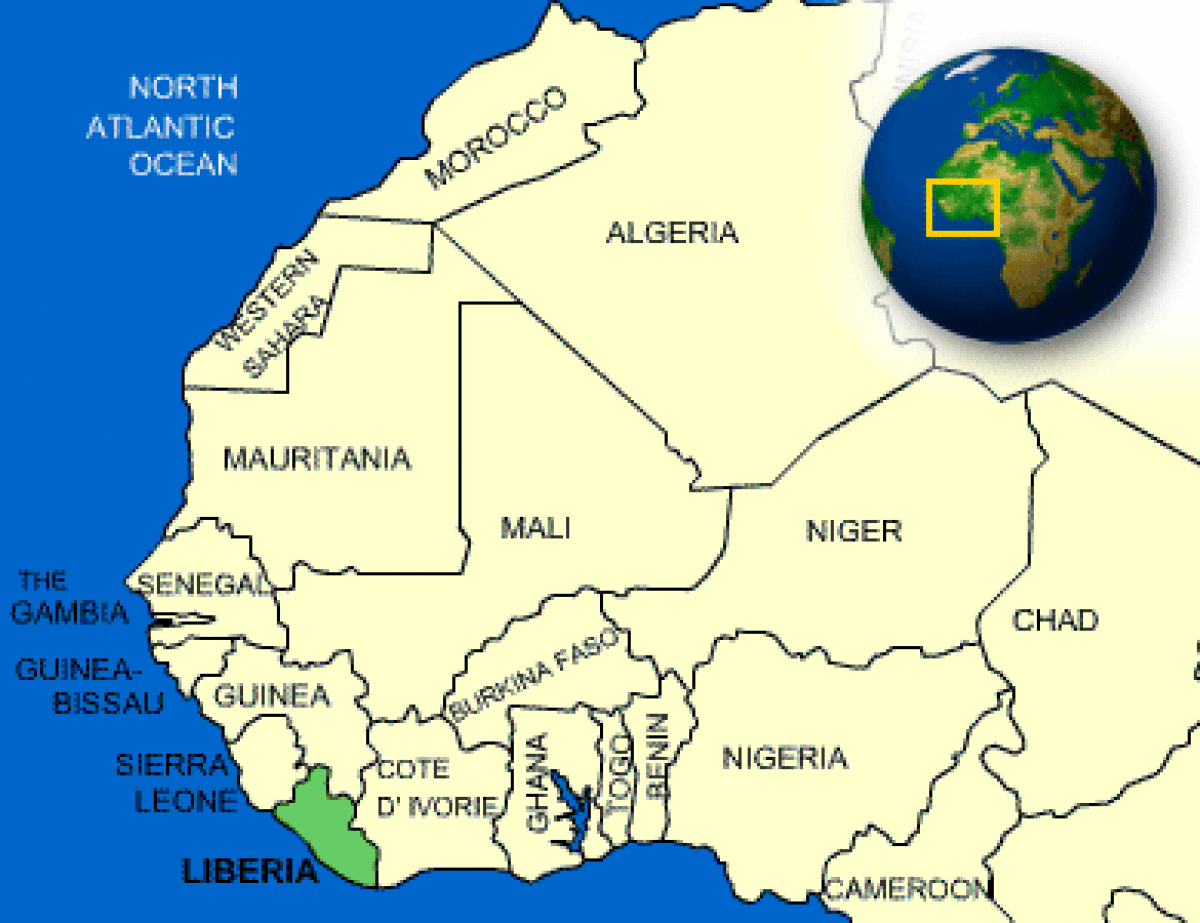
Where is Liberia located?
What countries border Liberia?
Liberia Weather
What is the current weather in Liberia?
Liberia Facts and Culture
What is Liberia famous for?
- Family: Large families are important. Because the Islam religion allows up to four wives, wealthy men usually have more than one... More
- Personal Apperance: Those who live in the city have adopted to Western style clothing however villagers continue in the traditions of their... More
- Recreation: Soccer is played many times with a homemade ball. Other pastimes include storytelling and music provided by the griots. Woaley... More
- Food and Recipes: Rice is a staple eaten almost every day. Cassava leaves are boiled and eaten. Sometimes with Sugar Cane you cut the... More
- Visiting: If a guest drops by at mealtime they will be invited to eat. Those who have been blessed with wealth... More
Liberia Facts
What is the capital of Liberia?
| Capital | Monrovia |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Liberian Dollar (LRD) |
| Total Area |
43,000 Square Miles 111,369 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Cote d'Ivoire and Sierra Leone |
| Language | English 20% (official), some 20 ethnic group languages, of which a few can be written and are used in correspondence |
| GDP - real growth rate | 0.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $900.00 (USD) |
Liberia Demographics
What is the population of Liberia?
| Ethnic Groups | indigenous African tribes 95% (including Kpelle, Bassa, Gio, Kru, Grebo, Mano, Krahn, Gola, Gbandi, Loma, Kissi, Vai, Dei, Bella, Mandingo, and Mende), Americo-Liberians 2.5% (descendants of immigrants from the US who had been slaves), Congo People 2.5% ( |
| Nationality Noun | Liberian(s) |
| Population | 5,073,296 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.56% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MONROVIA (capital) 750,000 |
| Urban Population | 48.200000 |
Liberia Government
What type of government does Liberia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Joseph BOAKAI (since 22 January 2024); Vice President Jeremiah KUONG (since 22 January 2024); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Joseph BOAKAI (since 22 January 2024); Vice President Jeremiah KUONG (since 22 January 2024) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, confirmed by the Senate elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 10 October 2023 with a runoff on 14 November 2023 (next to be held in October 2029) election results: 2023: Joseph BOAKAI elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - George WEAH (CDC) 43.8%, Joseph BOAKAI (UP) 43.4%, Edward APPLETON (GDM) 2.2%, Lusinee KAMARA (ALCOP) 2%, Alexander B. CUMMINGS, Jr. (CPP) 1.6%, Tiawan Saye GONGLOE (LPP) 1.4%, other 5.6%; percentage of vote in second round - Joseph BOAKAI 50.6%, George WEAH 49.4% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Liberia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 2 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 26 July (1847) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1847 (at independence); latest drafted 19 October 1983, revision adopted by referendum 3 July 1984, effective 6 January 1986 amendments: proposed by agreement of at least two thirds of both National Assembly houses or by petition of at least 10,000 citizens; passage requires at least two-thirds majority approval of both houses and approval in a referendum by at least two-thirds majority of registered voters; amended 2011, 2020 |
| Independence | 26 July 1847 |
Liberia Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Liberia Geography
What environmental issues does Liberia have?
| Overview | Liberia, the oldest independent republic in Africa, lies on the West African coast just 300 miles north of the Equator. It has a relatively long coastline of 350 miles. From the lagoons and mangrove swamps of the coastal plains, the land rises evenly along its length in belts parallel to the coast, from rolling hills, through a broader region of plateaus and low mountain ranges, into the foothills of the Guinea Highlands. Just beyond these 4,500-foot peaks originate the headwaters of the Niger. Half of the country is covered by tropical rain forest. |
| Climate |
Liberia is so situated in the Tropics as to be directly in the path of the seasonal winds. From May through November, the prevailing monsoon winds drop most of the nearly 200 inches of rain received annually in the capital city of Monrovia. From December through April, the red, dust-laden harmattan winds originating over the Sahara Desert prevail. The transition periods between the seasons are punctuated by violent thunderstorms and sudden torrential downpours. Temperatures average 81°F; humidity averages 82%. There is little variation over the course of the year. Precautions must be taken against mildew and rust caused by the heat, constant humidity, and the corrosive salt air of the coast. |
| Border Countries | Guinea 563 km, Cote d'Ivoire 716 km, Sierra Leone 306 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | tropical rain forest deforestation; soil erosion; loss of biodiversity; pollution of coastal waters from oil residue and raw sewage |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | mostly flat to rolling coastal plains rising to rolling plateau and low mountains in northeast |
Liberia Economy
How big is the Liberia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Liberia is a low-income country that relies heavily on foreign assistance and remittances from the diaspora. It is richly endowed with water, mineral resources, forests, and a climate favorable to agriculture. Its principal exports are iron ore, rubber, diamonds, and gold. Palm oil and cocoa are emerging as new export products. The government has attempted to revive raw timber extraction and is encouraging oil exploration. In the 1990s and early 2000s, civil war and government mismanagement destroyed much of Liberia's economy, especially infrastructure in and around the capital. Much of the conflict was fueled by control over Liberia’s natural resources. With the conclusion of fighting and the installation of a democratically elected government in 2006, businesses that had fled the country began to return. The country achieved high growth during the period 2010-13 due to favorable world prices for its commodities. However, during the 2014-2015 Ebola crisis, the economy declined and many foreign-owned businesses departed with their capital and expertise. The epidemic forced the government to divert scarce resources to combat the spread of the virus, reducing funds available for needed public investment. The cost of addressing the Ebola epidemic coincided with decreased economic activity reducing government revenue, although higher donor support significantly offset this loss. During the same period, global commodities prices for key exports fell and have yet to recover to pre-Ebola levels. In 2017, gold was a key driver of growth, as a new mining project began its first full year of production; iron ore exports are also increased as Arcelor Mittal opened new mines at Mount Gangra. The completion of the rehabilitation of the Mount Coffee Hydroelectric Dam increased electricity production to support ongoing and future economic activity, although electricity tariffs remain high relative to other countries in the region and transmission infrastructure is limited. Presidential and legislative elections in October 2017 generated election-related spending pressures. Revitalizing the economy in the future will depend on economic diversification, increasing investment and trade, higher global commodity prices, sustained foreign aid and remittances, development of infrastructure and institutions, combating corruption, and maintaining political stability and security. |
| Industries | rubber processing, palm oil processing, timber, diamonds |
| Currency Name and Code | Liberian Dollar (LRD) |
| Export Partners | Germany 52.7%, France 8.2%, Poland 6.8%, Denmark 5.3%, China 4.7%, Italy 4.4%, US 4% (2002) |
| Import Partners | South Korea 31.1%, Japan 19.5%, Germany 16%, France 9.3%, Singapore 8.1% (2002) |
Liberia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Liberia?
Source: Google News
Liberia Travel Information
What makes Liberia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Liberia is a country in West Africa that suffered from years of instability and conflict from 1990-2003, with attendant destruction of buildings, roads, infrastructure, and public institutions. A comprehensive peace accord ended the conflict in August 2003 and a United Nations peacekeeping force (UNMIL) was deployed to facilitate disarmament and demobilization, help arrange democratic elections, and provide for security of the country. In late 2005, Liberians went to the polls and elected Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf as president. A new government was inaugurated in January 2006, and has made progress towards restoring security and stability to the country. President Sirleaf was re-elected in November 2011.Despite ten years of peace and economic growth, Liberia is still one of the poorest countries in the world and many basic services (e.g., public power, water and sewage, landline phones) are either limited or unavailable. Facilities for foreign visitors are adequate in the capital, Monrovia, but virtually non-existent in the rest of the country. The official language of Liberia is English.
Crime
While incidence of crime in Liberia is high, most crimes that occur within the expat community are crimes of opportunity (which increase during the hours of darkness), to include residential burglary or armed robbery (with use of a knife or machete). Criminal activity has been reported in both urban and rural areas. The Liberian National Police have limited capacity to respond to crime events, thus, crime is much higher in Liberian communities where police are not visible. Driving in Monrovia presents a danger to residents and visitors, as traffic laws are either nonexistent or not enforced by police. Traffic accidents are frequent and often result in injury or loss of life. The police are poorly equipped and largely incapable of providing effective protection or investigation.Perpetrators of business fraud often target foreigners, including U.S. citizens. Formerly associated with Nigeria, these fraud schemes are now prevalent throughout western Africa, including Liberia, and pose a danger of both financial loss and physical harm. An increasing number of U.S. citizens have been the targets of such scams. The best way to avoid becoming a victim of fraud is common sense – if it looks too good to be true, it probably is. U.S. citizens should carefully check any unsolicited business proposal originating in Liberia before committing any funds, providing any goods or services, or undertaking any travel, particularly if the proposal involves the mining or sale of gold and diamonds. There has also been an increase in the number of Liberian/American Internet relationships in which there are eventual requests for financial assistance under fraudulent pretenses.
Petty corruption is rampant; poorly paid government officials may ask for fees for doing their job. Travelers may be inconvenienced for not paying them.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in another country, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods or engage in child pornography. While you are overseas, U.S. law may not apply. If you do something illegal overseas, your U.S. passport won’t shield you from local prosecution. It is very important to familiarize yourself with local laws, customs, and practices.Persons violating Liberian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Liberia are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Photographing military installations, air and sea ports, and important government buildings is prohibited. Visitors should not take photographs of sites or activities that might be considered sensitive, as police are liable to confiscate the camera.
If you are arrested in Liberia, you have the right to request authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Hospitals and medical facilities in Liberia are very poorly equipped and are incapable of providing many services. Emergency services comparable to those in the U.S. or Europe are non-existent, and the blood supply is unreliable and unsafe for transfusion. For serious medical problems, U.S. citizens in Liberia should consider traveling to the United States, Europe, or South Africa for treatment. Medicines are scarce, often beyond expiration dates, and generally unavailable in most areas. As there is neither an effective garbage removal service nor a functioning sewer system, sanitation throughout urban areas is very poor, which increases the potential for disease. Upper respiratory infections and diarrhea are common, as well as more serious diseases such as typhoid and malaria. All travelers to Liberia must be vaccinated against yellow fever and should carry a supply of all prescription medication, including anti-malaria medication, adequate for their entire stay. A typhoid vaccination is also recommended.
Safety and Security
The Department of State urges U.S. citizens to plan proposed travel to Liberia carefully and to exercise caution when traveling in Liberia. Before traveling to Liberia, U.S. citizens are urged to make arrangements for transportation from the international airport into the city center. Taxis are available at the international airport, which is located 40 miles outside of Monrovia, but public transportation (such as buses) is not available. U.S. citizens traveling to Liberia are also urged to ensure that they have confirmed reservations at a reputable hotel, as rooms can be scarce and difficult to find without advance plans.U.S. citizens who travel to or reside in Liberia should realize that Liberia's police force has limited resources and is rebuilding. There is a UN Mission in Liberia (UNMIL), but its mandate is to ensure political stability. UN Police (UNPOL) officers serve as advisors to the Liberian National Police. They do not have the authority to arrest or detain, and they are unarmed. The Liberia National Police has a strong presence in Monrovia, but less of a presence outside of Monrovia. The police can be both a source of assistance as well as a source of problems for visitors. Concerns about police corruption continue, and travelers may be detained by police officers soliciting bribes. U.S citizens are encouraged to carry a photocopy of their passports with them at all times so that, if questioned by local officials, proof of identity and citizenship is readily available. If detained or arrested, U.S. citizens should ask to contact the U.S. Embassy.
U.S. citizens in Liberia should be aware of their surroundings at all times and use caution when moving around, especially at night. Travel outside of Monrovia after dark is strongly discouraged, as roads are in poor condition and there are few public street lights. U.S. citizens should avoid crowds, political rallies, and street demonstrations, and should maintain security awareness at all times.
Stay up to date by bookmarking our Bureau of Consular Affairs' website, which contains the current Travel Warnings and Travel Alerts as well as the Worldwide Caution. Follow us on Twitter and the Bureau of Consular Affairs page on Facebook as well.
You can also call 1-888-407-4747 toll-free within the United States and Canada, or a regular toll line, 1-202-501-4444, from other countries. These numbers are available from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). Take some time before travel to consider your personal security – things are not the same everywhere as they are in the United States. Here are some useful tips for traveling safely abroad.
The Department of State urges U.S. citizens to take responsibility for their own personal security while traveling overseas.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Liberia is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Road travel in Liberia can be hazardous. Potholes and poor road surfaces are common, making safe driving extremely challenging. Cars, trucks, motorcycles, and taxis are often overloaded with people and goods and make frequent stops without signaling. Drivers overtake on the right as well as the left. Many vehicles operate with threadbare tires, and blowouts are frequent. Public taxis are poorly maintained and usually overloaded. Drivers should approach intersections with extreme caution. The widespread absence of public street lights makes it difficult to see pedestrians walking in city streets or on country roads. Drivers and pedestrians are cautioned that high-speed car convoys carrying governmentofficials require all other vehicles to pull off the road until they have passed.
Travelers should expect time-consuming detours around the many bridges and roads damaged by war, neglect, or the heavy annual rains occurring between May and November. Travelers can expect strict enforcement of border controls by Liberian, Ivorian, Sierra Leonean, and Guinean authorities. At times, border crossings to neighboring countries are closed.
