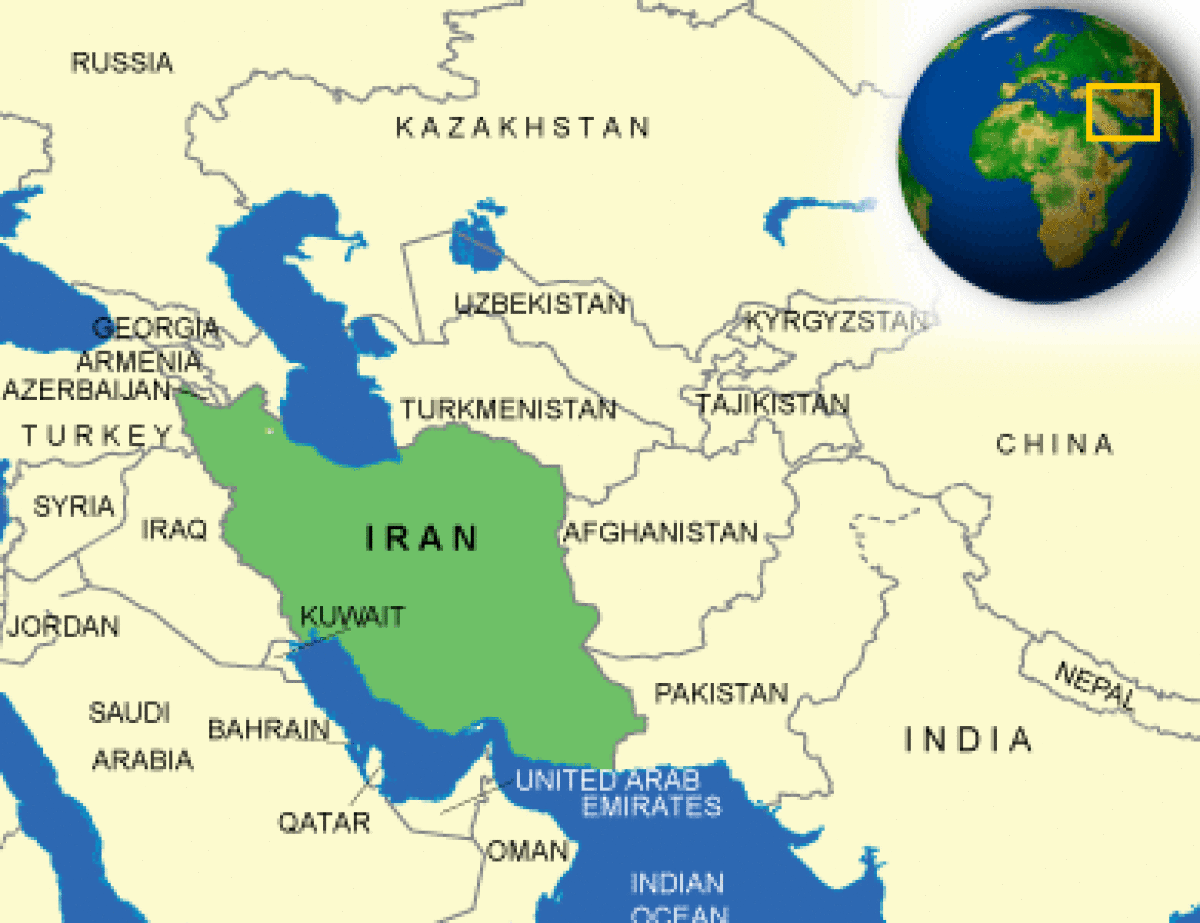
Where is Iran located?
What countries border Iran?
Iran Weather
What is the current weather in Iran?
Iran Facts and Culture
What is Iran famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Iranians have a rich cultural heritage, including the great Persian Empire, of which they are proud. The people are hospitable... More
- Family: It is legal for a man to have up to four wives. However, most men have only one wife.... More
- Personal Apperance: Men often wear Western styles, although traditional robes and turbans or hats are also worn in parts of the North... More
- Recreation: Iranians enjoy chess and many argue it was invented in Iran. Wrestling, weightlifting and squash are popular among urban Iranians.... More
- Diet: The diet varies throughout the country. Muslims do not eat pork or drink alcohol. Under current law, alcohol consumption is... More
- Food and Recipes: During Ramadan, devout Muslims do not eat or drink anything from sunrise to sundown; families eat and visit with friends... More
- Visiting: A guest is considered a gift from Allah, thus showing kindness towards a guest is a way of respecting Allah.... More
- Dating: Daughters are usually "protected" by their families to the point that they often do not speak to male strangers until... More
Iran Facts
What is the capital of Iran?
| Capital | Tehran |
| Government Type | theocratic republic |
| Currency | Iranian Rial (IRR) |
| Total Area |
636,368 Square Miles 1,648,195 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Middle East, bordering the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf, and the Caspian Sea, between Iraq and Pakistan |
| Language | Persian and Persian dialects 58%, Turkic and Turkic dialects 26%, Kurdish 9%, Luri 2%, Balochi 1%, Arabic 1%, Turkish 1%, other 2% |
| GDP - real growth rate | 0.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $17,800.00 (USD) |
Iran Demographics
What is the population of Iran?
| Ethnic Groups | Persian 51%, Azeri 24%, Gilaki and Mazandarani 8%, Kurd 7%, Arab 3%, Lur 2%, Baloch 2%, Turkmen 2%, other 1% |
| Languages | The official language in Iran is Persian, but many other languages or dialects are spoken. |
| Nationality Noun | Iranian(s) |
| Population | 84,923,314 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.24% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | TEHRAN (capital) 7.304 million; Mashhad 2.713 million; Esfahan 1.781 million; Karaj 1.635 million; Tabriz 1.509 million; Shiraz 1.321 million |
| Urban Population | 69.100000 |
Iran Government
What type of government does Iran have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Supreme Leader Ali Hoseini-KHAMENEI (since 4 June 1989) head of government: President Ebrahim RAISI (since 18 June 2021); First Vice President Mohammad MOKHBER (since 8 August 2021) cabinet: Council of Ministers selected by the president with legislative approval; the supreme leader has some control over appointments to several ministries elections/appointments: supreme leader appointed for life by Assembly of Experts; president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term and an additional nonconsecutive term); election last held on 18 June 2021 (next to be held in June 2025) election results: 2021: Ebrahim RAISI elected president; percent of vote - Ebrahim RAISI (independent) 72.4%, Mohsen REZAI (RFII) 13.8%, Abbdolnaser HEMATI (ECP) 9.8%, Amir-Hosein Qazizadeh-HASHEMI (Islamic Law Party) 4% 2017: Hasan Fereidun RUHANI reelected president; percent of vote - Hasan Fereidun RUHANI (Moderation and Development Party) 58.8%, Ebrahim RAISI (Combat Clergy Association) 39.4%, Mostafa Mir-SALIM Islamic Coalition Party) 1.2%, Mostafa HASHEMI-TABA (Executives of Construction Party) 0.5% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Iran dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Republic Day, 1 April (1979) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1906; latest adopted 24 October 1979, effective 3 December 1979 amendments: proposed by the supreme leader – after consultation with the Exigency Council – and submitted as an edict to the "Council for Revision of the Constitution," a body consisting of various executive, legislative, judicial, and academic leaders and members; passage requires absolute majority vote in a referendum and approval of the supreme leader; articles including Iran’s political system, its religious basis, and its form of government cannot be amended; amended 1989 |
| Independence | 1 April 1979 (Islamic Republic of Iran proclaimed); notable earlier dates: ca. 550 B.C. (Achaemenid (Persian) Empire established); A.D. 1501 (Iran reunified under the Safavid Dynasty); 1794 (beginning of Qajar Dynasty); 12 December 1925 (modern Iran established under the PAHLAVI Dynasty) |
Iran Video
YouTube, Rick Steves Iran
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Iran Geography
What environmental issues does Iran have?
| Climate | mostly arid or semiarid, subtropical along Caspian coast |
| Border Countries | Afghanistan 936 km, Armenia 35 km, Azerbaijan-proper 432 km, Azerbaijan-Naxcivan exclave 179 km, Iraq 1,458 km, Pakistan 909 km, Turkey 499 km, Turkmenistan 992 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution, especially in urban areas, from vehicle emissions, refinery operations, and industrial effluents; deforestation; overgrazing; desertification; oil pollution in the Persian Gulf; wetland losses from drought; soil degradation (salination); inadequate supplies of potable water; water pollution from raw sewage and industrial waste; urbanization |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | rugged, mountainous rim; high, central basin with deserts, mountains; small, discontinuous plains along both coasts |
Iran Economy
How big is the Iran economy?
| Economic Overview |
Iran, a country rich in history and culture, boasts a diverse and complex economy that has been shaped by its vast natural resources, strategic geopolitical position, and a series of economic reforms and sanctions. The economy of Iran is the 22nd largest in the world in terms of nominal GDP and the 18th largest in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). Despite its potential, Iran's economic growth has been hampered by various internal and external factors. Key Sectors Oil and Gas: The backbone of Iran's economy is its oil and gas sector, which accounts for a significant portion of government revenues and export earnings. Iran has the world's fourth-largest proven crude oil reserves and the second-largest natural gas reserves. However, international sanctions, particularly those imposed by the United States, have severely restricted Iran's ability to fully capitalize on these resources. Agriculture: Iran's diverse climate allows for the cultivation of a wide variety of crops. The agricultural sector employs around 20% of the workforce and contributes about 10% to the GDP. Key products include pistachios, saffron, wheat, and barley. Water scarcity and outdated farming techniques pose significant challenges to this sector. Manufacturing and Industry: Iran has a well-developed industrial base, producing automobiles, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and petrochemicals. The country is the largest car manufacturer in the Middle East. However, the industrial sector faces issues such as outdated technology, lack of investment, and trade barriers. Services: The service sector, including tourism, retail, and banking, plays a crucial role in Iran's economy. Despite its potential, tourism has been underdeveloped due to political instability and international perceptions. The banking sector is also under strain due to sanctions and isolation from the global financial system. Economic Challenges Sanctions: One of the most significant challenges facing Iran's economy is the series of international sanctions, primarily led by the United States. These sanctions have targeted Iran's oil exports, banking sector, and access to international financial markets, leading to reduced foreign investment and economic isolation. Inflation and Currency Devaluation: High inflation rates and the devaluation of the Iranian rial have eroded purchasing power and savings. Inflation has been driven by factors such as subsidy cuts, currency depreciation, and economic mismanagement. The government has struggled to stabilize the currency and control price rises. Unemployment: Unemployment remains a persistent issue, particularly among the youth. With a large and growing young population, creating enough jobs is a significant challenge. The official unemployment rate is around 12%, but it is believed to be higher in reality. Political Instability: Internal political struggles and external geopolitical tensions have created an uncertain business environment. Political instability affects investor confidence and hinders long-term economic planning. Recent Developments and Reforms Nuclear Deal and Sanctions Relief: The 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) agreement, known as the Iran nuclear deal, provided some relief from sanctions in exchange for limitations on Iran's nuclear program. However, the U.S. withdrawal from the agreement in 2018 and the subsequent re-imposition of sanctions have negated many of these benefits. Economic Diversification: The Iranian government has recognized the need to diversify the economy away from oil dependency. Efforts have been made to develop non-oil sectors, promote tourism, and attract foreign investment. However, progress has been slow due to ongoing sanctions and internal barriers. Privatization and Market Reforms: Iran has undertaken steps towards privatization and market-oriented reforms. The government has sold stakes in state-owned enterprises and encouraged private sector participation. However, bureaucratic red tape and corruption remain significant obstacles. Future Prospects The future of Iran's economy is uncertain, heavily dependent on the geopolitical landscape and the potential easing of sanctions. If sanctions are lifted or reduced, Iran could see significant economic growth through increased oil exports and foreign investment. Continued economic reforms, improved governance, and investment in technology and infrastructure are essential for sustainable growth. Iran's young and educated population, along with its strategic location and abundant natural resources, provides a foundation for future economic development. However, realizing this potential will require addressing the structural challenges and navigating the complex geopolitical environment. |
| Industries | petroleum, petrochemicals, textiles, cement and other construction materials, food processing (particularly sugar refining and vegetable oil production), metal fabricating, armaments |
| Currency Name and Code | Iranian Rial (IRR) |
| Export Partners | Japan 20.1%, China 9.9%, Italy 7.6%, South Korea 5.7% |
| Import Partners | Germany 17.1%, Switzerland 9.3%, UAE 9.1%, France 5.9%, Italy 5.8%, South Korea 4.8%, China 4.7%, Russia 4.3% |
Iran News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Iran?
Source: Google News
Iran Travel Information
What makes Iran a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Iran is a constitutional Islamic republic with a theocratic system of government where ultimate political authority is vested in the highest religious authority, the Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. He is the final authority on all domestic, foreign, and security policies for Iran, though he establishes and supervises those policies in consultation with other political bodies. Shia Islam is the official religion of Iran, and Islamic law is the basis of the authority of the state. The Iranian constitution guarantees freedom of worship to Jews, Christians, and Zoroastrians, though they and followers of other faiths are often the subject of discrimination and repression. The work week in Iran is Saturday through Thursday; however, many government offices and private companies are closed on Thursdays. Friday is the day of rest when all establishments are closed. Offices in Iran are generally open to the public during the morning hours only.
Crime
Major crime is generally not a problem for travelers in Iran, although foreigners occasionally become victims of petty street crime. Young men in unmarked cars have robbed foreigners and young men on motor bikes have snatched bags. There have been reports of robberies by police impersonators, usually in civilian clothing. Insist on seeing the officer’s identity card and request the presence of a uniformed officer/marked patrol car. Travelers should not surrender any documents or cash. You are advised to make a copy of your U.S. passport (biographical data page and the page with your Iranian visa) and to keep it separate from your original passport.Travelers should not carry large amounts of hard currency while on the streets. In view of the possibility of theft, passports, other important documents, and valuables should be kept in hotel safes or other secure locations. Pre-booked taxis are safer than those hailed from the street. U.S. citizens should check with their hotel or tour guide for information on local scams.
Don’t buy counterfeit or pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, purchasing them may also violate local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Iran, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit but still illegal in the United States; for example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Iran, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not in your destination country.U.S. citizens in Iran who violate Iranian laws, even unknowingly, including laws unfamiliar to Westerners (such as those regarding the proper wearing of apparel), may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Fines, public floggings, and long prison terms are common. Former Muslims who have converted to other religions, as well as persons who encourage Muslims to convert, are subject to arrest and possible execution. Drinking, possession of alcoholic beverages and drugs, un-Islamic dress, as well as public displays of affection with a member of the opposite sex are considered to be crimes. Relations between non-Muslim men and Muslim women are illegal, as are adultery and sex outside of marriage. DVDs depicting sexual relations and magazines showing unveiled women are forbidden. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Iran are severe and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Iran executes many people each year on drug-related charges.
The Iranian government reportedly has the names of all individuals who filed claims against Iran at the Iran-U.S. Claims Tribunal at The Hague pursuant to the 1981 Algerian Accords. In addition, the Iranian government reportedly has compiled a list of the claimants who were awarded compensation in the Iran Claims Program administered by the Foreign Claims Settlement Commission. The Iranian government has allegedly been targeting award-holders who travel to Iran. It has been reported that upon some claimants' entry into Iran, Iranian authorities have questioned them as to the status of payment of their respective awards with a view to recouping the award money. The Iranian government has also reportedly threatened to prevent U.S. claimants who visit Iran from departing the country until they make arrangements to repay their award either in part or its entirety.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the U.S. Interests Section at the Swiss Embassy in Tehran as soon as you are arrested or detained in Iran.
Languages
The official language in Iran is Persian, but many other languages or dialects are spoken.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Basic medical care and medicines are available in the principal cities, but may not be available in rural areas. Medical facilities do not meet U.S. standards and sometimes lack medicines and supplies. Iranian authorities confirmed outbreaks of avian influenza (bird flu) in January 2008 in northern Iran, as well as earlier reports of outbreaks among wild swans in the Anzali Wetlands and in domestic poultry in the northern provinces of Azerbaijan and Gilan. There were a number of confirmed cases of H1N1 influenza in 2009.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens who travel to Iran despite the Travel Warning should exercise caution throughout the country, but especially in the southeastern region where Westerners have been victims of criminal gangs often involved in the smuggling of drugs and other contraband. Terrorist explosions have killed a number of people in Iran in past years. U.S. citizens should avoid travel to areas within 100 kilometers of the border with Afghanistan, within 10 kilometers of the border with Iraq, and generally anywhere east of the line from Bam and Bandar Abbas toward the Pakistan border.U.S. citizens are advised to avoid demonstrations and large public gatherings. Increased tension between Iran and the West over the past several years is a cause of concern for U.S. citizen travelers. Large-scale demonstrations in response to politically motivated events have taken place sporadically throughout the country, resulting in a significant security presence, arrests, and occasional clashes between demonstrators and security officials. U.S. citizens should stay current with media coverage of local events and be aware of their surroundings at all times. U.S. passport holders who are arrested or detained by Iranian authorities should request assistance from the U.S. Interests Section at the Swiss Embassy in Tehran.
Iranian security personnel may at times place foreign visitors under surveillance. Hotel rooms, telephones, and fax machines may be monitored, and personal possessions in hotel rooms may be searched. Photography near military and other government installations is strictly prohibited and could result in serious criminal charges, including espionage, which carries the death penalty.
The United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) has advised that elevated regional tensions have increased the risk of maritime attacks being conducted by extremists to vessels operating in the Gulf of Oman, North Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden, and the Bab el Mandeb regions.
MARAD recommends vessels at anchor, operating in restricted maneuvering environments, or at slow speeds should be especially vigilant and report suspicious activity. U.S. flag vessels that observe suspicious activity in the area are advised to report such suspicious activity or any hostile or potentially hostile action to COMUSNAVCENT battlewatch captain at phone number 011-973-1785-3879. All suspicious activities and events are also to be reported to the U.S. Coast Guard National Response Center at the following toll free telephone: 1-800-424-8802, direct telephone 202-267-2675, or TDD 202-267-4477. The complete advisory is available on the MARAD website at www.MARAD.DOT.gov.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Iran, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Travelers in possession of International Driver’s Permits may drive in Iran, though the U.S. Interests Section in Iran does not recommend that tourists drive in Iran. Iran has a very high rate of traffic accidents, the second highest cause of mortality in the country. Drivers throughout Iran tend to ignore traffic lights, traffic signs, and lane markers. Urban streets are not well lit; it is therefore particularly dangerous to drive at night. Sidewalks in urban areas exist only on main roads and are usually obstructed by parked cars. In residential areas, few sidewalks exist. Drivers almost never yield to pedestrians at crosswalks. If you are involved in an accident, no matter how minor, do not leave the scene; wait until the police arrive to file a report.Iranian authorities sometimes set up informal roadblocks, both in cities and on highways, often manned by young, inexperienced officers who are suspicious of foreigners. Ensure you carry a form of identification with you and avoid getting into disputes.
Very high pollution levels from cars, particularly in Tehran, can trigger respiratory problems.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
