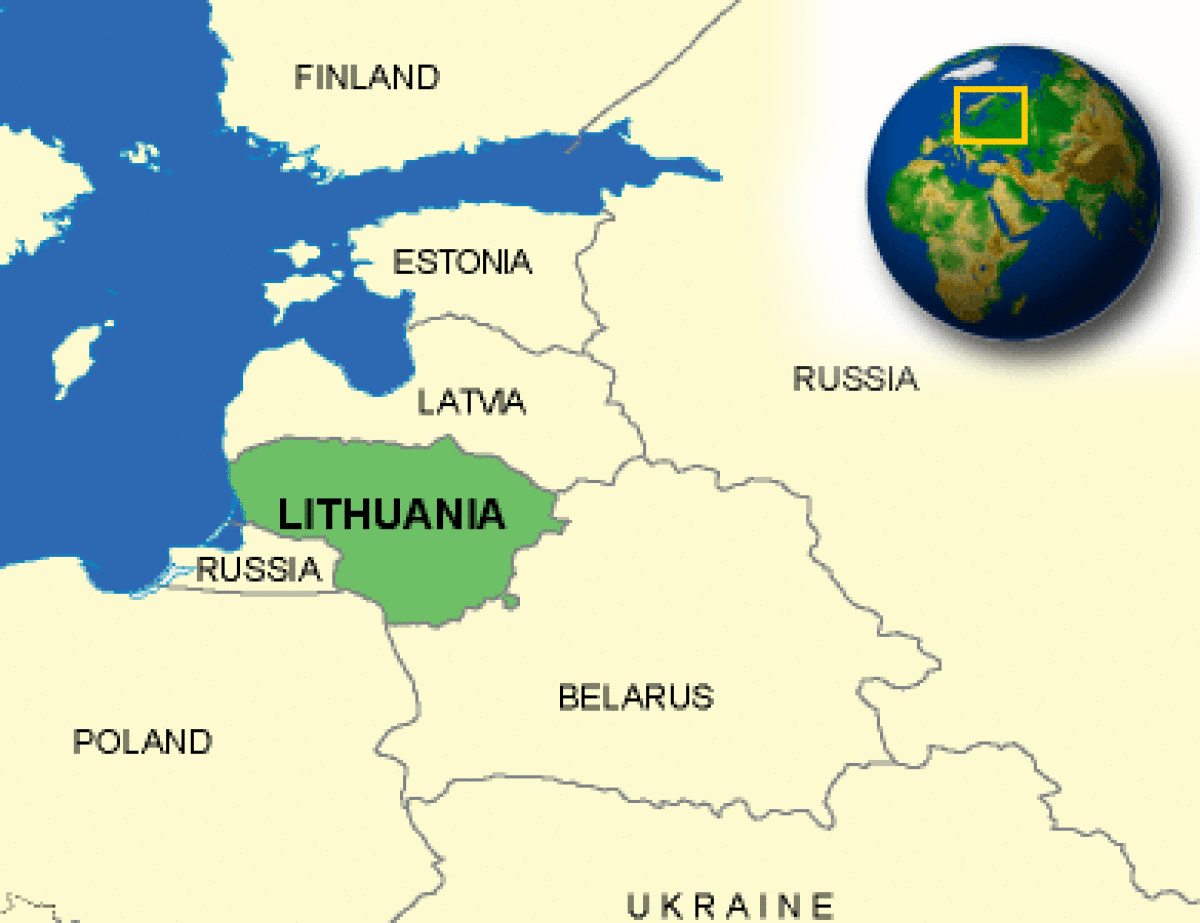
Where is Lithuania located?
What countries border Lithuania?
Lithuania Weather
What is the current weather in Lithuania?
Lithuania Facts and Culture
What is Lithuania famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Lithuanians are often reserved and sincere. Lithuanians are proud of their heritage but not of the Soviet period. More
- Family: Many Lithuanians live in apartments and maintain a small cottage in the country, where they can grow fruits and vegetables... More
- Personal Apperance: Western style clothing is worn. Traditional clothing is worn for festivals. The traditional costume for women is a colorful woven... More
- Recreation: Basketball is the country's most popular sport. On weekends and during vacations, many families spend time at cottages that they... More
- Diet: Traditional specialties include skilandis (smoked meat), ðaltibarðèai (cold beet soup), cepelinai (potato dumplings with minced meat filling), védarai (potato sausages)... More
- Visiting: Drinking vodka (for men only) is common during most social visits. Guests are expected to be punctual. Table manners are... More
Lithuania Facts
What is the capital of Lithuania?
| Capital | Vilnius |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
25,212 Square Miles 65,300 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Latvia and Russia |
| Language | Lithuanian (official), Polish, Russian |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $28,000.00 (USD) |
Lithuania Demographics
What is the population of Lithuania?
| Ethnic Groups | Lithuanian 80.6%, Russian 8.7%, Polish 7%, Belarusian 1.6%, other 2.1% |
| Nationality Noun | Lithuanian(s) |
| Population | 2,731,464 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.28% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | VILNIUS (capital) 546,000 |
| Urban Population | 67.100000 |
Lithuania Government
What type of government does Lithuania have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Gitanas NAUSEDA (since 12 July 2019) head of government: Prime Minister Ingrida SIMONYTE (since 24 November 2020) cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, appointed by the president, approved by Parliament elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 12 and 26 May 2019 (next to be held on 12 May 2024); prime minister appointed by the president, approved by Parliament election results: 2019: Gitanas NAUSEDA elected president in second round; percent of vote - Gitanas NAUSEDA (independent) 66.7%, Ingrida SIMONYTE (independent) 33.3% 2014: Dalia GRYBAUSKAITE elected president; percent of vote - Dalia GRYBAUSKAITE (independent) 59.1%, Zigmantas BALCYTIS (Social Democratic Party) 40.9% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Lithuania dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day (or National Day), 16 February (1918); note - 16 February 1918 was the date Lithuania established its statehood and its concomitant independence from Soviet Russia and Germany; 11 March 1990 was the date it declared the restoration of Lithuanian statehood and its concomitant independence from the Soviet Union |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted by referendum 25 October 1992, entered into force 2 November 1992 amendments: proposed by at least one fourth of all Parliament members or by petition of at least 300,000 voters; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of Parliament in each of two readings three months apart and a presidential signature; amendments to constitutional articles on national sovereignty and constitutional amendment procedure also require three-fourths voter approval in a referendum; amended many times, last in 2019 |
| Independence | 16 February 1918 (from Soviet Russia and Germany); 11 March 1990 (declared from the Soviet Union); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: 6 July 1253 (coronation of MINDAUGAS, traditional founding date); 1 July 1569 (Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth created) |
Lithuania Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Lithuania Geography
What environmental issues does Lithuania have?
| Overview |
Lithuania, covering an area of 26,173 square miles, is the largest of the three Baltic States, slightly larger than West Virginia. The country lies on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea at approximately the same latitude as Denmark and Scotland. Lithuania's neighbors are Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, and Poland and the Kaliningrad region of the Russian Federation to the south and southwest. Lithuanians believe that the geographical center of the European continent lies 20 kilometers north of Vilnius, the capital. A country known for its agrarian and wooded beauty, Lithuania is characterized by flat plains and rolling hills. The highest hill, Kruopine, is only 900 feet above sea level. Roughly one-fourth of the territory is covered by woodlands, consisting mainly of pine, spruce, and birch. One of the oldest oak trees in Europe, found in eastern Lithuania, is said to be about 1,500 years old. The forests are home to a variety of animals including elk, foxes, and wild boar; hunting is a popular pastime. Lithuanians especially enjoy mushroom collecting and berry picking. More than 700 rivers and creeks crisscross Lithuania. The largest river, the Nemunas, was once a strategically important shipping route through Lithuania. Its banks are dotted with castles and fortresses. There are numerous lakes, especially in eastern Lithuania, where the Aukstatija National Park is located. This region is home to the Ignalina nuclear power plant, which exports electricity to other countries in the region. |
| Climate | Lithuania's climate is moderate. Summer brings average temperatures of 65°F (afternoon highs in the 70s and 80s) and plentiful rain. July is the warmest month. Summer days are long, with only a few hours of darkness. Winters tend to be cold, damp, and overcast. Temperatures average about 30°F, and days are very short. Average annual precipitation amounts to about 26 inches. |
| Border Countries | Belarus 502 km, Latvia 453 km, Poland 91 km, Russia (Kaliningrad) 227 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | contamination of soil and groundwater with petroleum products and chemicals at military bases |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | lowland, many scattered small lakes, fertile soil |
Lithuania Economy
How big is the Lithuania economy?
| Economic Overview |
After the country declared independence from the Soviet Union in 1990, Lithuania faced an initial dislocation that is typical during transitions from a planned economy to a free-market economy. Macroeconomic stabilization policies, including privatization of most state-owned enterprises, and a strong commitment to a currency board arrangement led to an open and rapidly growing economy and rising consumer demand. Foreign investment and EU funding aided in the transition. Lithuania joined the WTO in May 2001, the EU in May 2004, and the euro zone in January 2015, and is now working to complete the OECD accession roadmap it received in July 2015. In 2017, joined the OECD Working Group on Bribery, an important step in the OECD accession process. The Lithuanian economy was severely hit by the 2008-09 global financial crisis, but it has rebounded and become one of the fastest growing in the EU. Increases in exports, investment, and wage growth that supported consumption helped the economy grow by 3.6% in 2017. In 2015, Russia was Lithuania’s largest trading partner, followed by Poland, Germany, and Latvia; goods and services trade between the US and Lithuania totaled $2.2 billion. Lithuania opened a self-financed liquefied natural gas terminal in January 2015, providing the first non-Russian supply of natural gas to the Baltic States and reducing Lithuania’s dependence on Russian gas from 100% to approximately 30% in 2016. Lithuania’s ongoing recovery hinges on improving the business environment, especially by liberalizing labor laws, and improving competitiveness and export growth, the latter hampered by economic slowdowns in the EU and Russia. In addition, a steady outflow of young and highly educated people is causing a shortage of skilled labor, which, combined with a rapidly aging population, could stress public finances and constrain long-term growth. |
| Industries | metal-cutting machine tools, electric motors, television sets, refrigerators and freezers, petroleum refining, shipbuilding (small ships), furniture making, textiles, food processing, fertilizers, agricultural machinery, optical equipment, electronic components, computers, amber |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | UK 13.4%, Russia 12.1%, Germany 10.4%, Latvia 9.7%, Denmark 5.1%, Sweden 4.2%, France 4.1% |
| Import Partners | Russia 22.2%, Germany 17.8%, Italy 5.1%, Poland 5% |
Lithuania News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Lithuania?
Source: Google News
Lithuania Travel Information
What makes Lithuania a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Lithuania is a stable democracy. Tourist facilities in Vilnius, the capital, and to a lesser extent in Kaunas and Klaipeda, are similar to those available in other European cities. In other parts of the country, however, some of the goods and services taken for granted in other countries may not be available.
Crime
Although Lithuania is relatively safe, both violent and non-violent crimes affecting tourists have occured throughout the country. You should maintain the same awareness and practice good personal security that you would in any U.S. metropolitan area. Large amounts of cash and expensive jewelry should be secured in a hotel safe or left at home. Common crimes against foreigners include pick-pocketing and thefts, so personal belongings should be well protected at all times. Thefts from cars and car thefts occur regularly. Valuables should not be left in plain sight in parked vehicles, as there have been increasing reports of car windows being smashed and items stolen. You should avoid walking alone at night or utilize a taxi service arranged by telephone. Isolated ATMs should be avoided after dark. Like in the United States., public inebriation should be avoided as criminals have been known to take advantage of drunken pedestrians. U.S. citizens have reported being robbed and/or scammed while intoxicated.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, you may be breaking local law too.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Lithuania, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in Lithuania, but still illegal in the United States; for instance, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Lithuania, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not.If you break Lithuanian laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Lithuania are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. For more information about arrest procedures in Lithuania please visit the Embassy’s website. While most authorities will automatically notify the U.S. Embassy if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested, this might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the Embassy as soon as you are arrested or detained.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in Lithuania has improved, but medical facilities do not always meet Western standards. There are a few private clinics with medical supplies and services that nearly equal Western European or U.S. standards. Most medical supplies are now widely available, including disposable needles, anesthetics, antibiotics, and other pharmaceuticals; however, hospitals and clinics still suffer from a lack of equipment and resources. Lithuania has highly trained medical professionals, some of whom speak English, but their availability is decreasing as they leave for employment opportunities abroad. Depending on a patient’s condition, an appointment with a specialist may not be available for several weeks. Western-quality dental care can be obtained in major cities. Elderly travelers who require medical care may face difficulties. Most pharmaceuticals sold in Lithuania are from Europe; travelers will not necessarily find the same brands that they use in the United States. Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation can cost thousands of dollars or more. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services, particularly if immigration status in Lithuania is unclear.Tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease are widespread throughout the country. Those intending to visit parks or forested areas in Lithuania are urged to speak with their health care practitioners about immunization. Rabies is also increasingly prevalent in rural areas.
Safety and Security
There have been no incidents of terrorism directed toward U.S. interests in Lithuania. Incidents of anti-Americanism are rare.Lithuania is not experiencing any civil unrest at this time. However, marches and protests do occur, especially in larger cities. Although such events have generally been peaceful in nature, U.S. citizens are reminded that even gatherings intended to be peaceful can become confrontational. Therefore, we urge you to avoid the areas of demonstrations, if possible, and exercise caution if within the vicinity of any event. You should stay current with media coverage of local events and be aware of their surroundings at all times.
From time to time, especially late at night near bars and night clubs, foreigners have been subject to violent crimes, such as muggings, or have become involved in altercations with inebriated individuals. Racially motivated verbal, and sometimes physical harassment of foreigners and ethnic minorities in major cities have occurred.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Lithuania, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.You may drive in Lithuania with a U.S. driver’s license for up to 90 days. U.S. citizens who reside in Lithuania for 185 days or more in one calendar year and who wish to continue driving in Lithuania must acquire a Lithuanian driver's license. An applicant for a driver’s license must take both the written and driving exams. The foreign license must be given to the Lithuanian Road Police to be processed by the Consular Department of the Lithuanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. For more information, please visit the Embassy’s website. Roads in Lithuania range from well-maintained two- to four-lane highways connecting major cities, to small dirt roads traversing the countryside. Violation of traffic rules is common. It is not unusual to be overtaken by other automobiles traveling at high speed, even in crowded urban areas. Driving at night-- especially in the countryside--can be particularly hazardous. In summer, older seasonal vehicles and inexperienced drivers can be extra hazards. Drive with caution at all times. Driving whileintoxicated is considered a very serious offense and carries heavy penalties. Be aware that such laws are significantly stricter than in many states in the United States. The speed limit is 50 km/hr in town and 90 km/hr out of town unless otherwise indicated. The phone number for roadside assistance is 8-800-01414 from a regular phone and 1414 from a GSM mobile phone. If you are involved in a traffic accident, be aware that moving the car before the police arrive can result in your being charged with hit and run.
Seatbelts are mandatory for the driver and all passengers. Children under the age of 3 must be seated in the back seat in a child seat appropriate for their age and size. Children under the age of 12 and under 150 cm (approximately 59 inches) may not be seated in the front seat.
During the winter, most major roads are cleared of snow. Winter or all-season tires are required from November 10th through April 1st. Studded tires are not allowed from April 10th through October 31st. Drivers must have at least their low-beam lights on at all times while driving.
Public transportation is generally safe, but you should maintain personal security awareness while on public transportation.
