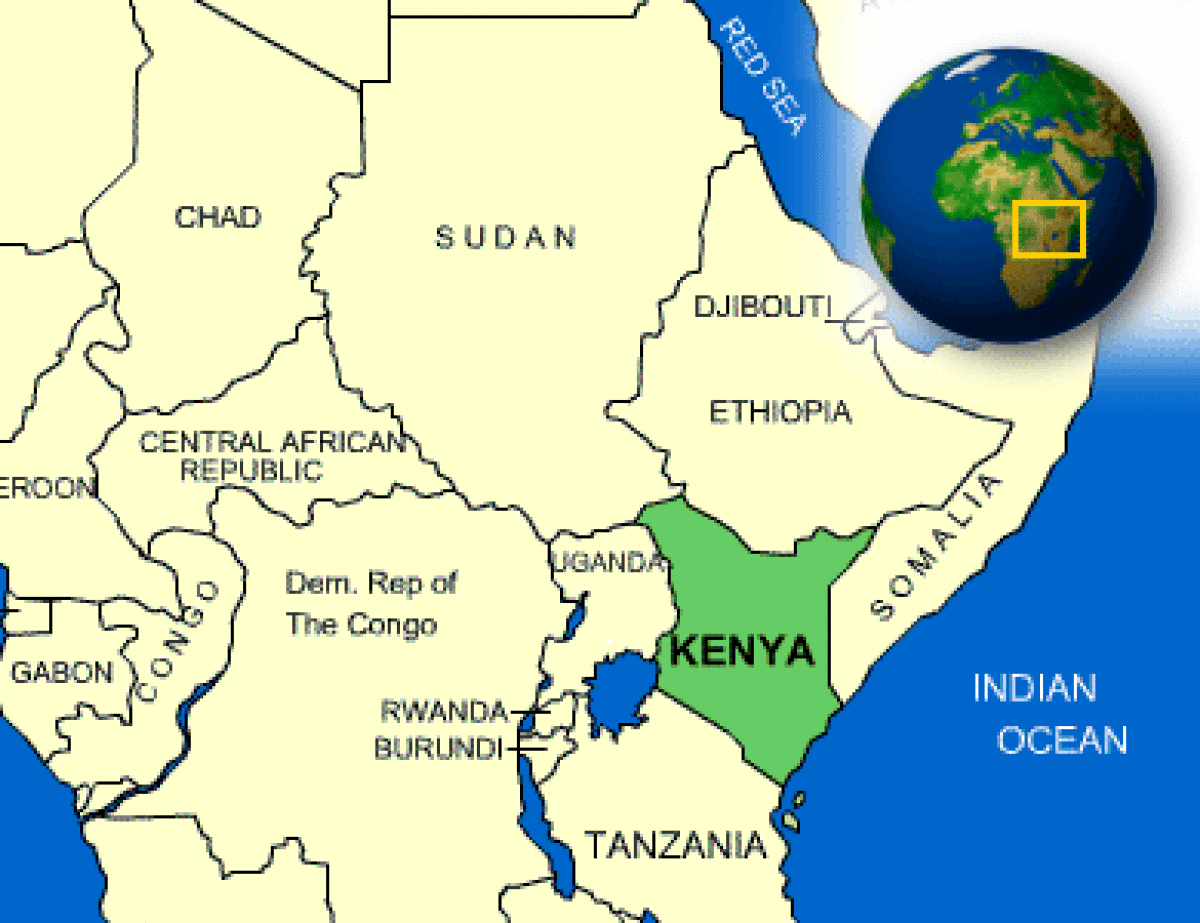
Where is Kenya located?
What countries border Kenya?
Kenya Weather
What is the current weather in Kenya?
Kenya Facts and Culture
What is Kenya famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Patriotism is evident in people’s respect for the national flag. When the flag is raised or lowered, Kenyans stop what... More
- Family: The family unit usually includes the extended family. There is much interaction between uncles, aunts, and cousins. In fact, children... More
- Personal Apperance: Kenyans generally are modestly dressed. Shorts (for women) are generally only appropriate in resort areas. Women usually wear dresses,... More
- Recreation: Football (soccer) is the national pastime. School sponsored sports include soccer, and track and field. Urban Kenyans often become members... More
- Diet: Popular meats consumed are fish, lamb, goat, beef and chicken. Milk, "ugali" (dough made from cornmeal, sorghum or millet), "uji"(porridge... More
- Food and Recipes: Afternoon tea is a daily custom throughout the country. Depending on the type of food, people may eat their food... More
- Visiting: Visiting is often done unannounced with people often dropping by for a visit and a cup of tea. ... More
- Dating: Men and women usually marry between the ages of eighteen and twenty-four. The dowry system, where a payment is made... More
Kenya Facts
What is the capital of Kenya?
| Capital | Nairobi |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Kenyan Shilling (KES) |
| Total Area |
224,080 Square Miles 580,367 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Africa, bordering the Indian Ocean, between Somalia and Tanzania |
| Language | English (official), Kiswahili (official), numerous indigenous languages |
| GDP - real growth rate | 6.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $3,300.00 (USD) |
Kenya Demographics
What is the population of Kenya?
| Ethnic Groups | Kikuyu 17.1%, Luhya 14.3%, Kalenjin 13.4%, Luo 10.7%, Kamba 9.8%, Somali 5.8%, Kisii 5.7%, Mijikenda 5.2%, Meru 4.2%, Maasai 2.5%, Turkana 2.1%, non-Kenyan 1%, other 8.2% |
| Language - note |
English is an official language and is widely used, especially for business and official purposes. However, Kiswahili (also called Swahili) was proclaimed the national language after independence and is therefore also official. One of the reasons Kiswahili is not a difficult language is that it's pronunciation never changes from word to word. A as the ‘a’ in ‘father’, E as the ‘e’ in ‘best’, or the ‘a’ in ‘hay’ , I as the ‘ee’ in ‘bee’, O as the ‘o’ in ‘cold’, U as the ‘ou” in “you”, Dh as the ‘th’ in ‘this’, Ng’ as the ‘ng’ in ‘sing’. |
| Languages | English (official), Kiswahili (official), numerous indigenous languages |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Kenyan(s) adjective: Kenyan |
| Population | 58,246,378 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.06% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 5.325 million NAIROBI (capital), 1.440 million Mombassa |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 29.5% of total population rate of urbanization: 4.09% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 29,091,800 female: 29,154,578 |
Kenya Government
What type of government does Kenya have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President William RUTO (since 13 September 2022); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President William RUTO (since 13 September 2022) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, subject to confirmation by the National Assembly elections/appointments: president and deputy president directly elected on the same ballot by majority vote nationwide and at least 25% of the votes cast in at least 24 of the 47 counties; failure to meet these thresholds requires a runoff between the top two candidates; election last held on 9 August 2022 (next to be held on 10 August 2027) election results: 2022: William RUTO elected president in first round; percent of vote - William RUTO (UDA) 50.5%, Raila ODINGA (ODM) 48.9%, other 0.6% 2017: Uhuru KENYATTA reelected president; percent of vote - Uhuru KENYATTA (JP) 98.3%, Raila ODINGA (ODM) 1%, other 0.7%; note - Kenya held a previous presidential election on 8 August 2017, but Kenya's Supreme Court on 1 September 2017 nullified the results, citing irregularities; the political opposition boycotted the October vote |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Kenya dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 4 out of the previous 7 years |
| National Holiday | Jamhuri Day (Independence Day), 12 December (1963); note - Madaraka Day, 1 June (1963) marks the day Kenya attained internal self-rule |
| Constitution |
history: current constitution passed by referendum on 4 August 2010 amendments: amendments can be proposed by either house of Parliament or by petition of at least one million eligible voters; passage of amendments by Parliament requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of both houses in each of two readings, approval in a referendum by majority of votes cast by at least 20% of eligible voters in at least one half of Kenya’s counties, and approval by the president; passage of amendments introduced by petition requires approval by a majority of county assemblies, approval by majority vote of both houses, and approval by the president |
| Independence | 12 December 1963 (from the UK) |
Kenya Video
YouTube, Devin Graham Africa - Into The Wild - VenTribe
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Kenya Geography
What environmental issues does Kenya have?
| Overview |
The northern and eastern three‑fifths of the country are arid. The southern two‑fifths, where most of the population and nearly all the economic production is centered, consists of a low‑lying coastal area and a plateau varying in altitude from 3,000 to 10,000 feet. Although only about 20% of the land is suitable for cultivation, agriculture is the most important economic activity. The Nairobi area offers the contrasts of green rolling uplands, thorn scrub of the famous game plains, coffee and tea estates, and entry to the Great Rift Valley. Farther afield are the forests and snows of Mount Kenya, the dairy and farm country of the highlands, the tropical beaches of the coastal strip, and the deserts of the northeast. Nairobi is 87 miles south of the Equator and some 300 miles west of the Indian Ocean. The downtown area has an elevation of 5,400 feet, but some residential areas are located at more than 6,000 feet. |
| Climate | Nairobi has four seasons, but overall temperature changes are moderate. Mid‑ December through March are mainly sunny and warm by day, cool at night, and generally dry. April and May constitute the principal rainy season with lower day temperatures. The months of June through September are mainly dry, but often cloudy and cool, with cool nights. October and November make up the short rainy season, with long sunny periods, warm days, and cool nights. Average annual rainfall in Nairobi is about 39 inches, but the actual amount varies widely in any year. |
| Border Countries | Ethiopia 861 km, Somalia 682 km, Sudan 232 km, Tanzania 769 km, Uganda 933 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | water pollution from urban and industrial wastes; degradation of water quality from increased use of pesticides and fertilizers; water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; poaching |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | low plains rise to central highlands bisected by Great Rift Valley; fertile plateau in west |
Kenya Economy
How big is the Kenya economy?
| Economic Overview |
Kenya is the economic, financial, and transport hub of East Africa. Kenya’s real GDP growth has averaged over 5% for the last decade. Since 2014, Kenya has been ranked as a lower middle income country because its per capita GDP crossed a World Bank threshold. While Kenya has a growing entrepreneurial middle class and steady growth, its economic development has been impaired by weak governance and corruption. Although reliable numbers are hard to find, unemployment and under-employment are extremely high, and could be near 40% of the population. In 2013, the country adopted a devolved system of government with the creation of 47 counties, and is in the process of devolving state revenues and responsibilities to the counties. Agriculture remains the backbone of the Kenyan economy, contributing one-third of GDP. About 75% of Kenya’s population of roughly 48.5 million work at least part-time in the agricultural sector, including livestock and pastoral activities. Over 75% of agricultural output is from small-scale, rain-fed farming or livestock production. Tourism also holds a significant place in Kenya’s economy. In spite of political turmoil throughout the second half of 2017, tourism was up 20%, showcasing the strength of this sector. Kenya has long been a target of terrorist activity and has struggled with instability along its northeastern borders. Some high visibility terrorist attacks during 2013-2015 (e.g., at Nairobi’s Westgate Mall and Garissa University) affected the tourism industry severely, but the sector rebounded strongly in 2016-2017 and appears poised to continue growing. Inadequate infrastructure continues to hamper Kenya’s efforts to improve its annual growth so that it can meaningfully address poverty and unemployment. The KENYATTA administration has been successful in courting external investment for infrastructure development. International financial institutions and donors remain important to Kenya's growth and development, but Kenya has also successfully raised capital in the global bond market issuing its first sovereign bond offering in mid-2014, with a second occurring in February 2018. The first phase of a Chinese-financed and constructed standard gauge railway connecting Mombasa and Nairobi opened in May 2017. In 2016 the government was forced to take over three small and undercapitalized banks when underlying weaknesses were exposed. The government also enacted legislation that limits interest rates banks can charge on loans and set a rate that banks must pay their depositors. This measure led to a sharp shrinkage of credit in the economy. A prolonged election cycle in 2017 hurt the economy, drained government resources, and slowed GDP growth. Drought-like conditions in parts of the country pushed 2017 inflation above 8%, but the rate had fallen to 4.5% in February 2018. The economy, however, is well placed to resume its decade-long 5%-6% growth rate. While fiscal deficits continue to pose risks in the medium term, other economic indicators, including foreign exchange reserves, interest rates, current account deficits, remittances and FDI are positive. The credit and drought-related impediments were temporary. Now In his second term, President KENYATTA has pledged to make economic growth and development a centerpiece of his second administration, focusing on his "Big Four" initiatives of universal healthcare, food security, affordable housing, and expansion of manufacturing. |
| Industries | small-scale consumer goods (plastic, furniture, batteries, textiles, soap, cigarettes, flour), agricultural products processing; oil refining, cement; tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Kenyan Shilling (KES) |
| Export Partners | Uganda 18.5%, UK 13%, US 8.1%, Netherlands 7.6%, Pakistan 5%, Egypt 4.1% |
| Import Partners | UAE 12%, Saudi Arabia 8.7%, South Africa 8.1%, US 8.1%, UK 7.1%, France 5.8%, China 5.5%, Japan 5%, India 4.8% |
Kenya News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Kenya?
Source: Google News
Kenya Travel Information
What makes Kenya a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Kenya is a developing East African country known for its wildlife and national parks. The capital city is Nairobi. The second largest city is Mombasa, located on the southeast coast. Tourist facilities are widely available in Nairobi, the game parks, the reserves, and on the coast. English and Kiswahili are Kenya’s two official languages.
Crime
Violent and sometimes fatal criminal attacks, including armed carjackings, grenade attacks, home invasions and burglaries, and kidnappings can occur at any time and in any location. U.S. citizens, including U.S. Embassy employees, have been victims of such crimes within the past year. Crime is high in all regions of Kenya, particularly Nairobi, Mombasa, Kisumu, and at coastal beach resorts. There are regular reports of attacks against tourists by groups of armed assailants. Pickpockets and thieves carry out "snatch and run" crimes on city streets and near crowds. Visitors have found it safer not to carry valuables, but rather to store them in hotel safety deposit boxes or safe rooms. However, there have been reports of safes being stolen from hotel rooms and hotel desk staff being forced to open safes. Walking alone or at night, especially in downtown areas, public parks, along footpaths, on beaches, and in poorly lit areas, is dangerous and discouraged.Nairobi averages about ten vehicle hijackings per day and Kenyan authorities have limited capacity to deter and investigate such acts. Matatus (public transportation) tend to be targeted since they carry up to 14 passengers. Although these attacks are often violent, victims are generally not injured if they do not resist. There is also a high incidence of residential break-ins and occupants should take additional security measures to protect their property. Thieves and con artists have been known to impersonate police officers, thus U.S. citizens are strongly encouraged to ask for identification if approached by individuals identifying themselves as police officials, uniformed or not. U.S. citizens have fallen victim to such crimes within the past year. U.S. citizens in Kenya should be extremely vigilant with regard to their personal security, particularly in public places frequented by foreigners such as clubs, hotels, resorts, upscale shopping centers, restaurants, and places of worship. U.S. citizens should also remain alert in residential areas, at schools, and at outdoor recreational events.
Thieves routinely snatch jewelry and other objects from open vehicle windows while motorists are either stopped at traffic lights or in heavy traffic. Vehicle windows should be up and doors locked regardless of the time of day or weather. Thieves on matatus, buses, and trains may steal valuables from inattentive passengers. U.S. citizens should guard their backpacks or hand luggage and ensure these items are not left unattended. Purchasing items from street vendors is strongly discouraged – visitors should only use reputable stores or businesses. Many scams, perpetrated against unsuspecting tourists, are prevalent in and around the city of Nairobi. Many of these involve people impersonating police officers and using fake police ID badges and other credentials. Nevertheless, police checkpoints are common in Kenya and all vehicles are required to stop if directed to do so.
Highway banditry is common in much of Mandera, Wajir, Garissa, Marsabit, and northern Tana River counties, as well as Turkana county. These areas are remote and sparsely populated. Incidents also occur occasionally on Kenya's main highways, particularly after dark. Due to increased bandit activity, air travel is the recommended means of transportation when visiting any of the coastal resorts north of Malindi. Travelers to North Eastern Kenya and the North Rift Valley Region should travel with police escorts or convoys organized by the government of Kenya.
There have been reports of armed banditry in or near many of Kenya's national parks and game reserves, particularly the Samburu, Leshaba, and Masai Mara game reserves. In response, the Kenya Wildlife Service and police have taken steps to strengthen security in the affected areas, but the problem has not been eliminated. Travelers who do not use the services of reputable travel firms or knowledgeable guides or drivers are especially at risk. Safaris are best undertaken with a minimum of two vehicles so that there is a backup in case of mechanical failure or other emergency. Camping alone is always risky.
The Kenyan mail system can be unreliable and monetary instruments (credit cards, checks, etc.) are frequently stolen. International couriers provide the safest means of shipping envelopes and packages, although anything of value should be insured.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Kenya, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. Driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. There are also some activities that might be legal in Kenya, but illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law. For example, engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Kenya, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not where you are going.Persons violating Kenya's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Kenya are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Kenya has recently enacted strict legislation regulating the sale and consumption of alcohol and cigarettes. Please see the Special Circumstances section below.
Arrest notifications in host country:
Kenya is a signatory to the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations (VCCR), and is required by the VCCR to ask any detained U.S. citizen if he/she would like the U.S. Embassy to be notified and to contact the U.S. Embassy if the detained U.S. citizen requests it. Kenya does not routinely comply with its VCCR obligation. Any U.S. citizen who is detained should request U.S. Embassy notification if he/she would like consular assistance. U.S. citizens are encouraged to carry a copy of their U.S. passport with them at all times, so that proof of identity and U.S. citizenship is readily available if questioned by local officials.
Languages
English (official), Kiswahili (official), numerous indigenous languages
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical services are available in Nairobi. Frequent outbreaks of cholera and malaria are endemic in Kenya outside Nairobi. In addition, diseases such as Ebola, Rift Valley Fever, and anthrax from handling sheep skins occur periodically. Travelers, who become ill with a fever or flu-like illness while traveling in a malaria-risk area, and up to one year after returning home, should seek prompt medical attention and tell the physician their travel history and what anti-malarial drugs they have been taking. For additional information on malaria, protection from insect bites, and anti-malarial drugs, please visit the CDC Travelers' Health web site.Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Kenya. For further information, please consult the CDC's Information on TB.
On May 17, the CDC issued a Travel Notice regarding an outbreak of dengue in Mombasa, Kenya’s second-largest city and a major tourist destination. Dengue is spread by mosquitoes, and travelers to Kenya’s coastal areas should plan to protect themselves from mosquito bites through covering exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats, and using insect repellent as directed on the packaging. For more information on dengue, please visit the CDC web page on dengue.
The CDC issued a Travel Notice on June 3, regarding the recent diagnosis of polio in Kenya. All travelers to Kenya and surrounding countries should be fully vaccinated against polio. In addition, adults previously vaccinated as children should receive a one-time booster dose of polio vaccine.
Safety and Security
All travelers to Kenya should review the Department of State’s Travel Warning for Kenya that provides detailed information about security issues affecting the country. Though thousands of U.S. citizens visit Kenya safely each year, the U.S. government continues to receive information regarding potential terrorist threats aimed at U.S., Western, and Kenyan interests in Kenya. Terrorist acts could include suicide operations, bomb and grenade attacks, kidnappings, attacks on civil aviation, and attacks on maritime vessels in or near Kenyan ports. Although there have been recent gains in the pursuit of those responsible for previous terrorist activities, many of those involved remain at large and continue to operate in the region. Travelers should consult the Worldwide Caution on the Travel.State.Gov website for further information and details.Kenya initiated military action against al-Qaida affiliate al-Shabaabby crossing into Somalia on October 16, 2011, and, on June 2, 2012, signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) whereby it formally joined the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM). Kenyan troops within AMISOM are now actively pursuing al-Shabaab in southeastern Somalia. In response to the Kenyan intervention, al-Shabaab and its sympathizers have conducted retaliatory attacks against civilian and government targets in Kenya.
In the past year, there have been numerous attacks involving grenades or explosive devices in Kenya. At least 76 people died in these attacks, and around 220 people were injured. No U.S. citizens were among the casualties. Approximately twenty-five of these attacks occurred in North Eastern Province, mainly in Dadaab, Wajir, Mandera, and Garissa. Four attacks occurred in Mombasa. Twelve grenade and improvised explosive device (IED) attacks have occurred in Nairobi, illustrating an increase in the number of attacks and an advance in the sophistication of attacks. Targets included police stations and police vehicles, nightclubs and bars, churches, a mosque, a religious gathering, a downtown building of small shops, and a bus station. One of the deadliest attacks occurred in Nairobi on November 18, 2012, when an IED detonated on a passenger bus in Eastleigh, killing ten. Seventeen people were killed and about 50 people were injured in a deadly attack on July 1, 2012, with two simultaneous assaults on churches in Garissa. Additionally, Kenyan law enforcement has disrupted several terrorist plots, which resulted in the discoveries of weapons caches and other dangerous materials, and the arrests of several individuals. Multiple kidnappings of Westerners have occurred in Kenya.
In September 2011, a British woman was kidnapped and her husband murdered at a coastal resort near the Kenya-Somali border. The British hostage was released in March 2012 after payment of ransom. In October 2011, a French national was kidnapped from a private residence on the popular tourist destination of Lamu Island on Kenya's north coast. She died while in captivity in Somalia. Also in October 2011, two Spanish nationals working for a NGO were kidnapped in Dadaab refugee camp, in northeastern Kenya. They are still being held. On June 29, 2012, four international aid workers (from Canada, Pakistan, Norway, and the Philippines) were kidnapped in Dadaab. All were rescued on July 1, 2012.
Following a series of security incidents attributed to violent extremists, including al-Shabaab, the Government of Kenya announced on December 13, 2012 that all urban refugees (primarily Somalis) should relocate to refugee camps. This directive is being challenged in court and is not currently being enforced; however, U.S. citizens of Somali descent should be aware that they may encounter interruptions in their travel due to increased police scrutiny based on the directive. It is very important to carry proof of identity and legal status in Kenya (e.g., valid visa). If you are detained by police or immigration officials, you should request to speak to someone from the Consular Section of the U.S. Embassy in Nairobi.
As a result of these recent events and threats, U.S. government employees, contractors, grantees, and their dependents are prohibited from traveling to the cities of El Wak, Wajir, Garissa, Mandera, and Liboi. U.S. government personnel are restricted from traveling to the coastal area north of Pate Island, including Kiwayu and north to Kiunga on the Kenya/Somalia border.
Although these restrictions do not apply to travelers not associated with the U.S. government, U.S. citizens already in Kenya should take these restrictions into account when planning trips. The Embassy regularly reviews the security of these areas for possible modification.
Clashes occasionally occur in and around Isiolo and Moyale and in 2012 there were numerous instances of sporadic violence and protests elsewhere in the country. Rioting occurred in Mombasa shortly after a local Muslim cleric with alleged ties to al-Shabaab was killed in a drive-by shooting, resulting in the deaths of three policemen and four church burnings. Demonstrations in Kisumu following the murder of two prominent Kenyan citizens in October 2012 turned violent, leaving at least four protestors dead. More than 160 people were killed in clashes in late 2012 between two communities in Tana River County. While this violence is not directed at foreigners, protests and ethnic clashes are unpredictable. U.S. citizens are advised to check conditions and monitor local media reports before traveling to these areas.
Villagers in rural areas are sometimes suspicious of strangers. There have been several incidents of violence against Kenyan and foreign adults in rural areas who are suspected of stealing children. U.S. visitors to rural areas should be aware that close contact with children, including taking their pictures or giving them candy, can be viewed with deep alarm and may provoke panic and violence. Adoptive parents traveling with their adopted child should exercise particular caution and are urged to carry complete copies of their adoption paperwork with them at all times.
Travelers should keep informed of local developments by following local press, radio, and television reports prior to their visits. Visitors should also consult their hosts, including U.S. and Kenyan business contacts, hotels, tour guides, and travel organizers.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
Road Conditions and Safety: Road accidents are a major threat to travelers in Kenya. Roads are poorly maintained and are often bumpy, potholed, and unpaved.• Traffic moves on the left side of the road, which can be very disorienting to those not accustomed to it.
• Beware of vehicles traveling at excessive speed, and unpredictable local driving habits.
• Many vehicles are poorly maintained and lack basic safety equipment.
• Heavy traffic jams, either due to rush hour or because of accidents, are common.
• Some vehicles will cross the median strip and drive against the flow of traffic.
U.S. citizens have been fatally injured in accidents involving long-distance, inter-city buses and local buses and vans called “matatus”. Matatus are commonly known to be the greatest danger to other vehicles and pedestrians. U.S. government personnel are prohibited from using matatus.
Injuries and fatalities involving two-wheeled motorcycle taxis, called “boda bodas,” are equally common. Boda bodas often fail to observe basic safety precautions and ignore traffic rules. Inter-city nighttime road travel should be avoided due to the poor road and streetlight conditions and the threat of banditry throughout the country. U.S. government personnel are prohibited from using boda bodas.
During the rainy season, some unpaved roads are impassable even with four-wheel drive vehicles with high clearance. Travelers are urged to consult with local officials regarding road conditions.
Most passenger trains are considered unsafe, particularly during rainy seasons, because of the lack of routine maintenance and safety checks. The only approved train route for U.S. government personnel is the SGR from Nairobi to Mombasa. However, passengers should ride only in the first-class cabin to avoid pickpockets and facilitate a rapid exit if necessary.
