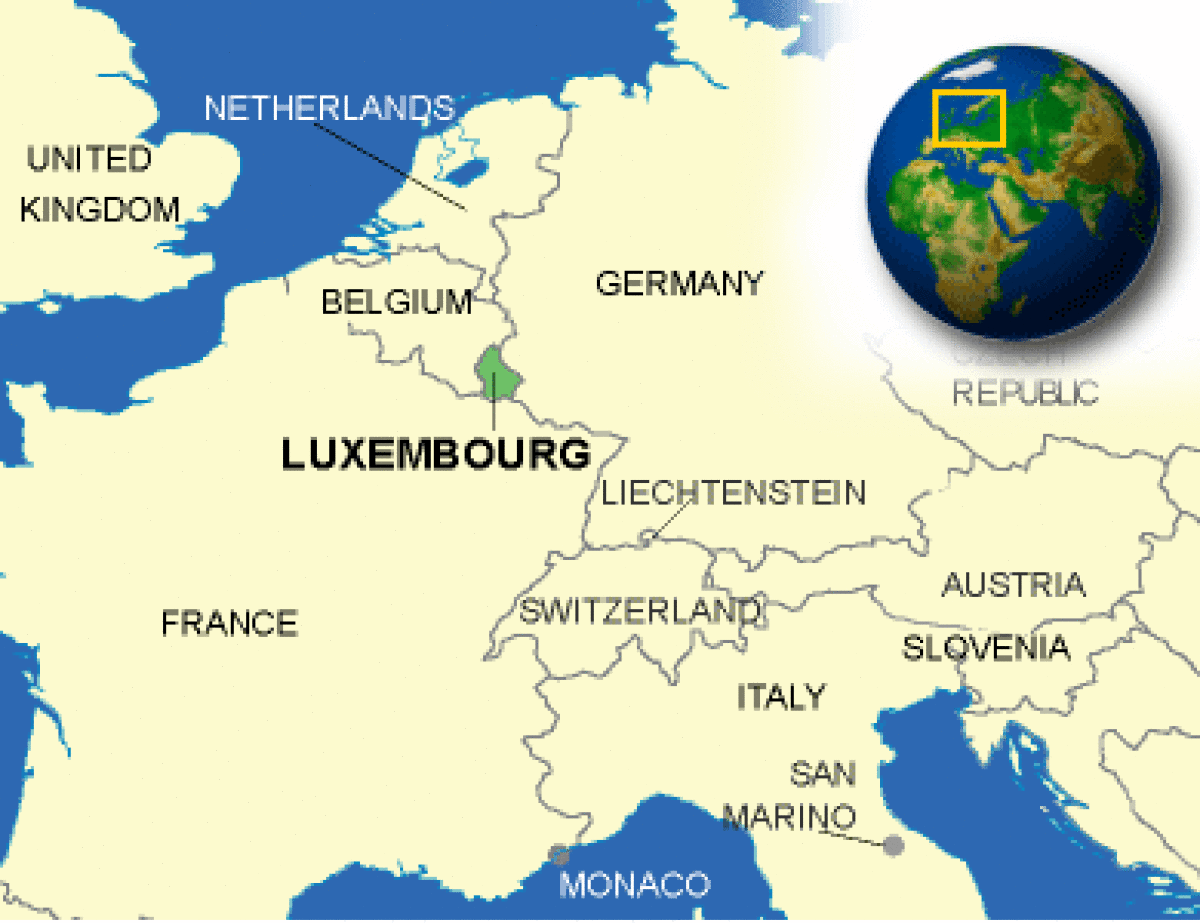
Where is Luxembourg located?
What countries border Luxembourg?
Luxembourg Weather
What is the current weather in Luxembourg?
Click for weather forecast
Luxembourg Facts and Culture
What is Luxembourg famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Luxembourg has a highly developed welfare system that allows people to put food on the table weather they are working... More
- Family: National law requires adults to take care of their aging parents. Family size is usually one or two children. More
- Personal Apperance: Most people take their fashion ideas from Europe, and the clothing in Luxembourg is very similar to the French, Germans,... More
- Recreation: The national sport is soccer, like most other European nations. Luxembourg's appearances on the international sports scene although are predominantly... More
- Food and Recipes: Hearty appetites and large portions are standard for meals. Luxembourg is known for its delicious pastries. Quetsch a plum tart... More
- Visiting: Typical ways people socialize in public include restaurants, bars, or meals among neighbors (especially barbecues in the summer) If one... More
Luxembourg Facts
What is the capital of Luxembourg?
| Capital | Luxembourg |
| Government Type | constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
998 Square Miles 2,586 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Europe, between France and Germany |
| Language | Luxembourgish (national language), German (administrative language), French |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $102,900.00 (USD) |
Luxembourg Demographics
What is the population of Luxembourg?
| Ethnic Groups | Celtic base (with French and German blend), Portuguese, Italian, Slavs (from Montenegro, Albania, and Kosovo) and European (guest and resident workers) |
| Nationality Noun | Luxembourger(s) |
| Population | 628,381 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.13% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | LUXEMBOURG (capital) 94,000 |
| Urban Population | 85.400000 |
Luxembourg Government
What type of government does Luxembourg have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Grand Duke HENRI (since 7 October 2000); Heir Apparent Prince GUILLAUME (son of the monarch, born 11 November 1981) head of government: Prime Minister Luc FRIEDEN (since 17 November 2023); Deputy Prime Minister Xavier BETTEL (since 17 November 2023) cabinet: Council of Ministers recommended by the prime minister, appointed by the monarch elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following elections to the Chamber of Deputies, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch; deputy prime minister appointed by the monarch; prime minister and deputy prime minister are responsible to the Chamber of Deputies |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: limited to situations where the parents are either unknown, stateless, or when the nationality law of the parents' state of origin does not permit acquisition of citizenship by descent when the birth occurs outside of national territory citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Luxembourg dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | National Day (birthday of Grand Duke HENRI), 23 June; note - this date of birth is not the true date of birth for any of the Royals, but the national festivities were shifted in 1962 to allow observance during a more favorable time of year |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1842 (heavily amended 1848, 1856); latest effective 17 October 1868 amendments: proposed by the Chamber of Deputies or by the monarch to the Chamber; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Chamber in two successive readings three months apart; a referendum can be substituted for the second reading if approved by more than a quarter of the Chamber members or by 25,000 valid voters; adoption by referendum requires a majority of all valid voters; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 1839 (from the Netherlands) |
Luxembourg Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Luxembourg Geography
What environmental issues does Luxembourg have?
| Overview | Geographically, the Grand Duchy is divided into two sections. The forested and hilly northern half of the country is a continuation of the Belgian Ardennes. In the south, the Lorraine Plateau extends from France, creating an open, rolling countryside with an average elevation of 1,000 feet. The Our, Sure, and Moselle Rivers flow north-south along the frontier between Luxembourg and Germany. |
| Climate | Temperatures range from 5°F (-15°C) to 90°F (32°C), with an annual mean temperature of 49°F (9°C). Summer temperatures average 60°F (15°C) and winters are mild with an average low of 29°F (-1.7°C). July and August are the warmest months; May and June are the sunniest; and January and February are the coldest months. Luxembourg has a climate much like that of the U.S. Pacific Northwest-cool, temperate, and rainy. The northwesterly winds that traverse the western, lower portion of the Belgian Ardennes cause abundant clouds, fog, and rain. Average annual rainfall is 30 inches; some rain falls 50% of the year. |
| Border Countries | Belgium 148 km, France 73 km, Germany 138 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air and water pollution in urban areas, soil pollution of farmland |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification |
| Terrain | mostly gently rolling uplands with broad, shallow valleys; uplands to slightly mountainous in the north; steep slope down to Moselle flood plain in the southeast |
Luxembourg Economy
How big is the Luxembourg economy?
| Economic Overview |
This small, stable, high-income economy has historically featured solid growth, low inflation, and low unemployment. Luxembourg, the only Grand Duchy in the world, is a landlocked country in northwestern Europe surrounded by Belgium, France, and Germany. Despite its small landmass and small population, Luxembourg is the fifth-wealthiest country in the world when measured on a gross domestic product (PPP) per capita basis. Luxembourg has one of the highest current account surpluses as a share of GDP in the euro zone, and it maintains a healthy budgetary position, with a 2017 surplus of 0.5% of GDP, and the lowest public debt level in the region. Since 2002, Luxembourg’s government has proactively implemented policies and programs to support economic diversification and to attract foreign direct investment. The government focused on key innovative industries that showed promise for supporting economic growth: logistics, information and communications technology (ICT); health technologies, including biotechnology and biomedical research; clean energy technologies, and more recently, space technology and financial services technologies. The economy has evolved and flourished, posting strong GDP growth of 3.4% in 2017, far outpacing the European average of 1.8%. Luxembourg remains a financial powerhouse – the financial sector accounts for more than 35% of GDP - because of the exponential growth of the investment fund sector through the launch and development of cross-border funds (UCITS) in the 1990s. Luxembourg is the world’s second-largest investment fund asset domicile, after the US, with $4 trillion of assets in custody in financial institutions. Luxembourg has lost some of its advantage as a favorable tax location because of OECD and EU pressure, as well as the "LuxLeaks" scandal, which revealed advantageous tax treatments offered to foreign corporations. In 2015, the government’s compliance with EU requirements to implement automatic exchange of tax information on savings accounts - thus ending banking secrecy - has constricted banking activity. Likewise, changes to the way EU members collect taxes from e-commerce has cut Luxembourg’s sales tax revenues, requiring the government to raise additional levies and to reduce some direct social benefits as part of the tax reform package of 2017. The tax reform package also included reductions in the corporate tax rate and increases in deductions for families, both intended to increase purchasing power and increase competitiveness. |
| Industries | banking, iron and steel, food processing, chemicals, metal products, engineering, tires, glass, aluminum |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 23.9%, France 20.1%, Belgium 10.5%, UK 8.7%, Italy 6.1%, Spain 4.5%, Netherlands 4.4% |
| Import Partners | Belgium 29.7%, Germany 23%, France 13.2%, Taiwan 7.3%, Netherlands 4.6% |
Luxembourg News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Luxembourg?
Source: Google News
Luxembourg Travel Information
What makes Luxembourg a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Luxembourg is a highly developed, stable constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. There are many tourist facilities in Luxembourg.
Crime
The predominant forms of crime in Luxembourg are non-violent. Such crimes include the theft of valuables through snatching of purses/bags, and breaking and entering of unoccupied homes. Crime is more pronounced in Luxembourg City, especially at bus terminals and the main train station and its surroundings. Street robbery can turn violent if the victim is isolated and cannot seek help from by-passers. You should take common-sense precautions while in Luxembourg; be vigilant with your personal belongings and refrain from carrying visible jewelry and more cash than necessary. Pickpockets often operate in teams, usually one team member distracts the victim while another empties the pockets or bag. You should be especially careful when taking the train to/from Brussels; theft of backpacks, laptops, or other valuables regularly occurs on this route.Luxembourg has many public parks that are safe during the daylight hours, though the volume of low-level drug vending has increased in some of the city parks. You should avoid these parks after dark, though, because they pose a higher risk. During the summer season, you should be particularly alert to purse snatchings and confidence scams against tourists. Incidents of petty crime spike during the annual “Schueberfouer,” a three-week event held every summer.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Luxembourg, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. Criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods abroad. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Luxembourg, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Persons violating Luxembourg's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Luxembourg are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Arrest notifications in Luxembourg:
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are widely available. Dial 112 for a medical emergency or the fire department, and 113 for the police. Hospitals in Luxembourg operate on a 24-hour rotation system. We do not advise self-referral to any hospital, with an exception: the “Centre Hospitalier” is always on-call for emergency cases involving children under the age of 14. In Luxembourg City, three major hospitals offer comprehensive general medical and surgical treatment. Additionally, there are two pediatric clinics and two obstetric clinics in Luxembourg City. There are also hospitals in the south of the country (Esch-sur-Alzette) and in the north (Wiltz). For more specialized care, including major burns, transfer to a regional burn center in Belgium or France is necessary. Three medical services (maisons médicales) provide general medical treatment (not suitable for emergency cases) after hours, on weekends, and holidays, when a treating physician is not available. Please see information on all medical facilities in Luxembourg at the following website.Most drugstores are located in Luxembourg City but can also be found throughout the country in all major communes. Drugstores operate on a 24-hour rotation system for after-hours services, including emergency prescriptions. The on-call pharmacy is listed daily in the local newspaper or can be ascertained by calling 112. A doctor's prescription is sometimes necessary for drugs that are sold over the counter in the United States.
Safety and Security
Terrorist incidents are rare in Luxembourg. Luxembourg's open borders, however, could possibly allow terrorist groups to enter/exit the country unnoticed.Prior police approval is required for public demonstrations in Luxembourg. Police routinely provide supervision to ensure adequate security for participants and passers-by. Nonetheless, situations may develop which could pose threats to public safety. We advise you to avoid areas where public demonstrations are taking place.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
Persons residing in Luxembourg who wish to drive must have their driver’s license transcribed within one year. To start the process, the driver must have been a registered resident of Luxembourg for at least 185 days and the license must have been issued in the country where the person was actually residing at the time of issuance. Additional documents to be submitted with the application include a recent medical certificate, a criminal record (affidavit from the U.S. Embassy), and a residence permit for Luxembourg. It is not possible to receive a Luxembourg driver’s license and keep the foreign (U.S.) license, which has to be surrendered to the driver’s license office and will be returned to the issuing authority.While in Luxembourg, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Luxembourg has a modern, well-maintained system of highways and secondary roads. Road signs and markings are clear and primarily worded in French. Streets in the city, construction sites, and crossroads are well illuminated at night. On highways, a digital alert system warns drivers of incidents or detours. Roads into and out of Luxembourg City are congested during the morning and evening rush hour. Visitors should drive defensively in high-volume commuter traffic. During the fall and winter, fog and ice can cause sudden slowdowns on highways and secondary roads.
In case of a car accident involving injury or dispute, it is a good idea to call the police at 113. The police will make an official assessment of the accident's circumstances that can subsequently be used if further legal action becomes necessary.
The daily mix of drivers from Luxembourg and its three neighboring countries results in a variety of driving practices and courtesies. While most drivers respect speed limits, traffic signals, and rules, some do not. Vehicle maintenance for cars registered in Luxembourg is controlled by the mandatory yearly car inspection; police can perform random road checks at any time. The possibility of encountering an intoxicated driver increases on weekends, especially during the late evening hours. Driving while intoxicated may result in penalties including imprisonment from eight days up to two years, plus a fine of 251 to 5,000 Euros (approximately $326 to $6,500).
Public transportation throughout the country, including bus services and taxis, is highly developed and is considered very safe.
Emergency road services in Luxembourg are excellent. For breakdown and towing service call the Automobile Club of Luxembourg (ACL) at 26000. In case of an accident, call 112 for a medical emergency and 113 for the police.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
