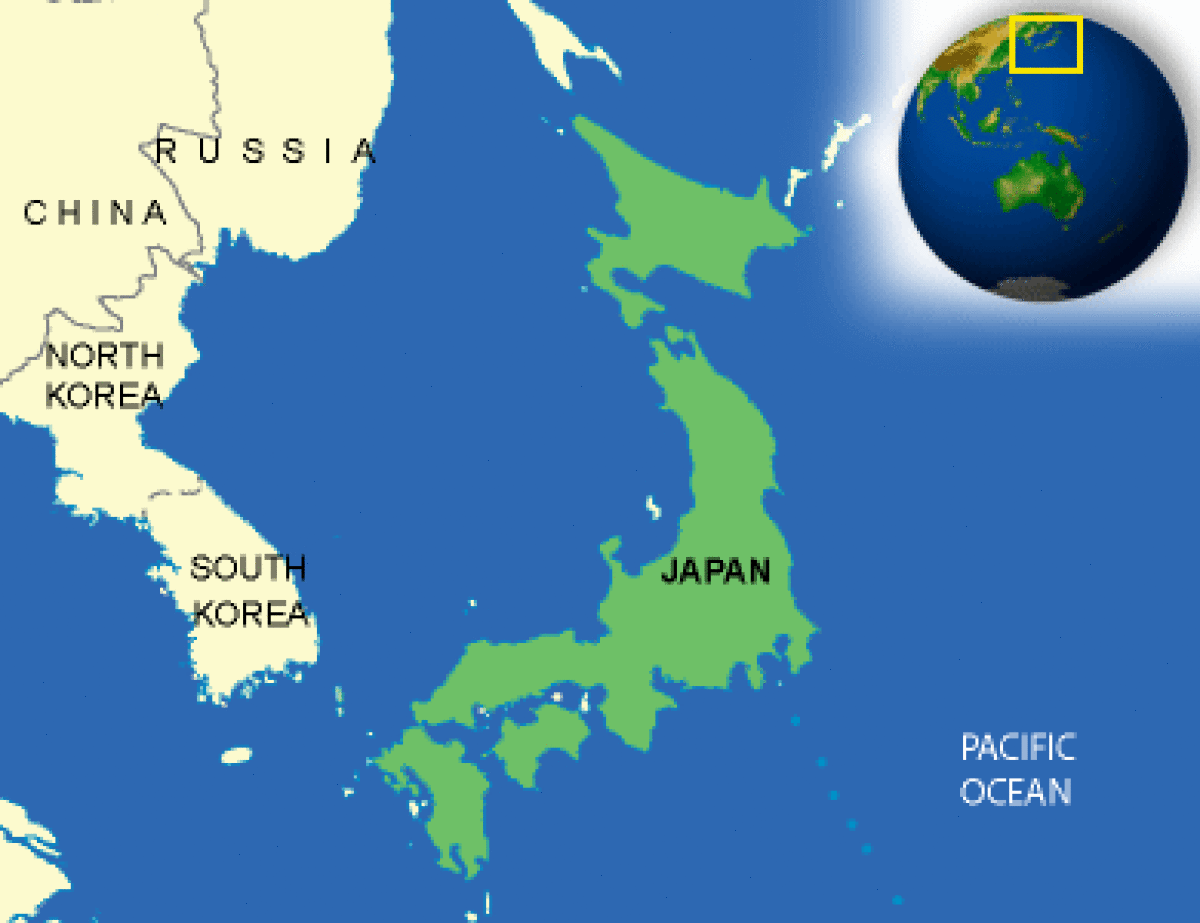
Where is Japan located?
What countries border Japan?
Japan Weather
What is the current weather in Japan?
Japan Facts and Culture
What is Japan famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Japanese believe in returning favors and giving gifts when they have personally received them from others. Age and tradition... More
- Family: The family is considered the foundation of society. Reputation and responsibility are important attributes in Japanese society. The... More
- Personal Apperance: Most Japanese adults dress to be like the rest of the crowd. Business people usually wear suits with ties.... More
- Recreation: Japanese children enjoy kite flying and origami, the ancient art of paper folding. Card games such as Karuta or board... More
- Diet: The Japanese diet consists largely of rice, fresh vegetables, seafood, fruit, and small portions of meat. Rice and tea are... More
- Food and Recipes: Although many youths eat while walking in public, it is generally considered bad manners for adults to do so. Snack... More
- Visiting: Visiting is normally arranged in advance; surprise visits between neighbors are uncommon, especially in urban areas. Shoes are removed before... More
- Dating: Youth, in Japan, generally start to consider dating at the of age fifteen. They enjoy movies, dancing, shopping, and eating... More
Japan Facts
What is the capital of Japan?
| Capital | Tokyo |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Yen (JPY) |
| Total Area |
145,913 Square Miles 377,915 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Asia, island chain between the North Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan, east of the Korean Peninsula |
| Language | Japanese |
| GDP - real growth rate | 0.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $38,200.00 (USD) |
Japan Demographics
What is the population of Japan?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent population by nationality; up to 230,000 Brazilians of Japanese origin migrated to Japan in the 1990s to work in industries; some have returned to Brazil |
| Ethnic Groups | Japanese 97.5%, Chinese 0.6%, Vietnam 0.4%, South Korean 0.3%, other 1.2% (includes Filipino, Brazilian, Nepalese, Indonesian, American, and Taiwanese) |
| Language - note | Japanese is the official language. The Japanese place great value on nonverbal language or communication. For example, much can be said with a proper bow. In fact, one is often expected to sense another person’s feelings on a subject without verbal communication. Westerners often misinterpret this as a Japanese desire to be vague or incomplete. The Japanese may consider a person’s inability to interpret feelings through body language as insensitivity. |
| Languages | Japanese |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Japanese (singular and plural) adjective: Japanese |
| Population | 123,201,945 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.43% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 37.194 million TOKYO (capital), 19.013 million Osaka, 9.569 million Nagoya, 5.490 million Kitakyushu-Fukuoka, 2.937 million Shizuoka-Hamamatsu, 2.666 million Sapporo |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 92% of total population (2023) rate of urbanization: -0.25% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 59,875,269 female: 63,326,676 |
Japan Government
What type of government does Japan have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Emperor NARUHITO (since 1 May 2019); note - succeeded his father who abdicated on 30 April 2019 head of government: Prime Minister Fumio KISHIDA (since 4 October 2021) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; the leader of the majority party or majority coalition in the House of Representatives usually becomes prime minister election results: 2021: Fumio KISHIDA reelected prime minister on 10 November 2021; upper house vote - Fumio KISHIDA (LDP) 141, Yukio EDANO (CDP) 60; lower house vote - Fumio KISHIDA 297, Yukio EDANO 108 |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Japan dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Birthday of Emperor NARUHITO, 23 February (1960); note - celebrates the birthday of the current emperor |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1890; latest approved 6 October 1946, adopted 3 November 1946, effective 3 May 1947 amendments: proposed by the Diet; passage requires approval by at least two-thirds majority of both houses of the Diet and approval by majority in a referendum; note - the constitution has not been amended since its enactment in 1947 |
| Independence | 3 May 1947 (current constitution adopted as amendment to Meiji Constitution); notable earlier dates: 11 February 660 B.C. (mythological date of the founding of the nation by Emperor JIMMU); 29 November 1890 (Meiji Constitution provides for constitutional monarchy) |
Japan Video
YouTube: DevinSuperTramp - Visual Escape Japan in 8K - Relaxing Music - Visual Escape
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Japan Geography
What environmental issues does Japan have?
| Overview |
Japan, a country of islands, extends along the eastern or Pacific coast of Asia. The main islands, running from north to south, are Hokkaido, Honshu, or the mainland Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa, which is about 380 miles southwest of Kyushu. About 3,000 smaller islands are included in the archipelago. About 71% of the country is mountainous, with a chain running through each of the main islands. Japan’s highest mountain is the world-famous Mt. Fuji (12,385 feet). Since so little flat area exists, many hills and mountainsides are cultivated all the way to the top. Situated as it is in a volcanic zone along the Pacific deep, frequent low-intensity earth tremors and occasional volcanic activity are felt throughout the islands. Hot springs are numerous; some have been developed as resorts. |
| Climate |
Temperature extremes are fewer than in the U.S. since no part of the interior is more than 100 miles from the coast. At the same time, because the islands run almost directly north-south, the climate varies. Sapporo, on the northern island, has warm summers and long, cold winters with heavy snowfall. Tokyo, Nagoya, Kyoto, Osaka, and Kobe, on the southern part of the largest island of Honshu, experience relatively mild winters with little or no snowfall and hot, humid summers. Fukuoka, on the island of Kyushu, has a climate with mild winters and short summers. Okinawa is subtropical. Spring, with its profusion of cherry blossoms and other flowering trees and shrubs, and autumn, with its gold and flaming red trees and lovely fall flowers, are the most pleasant seasons. The hot, humid summers are difficult in the cities, but the sandy beaches along the coast and the many fine mountain resorts provide pleasant relief. With rather mild and dry winters it rarely snows or rains in the Tokyo area at this time of year. |
| Environment - Current Issues | Air pollution from power plant emissions results in acid rain; acidification of lakes and reservoirs degrading water quality and threatening aquatic life; Japan is one of the largest consumers of fish and tropical timber, contributing to the depletion of these resources in Asia and elsewhere |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Mostly rugged and mountainous |
Japan Economy
How big is the Japan economy?
| Economic Overview |
Over the past 70 years, government-industry cooperation, a strong work ethic, mastery of high technology, and a comparatively small defense allocation (slightly less than 1% of GDP) have helped Japan develop an advanced economy. Two notable characteristics of the post-World War II economy were the close interlocking structures of manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors, known as keiretsu, and the guarantee of lifetime employment for a substantial portion of the urban labor force. Both features have significantly eroded under the dual pressures of global competition and domestic demographic change. Measured on a purchasing power parity basis that adjusts for price differences, Japan in 2017 stood as the fourth-largest economy in the world after first-place China, which surpassed Japan in 2001, and third-place India, which edged out Japan in 2012. For three postwar decades, overall real economic growth was impressive - averaging 10% in the 1960s, 5% in the 1970s, and 4% in the 1980s. Growth slowed markedly in the 1990s, averaging just 1.7%, largely because of the aftereffects of inefficient investment and the collapse of an asset price bubble in the late 1980s, which resulted in several years of economic stagnation as firms sought to reduce excess debt, capital, and labor. Modest economic growth continued after 2000, but the economy has fallen into recession four times since 2008. Japan enjoyed an uptick in growth since 2013, supported by Prime Minister Shinzo ABE’s "Three Arrows" economic revitalization agenda - dubbed "Abenomics" - of monetary easing, "flexible" fiscal policy, and structural reform. Led by the Bank of Japan’s aggressive monetary easing, Japan is making modest progress in ending deflation, but demographic decline – a low birthrate and an aging, shrinking population – poses a major long-term challenge for the economy. The government currently faces the quandary of balancing its efforts to stimulate growth and institute economic reforms with the need to address its sizable public debt, which stands at 235% of GDP. To help raise government revenue, Japan adopted legislation in 2012 to gradually raise the consumption tax rate. However, the first such increase, in April 2014, led to a sharp contraction, so Prime Minister ABE has twice postponed the next increase, which is now scheduled for October 2019. Structural reforms to unlock productivity are seen as central to strengthening the economy in the long run. Scarce in critical natural resources, Japan has long been dependent on imported energy and raw materials. After the complete shutdown of Japan’s nuclear reactors following the earthquake and tsunami disaster in 2011, Japan's industrial sector has become even more dependent than before on imported fossil fuels. However, ABE’s government is seeking to restart nuclear power plants that meet strict new safety standards and is emphasizing nuclear energy’s importance as a base-load electricity source. In August 2015, Japan successfully restarted one nuclear reactor at the Sendai Nuclear Power Plant in Kagoshima prefecture, and several other reactors around the country have since resumed operations; however, opposition from local governments has delayed several more restarts that remain pending. Reforms of the electricity and gas sectors, including full liberalization of Japan’s energy market in April 2016 and gas market in April 2017, constitute an important part of Prime Minister Abe’s economic program. Under the Abe Administration, Japan’s government sought to open the country’s economy to greater foreign competition and create new export opportunities for Japanese businesses, including by joining 11 trading partners in the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP). Japan became the first country to ratify the TPP in December 2016, but the United States signaled its withdrawal from the agreement in January 2017. In November 2017 the remaining 11 countries agreed on the core elements of a modified agreement, which they renamed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). Japan also reached an agreement with the European Union on an Economic Partnership Agreement in July 2017 and is likely to seek to ratify both agreements in the Diet this year. |
| Industries | Among the world's largest and most technologically advanced producers of motor vehicles, electronic equipment, machine tools, steel and nonferrous metals, ships, chemicals, textiles, processed foods |
| Currency Name and Code | Yen (JPY) |
| Export Partners | China 19.7%, United States 15.5%, South Korea 8%, Hong Kong 5.2%, Thailand 4.6% |
| Import Partners | China 21.5%, United States 8.9%, Australia 6.6%, Saudi Arabia 5.9%, United Arab Emirates 5%, South Korea 4.7% |
Japan News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Japan?
Source: Google News
Japan Travel Information
What makes Japan a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Japan is a stable, highly developed parliamentary democracy with a modern economy. Tourist facilities are widely available, except in coastal areas of Northeast Japan still recovering from the aftermath of the March 11, 2011, earthquake and tsunami.
Crime
The general crime rate in Japan is well below the U.S. national average. Crimes against U.S. citizens in Japan usually involve personal disputes, theft, or vandalism. Violent crime is rare, but it does exist. Sexual assaults are not often reported, but they do occur, and females may be randomly targeted. Hate-related violent crimes rarely occur, although some U.S. citizens have reported being the target of comments or actions because of their nationality or their race. U.S. citizens have reported incidents of pickpocketing in crowded shopping areas, on trains, and at airports. Every year, a number of U.S. citizens report their passports lost or stolen at international airports, especially passports that were carried in their pockets. Robberies committed after a victim has been drugged or “drink spiked” are increasing (see below).Some U.S. citizens report that Japanese police procedures appear to be less sensitive and responsive to a victim's concerns compared to the procedures in the United States, particularly in cases of domestic violence or sexual assault, or when both the victim and the perpetrator are foreigners. Few victim's assistance resources or battered women's shelters exist in major urban areas, and they are generally unavailable in rural areas. Investigations of sexual assault crimes are often conducted without female police officers present, and police typically ask about the victim's sexual history and previous relationships. The quality of Japanese-English interpretation services can vary, and for some U.S. citizen victims, this has caused a problem.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are such goods illegal in the United States, but if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Concerns Regarding Roppongi and other Entertainment and Nightlife Districts in Tokyo:
Roppongi is an entertainment district in Tokyo that caters to foreign clientele and is considered a high-risk area for crime, particularly the misappropriation of credit card information in bars to make fraudulent credit card charges. Other high-risk areas for crime in the Tokyo area include Shinjuku (especially the area of Kabuki-cho), Shibuya, and Ikebukuro. However, you should use caution in all entertainment and nightlife districts throughout Japan. Incidents involving U.S. citizens in these areas include physical and sexual assaults, drug overdoses, theft of purses, wallets, cash, and credit cards at bars or clubs, and drugs allegedly slipped into drinks.
Never accept drinks from strangers or turn your back to your drink while in a bar or club. Drink-spiking at bars and entertainment venues, especially in areas such as Roppongi and Kabuki-cho, near Shinjuku, has routinely led to robbery and has also resulted in physical and sexual assaults. In most drink-spiking reports, the victim unknowingly drinks a beverage that has been mixed with a drug that makes the victim unconscious or dazed for several hours, during which time the victim’s credit card is used for large purchases or the card is stolen. Some victims regain consciousness in the bar or club; other victims may awaken on the street or in other unknown locations. Several U.S. citizens have also reported being charged exorbitant bar tabs in some bars and clubs in Roppongi and other entertainment and nightlife districts. Although firearms and brandishing knives in public are illegal in Japan, there have been reports by U.S. citizens of being threatened with gun or knife violence in such venues in order to force them to pay bar tabs or withdraw money. There have also been reports of beatings of U.S. citizens who have refused to pay or hand over money.
There have been recent reports of U.S. citizens being forcibly taken to ATM machines and robbed, or forced to withdraw funds after being unable to pay exorbitant bar tabs. Please be aware that Roppongi and other entertainment and nightlife districts have also been the scenes of violence between criminal syndicates in the past. In 2012, a member of a Japanese criminal organization was beaten to death in a bar in Roppongi by several masked men.
We urge you to keep these incidents in mind and use caution in all entertainment areas and nightlife districts. Some travelers have reported that their credit cards have been unreasonably over-charged without their knowledge in these areas. If you believe that you are a victim of a crime, you must file a police report at the nearest police station before you leave Japan. The Japanese police do not provide you with a copy of the police report, but rather issue a report number. You can provide this report number to your credit card company in order to confirm the incident with the police. The Japanese police cannot accept reports filed from overseas by phone or email.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in another country, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In Japan, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport or Japanese residence card to show your identity and visa status. Driving under the influence could also land you immediately in jail. If you violate Japanese law, even unknowingly, you may be arrested, imprisoned, or deported. If you are arrested in Japan, even for a minor offense, you may be held in detention without bail for several months or more during the investigation and legal proceedings. A list of English-speaking lawyers located throughout Japan is available on our website. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods or purchase child pornography. While you are overseas, U.S. laws don’t apply. If you do something illegal in your host country, you are subject to the laws of the country even though you are a U.S. citizen. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Illegal Drugs: Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs, including marijuana, are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and fines. In most drug cases, suspects are detained and barred from receiving visitors or corresponding with anyone other than a lawyer or a U.S. consular officer until after the first hearing, which at times has taken a year to take place. Solitary confinement is common.
You could be convicted of drug use based on a positive blood or urine tests alone, and several U.S. citizens are now serving time in Japanese prisons as the result of sting operations that used informants. The Japanese police routinely share information on drug arrests with Interpol, assuring that notification of the arrest will reach U.S. law enforcement agencies. The majority of all U.S. citizens now in prison in Japan are incarcerated for drug-related crimes. In recent months, there have been arrests of individuals selling and possessing synthetic drug-like substances, such as the synthetic marijuana called "spice."
Japanese authorities aggressively pursue drug smugglers with sophisticated detection equipment, "sniffing" dogs, and other methods. When entering Japan, you and your luggage will be screened at ports of entry. Incoming and outgoing mail, as well as international packages sent via DHL or FedEx, are also checked carefully. The Japanese police make arrests for even the smallest amounts of illegal drugs. Several U.S. citizens have been arrested, tried, and convicted after having mailed illegal drugs to themselves from other countries, or for having tried to bring drugs into Japan as paid couriers working out of Southeast Asia or Europe. In 2013, several U.S. citizens were arrested at Japanese airports for smuggling illegal drugs on flights originating in India. All claim that they did not realize they were carrying drugs. When traveling to Japan, never transport packages that do not belong to you, and keep immediate control of your luggage at all times.
Knives: Possession of a knife with a locking blade, or a folding blade that is longer than 5.5 cm (a little more than two inches), is illegal in Japan. U.S. citizens and U.S. military personnel have been arrested and detained for more than 10 days for carrying pocket knives that are legal in the United States but illegal in Japan.
Immigration Penalties: Japanese work visas are not transferable and are issued outside of Japan for a specific job with a specific employer at a specific place of employment. It is illegal for you to work in Japan while in tourist or visa-waiver status. Japanese authorities do not allow foreigners to change their immigration status from visa-waiver status to work status while in Japan. Japanese immigration officers may deny you entry if you appear to have no visible means of support. Please contact the Japanese Embassy or the nearest Japanese consulate in the United States for information on what is considered enough financial support. If you work in Japan without a work visa, you may be subject to arrest, which can involve several weeks or months of incarceration, followed by conviction and imprisonment or deportation. If you are deported, you will have to pay the cost of deportation, including legal expenses and airfare.
Overstaying your visa or working illegally may lead to fines of several thousands of dollars, and in some cases, re-entry bans can be as long as ten years or indefinitely for drug offenders. For additional information please see Japan’s Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act.
Arrest notifications in Japan: Generally, when you are arrested in Japan, the police will ask if you would like the U.S. embassy or consulate to be notified of your arrest. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Consular Access: You must carry your U.S. passport or Japanese Residence Card (Zairyu Kado) with you at all times so that if questioned by local officials, you can prove your identity, citizenship, and immigration status. Under Japanese law, the police may stop any person on the street at any time and demand to see identification. If you do not have with you either a passport or a valid Japanese Residence Card, you are subject to arrest. In accordance with the U.S.-Japan Consular Convention, U.S. consular officers are generally notified within 24 hours of the arrest of a U.S. citizen, if the U.S. citizen requests consular notification.
Conditions at Prisons and Detention Facilities: Japanese prisons and detention facilities maintain internal order through a regime of very strict discipline. U.S. citizen prisoners often complain of stark, austere living conditions and psychological isolation. No one arrested in Japan is allowed access to personal medication of any type, often causing problems and health risks to those arrested with medical conditions, as substitute medication provided by prison medical officials is seldom the same in effect or strength. As a prisoner, you can become eligible for parole only after having served approximately 60-70% of your sentence. Early parole is not allowed for any reason - humanitarian, medical, or otherwise. Access to interpreters is not always required under Japanese criminal law. Additional information on arrests in Japan is available on the United States' embassy website. Japan acceded to the Council of Europe Convention on the Transfer of Sentenced Persons on June 1, 2003.
Languages
Japanese
Medical Facilities and Health Information
While medical care in Japan is good, English-speaking physicians and medical facilities that cater to U.S. citizens’ expectations are expensive and not widespread. Japan has a national health insurance system that is available only to those foreigners with long-term visas for Japan. National health insurance does not pay for medical evacuation. Medical caregivers in Japan require payment in full at the time of treatment or concrete proof of ability to pay before they will treat a foreigner who is not a member of the national health insurance plan.U.S.-style and standard psychiatric care can be difficult to locate in major urban centers in Japan and generally is not available outside of Japan's major cities. Extended psychiatric care for foreigners in Japan is difficult to obtain at any price.
U.S. prescriptions are not honored in Japan, so if you need ongoing prescription medicine you should arrive with a sufficient supply for your stay in Japan or enough until you are able to see a local care provider. Certain medications, including some commonly prescribed for depression and Attention Deficient Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), are not widely available.
Safety and Security
There have been no major terrorist incidents in Japan since 1995. However, you should be aware of the potential risks and take these into consideration when making travel plans.The Government of Japan maintains heightened security measures at key facilities and ports of entry as antiterrorism precautions. At times, these security measures may increase because of regional tensions. The Government of Japan is vigilant in tracking terrorist threat indicators and remains on a high state of alert. You can contact local police substations (koban) and police emergency dispatchers (tel. 110) to report any suspicious activity.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Japan is provided for general reference only, and it may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Driving in Japan is quite complicated and expensive. Traffic moves on the left side of the road. Those who cannot read the language will have trouble understanding road signs. Highway tolls can be as high as $1 (U.S.) or more per mile. City traffic is often very congested. A 20-mile trip in the Tokyo area may take two hours. There is virtually no legal roadside parking, however, traffic is commonly blocked or partially blocked by those who illegally parked curbside. In mountainous areas, roads are often closed during the winter, and cars should be equipped with tire chains. Roads in Japan are much narrower than those in the United States. Japanese compulsory insurance (JCI) is mandatory for all automobile owners and drivers in Japan. Most short-term visitors choose not to drive in Japan. Other than a few exceptions, turning on red lights is generally not permitted.
Japanese law provides that all drivers in Japan are held liable in the event of an accident, and assesses fault in an accident on all parties. Japan has a national zero percent blood-alcohol level standard for driving, and drivers stopped for driving under the influence of intoxicants will have their licenses confiscated. If you’re found guilty of "drunken, speeding, or blatantly careless driving resulting in injury" you are subject to up to 15 years in prison.
All passengers are required to fasten their seat belts.
The National Police Agency (NPA) oversees the administration and enforcement of traffic laws in Japan.
Emergency Assistance: Within Japan, please dial 110 for police, and 119 for an ambulance. For roadside assistance, please contact the Japan Automobile Federation (JAF) at 03-5730-0111 in Tokyo, 072-645-0111 in Osaka, 011-857-8139 in Sapporo, 092-841-5000 in Fukuoka, or 098-877-9163 in Okinawa.
For specific information concerning Japanese driving permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, and mandatory insurance, please refer to the Japan National Tourist Organization website for locations in Chicago, Los Angeles, New York, or San Francisco. In addition, information about roadside assistance, rules of the road, and obtaining a Japanese driver's license is available in English from the Japan Automobile Federation (JAF) website.
International Driving Permits (IDPs): An international driving permit (IDP) issued in the United States by the American Automobile Association (AAA) or the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA) is required of short-term visitors who drive in Japan. You must obtain an IDP issued in your country of residence prior to arriving in Japan. The U.S. Embassy or its consulates do not issue IDPs. IDPs issued via the Internet and/or by other organizations are not valid in Japan.
"Residents" – the exact definition is unclear - must convert to or obtain a Japanese driver’s license. Residents in Japan who use an international driver’s license may be fined or arrested. In practice, the term “resident” involves more than simply visa status or length of stay in Japan and is determined by the police. In short, an international license is not a substitute for a valid Japanese license. See the United States Department of State's website for more information on driving in Japan.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
