea-Bissau, a small country in western Africa, is one of the world’s poorest nations. The capital is Bissau and the official language is Portuguese. Many people outside of Bissau speak only an indigenous language or Creole. English is not widely used. The country’s 1998-99 civil war devastated the economy. Tourist facilities and infrastructure in general are very limited and not up to U.S. standards.
Crime
Guinea-Bissau is rated high for crime due to the frequency of crimes committed and lack of law enforcement resources and capabilities. Foreigners are primarily the targets of crimes of opportunity to include, petty-theft, pick-pocketing, theft of valuables from vehicles, and minor assaults. In particular, low-level criminal activity occurs in crowded areas such as the Bandim Market and port in central Bissau. Criminals take advantage of foreigners attempting to navigate through the crowded markets. Exercise good personal security practices to reduce the risk of being victimized. Keep a low profile, remain vigilant, and avoid potential conflict situations. Do not wear flashy clothing or jewelry, and be cautious about displaying any amount of currency in public.To avoid theft do not walk alone in isolated areas, particularly at night, and lock all doors and close all windows when driving. Do not walk on dark streets at night, even in groups. To minimize inconvenience in the event of theft, carry copies, rather than originals, of your passport and other identification documents. While some of the larger hotels may accept credit cards, Bissau is largely a cash based economy and it is therefore recommended that travelers plan for and bring appropriate amounts of currency. Valuables should be stored in hotel safes.
In conjunction with the high crime rate, the poor infrastructure and lack of lighting at night also present a more opportune environment for criminals to exploit. It is recommended to arrange for transportation and limit walking around Bissau at night to reduce the risk of being a victim of a crime. In addition, banditry also occurs with some regularity on the main highways throughout the country after dark. The U.S. Embassy recommends that travel be completed during daylight hours only and, if possible, in convoy.
The unstable security environment and high rates of unemployment strongly influence criminals to go to extreme measures to achieve their goals. While most criminals in Guinea-Bissau seek crimes of opportunity with low risk of confrontation, they are not afraid to exert violence. In many cases, criminal elements in Bissau operate in small, loosely affiliated groups to perpetrate a crime. Criminals use one or two individuals to cause a distraction or remain on lookout, while the others commit the crime.
While violent crime towards foreigners are not common in Guinea-Bissau, the increase in narcotics trafficking has contributed to an increase in criminal activity and aggressive assaults among the local population in more rural areas of Guinea-Bissau.
The Bandim market and other vendors in Bissau offer a wide variety of illicit and counterfeit goods. While the items are widely available, all travelers are urged to not purchase any illicit items to prevent breaking local laws and U.S. laws if brought back to the United States.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Guinea-Bissau, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Guinea-Bissau, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Persons violating Bissau-Guinean laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Guinea-Bissau are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Drug trafficking is endemic in Guinea-Bissau.
The United States does not have an agreement with Guinea-Bissau requiring notification of the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are arrested in Guinea-Bissau, you should use whatever means of communication available to alert the U.S. Embassy in Dakar, Senegal.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Modern medical facilities are virtually nonexistent in Guinea-Bissau, and travelers should not rely on them. More acceptable levels of medical care are available in Dakar, Senegal; however, as of this writing, there are extremely limited air travel options available between Dakar and Bissau. In addition, malaria, a serious and sometimes fatal disease, is a risk for travelers to Guinea-Bissau. Guinea-Bissau has a high HIV/AIDS infection rate.
Safety and Security
Guinea-Bissau is one of the poorest countries in West Africa and lacks sufficient resources and infrastructure to insure a stable security environment. Since Guinea-Bissau gained independence from Portugal in 1974, the country has been plagued by coups, political assassinations, and a civil war. The country’s fragile political system and weak governance allows for widespread corruption directly influenced by illicit activity. Criminals, corrupt officials, and drug cartels continue to undermine the rule of law and utilize the country for criminal activity, including using Guinea-Bissau as a major transit-point for cocaine and light-arms trafficking, and for illegal immigration. Guinea-Bissau’s unprotected coastline and archipelago, with over 90 islands, many un-policed, and remote airstrips, is a haven for narcotics trafficking and other criminal activity. Due to the current political, economic, and security instability in Guinea-Bissau, all U.S. citizens and organizations should exercise heightened personal security awareness.Guinea-Bissau continues to experience periodic political disruptions and instability; all travelers to the country should closely monitor the political situation. In January 2012, Bissau-Guinean President Malam Bacai Sanhá died from natural causes. A transitional government is in place following a coup d’état on April 12, 2012, that interrupted elections to replace him. The government plans to hold presidential and legislative elections in 2013.
Visitors should avoid political gatherings and street demonstrations. Demonstrations typically begin or end in front of the former Presidential Palace in “Praca dos Herois Nacionais.” While most demonstrations in Bissau are non-violent, the imbalance of power in the country can lead to violent demonstrations.
Unexploded military ordnance and landmines remain scattered throughout the country. Although the capital city of Bissau was declared “mine-free” in June 2006 by the national de-mining center (CAAMI), there have been occasional findings or unintentional mine explosions. Two non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have been active in successfully removing mines. Avoid driving in rural areas at night and remain on well-traveled roads at all times to minimize the risks posed by landmines.
The U.S. Embassy in Bissau suspended operations on June 14, 1998, at the outbreak of a violent civil war. There is currently no permanent U.S. diplomatic or consular presence in Guinea-Bissau. The U.S. Embassy in Dakar, Senegal, is accredited for all diplomatic and security concerns to the Government of Guinea-Bissau. In 2007, the U.S. government opened a U.S. Liaison Office in Bissau (BLO), staffed by locally employed personnel who provided limited services to U.S. citizens in the event of an emergency. The Bissau Liaison Office suspended operations on April 4, 2013. All security and consular services should be coordinated through the American Citizens Services Section and the Regional Security Office at the U.S. Embassy in Dakar, Senegal.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Guinea-Bissau, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Guinea-Bissau is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.The public transportation system, urban and rural road conditions, and availability of roadside assistance are all poor. There is no consistent public electricity in the capital, and the lack of lighting at night makes careful driving essential. Since there are landmines left in place from the civil war and the war of independence, travelers should not leave designated roads and pathways. The landmines are scattered in several areas throughout Guinea-Bissau, including the Bafata, Oio, Biombo, Quinara, and Tombali regions. While there has been significant progress in locating and removing landmines, a substantial number remain. Speak with local authorities first and use caution if leaving a main road or highway to enter a trail network or to make other types of cross-country movement.
Passengers should also exercise caution if choosing to use a taxi for transportation because many are in sub-standard condition. If a taxi is used, it is important for passengers to inform taxi drivers that they do not want additional patrons to be picked up along the route. Taxis in Bissau serve as a bus service, in which each passenger pays for a seat. Furthermore, the Embassy does not recommend that visitors use the unconventional bus system in Bissau, the “Bus Rapides” or “Toca-Tocas.”
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
