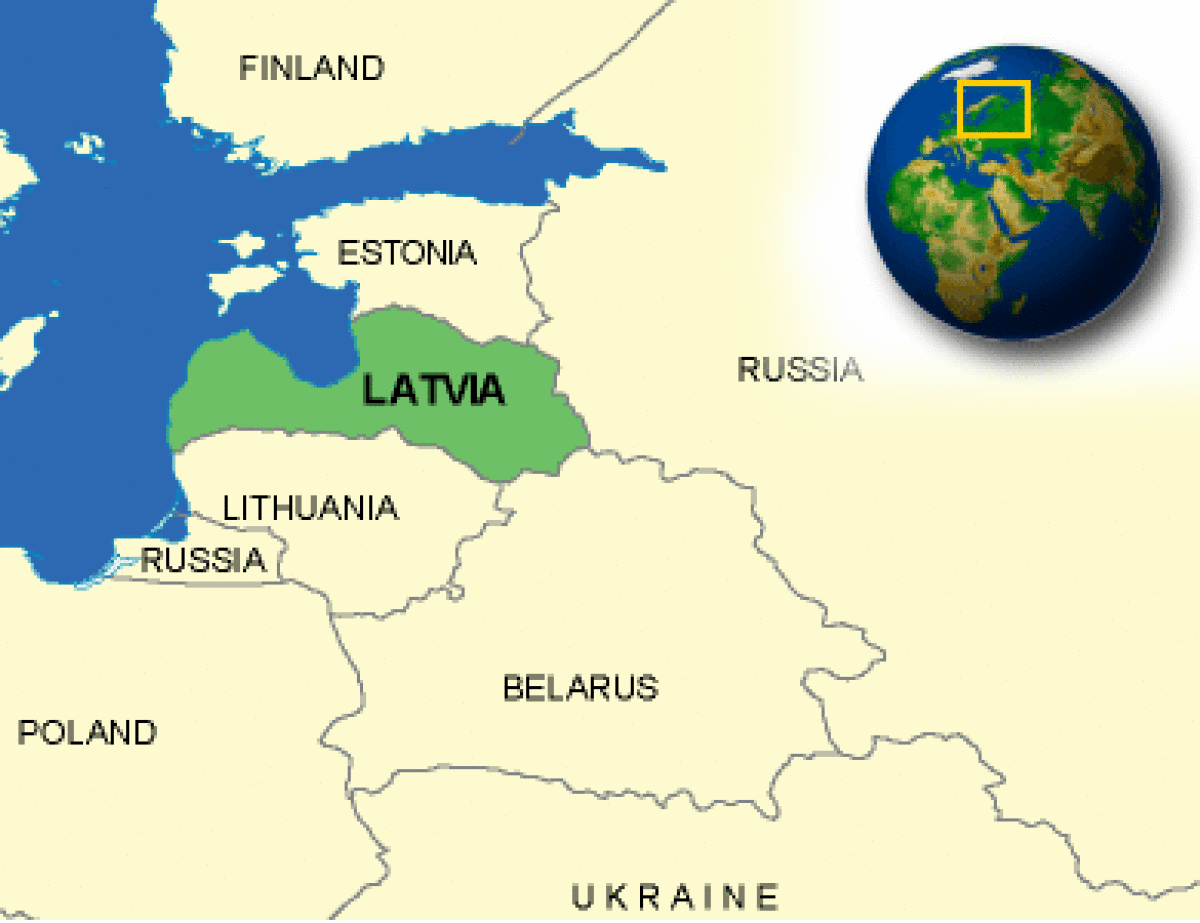
Where is Latvia located?
What countries border Latvia?
Latvia Weather
What is the current weather in Latvia?
Latvia Facts and Culture
What is Latvia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Latvians are kinds and trusting with friends and networks that exist through friends and family. Latvians are reserved and have... More
- Family: Several generations may share a single living space. Grandparents may care for children, and the elderly are looked after in... More
- Personal Apperance: Men wear suits, shirts and ties to work. Women wear dresses. For casual wear, people wear neat slacks and sweaters.... More
- Recreation: An early age children start playing many type sport, like: badminton, football, hockey, basketball, swimming, skiiing, and others. In school... More
- Diet: Whole grain and rye breads are popular. Summer fruits are imported to add to the local produce of root... More
- Food and Recipes: Eating together as a family is highly valued. Bread is usually served at every meal. Lunch is usually the... More
- Visiting: The way the food is presented is extremely important, and after the meal, the gathering often breaks into song. There... More
Latvia Facts
What is the capital of Latvia?
| Capital | Riga |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
24,938 Square Miles 64,589 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Estonia and Lithuania |
| Language | Latvian (official), Lithuanian, Russian, other |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $24,500.00 (USD) |
Latvia Demographics
What is the population of Latvia?
| Ethnic Groups | Latvian 57.7%, Russian 29.6%, Belarusian 4.1%, Ukrainian 2.7%, Polish 2.5%, Lithuanian 1.4%, other 2% (2002) |
| Language - note | Russian is still used in commerce and daily life. English and German are also widely used. Latvian is related to the Lithuanian language. Latvian is based on the Latin alphabet but contains many diacritical marks. It is now the official language. |
| Languages | Latvian (official) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4%; note - data represent language usually spoken at home. |
| Nationality Noun | Latvian(s) |
| Population | 1,881,232 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.61% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | RIGA (capital) 701,000 |
| Urban Population | 67.700000 |
Latvia Government
What type of government does Latvia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Edgars RINKEVICS (since 8 July 2023) head of government: Prime Minister Evika SILINA (since 15 September 2023) cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, appointed by Parliament elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by Parliament for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 31 May 2023 (next to be held in 2027); prime minister appointed by the president, confirmed by Parliament election results: 2023: Edgars RINKEVICS elected president in the third round; Parliament vote - Edgars RINKEVICS (Unity Party) 52, Uldis Pīlēns (independent) 25; Evika SILINA confirmed as prime minister 53-39 2019: Egils LEVITS elected president; Parliament vote - Egils LEVITS (independent) 61, Didzis SMITS (KPV LV) 24, Juris JANSONS (independent) 8; Krisjanis KARINS confirmed as prime minister 61-39 note: on 15 September 2023, Parliament voted 53-39 to approve Prime Minister Evika SILINA |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Latvia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day (Republic of Latvia Proclamation Day), 18 November (1918); note - 18 November 1918 was the date Latvia established its statehood and its concomitant independence from Soviet Russia; 4 May 1990 was the date it declared the restoration of Latvian statehood and its concomitant independence from the Soviet Union |
| Constitution |
history: several previous (pre-1991 independence); note - following the restoration of independence in 1991, parts of the 1922 constitution were reintroduced 4 May 1990 and fully reintroduced 6 July 1993 amendments: proposed by two thirds of Parliament members or by petition of one tenth of qualified voters submitted through the president; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of Parliament in each of three readings; amendment of constitutional articles, including national sovereignty, language, the parliamentary electoral system, and constitutional amendment procedures, requires passage in a referendum by majority vote of at least one half of the electorate; amended several times, last in 2019 |
| Independence | 18 November 1918 (from Soviet Russia); 4 May 1990 (declared from the Soviet Union); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union) |
Latvia Video
YouTube: Unesco Suiti cultural space
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Latvia Geography
What environmental issues does Latvia have?
| Overview | The Republic of Latvia is situated on the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga, bordered by Estonia to the northeast, Russia and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania to the southwest. Its 25,499 square-mile area is about the size of West Virginia in the U.S. or Belgium and the Netherlands combined in Europe. Grassland, marshy meadows, low hills, and rolling plains make up most of the country, which has an average elevation of 292 feet above sea level. Pine, oak, and birch forests cover about one quarter of the country. Latvia is rich in lakes and rivers. It has a coastline of 307 miles, half lying on the Baltic Sea and half on the Gulf of Riga. |
| Climate | Only three European countries-Estonia, Finland, and Iceland-are farther north in their entirety than Latvia, which has latitude of between 55° and 58° and a longitude of between 20° and 28°. During most of December and January, the sun does not rise until after 9 a.m. and sets as early as 3 p.m. On the other hand, to compensate, the longest day of summer lasts almost 18 hours. In spite of its northern location, daytime winter temperatures average only slightly below freezing because of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf Stream. Daytime summer temperatures average about 70°F. The maritime climate also accounts for the country's frequent cloud cover and considerable precipitation (average per year is about 25 inches). |
| Border Countries | Belarus 141 km, Estonia 339 km, Lithuania 453 km, Russia 217 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Latvia's environment has benefited from a shift to service industries after the country regained independence; the main environmental priorities are improvement of drinking water quality and sewage system, household and hazardous waste management, and reduction of air pollution; in 2001, Latvia closed the EU accession negotiation chapter on environment committing to full enforcement of EU environmental directives by 2010 |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | low plain |
Latvia Economy
How big is the Latvia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Latvia is a small, open economy with exports contributing more than half of GDP. Due to its geographical location, transit services are highly-developed, along with timber and wood-processing, agriculture and food products, and manufacturing of machinery and electronics industries. Corruption continues to be an impediment to attracting foreign direct investment and Latvia's low birth rate and decreasing population are major challenges to its long-term economic vitality. Latvia's economy experienced GDP growth of more than 10% per year during 2006-07, but entered a severe recession in 2008 as a result of an unsustainable current account deficit and large debt exposure amid the slowing world economy. Triggered by the collapse of the second largest bank, GDP plunged by more than 14% in 2009 and, despite strong growth since 2011, the economy took until 2017 return to pre-crisis levels in real terms. Strong investment and consumption, the latter stoked by rising wages, helped the economy grow by more than 4% in 2017, while inflation rose to 3%. Continued gains in competitiveness and investment will be key to maintaining economic growth, especially in light of unfavorable demographic trends, including the emigration of skilled workers, and one of the highest levels of income inequality in the EU. In the wake of the 2008-09 crisis, the IMF, EU, and other international donors provided substantial financial assistance to Latvia as part of an agreement to defend the currency's peg to the euro in exchange for the government's commitment to stringent austerity measures. The IMF/EU program successfully concluded in December 2011, although, the austerity measures imposed large social costs. The majority of companies, banks, and real estate have been privatized, although the state still holds sizable stakes in a few large enterprises, including 80% ownership of the Latvian national airline. Latvia officially joined the World Trade Organization in February 1999 and the EU in May 2004. Latvia also joined the euro zone in 2014 and the OECD in 2016. |
| Industries | buses, vans, street and railroad cars, synthetic fibers, agricultural machinery, fertilizers, washing machines, radios, electronics, pharmaceuticals, processed foods, textiles; note - dependent on imports for energy and raw materials |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 15.3%, UK 14.4%, Sweden 10.4%, Lithuania 8.2%, Estonia 5.9%, Russia 5.8%, Denmark 5.6%, US 4.3% |
| Import Partners | Germany 17.2%, Lithuania 9.8%, Russia 8.8%, Finland 8%, Sweden 6.4%, Estonia 6.2%, Poland 5%, Italy 4.2% |
Latvia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Latvia?
Source: Google News
Latvia Travel Information
What makes Latvia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Latvia is a stable democracy and has one of the fastest growing economies in the European Union. On January 1, 2014, Latvia is set to join the euro zone. , Most goods and services can be found in the capital of Latvia, Riga. However, in other areas outside of the capital, many western goods and services cannot be located.
Crime
Latvia is a relatively safe country, and crime is generally non-violent in nature; however, serious violent assaults and robberies have occurred. Harassment of foreigners, ethnic minorities, and homosexuals has also occurred in Latvia.The Riga Tourist Police Unit has a 24/7 English-speaking operator at 371 6718 1818 and English-speaking officers who frequently patrol the Old City. The most common crimes encountered by foreign tourists are purse snatching, pick-pocketing, and mugging, especially during the summer tourism season. Tourists -- particularly those carrying backpacks -- are targeted by individuals or small groups of thieves working together. Riga’s Old Town (Vecriga), Central train station (Dzelzcela stacija), Central bus station (Autoosta) and Central market (Centraltirgus) are crowded public places that are targeted by thieves.
Please be aware that there are numerous scam artists targeting foreigners in the tourist pubs and restaurants. You should pay special attention to the drink prices at bars. There have been instances of travelers being charged exorbitant prices. Bills have been as high as several thousand dollars for drinks, and in some establishments the management may use force to secure payment.
If possible, you should avoid walking alone at night and avoid using ATMs after dark.
In addition, Internet crime is a growing concern in Latvia. Common fraudulent schemes involve both Internet auction sites and Internet job-search sites. In the first scam, criminals offer you valuable items for sale at low prices on Internet auctions and request that your payments are sent by wire transfer to a bank in Latvia or through a fraudulent escrow site that they have created themselves. In this scheme, your money passes through a bank in Latvia and is quickly withdrawn at an ATM or transferred to a bank in another country. It is very difficult in these cases to discover the identities of the account holders or recover the funds.
The second common scam involves identity theft through false job offers. In this scheme, a company claiming to be located in Latvia, but which has a non-existent address, offers you employment as a U.S.-based agent or freight forwarder. When you respond to the job offer, commonly posted on one of several popular Internet job sites, you are asked for a Social Security Number and other identifying information under the guise of conducting a background check.
Criminal Penalties
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, but by buying them you may also be breaking local law. While you are traveling in another country, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen.Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods abroad. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.
If you do something illegal in Latvia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Persons violating Latvian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Latvia are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Latvia, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the U.S. Embassy.
Languages
Latvian (official) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4%; note - data represent language usually spoken at home.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
The quality of medical care in Latvia continues to improve, but still often falls short of Western standards. Latvia has many highly trained medical professionals, but hospitals and clinics still suffer from a lack of equipment and resources. The 2008-2009 economic crisis has resulted in further strains in health service budgets. Many doctors speak at least some English. There are few private clinics in major cities that offer services equal to Western European or U.S. standards. Elderly travelers and those with health problems may be at increased risk.Western-quality dental care can be obtained in Riga. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services, particularly if immigration status in Latvia is unclear.
Ambulance service for emergencies is available by dialing 113; however, response time is poor in rural areas. Air ambulance service is available for medical evacuations; however, it is very expensive and advance payment or guarantee letter from an insurance company is required before a patient is transported.
Pharmaceuticals sold in Latvia are produced by companies certified in accordance with EU standards. Products of most major pharmaceutical manufacturers are sold in pharmacies in Latvia; however, they will not necessarily be labeled the same as in the United States and instructions are often not printed in English.
Tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease are widespread throughout the country. Those intending to visit parks or forested areas in Latvia are urged to speak with their health care practitioners. Tick-borne encephalitis vaccinations are given as a series of three doses, and are not available in the United States. There are no vaccines against Lyme disease. Hepatitis A is also a significant problem in Latvia.
Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Latvia.
Safety and Security
Civil unrest is generally not a problem in Riga, and there have been no incidents of terrorism directed toward U.S. interests. Incidents of anti-Americanism are rare.Nonetheless, in the past, Riga has experienced large, peaceful demonstrations related to internal political issues. While such events have generally been peaceful, we remind you that gatherings intended to be peaceful can become confrontational. Therefore, you should avoid the areas of demonstrations, if possible, and exercise caution if within the vicinity of any event.
Each winter, several people in Latvia sustain serious injuries from falling icicles. Pay careful attention to sidewalks that are blocked by rope or tape and be cautious of work crews clearing ice and snow from building rooftops. Sidewalks and roads can also be extremely slippery in the winter months; exercise caution while crossing streets, even if you have the right of way.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Latvia, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.Foreign visitors to Latvia planning to operate a motor vehicle are required to obtain an International Driving Permit. You may get these through the American Automobile Association (AAA) or the American Automobile Touring Alliance for a small fee. Your U.S. state driver’s license is not sufficient for driving in Latvia. These requirements apply if you are using rental cars as well, whether or not the rental company chooses to enforce the requirement as a condition of rental. If you drive without an International Driving Permit, you may have your vehicle confiscated by the police. U.S. citizens resident in Latvia for more than six months are required to apply for a Latvian driver’s license. Upon receipt of a Latvian driver’s license, U.S. citizens are required to surrender their U.S. driver’s license to the Latvian authorities. The licenses are then returned to their respective states of issuance.
Latvia’s rate of automobile accidents and fatalities is one of the highest in Europe. You should be alert for pedestrians and slow-moving vehicles in traffic. Additionally, violation of traffic rules is common, and it is not unusual to be passed by other automobiles traveling at high speeds, even in crowded urban areas. In Latvia, it is required by law to yield to pedestrians at marked intersections. However, many drivers fail to do so. Be alert to approaching vehicles when crossing the street. During winter, most major roads are cleared of snow; however, you should be alert for fog, snow, and ice while driving. Driving while intoxicated is a very serious offense and carries heavy penalties. Local authorities use roadblocks and breathalyzer tests as enforcement tools. Be alert to the possibility of drunk drivers and drunken pedestrians wandering on the road. You must use headlights at all times, and note that there can be as little as six hours of daylight during the winter months. Speed limits are usually 50 km/hr in the city and 90 km/hr on the highways. As of late 2011, Latvia began using an extensive photo speed enforcement program with cameras deployed throughout the country. Public transportation is generally considered safe, but travelers are encouraged to select well-marked taxis. Emergency services are fair but improving (See section on Medical Facilities above); response time may be especially slow in traffic or in rural settings. Dial 112 for police assistance, or 113 for ambulance service.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
