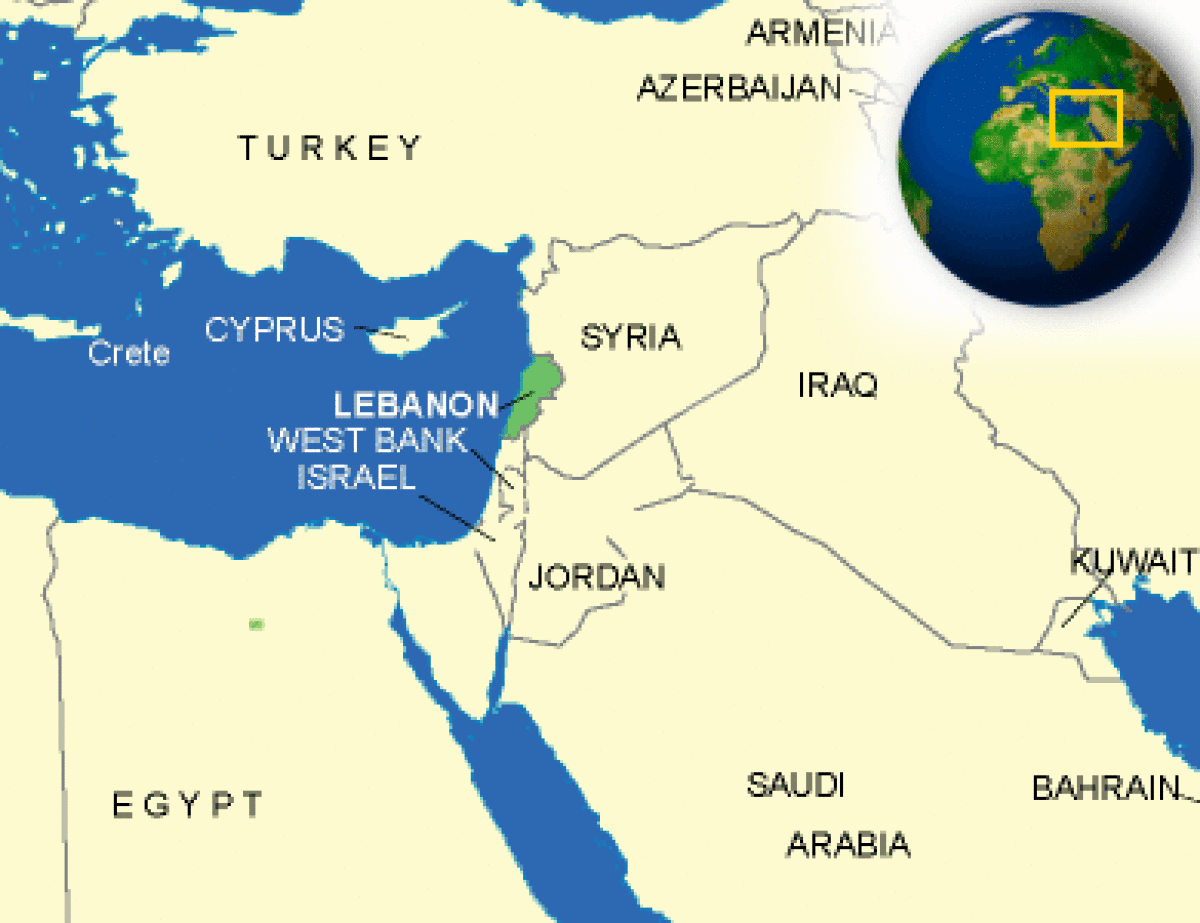
Where is Lebanon located?
What countries border Lebanon?
Lebanon Weather
What is the current weather in Lebanon?
Lebanon Facts and Culture
What is Lebanon famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Attitudes vary greatly among the people. Life in Lebanon is still fairly relaxed and slow paced. People tend to care... More
- Personal Apperance: Western-style clothing is common in urban areas. However traditional Muslim clothing, such as a woman's "chador" (long dress) is also... More
- Recreation: Soccer, basketball and volleyball are popular. Cross-country running in the mountains and martial arts are also enjoyed. Many Lebanese also... More
- Diet: Stews are popular in Lebanon. The cuisine is often spicy and hot. But because of the warm climate, many dishes... More
- Food and Recipes: Guests should at least try food served by host before refusing it, but politely declining a full meal can be... More
- Visiting: Hosts usually serve guests something to drink; usually coffee or tea and is prepared and served without asking the guests.... More
- Dating: Traditionally, neither Christians nor Muslims dated each other. Many marriages are arranged by the family. Today, Christians and many urban... More
Lebanon Facts
What is the capital of Lebanon?
| Capital | Beirut |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Lebanes Pouind (LBP) |
| Total Area |
4,015 Square Miles 10,400 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Israel and Syria |
| Language | Arabic (official), French, English, Armenian |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $18,600.00 (USD) |
Lebanon Demographics
What is the population of Lebanon?
| Ethnic Groups | Arab 95%, Armenian 4%, other 1% |
| Nationality Noun | Lebanese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 5,469,612 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.04% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | BEIRUT (capital) 2.022 million |
| Urban Population | 87.200000 |
Lebanon Government
What type of government does Lebanon have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Joseph AOUN (since 9 January 2025) head of government: Prime Minister Nawaf SALAM (since 8 February 2025) cabinet: Cabinet chosen by the prime minister in consultation with the president and the National Assembly election/appointment process: president indirectly elected by a qualified majority of two-thirds of Parliament members in the first round and, if needed, a two-thirds quorum of members by simple-majority popular vote for a 6-year term (eligible for non-consecutive terms); prime minister appointed by the president in consultation with the National Assembly most recent election date: 9 January 2025 election results: 2025: Joseph AOUN elected president in second round; National Assembly vote - 99 of 128 2016: Michel AWN elected president in second round; National Assembly vote - Michel AWN (FPM) 83; the president elected in its 46th attempt on 31 October 2016 expected date of next election: 2031 |
| Suffrage | 21 years of age; authorized for all men and women regardless of religion; excludes persons convicted of felonies and other crimes or those imprisoned; excludes all military and security service personnel regardless of rank |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Lebanon dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: unknown |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 22 November (1943) |
| Constitution |
history: drafted 15 May 1926, adopted 23 May 1926 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic and introduced as a government bill to the National Assembly or proposed by at least 10 members of the Assembly and agreed upon by two thirds of its members; if proposed by the National Assembly, review and approval by two-thirds majority of the Cabinet is required; if approved, the proposal is next submitted to the Cabinet for drafting as an amendment; Cabinet approval requires at least two-thirds majority, followed by submission to the National Assembly for discussion and vote; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of a required two-thirds quorum of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the president; amended several times, last in 2004 |
| Independence | 22 November 1943 (from League of Nations mandate under French administration) |
Lebanon Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Lebanon Geography
What environmental issues does Lebanon have?
| Overview | Lebanon is renowned for its scenic beauty, although uncontrolled development and exploitation mar many areas. Along the Mediterranean there is a narrow coastal strip, with cities, suburbs, and some banana, citrus, and olive groves. A dramatic mountain chain rises to over 10,000 feet within 20 miles of the coast, with impressive terracing and cultivation. Although pine forests abound, the famed Cedars of Lebanon now exist only in a few small groves preserved in the north and central regions. Distances are short in Lebanon, and travel from the seashore to mountain areas can be done easily in an hour by car. |
| Climate | From May through October, sunny weather prevails and rain is infrequent. Temperatures rarely go above 90°F in the summer. Fall and spring are relatively short. Winters are mild (in the city, winter temperatures rarely drop below 40°F and damp. Most of the country's annual rainfall (about 36 inches) occurs from December through March. Winter storms frequently are accompanied by high winds, lightning, and thunder. |
| Border Countries | Israel 79 km, Syria 375 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; air pollution in Beirut from vehicular traffic and the burning of industrial wastes; pollution of coastal waters from raw sewage and oil spills |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | narrow coastal plain; El Beqaa (Bekaa Valley) separates Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon Mountains |
Lebanon Economy
How big is the Lebanon economy?
| Economic Overview |
Lebanon has a free-market economy and a strong laissez-faire commercial tradition. The government does not restrict foreign investment; however, the investment climate suffers from red tape, corruption, arbitrary licensing decisions, complex customs procedures, high taxes, tariffs, and fees, archaic legislation, and inadequate intellectual property rights protection. The Lebanese economy is service-oriented; main growth sectors include banking and tourism. The 1975-90 civil war seriously damaged Lebanon's economic infrastructure, cut national output by half, and derailed Lebanon's position as a Middle Eastern banking hub. Following the civil war, Lebanon rebuilt much of its war-torn physical and financial infrastructure by borrowing heavily, mostly from domestic banks, which saddled the government with a huge debt burden. Pledges of economic and financial reforms made at separate international donor conferences during the 2000s have mostly gone unfulfilled, including those made during the Paris III Donor Conference in 2007, following the July 2006 war. The "CEDRE" investment event hosted by France in April 2018 again rallied the international community to assist Lebanon with concessional financing and some grants for capital infrastructure improvements, conditioned upon long-delayed structural economic reforms in fiscal management, electricity tariffs, and transparent public procurement, among many others. The Syria conflict cut off one of Lebanon's major markets and a transport corridor through the Levant. The influx of nearly one million registered and an estimated 300,000 unregistered Syrian refugees has increased social tensions and heightened competition for low-skill jobs and public services. Lebanon continues to face several long-term structural weaknesses that predate the Syria crisis, notably, weak infrastructure, poor service delivery, institutionalized corruption, and bureaucratic over-regulation. Chronic fiscal deficits have increased Lebanon’s debt-to-GDP ratio, the third highest in the world; most of the debt is held internally by Lebanese banks. These factors combined to slow economic growth to the 1-2% range in 2011-17, after four years of averaging 8% growth. Weak economic growth limits tax revenues, while the largest government expenditures remain debt servicing, salaries for government workers, and transfers to the electricity sector. These limitations constrain other government spending, limiting its ability to invest in necessary infrastructure improvements, such as water, electricity, and transportation. In early 2018, the Lebanese government signed long-awaited contract agreements with an international consortium for petroleum exploration and production as part of the country’s first offshore licensing round. Exploration is expected to begin in 2019. |
| Industries | banking; food processing; jewelry; cement; textiles; mineral and chemical products; wood and furniture products; oil refining; metal fabricating |
| Currency Name and Code | Lebanes Pouind (LBP) |
| Export Partners | UAE 11%, Switzerland 9.1%, Saudi Arabia 8.2%, US 6.2%, Jordan 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Italy 11.3%, France 10.7%, Germany 8.3%, US 5.6%, Syria 5.4%, China 4.8%, Belgium 4.5%, UK 4.2% |
Lebanon News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Lebanon?
Source: Google News
Lebanon Travel Information
What makes Lebanon a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Republic of Lebanon is a parliamentary republic. Political power is concentrated in the office of the President, Speaker of Parliament, and Prime Minister, each representing one of Lebanon's three largest religious sects (Maronite Christians, Shia and Sunni Muslims, respectively). Since 1973, Lebanon has been in a state of war with Israel; UN peacekeeping forces are present in Lebanon to monitor the ceasefire that went into effect with the passage of UN Security Council Resolution 1701.
Crime
The crime rate in Lebanon is moderate, and both car theft and burglaries occur. Violent crime and sexual assault are rare, but do happen. The Embassy receives regular reports, however, of domestic abuse. Petty theft -- such as pick pocketing and purse snatching -- is common in crowded public areas. Police are responsive but often unable to affect a positive outcome. There are no special concerns with regard to targeted victimization of U.S. citizens in scams or confidence schemes.There have been incidents involving a theft ring that appear to target foreigners using service cars. Service cars are privately owned vehicles bearing red license plates that act as public transportation for multiple passengers at one time. Typically, a service car that already contained two people (the driver and one passenger), picked up the potential passenger. The driver then took the victim to a more isolated area or the freeway where the first “passenger” robbed the second passenger by threatening him/her with a gun. Because of the risks inherent in using any unknown transportation, U.S. citizens should be wary of these service cars and carry the number of a reputable taxi company in case of emergencies.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Lebanon, you are subject to all Lebanese laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. For example, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport with you. It is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings, including some government buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States; for example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Lebanon your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not where you are going.While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
n Beirut and the surrounding areas, modern medical care and medicines are widely available. Modern facilities are not always available in outlying areas, although no location in the country is more than three hours from the capital. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for services, and without such payment, may deny service even in emergency cases. A list of doctors who speak English and a list of hospitals are available from the U.S. Embassy and at the Embassy's website.
Safety and Security
The current Department of State Travel Warning advises U.S. citizens against travel to Lebanon. U.S. citizens who visit or reside in Lebanon despite the Travel Warning should be aware that there are a number of serious security concerns, and should consult the Travel Warning for up-to-date information.U.S. citizens traveling to Lebanon should also be aware that personnel from the U.S. Embassy are not able to travel in all areas of Lebanon. In the case of an emergency involving a U.S. citizen in areas where it is unsafe for Embassy personnel to travel, the Embassy may not be able to render assistance.
In the event that the security climate in the country worsens, U.S. citizens will be responsible for arranging their own travel out of Lebanon. U.S. citizens with special medical or other needs should be aware of the risks of remaining given their condition and should be prepared to seek treatment in Lebanon if they cannot arrange for travel out of the country.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Lebanon is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.An international driver’s license is required for visitors to Lebanon. Drivers in Lebanon often maneuver aggressively and pay little regard to traffic lights and stop signs. Lanes are generally unmarked and roads outside the capital may be poorly lighted. Pedestrians should exercise particular caution. Intercity directional signs and street markers are slowly improving throughout the country, but side roads are often not signposted at all. Public transportation is generally safe.
While there is limited enforcement, the laws of Lebanon prohibit both drunk driving as well as cell phone usage when driving.
Emergency services in Lebanon are adequate. In case of a road accident, emergency numbers are “140” for the Red Cross and “125” for the emergency civil police.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
