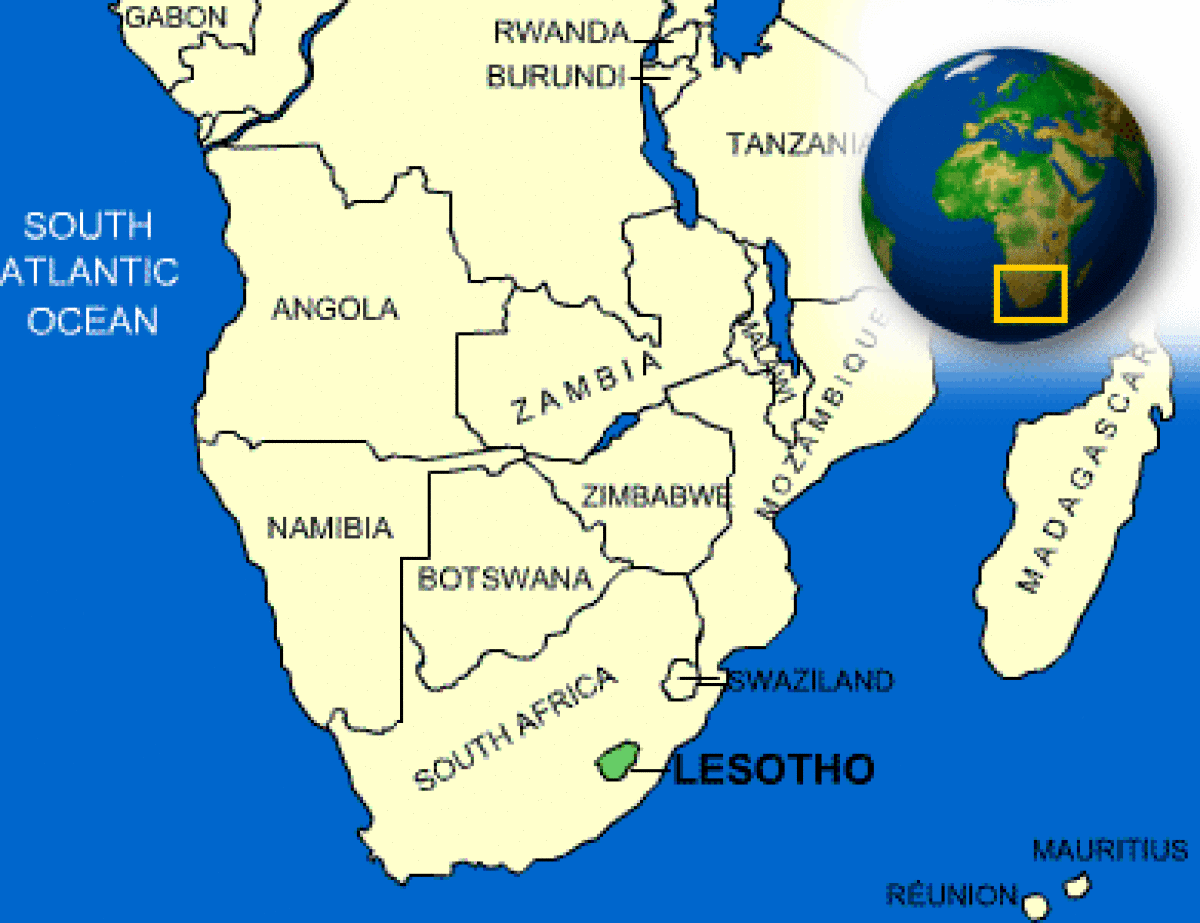
Where is Lesotho located?
What countries border Lesotho?
Lesotho Weather
What is the current weather in Lesotho?
Lesotho Facts and Culture
What is Lesotho famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Politeness, good manners and willingness to server are values that are strongly encouraged in children.The general attitude of childhood is... More
- Family: The man is considered the head of the household. Women are defined as farmers and bearers of children. Marriages where... More
- Personal Apperance: Western style clothing is the norm in Lesotho. The most acceptable form of clothing for women is a dress. Women... More
- Recreation: Lesotho children like to play soccer. The only sports the children compete in at school are netball and running, these... More
- Food and Recipes: Staple foods are maize (corn) eaten as a thick paste and bread. Beef, chicken and mutton (lamb) are popular meats.... More
- Visiting: Hospitality and generosity are expected and even those with very little will share their food with visitors. More
Lesotho Facts
What is the capital of Lesotho?
| Capital | Maseru |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Loti (LSL) |
| Total Area |
11,720 Square Miles 30,355 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Africa, an enclave of South Africa |
| Language | Sesotho (southern Sotho), English (official), Zulu, Xhosa |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $3,000.00 (USD) |
Lesotho Demographics
What is the population of Lesotho?
| Ethnic Groups | Sotho 99.7%, Europeans, Asians, and other 0.3%, |
| Nationality Noun | Mosotho (singular), Basotho (plural) |
| Population | 1,969,334 |
| Population - note | note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.34% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MASERU (capital) 239,000 |
| Urban Population | 27.600000 |
Lesotho Government
What type of government does Lesotho have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King LETSIE III (since 7 February 1996); note - King LETSIE III formerly occupied the throne from November 1990 to February 1995 while his father was in exile head of government: Prime Minister Ntsokoane Samuel MATEKANE (28 October 2022) cabinet: consists of the prime minister, appointed by the King on the advice of the Council of State, the deputy prime minister, and 18 other ministers; the prime minister is the leader of the majority party or majority coalition in the National Assembly elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary, but under the terms of the constitution that came into effect after the March 1993 election, the monarch is a "living symbol of national unity" with no executive or legislative powers; under traditional law, the College of Chiefs has the power to depose the monarch, to determine next in line of succession, or to serve as regent in the event that a successor is not of mature age |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 4 October (1966) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1959, 1967; latest adopted 2 April 1993 (effectively restoring the 1967 version) amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage of amendments affecting constitutional provisions, including fundamental rights and freedoms, sovereignty of the kingdom, the office of the king, and powers of Parliament, requires a majority vote by the National Assembly, approval by the Senate, approval in a referendum by a majority of qualified voters, and assent of the king; passage of amendments other than those specified provisions requires at least a two-thirds majority vote in both houses of Parliament; amended several times, last in 2011 |
| Independence | 4 October 1966 (from the UK) |
Lesotho Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Lesotho Geography
What environmental issues does Lesotho have?
| Overview |
Lesotho (Leh‑SOO‑too) is a landlocked country in the east‑central part of the Republic of South Africa. Slightly larger than Maryland and slightly smaller than Belgium, Lesotho covers an area of 11,116 square miles. It is roughly in the form of a circle, 125 miles across. The western one‑quarter of Lesotho is lowlands where the altitude varies from 5,000 to 6,000 feet above sea level. This is the country’s main agricultural zone and contains most of the population. The rest of the country is composed of highlands that rise to 11,400 feet in the Drakensburg Range, which forms the eastern boundary with KwaZulu Natal. Thabana‑Ntlenyana, the highest peak in Southern Africa at 11,424 feet, is just inside Lesotho’s eastern border near the Sani Pass. Maseru (Muh‑SEH‑roo), the capital, has an estimated population of 150,000. It is located 5,000 feet above sea level on the Caledon River, which forms the western boundary between Lesotho and the Free State in South Africa. Surrounded by scenic bluffs and mesas, Maseru has a small central business district and several neighborhoods with good housing. Beyond that, the city sprawls for miles with collections of small tin‑roofed houses and roadside businesses. The surrounding countryside is severely affected by soil erosion, and despite sufficient water, the lowlands have little natural vegetation for much of the year. The landscape, mountainous, bare, dotted with picturesque villages, is starkly beautiful. |
| Climate |
The climate is temperate year round. Rainfall, occurring mostly from October to April, ranges from 24 inches a year over most of the lowlands to over 40 inches a year in the mountains. A windy season during August and September occasionally brings dust storms. Average daytime temperatures are in the high 80°F in summer and can reach 100°F in Maseru. In winter, daytime temperatures average in the mid 60°F and at night sometimes drop to the teens in Maseru. Nighttime temperatures are regularly below freezing in June, July and August. Temperatures in the mountains are even more extreme with snowfalls common in winter. The humidity year round is quite low. |
| Border Countries | South Africa 909 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | population pressure forcing settlement in marginal areas results in overgrazing, severe soil erosion, and soil exhaustion; desertification; Highlands Water Project controls, stores, and redirects water to South Africa |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly highland with plateaus, hills, and mountains |
Lesotho Economy
How big is the Lesotho economy?
| Economic Overview |
Small, mountainous, and completely landlocked by South Africa, Lesotho depends on a narrow economic base of textile manufacturing, agriculture, remittances, and regional customs revenue. About three-fourths of the people live in rural areas and engage in animal herding and subsistence agriculture, although Lesotho produces less than 20% of the nation's demand for food. Agriculture is vulnerable to weather and climate variability. Lesotho relies on South Africa for much of its economic activity; Lesotho imports 85% of the goods it consumes from South Africa, including most agricultural inputs. Households depend heavily on remittances from family members working in South Africa in mines, on farms, and as domestic workers, though mining employment has declined substantially since the 1990s. Lesotho is a member of the Southern Africa Customs Union (SACU), and revenues from SACU accounted for roughly 26% of total GDP in 2016; however, SACU revenues are volatile and expected to decline over the next 5 years. Lesotho also gains royalties from the South African Government for water transferred to South Africa from a dam and reservoir system in Lesotho. However, the government continues to strengthen its tax system to reduce dependency on customs duties and other transfers. The government maintains a large presence in the economy - government consumption accounted for about 26% of GDP in 2017. The government remains Lesotho's largest employer; in 2016, the government wage bill rose to 23% of GDP – the largest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Lesotho's largest private employer is the textile and garment industry - approximately 36,000 Basotho, mainly women, work in factories producing garments for export to South Africa and the US. Diamond mining in Lesotho has grown in recent years and accounted for nearly 35% of total exports in 2015. Lesotho managed steady GDP growth at an average of 4.5% from 2010 to 2014, dropping to about 2.5% in 2015-16, but poverty remains widespread around 57% of the total population. |
| Industries | food, beverages, textiles, apparel assembly, handicrafts; construction; tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Loti (LSL) |
| Export Partners | US 97.1%, Canada 0.9%, France 0.6% |
| Import Partners | Hong Kong 48.3%, China 23.2%, Singapore 3.7% |
Lesotho News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Lesotho?
Source: Google News
Lesotho Travel Information
What makes Lesotho a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Kingdom of Lesotho is an enclave located entirely within the Republic of South Africa. It is roughly the size of Maryland and has a population of about 1.8 million people. Nearly all of Lesotho lies above 5,000 ft (1,500M), and the country features Africa's highest mountain south of Kilimanjaro, Thabana Ntlenyana, at 11,400 feet (3,500M), as well as one of Africa's only ski resorts. Facilities for tourism are expanding. The capital city of Maseru provides shopping, dining and entertainment options, and Lesotho’s countryside offers an array of outdoor activities, including off-roading, mountain biking, horseback riding, and hiking. Lesotho is a politically stable constitutional monarchy. Its growing economy principally exports textiles, manufactured goods, diamonds and water.
Crime
Lesotho has a high crime rate, and foreigners must remain vigilant at all times. Foreigners are frequently targeted and robbed, and have occasionally been car-jacked and killed. A number of U.S. citizens have reported incidents – including sexual assault, armed and unarmed confrontation, and home invasion – occurring in broad daylight. There are no indications that U.S. citizens are targeted due to their nationality.Crime can occur anywhere in Lesotho, but is most prevalent in urban areas. Crime scenes have included popular restaurants, poorly lit or unlit roads, and locations foreigners are known to frequent. Victims have included tourists, volunteer workers, and employees of non-governmental organizations.
U.S. citizens are advised to avoid walking or driving at night. Extra caution should be exercised while walking through downtown Maseru, even in daylight hours, as there have been numerous recent incidents in the middle of the day. Residences with 24-hour guards are generally less likely to be targeted. Traveling alone or at night is particularly dangerous, due to limited street lighting and undeveloped road conditions. The Lesotho Mounted Police Service (LMPS) is responsible for policing duties, but due to limited resources, LMPS response times can vary widely. U.S. citizens should report crime to the police and to the consular section of the U.S. Embassy.
There is a serious problem with theft from baggage at O.R. Tambo International Airport (Johannesburg), a required transit point for air travel to Lesotho. Travelers are encouraged to secure their luggage with Transportation Security Administration (TSA) approved locks, use an airport plastic wrapping service and avoid placing any items of value in checked luggage. Make an inventory of items in checked baggage to aid in claims processing if theft does occur. The claims processing procedure can be time-consuming.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Lesotho, you are subject to its laws, even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you or if you take pictures of certain government buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but are still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Lesotho, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Arrest notifications in host country:
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. Embassy as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Lesotho are limited and there is no reliable ambulance service. Specialist care is available in Bloemfontein, South Africa, 90 miles west of Maseru. U.S. Embassy Maseru maintains a list of physicians and other health care professionals, but the Embassy does not guarantee service or provide recommendations.Many medicines are unavailable at facilities in Lesotho; travelers should carry with them an adequate supply of necessary medicines and/or prescription drugs, along with copies of their prescriptions. Lesotho has a very high HIV prevalence, currently estimated at 23 percent of the adult population. Tuberculosis is a serious health concern in Lesotho.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens should avoid political gatherings and street demonstrations. Large gatherings can potentially become violent at any time.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Lesotho, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Traffic moves on the left, with right-hand drive vehicles. Never assume right-of-way, as aggressive and unpredictable local driving habits result in frequent collisions. Lesotho has a high number of traffic-related deaths and injuries. Driving after dark is dangerous due to the absence of street lighting, livestock on the roads, and the prevalence of crime—including incidents of carjacking.
Travel is best done by private car. Rental cars are available in Maseru, and cars rented in neighboring South Africa may be brought into Lesotho with the written permission of the rental company. Although bus and public taxi services exist, chronic overloading combined with inadequate vehicle maintenance and lack of driver training make them unsafe. Some private taxi services are available in the capital, but roving mini-bus taxis should be avoided. There is no passenger train service in Lesotho.
Although the number of paved roads is gradually increasing, the majority of Lesotho’s 5,000 miles of roads remain unpaved. A few main rural highways are comparable to U.S. two-lane rural roads, but lane markings, signs, shoulders and guardrails do not meet U.S. standards. Lesotho's mountainous terrain makes driving on secondary roads hazardous. Unpaved roads in the interior—often narrow, winding and steep—are poorly maintained. For travel in the interior, especially in wet or snowy weather, a high ground clearance or four-wheel-drive vehicle is recommended. Four-wheel-drive is also a requirement for entering or departing Lesotho through the Sani Pass on the eastern border. The authority for road safety issues rests with the Lesotho Mounted Police Service ; there are no auto clubs or reliable ambulance services. Drivers should contact the police in case of road emergencies.
