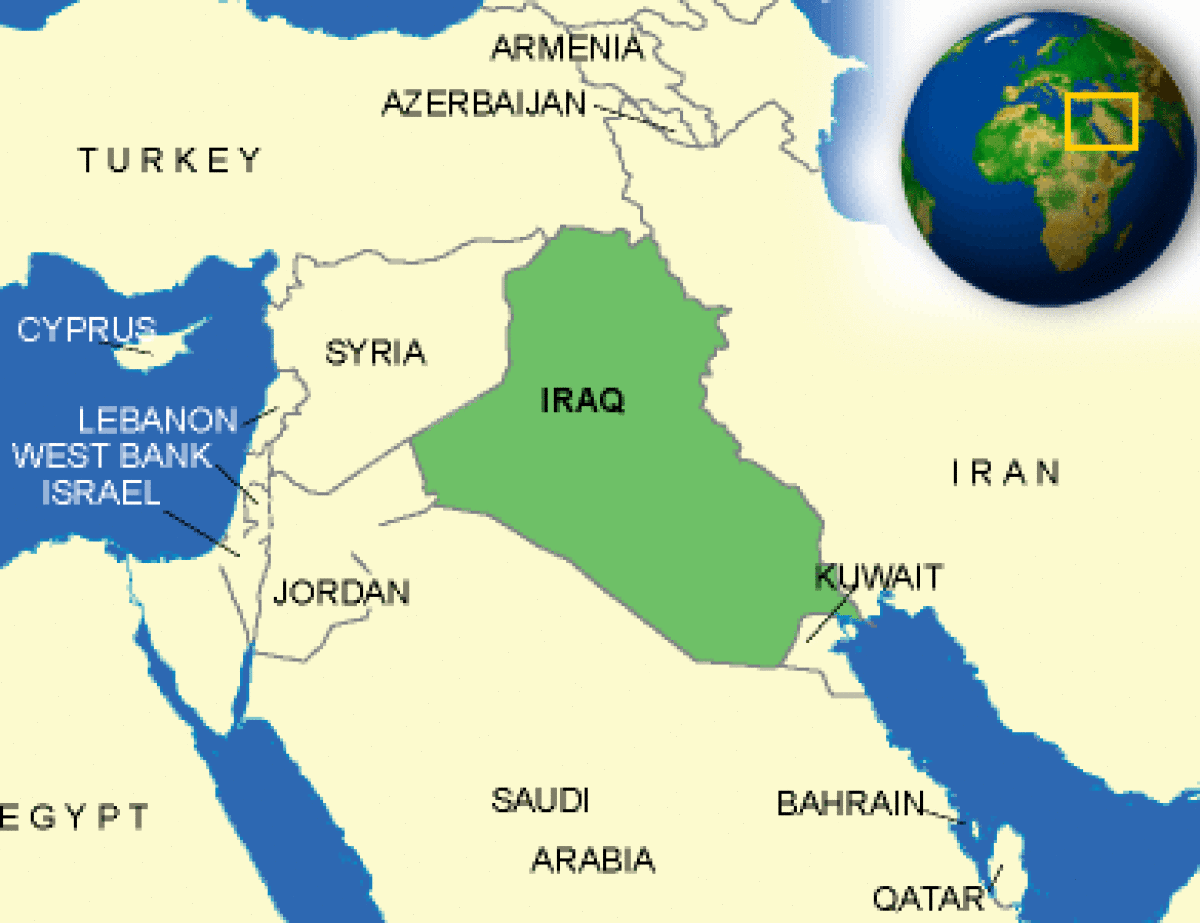
Where is Iraq located?
What countries border Iraq?
Iraq Weather
What is the current weather in Iraq?
Iraq Facts and Culture
What is Iraq famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Generally, reserve is the norm, and respect for the older generation is a key. People always give up seats on... More
- Family: Couples can live either with the husband's extended family, or in a nuclear unit. Due to economic hardship, the extended... More
- Personal Apperance: The urban population dress conservatively, and most women wear a scarf or head shawl. In rural areas, men wear the... More
- Recreation: Football (soccer) is Iraq’s national passion. A popular venue in Baghdad is Al-Sha’ab (“People’s”) Stadium, where throngs of Iraqis wait outside the gates... More
- Diet: Devout Muslims do not eat pork, and eat only halaal meat. The Iraq diet is based around rice, unleavened bread,... More
- Food and Recipes: Women may eat in a different area, and serve the men. Food is prepared in abundance for the guests. The... More
- Visiting: Friends and relatives visit unannounced, but otherwise warning is appreciated. Shoes are removed at the door, and usually slippers are... More
- Dating: In urban settings, women and men have more choice over their partner, but introductions (and outings) are often set up... More
Iraq Facts
What is the capital of Iraq?
| Capital | Baghdad |
| Government Type | federal parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Iraqi Dinar (IQD) |
| Total Area |
169,234 Square Miles 438,317 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait |
| Language | Arabic, Kurdish (official in Kurdish regions), Assyrian, Armenian |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $15,500.00 (USD) |
Iraq Demographics
What is the population of Iraq?
| Ethnic Groups | Arab 75%-80%, Kurdish 15%-20%, Turkoman, Assyrian or other 5% |
| Languages | The majority of Iraqis speak Arabic, with variations in dialect according to region. Modern standard Arabic is spoken by educated Iraqis and is the written language. Other languages spoken include Chaldean, Armenian, Syriac, Turkish dialects and Persian. English is the most widely used foreign language and is taught in Iraqi schools. |
| Nationality Noun | Iraqi(s) |
| Population | 38,872,655 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.29% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | BAGHDAD (capital) 6.036 million; Mosul 1.494 million; Erbil 1.039 million; Basra 942,000; As Sulaymaniyah 867,000; Najaf 779,000 |
| Urban Population | 66.500000 |
Iraq Government
What type of government does Iraq have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Latif RASHID (since 13 October 2022); vice presidents (vacant) head of government: Prime Minister Mohammed Shia al-SUDANI (since 27 October 2022) cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, approved by Council of Representatives (COR) elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by COR to serve a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); COR parliamentary election for president last held on 13 October 2022 (next to be held NA) election results: 2022: Latif RASHID elected president in second round; COR vote in first round - Latif RASHID (PUK) 157, Barham SALIH (PUK) 99; COR vote in second round - Latif RASHID 167, Barham SALIH 99; Mohammed Shia' al-SUDANI approved as prime minister 2018: Barham SALIH elected president in second round; COR vote in first round - Barham SALIH (PUK) 165, Fuad HUSAYN (KDP) 90; COR vote in second round - Barham SALIH 219, Fuad HUSAYN 22; Adil ABD AL-MAHDI approved as prime minister |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Iraq dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 3 October (1932); Republic Day, 14 July (1958) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted by referendum 15 October 2005 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic and the Council of Minsters collectively, or by one fifth of the Council of Representatives members; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Council of Representatives, approval by referendum, and ratification by the president; passage of amendments to articles on citizen rights and liberties requires two-thirds majority vote of Council of Representatives members after two successive electoral terms, approval in a referendum, and ratification by the president |
| Independence | 3 October 1932 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration); note - on 28 June 2004 the Coalition Provisional Authority transferred sovereignty to the Iraqi Interim Government |
Iraq Video
YouTube: Unesco The Iraqi Maqam
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Iraq Geography
What environmental issues does Iraq have?
| Overview | Iraq is bordered by Kuwait, Iran, Turkey, Syria, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia. The country slopes from mountains over 3,000 meters (10,000 ft.) above sea level along the border with Iran and Turkey to the remnants of sea-level, reedy marshes in the southeast. Much of the land is desert or wasteland. The mountains in the northeast are an extension of the alpine system that runs eastward from the Balkans into southern Turkey, northern Iraq, Iran, and Afghanistan, terminating in the Himalayas. |
| Climate |
mostly desert; mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers; northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding. Average temperatures range from higher than 48oC (120oF) in July and August to below freezing in January. Most of the rainfall occurs from December through April and averages between 10 and 18 centimeters (4-7 in.) annually. The mountainous region of northern Iraq receives appreciably more precipitation than the central or southern desert region. |
| Border Countries | Iran 1,458 km, Jordan 181 km, Kuwait 240 km, Saudi Arabia 814 km, Syria 605 km, Turkey 352 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | government water control projects have drained most of the inhabited marsh areas east of An Nasiriyah by drying up or diverting the feeder streams and rivers; a once sizable population of Marsh Arabs, who inhabited these areas for thousands of years, has been displaced; furthermore, the destruction of the natural habitat poses serious threats to the area's wildlife populations; inadequate supplies of potable water; development of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers system contingent upon agreements with upstream riparian Turkey; air and water pollution; soil degradation (salination) and erosion; desertification |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification |
| Terrain | mostly broad plains; reedy marshes along Iranian border in south with large flooded areas; mountains along borders with Iran and Turkey |
Iraq Economy
How big is the Iraq economy?
| Economic Overview |
Iraq's GDP growth slowed to 1.1% in 2017, a marked decline compared to the previous two years as domestic consumption and investment fell because of civil violence and a sluggish oil market. The Iraqi Government received its third tranche of funding from its 2016 Stand-By Arrangement (SBA) with the IMF in August 2017, which is intended to stabilize its finances by encouraging improved fiscal management, needed economic reform, and expenditure reduction. Additionally, in late 2017 Iraq received more than $1.4 billion in financing from international lenders, part of which was generated by issuing a $1 billion bond for reconstruction and rehabilitation in areas liberated from ISIL. Investment and key sector diversification are crucial components to Iraq’s long-term economic development and require a strengthened business climate with enhanced legal and regulatory oversight to bolster private-sector engagement. The overall standard of living depends on global oil prices, the central government passage of major policy reforms, a stable security environment post-ISIS, and the resolution of civil discord with the Kurdish Regional Government (KRG). Iraq's largely state-run economy is dominated by the oil sector, which provides roughly 85% of government revenue and 80% of foreign exchange earnings, and is a major determinant of the economy's fortunes. Iraq's contracts with major oil companies have the potential to further expand oil exports and revenues, but Iraq will need to make significant upgrades to its oil processing, pipeline, and export infrastructure to enable these deals to reach their economic potential. In 2017, Iraqi oil exports from northern fields were disrupted following a KRG referendum that resulted in the Iraqi Government reasserting federal control over disputed oil fields and energy infrastructure in Kirkuk. The Iraqi government and the KRG dispute the role of federal and regional authorities in the development and export of natural resources. In 2007, the KRG passed an oil law to develop IKR oil and gas reserves independent of the federal government. The KRG has signed about 50 contracts with foreign energy companies to develop its reserves, some of which lie in territories taken by Baghdad in October 2017. The KRG is able to unilaterally export oil from the fields it retains control of through its own pipeline to Turkey, which Baghdad claims is illegal. In the absence of a national hydrocarbons law, the two sides have entered into five provisional oil- and revenue-sharing deals since 2009, all of which collapsed. Iraq is making slow progress enacting laws and developing the institutions needed to implement economic policy, and political reforms are still needed to assuage investors' concerns regarding the uncertain business climate. The Government of Iraq is eager to attract additional foreign direct investment, but it faces a number of obstacles, including a tenuous political system and concerns about security and societal stability. Rampant corruption, outdated infrastructure, insufficient essential services, skilled labor shortages, and antiquated commercial laws stifle investment and continue to constrain growth of private, nonoil sectors. Under the Iraqi constitution, some competencies relevant to the overall investment climate are either shared by the federal government and the regions or are devolved entirely to local governments. Investment in the IKR operates within the framework of the Kurdistan Region Investment Law (Law 4 of 2006) and the Kurdistan Board of Investment, which is designed to provide incentives to help economic development in areas under the authority of the KRG. Inflation has remained under control since 2006. However, Iraqi leaders remain hard-pressed to translate macroeconomic gains into an improved standard of living for the Iraqi populace. Unemployment remains a problem throughout the country despite a bloated public sector. Overregulation has made it difficult for Iraqi citizens and foreign investors to start new businesses. Corruption and lack of economic reforms - such as restructuring banks and developing the private sector – have inhibited the growth of the private sector. |
| Industries | petroleum, chemicals, textiles, construction materials, food processing |
| Currency Name and Code | Iraqi Dinar (IQD) |
| Export Partners | US 37.4%, Taiwan 7.7%, Canada 7.5%, France 7.5%, Jordan 6.9%, Netherlands 5.8%, Italy 4.9%, Morocco 4.3%, Spain 4.1% |
| Import Partners | Jordan 10.4%, France 8.4%, China 7.9%, Vietnam 7.9%, Germany 7.2%, Russia 6.9%, Australia 6.8%, Italy 6.1%, Japan 5.3% |
Iraq News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Iraq?
Source: Google News
Iraq Travel Information
What makes Iraq a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Iraq is a parliamentary democracy located in the Middle East with a population of more than 31 million people. Iraq held parliamentary elections in March 2010 and has a coalition government. Iraq is a country with a developing infrastructure and extremely limited tourist facilities. Iraqi forces have full responsibility for providing security in Iraq. The Government of Iraq (GOI) has made significant politicalandeconomic progress in recent years, but the country still faces many challenges. Those challenges include overcoming three decades of war and government mismanagement that stunted Iraq's economy; sectarian and ethnic tensions that have slowed progress toward national reconciliation; and ongoing criminal and terrorist violence. The slight decline and leveling off in the number of insurgent attacks in 2011-12spurred economic growth in Iraq; however, during 2013 there has been a marked increasein insurgent attacks and civilian casualties. Conditions throughout the country remain dangerous. The ability of the U.S. Embassy to provide consular services to U.S. citizens outside Baghdad is particularly limited given the security environment. Host government emergency services and support are limited.
Crime
Petty theft is common in Iraq; this includes pick-pocketing in busy areas (e.g. markets), as well as the theft of money, jewelry, or other valuables from hotel roomsand private residences.Historically, carjacking by armed thieves has been very common, even during daylight hours, and particularly on the highways from Jordan and Kuwait to Baghdad. Both foreigners - especially dual American-Iraqi citizens - and Iraqi citizens are targets of kidnapping. Kidnappers often demand money but have also carried out kidnappings for political/religious reasons. Many hostages have been killed.The number of murders reported in 2013, especially in the Baghdad area, has increased, likely due to terrorism, tribal and family disputes, and religious/sectarian tensions.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Iraq, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’thave your passport with youor if you take pictures of certain buildings.In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminalpenalties will varyfrom country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, andyou can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Iraq, your U.S. passport won’thelp you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’svery important to know what’slegal and what’snot wherever you go. Persons violating Iraq’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for the possession, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Iraq are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines, and in some cases may be subject to the death penalty.Arrest notifications in host country: While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrestedin a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Languages
The majority of Iraqis speak Arabic, with variations in dialect according to region. Modern standard Arabic is spoken by educated Iraqis and is the written language. Other languages spoken include Chaldean, Armenian, Syriac, Turkish dialects and Persian. English is the most widely used foreign language and is taught in Iraqi schools.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Basic modern medical care and medicines are not widely available in Iraq. Conflict has left some medical facilities non-operational and medical stocks and supplies severely depleted. The facilities in operation do not meet U.S. standards, and the majority lack medicines, equipment, and supplies. Some private companies facilitate medical evacuations. Blood banks exist in Iraq, though blood supply may not be sufficient in the event of an emergency. In addition, many areas suffer rolling power outages and generators are not always available for back-up.
Safety and Security
Violence and threats against U.S. citizens persist. U.S. citizens in Iraq remain at risk for kidnapping. Methods of attack in the past have included roadside improvised explosive devices (IEDs), including Explosively Formed Penetrators (EFPs); magnetic IEDs placed on vehicles; human and vehicle-borne IEDs, mines placed on or concealed near roads; mortars and rockets, and shootings using various direct fire weapons. Numerous insurgent groups, including Al Qaida in Iraq, are increasingly active throughout Iraq. Although Iraqi Security Forces (ISF) operations against these groups continue, terrorist activity persists in many areas of the country. Sectarian and terrorist violence has increased since the beginning of 2013 in Iraq, most notably in the provinces of Baghdad, Ninewa, Salah adDin, Anbar, and Diyala.The U.S. government considers the potential threat to U.S. government personnel in Iraq to be serious enough to require them to live and work under strict security guidelines. All U.S. government employees under the authority of the U.S. Chief of Mission must follow strict safety and security procedures when traveling outside the Embassy. State Department guidance to U.S. businesses in Iraq advises the use of protective security details. Detailed security information is available at the U.S. Embassy website.
Some regions within Iraq have experienced fewer violent incidents than others in recent years, in particular the Iraqi Kurdistan Region (IKR).The security situation in the IKR,which includes the provinces of Sulymaniya, Erbil, and Dohuk, has been more stable relative to the rest of Iraq in recent years, but threats remain. U.S. government personnel in northern Iraq are required to be accompanied by a protective security detail when traveling outside secure facilities. Although there have been significantly fewer terrorist attacks and lower levels of insurgent violence in the IKR than in other parts of Iraq, the security situation throughout the country remains dangerous.
U.S. citizens should avoid areas near the Syrian, Turkish and Iranian borders in northern Iraq.The Governments of Turkey and Iran continue to carry out military operations against insurgent groups in the mountain regions bordering Iraq. These operations have included troop movements and both aerial and artillery bombardments. Extensive unmarked minefields also remain along these borders. The unrest in Syria has resulted in large numbers of people seeking refuge in the area. In addition, borders in these areas are not always clearly defined. In 2009, three U.S. citizens were detained by Iranian authorities while hiking in the vicinity of the Iranian border in the IKR.The resources available to the U.S. Embassy to assist U.S. citizens who venture close to or cross the border with Iran are extremely limited. The Department of State discourages travel in close proximity to the Iranian border.
