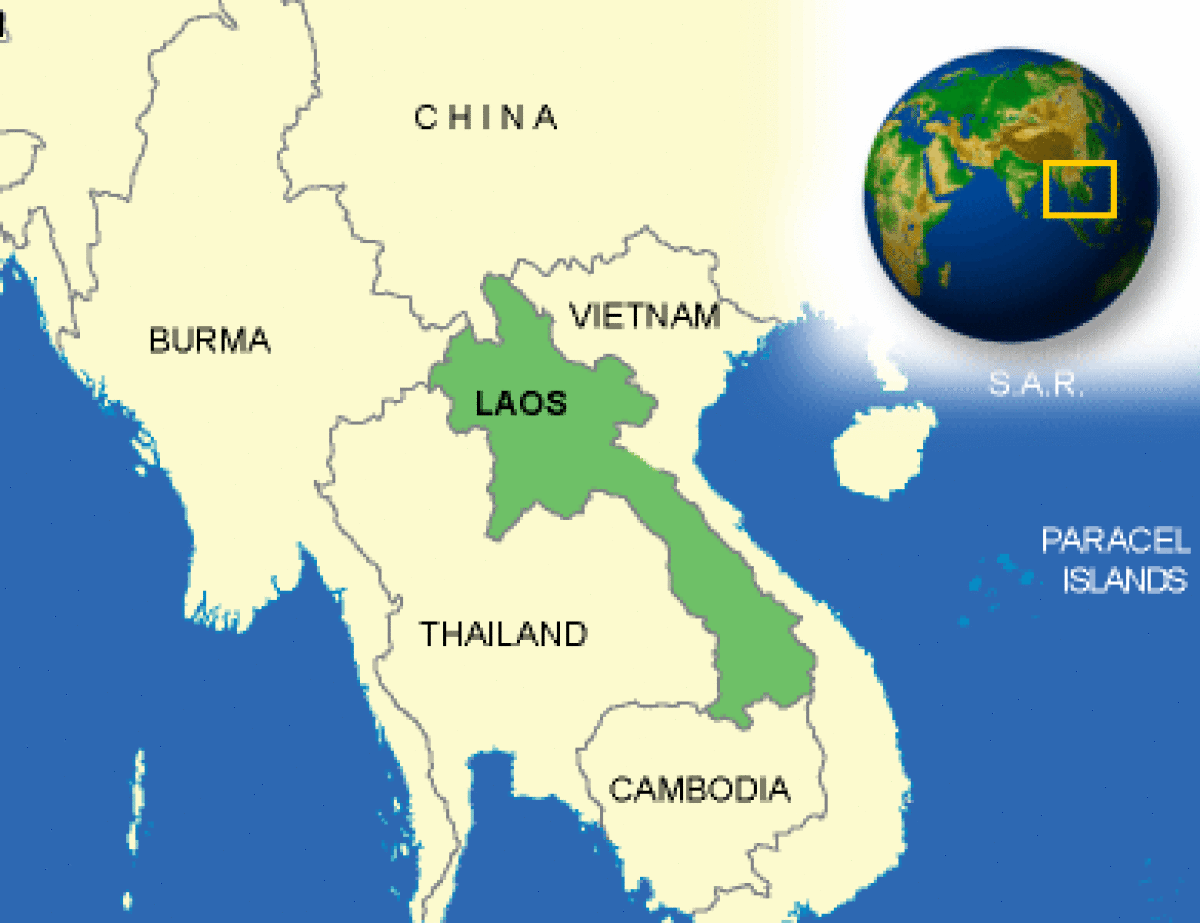
Where is Laos located?
What countries border Laos?
Laos Weather
What is the current weather in Laos?
Laos Facts and Culture
What is Laos famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Showing anger in public is inappropriate. The Lao are generally a courteous people. It is considered rude criticize a... More
- Family: The eldest man is the patriarch of the family. The Lao have great respect for their parents and elders.... More
- Personal Apperance: Lao women wear western- style blouses with colorful calf-length, sarong-style skirts made of locally hand-woven materials in multicolor designs and... More
- Recreation: One popular traditional game is called "kataw". It is played with a small ball woven out of rattan (modern balls... More
- Diet: Beverages include tea and coffee. Rice is the main Lao diet. Other foods include eggs, fish, owl, chicken and... More
- Food and Recipes: In a home setting, meals are served while siting on a mat. The Lao eat with a fork in... More
- Visiting: Bringing a gift when visiting is not necessary. Women frequently sit with legs off to one's side. It... More
- Dating: Young people can meet eligible partners at dances held during festivals, where they are free to sit and talk privately.... More
Laos Facts
What is the capital of Laos?
| Capital | Vientiane (Viangchan) |
| Government Type | communist state |
| Currency | Kip (LAK) |
| Total Area |
91,428 Square Miles 236,800 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Asia, northeast of Thailand, west of Vietnam |
| Language | Lao (official), French, English, and various ethnic languages |
| GDP - real growth rate | 7.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $5,400.00 (USD) |
Laos Demographics
What is the population of Laos?
| Ethnic Groups | Lao Loum (lowland) 68%, Lao Theung (upland) 22%, Lao Soung (highland) including the Hmong and the Yao 9%, ethnic Vietnamese/Chinese 1% |
| Languages | <p>Some ethnic minority languages have never been codified in written form. A small percentage of older people and those who attended high school prior to 1975 speak French, which has been the language of international commerce in the past. Some English is spoken.</p><p> The official language is Lao, the native language of the lowland Lao which is used in all official communications and taught in schools. Other main languages include Thai, Hmong, and midland Lao.</P |
| Nationality Noun | Lao(s) or Laotian(s) |
| Population | 7,447,296 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.63% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | VIENTIANE (capital) 810,000 |
| Urban Population | 34.300000 |
Laos Government
What type of government does Laos have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President THONGLOUN Sisoulith (since 22 March 2021); Vice Presidents PANY Yathotou and BOUNTHONG Chitmany (since 22 March 2021) head of government: Prime Minister SONEXAY Siphandon (since 30 December 2022) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president and approved by the National Assembly elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 22 March 2021 (next to be held in March 2026); prime minister nominated by the president, elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term election results: 2021: THONGLOUN Sisoulith elected president; National Assembly vote - THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) 161-1; PANY Yathotou and BOUNTHONG Chitmany (LPRP) elected vice presidents; National Assembly vote - NA; PHANKHAM Viphavanh (LPRP) elected prime minister; National Assembly vote - 158-3 2016: BOUNNHANG Vorachit (LPRP) elected president; PHANKHAM Viphavanh (LPRP) elected vice president; percent of National Assembly vote - NA; THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) elected prime minister; percent of National Assembly vote - NA |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Laos dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Republic Day (National Day), 2 December (1975) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1947 (preindependence); latest promulgated 13-15 August 1991 amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the president of the republic; amended 2003, 2015 |
| Independence | 19 July 1949 (from France by the Franco-Lao General Convention); 22 October 1953 (Franco-Lao Treaty recognizes full independence) |
Laos Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Laos Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Laos Geography
What environmental issues does Laos have?
| Overview |
The Lao People’s Democratic Republic, a landlocked nation, lies in the center of the Southeast Asian Peninsula and borders on five countries. Dense jungle and rugged mountains in the north and east cover 6% of the country’s surface. Mountainous topography is characteristic of all of Laos outside the Mekong River Basin. Phu Bia, in Xieng Khouang Province, the highest point in the country, rises 9,249 feet above sea level. The Mekong River, with its headwaters in Tibet, flows over 2,600 miles to its mouth in the south of Vietnam. One of the world's great rivers, it forms the country’s western boundary for the greater part of its length and is the cradle of Lao culture. Most major Lao towns are on its banks. The largest population center in Laos removed from the Mekong River is Phonsavanh in Xieng Khouang Province. Lately, the Lao Government has encouraged the establishment of new towns and villages in the country's interior. |
| Climate | Laos has a monsoon climate with three overlapping seasons. The rainy season is about 5 months, June-September. In October, rains start to taper off, and the cool season begins in November, lasting through February. In March "mango rains" occur. March, April, and May are hot and humid. In April, the hottest month, temperatures in Vientiane range from 72°F to 93°F, and in January, the coolest month, 52°F to 83°F. Temperature extremes of 103°F (April) and 39°F (January) have been recorded. |
| Border Countries | Burma 235 km, Cambodia 541 km, China 423 km, Thailand 1,754 km, Vietnam 2,130 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | unexploded ordnance; deforestation; soil erosion; most of the population does not have access to potable water |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly rugged mountains; some plains and plateaus |
Laos Economy
How big is the Laos economy?
| Economic Overview |
The government of Laos, one of the few remaining one-party communist states, began decentralizing control and encouraging private enterprise in 1986. Economic growth averaged more than 6% per year in the period 1988-2008, and Laos' growth has more recently been amongst the fastest in Asia, averaging more than 7% per year for most of the last decade. Nevertheless, Laos remains a country with an underdeveloped infrastructure, particularly in rural areas. It has a basic, but improving, road system, and limited external and internal land-line telecommunications. Electricity is available to 83% of the population. Agriculture, dominated by rice cultivation in lowland areas, accounts for about 20% of GDP and 73% of total employment. Recently, the country has faced a persistent current account deficit, falling foreign currency reserves, and growing public debt. Laos' economy is heavily dependent on capital-intensive natural resource exports. The economy has benefited from high-profile foreign direct investment in hydropower dams along the Mekong River, copper and gold mining, logging, and construction, although some projects in these industries have drawn criticism for their environmental impacts. Laos gained Normal Trade Relations status with the US in 2004 and applied for Generalized System of Preferences trade benefits in 2013 after being admitted to the World Trade Organization earlier in the year. Laos held the chairmanship of ASEAN in 2016. Laos is in the process of implementing a value-added tax system. The government appears committed to raising the country's profile among foreign investors and has developed special economic zones replete with generous tax incentives, but a limited labor pool, a small domestic market, and corruption remain impediments to investment. Laos also has ongoing problems with the business environment, including onerous registration requirements, a gap between legislation and implementation, and unclear or conflicting regulations. |
| Industries | tin and gypsum mining, timber, electric power, agricultural processing, construction, garments, tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Kip (LAK) |
| Export Partners | Thailand 21.5%, Vietnam 16.9%, France 8.6%, Germany 5.6% |
| Import Partners | Thailand 60.7%, Vietnam 10.5%, China 8.2%, Singapore 4% |
Laos News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Laos?
Source: Google News
Laos Travel Information
What makes Laos a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Lao People's Democratic Republic (Laos) is a developing country ruled by a one-party, Communist government. Political power is centralized in the Lao People's Revolutionary Party. Services and facilities for tourists are adequate in the capital, Vientiane, and in the UNESCO World Heritage town of Luang Prabang, but are extremely limited in other parts of the country.
Crime
Laos generally has a low rate of violent crime, but you should remain aware of your surroundings and exercise appropriate security precautions. Residential burglary is commonplace. The number of thefts and assaults in Laos has increased, and some have turned violent. Sexual assaults do occur in Laos. You should exercise caution, particularly after dark, at roadside restaurants, bars, and stalls. Foreigners are often victims of purse snatchings while they are dining or riding bicycles or motorcycles. Please be careful when carrying purses, bags, and other personal items.Local law enforcement responses to crimes, even violent crimes, are often limited. Foreigners attempting to report crimes have reported finding police stations closed, emergency telephone numbers unanswered, or policemen lacking transportation or authorization to investigate crimes that occur at night. If you move to Laos, please contact the U.S. Embassy Vientiane for security information.
If you travel to Vang Vieng, be aware that some tourists have been robbed and sexually assaulted in that area. Many restaurants in the Vang Vieng area offer menu items, particularly “pizzas,” “shakes,” or “teas,” that may contain unknown substances or opiates. These products are often advertised as “happy” or “special” items. These unknown substances or opiates can be dangerous, causing serious illness or even death. Travelers in Vang Vieng have been fined and detained for purchasing, possessing, or using illegal substances. In recent years, foreigners, including U.S. citizens, have died in Laos after using illegal drugs, such as methamphetamines, opium, or heroin. The potency of some of these drugs can be several times that of similar substances found in the United States.
Please exercise caution on overnight bus trips, particularly on buses travelling to/from Vietnam. The Embassy has received reports of scams and thefts of personal belongings on these trips.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Laos, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. Driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. There are also some things that might be legal in Laos, but still illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with minors or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Laos, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Arrest notifications in Laos: If you are arrested in Laos, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy in Vientiane of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the Embassy.
Languages
<p>Some ethnic minority languages have never been codified in written form. A small percentage of older people and those who attended high school prior to 1975 speak French, which has been the language of international commerce in the past. Some English is spoken.</p><p> The official language is Lao, the native language of the lowland Lao which is used in all official communications and taught in schools. Other main languages include Thai, Hmong, and midland Lao.</P
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities and services in Laos are limited and do not meet Western standards. In Vientiane, U.S. citizens may wish to contact the Primary Care Center, also known as the Centre medical de L’Ambassade de France (CMAF), which is supported by the French Embassy. The CMAF is located on Khou Vieng Road across the street from the Green Park Hotel, tel. 856-21-214-150, or 856-20-5558-4617, or email. The Australian government also supports a fee-for-service clinic located at the Australian Embassy, which is located at Kilometer 4 on Thadeua Road, tel. 21-353-840. Both facilities have well-trained physicians who can handle routine and urgent health problems and provide travel medicine services. The Alliance Clinic, operated by the Wattana Hospital group from Thailand, is located in the Honda building near the airport. It has basic clinical services provided by Thai physicians.U.S. citizens in Laos often seek medical care in Thailand. The Friendship Bridge linking Vientiane, Laos, to Nong Khai, Thailand, is open daily 6:00 a.m. to 10:00 p.m. Officials generally will allow travelers to cross after hours in cases of medical emergency. AEK International Hospital (tel: 66-42-342-555) and North Eastern Wattana General Hospital, both in Udorn, Thailand (tel: 66-1-833-4262), have English-speaking staff accustomed to dealing with foreign patients. Ambulances for both AEK International Hospital and Nong Khai Wattana Hospital have permission to cross the Friendship Bridge to collect patients from Vientiane. In Vientiane, the Setthatirat Hospital ambulance (tel: 021-413-720) can take patients to Thailand. The Department of State assumes no responsibility for the professional ability or reputation of these hospitals.
Counterfeit pharmaceuticals are a problem throughout Southeast Asia. Please be aware of this problem and purchase pharmaceuticals only through the most reputable pharmacies and with a physician’s prescription.
Avian influenza (H5N1) continues to be a concern in Laos. In Laos and other Southeast Asian countries affected by avian influenza, you should avoid poultry farms, contact with animals in live food markets, and any surfaces that appear to be contaminated with feces from poultry or other animals.
Safety and Security
here have been reports in the past of violent incidents carried out by anti-government forces. The Department of State recommends that if you travel to or reside in Laos, exercise caution and be alert to your surroundings at all times.The Lao government security forces often stop and check all transport on main roads, particularly at night. You must comply with requests to stop at checkpoints and roadblocks. Especially if you are considering travel outside urban centers, please contact relevant Lao government offices, such as Lao Immigration Police Headquarters in Vientiane, the Lao Tourist Police, local police and customs offices, or the U.S. Embassy for the most current security information. To avoid trouble with the authorities, if you are traveling outside of normal tourist areas or contemplating any unusual activity (including, but not limited to, engaging in business, extensive photography, or scientific research of any kind), be sure to seek advance permission from the Village Chief, District Head, Provincial Governor, or National Tourism Authority, as appropriate.
The large amount of unexploded ordnance (UXO) left over from the Indochina War causes more than 200 casualties a year. UXO can be found in some parts of Savannakhet, Xieng Khouang, Saravane, Khammouane, Sekong, Champassak, Houaphan, Attapeu, Luang Prabang, and Vientiane Provinces. In addition, numerous mine fields are left over from the Indochina war along Route 7 (from Route 13 to the Vietnam border), Route 9 (Savannakhet to the Vietnam border), and Route 20 (Pakse to Saravane). Never pick up unknown metal objects and avoid traveling off well-used roads, tracks, and paths.
You should also exercise caution in remote areas along the Lao border with Burma. Bandits, drug traffickers, and other people pursuing illegal activities operate in these border areas, as do armed insurgent groups opposed to the Government of Burma.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Laos, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Laos is provided for general reference only and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.The number of road accidents and fatalities in Laos has risen sharply in the last decade as the number of motor vehicles has increased. U.S. citizens involved in traffic accidents have been barred from leaving Laos before paying compensation for property damage or injuries, regardless of who was at fault. A driver involved in a traffic accident should remain at the scene and attempt to contact the police or wait for them to arrive to prepare an accident report. If renting a car or motorcycle, contact the rental company and its insurance agent. If there is major damage, injury or death, contact the Consular Section or the Duty Officer at the U.S. Embassy. When renting a car, motorcycle, or bicycle, do not give your original U.S. passport to the owner of the vehicle as surety against loss, theft, or damage to the vehicle.
Traffic in Laos is chaotic, and road conditions are very rough. Few roads have lane markings. Where lane markings, road signs, and stoplights do exist, they are widely ignored. Many drivers are unlicensed, inexperienced, and uninsured. Driving under the influence of alcohol or illegal drugs is not uncommon, and penalties for such offenses may not be enforced. Theoretically, traffic moves on the right, but vehicles use all parts of the road. Motorcyclists pay little or no heed to cars. Motorcycles carry as many as five people, greatly impeding the drivers' ability to react to traffic. The evening hours are particularly dangerous. Road construction sites are poorly marked, appear with no advance warning, and can be difficult to see at night. Roads are poorly lit, many vehicles have no operating lights, few bicycles have reflectors, and trucks without reflectors commonly park on unlit roads.
Exercise caution when traveling the roads of Laos, and be sure to check with local authorities, transport companies, other travelers, and/or the Embassy regarding any recent road developments prior to travel. Road obstacles, such as changes in surface conditions due to the weather, occur frequently.
Public transportation is unreliable and is limited after sunset. Automobile taxis or cars for hire are available at the airport, the Friendship Bridge, most major hotels, and near the Morning Market in Vientiane. The most common form of public transport is a three-wheeled, open-sided taxi called "tuk-tuks.” Tuk-tuks and taxis are frequently in poor repair, and drivers generally speak little or no English. Inter-city transport is provided by buses, vans, pickups, and trucks, any of which may also be in poor repair.
Emergency services in Laos are either unreliable or non-existent. Lao road traffic regulations require any driver coming upon a road accident to assist in transporting injured persons to a hospital.
