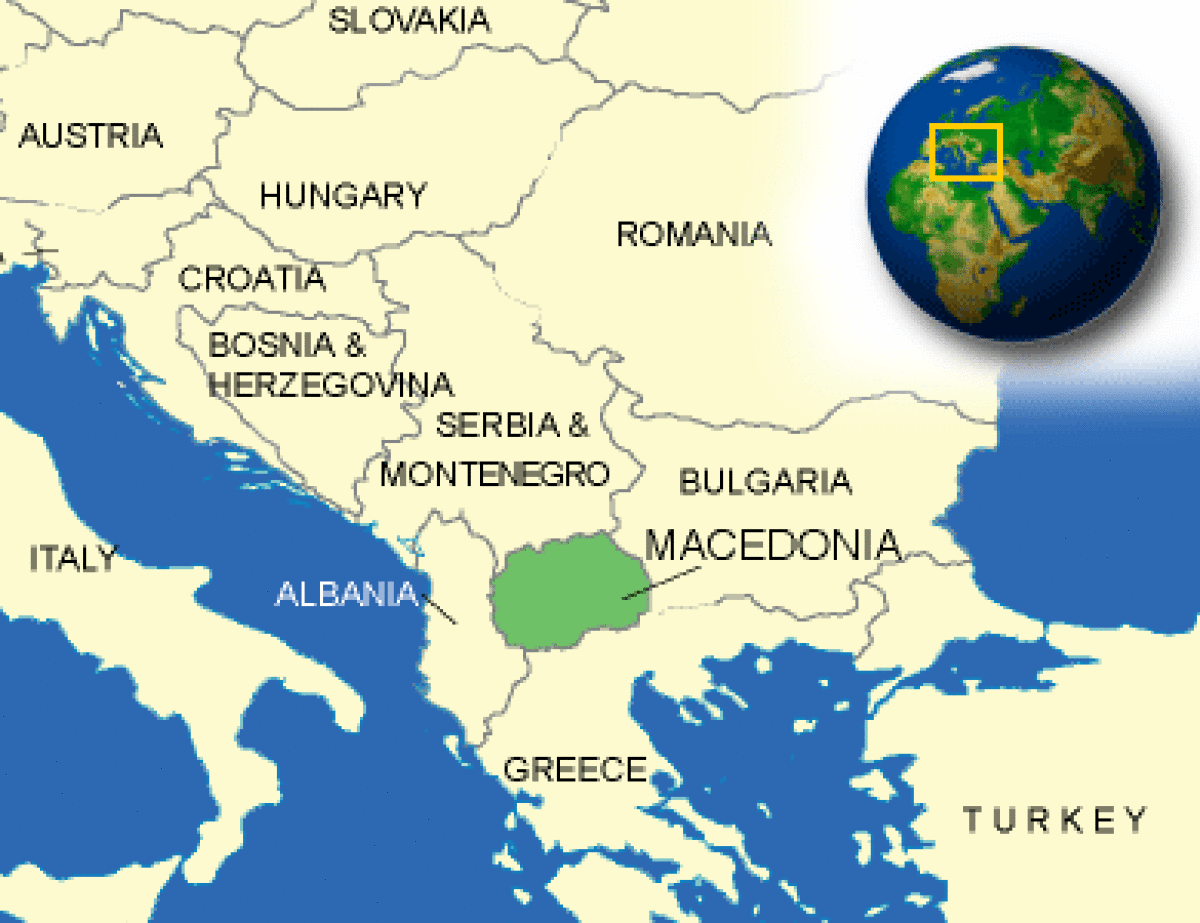
Where is North Macedonia located?
What countries border North Macedonia?
North Macedonia Weather
What is the current weather in North Macedonia?
North Macedonia Facts and Culture
What is North Macedonia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Macedonian culture stresses the importance of the family. Parents sacrifice a great deal to support their children into adulthood, and... More
- Family: The traditional family unit is an extended family consisting of a married couple, their unmarried daughters and their sons with... More
- Personal Apperance: Western European styles are followed by the majority of urban Macedonians, within the limits of the budget. A clean, tidy... More
- Recreation: Soccer and basketball are the two most popular sports. Table tennis and chess are also popular. In the cities a... More
- Diet: Breakfast consists of bread, cheese and sometimes eggs. Root vegetables, grains and fruit, wine and meats are staples. Bean casserole... More
- Food and Recipes: Breakfast is eaten about 9 AM by office workers, but earlier by factory laborers and rural residents. Dinner is the... More
- Visiting: Relatives, friends and neighbors visit regularly and informally. However, it is important to give advance notice of a visit if... More
- Dating: Children often live with their parents till they are married. Young people are permitted to go out to movies, parks,... More
North Macedonia Facts
What is the capital of North Macedonia?
| Capital | Skopje |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Macedonian Denar (MKD) |
| Total Area |
9,928 Square Miles 25,713 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Europe, north of Greece |
| Language | Macedonian 68%, Albanian 25%, Turkish 3%, Serbo-Croatian 2%, other 2% |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $14,000.00 (USD) |
North Macedonia Demographics
What is the population of North Macedonia?
| Ethnic Group - note | note: Romani populations are usually underestimated in official statistics and may represent 6.5–13% of North Macedonia’s population |
| Ethnic Groups | Macedonian 58.4%, Albanian 24.3%, Turkish 3.9%, Romani 2.5%, Serb 1.3%, other 2.3%, persons for whom data were taken from administrative sources and no ethnic affiliation data was available 7.2% |
| Languages | The official language is Macedonian, which is written in a Cyrillic script. Albanian, Turkish, and Serbian are spoken widely. Sixty-seven per cent of the population in Macedonia are Macedonian, 22.9% are Albanian and there are between 2-3% Gypsy and Serb minorities. |
| Nationality Noun | Macedonian(s) |
| Population | 2,125,971 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.22% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | SKOPJE (capital) 499,000 |
| Urban Population | 59.300000 |
North Macedonia Government
What type of government does North Macedonia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Stevo PENDAROVSKI (since 12 May 2019) head of government: Caretaker Prime Minister Talat XHAFERI (since 28 January 2024) cabinet: Council of Ministers elected by the Assembly by simple majority vote elections/appointments: president directly elected using a modified 2-round system; a candidate can only be elected in the first round with an absolute majority from all registered voters; in the second round, voter turnout must be at least 40% for the result to be deemed valid; president elected for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 21 April and 5 May 2019 (next to be held in 2024); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition is usually elected prime minister by the Assembly election results: 2024: Talat XHAFERI elected caretaker Prime Minister; Assembly vote - 65 for (opposition boycott) 2022: Dimitar KOVACEVSKI elected Prime Minister; Assembly vote - NA 2019: Stevo PENDAROVSKI elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Stevo PENDAROVSKI (SDSM) 44.8%, Gordana SILJANOVSKA-DAVKOVA (VMRO-DPMNE) 44.2%, Blerim REKA (independent) 11.1%; percent of vote in second round - Stevo PENDAROVSKI 53.6%, Gordana SILJANOVSKA-DAVKOVA 46.4% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of North Macedonia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 8 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 8 September (1991), also known as National Day |
| Constitution |
history: several previous (since 1944); latest adopted 17 November 1991, effective 20 November 1991 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic, by the government, by at least 30 members of the Assembly, or by petition of at least 150,000 citizens; final approval requires a two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; amended several times, last in 2019; this amendment was the result of the 2018 Prespa Agreement with Greece, in which the constitutional name of the country would be modified to Republic of North Macedonia in exchange for assurances that Greece would no longer object to its integration in international organizations; note - a referendum on amendments to the constitution is expected in 2024 |
| Independence | 8 September 1991 (referendum by registered voters endorsed independence from Yugoslavia) |
North Macedonia Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Macedonia Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)North Macedonia Geography
What environmental issues does North Macedonia have?
| Overview |
The Republic of Macedonia is a landlocked mountainous country. It is situated in southern Europe on the Balkan Peninsula. Occupying a central geographical position in the Balkans, it is a transportation and communications crossroad linking Europe, Asia, and Africa. Macedonia is a land of sunshine, lakes, valleys and mountains. A country of great history and tradition, it covers an area of 25,713 square kilometers and lies 245 meters above sea level. The Republic of Macedonia has 1,100 water sources. These sources run into three different basins: the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Seas. The Aegean basin is the largest. The Vardar River, which runs through Skopje, flows into this basin. Macedonia’s lakes are an important country resource for food and developing of tourism. The largest three lakes are: Ohrid, the largest in the Balkans, situated in the southwestern corner of Macedonia and shared with Albania; Prespa, in the same area; and Dojran in southeastern Macedonia. Twenty-five other small glacial lakes are scattered throughout the country. |
| Climate | Mostly a country of hills and mountains, Macedonia has a continental Mediterranean climate characterized by long, dry, rather hot summers and short, cold winters. The average air temperature in the summer is 25°C (77°F) and 0.5°C (33°F) in winter. However, short periods of extreme temperatures of 110-115°F in summer and low 20s in the winter are common. The average annual precipitation is 445.5 mm. The humidity in Macedonia averages 66%. Occasionally, there are dust storms in the Vardar River valley. Macedonia is on a fault line and the country averages four earthquakes a year (most go unnoticed) with a median reading of 6 on the Medvedev-Sponheuer-Karnik International Seismological Scale. |
| Border Countries | Albania 151 km, Bulgaria 148 km, Greece 246 km, Serbia and Montenegro 221 km |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
North Macedonia Economy
How big is the North Macedonia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Since its independence in 1991, Macedonia has made progress in liberalizing its economy and improving its business environment. Its low tax rates and free economic zones have helped to attract foreign investment, which is still low relative to the rest of Europe. Corruption and weak rule of law remain significant problems. Some businesses complain of opaque regulations and unequal enforcement of the law. Macedonia’s economy is closely linked to Europe as a customer for exports and source of investment, and has suffered as a result of prolonged weakness in the euro zone. Unemployment has remained consistently high at about 23% but may be overstated based on the existence of an extensive gray market, estimated to be between 20% and 45% of GDP, which is not captured by official statistics. Macedonia is working to build a country-wide natural gas pipeline and distribution network. Currently, Macedonia receives its small natural gas supplies from Russia via Bulgaria. In 2016, Macedonia signed a memorandum of understanding with Greece to build an interconnector that could connect to the Trans Adriatic Pipeline that will traverse the region once complete, or to an LNG import terminal in Greece. Macedonia maintained macroeconomic stability through the global financial crisis by conducting prudent monetary policy, which keeps the domestic currency pegged to the euro, and inflation at a low level. However, in the last two years, the internal political crisis has hampered economic performance, with GDP growth slowing in 2016 and 2017, and both domestic private and public investments declining. Fiscal policies were lax, with unproductive public expenditures, including subsidies and pension increases, and rising guarantees for the debt of state owned enterprises, and fiscal targets were consistently missed. In 2017, public debt stabilized at about 47% of GDP, still relatively low compared to its Western Balkan neighbors and the rest of Europe. |
| Industries | coal, metallic chromium, lead, zinc, ferronickel, textiles, wood products, tobacco, food processing, buses, steel |
| Currency Name and Code | Macedonian Denar (MKD) |
| Export Partners | Greece 15.5%, Germany 13.1%, Serbia and Montenegro 10.4%, Slovenia 8.6%, Bulgaria 8.1%, Turkey 6%, Romania 4.7% |
| Import Partners | Greece 15.5%, Germany 13.1%, Serbia and Montenegro 10.4%, Slovenia 8.6%, Bulgaria 8.1%, Turkey 6%, Romania 4.7% |
North Macedonia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in North Macedonia?
Source: Google News
North Macedonia Travel Information
What makes North Macedonia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Macedonia is a parliamentary democracy that is slowly but steadily transforming its economy. Tourist facilities are available in the capital, Skopje, and other major towns. In tourist centers, such as Skopje and Ohrid, European-standard hotels and other travel amenities are available. The standard of tourist facilities throughout the rest of the country varies considerably.
Crime
You should take the same precautions against becoming crime victims as you would in any U.S. city. Violent crime against U.S. citizens is rare. Pick-pocketing, theft, and other petty street crimes do occur, particularly in areas where tourists and foreigners congregate. Do not leave valuables, including cell phones and electronic items, in plain view in unattended vehicles. You should securely lock the windows and doors of your residence when it is not occupied. Organized crime is present in Macedonia; organized criminal activity occasionally results in violent confrontations between members of rival organizations. ATM use is generally safe; however, travelers should take standard safety precautions.Pickpockets remain a problem in crowded areas of Skopje. Be aware of your belongings and surroundings at all times. Pickpockets use various diversionary tactics to distract victims; one method involves groups of children swarming around you and asking for money to find and take your wallet. Victims of pick pocketing should report the crime to the police and cancel their credit cards as soon as possible.
Taxis are a common and generally safe form of transportation. Use a legitimate, metered taxi to avoid conflicts about the fare.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Macedonia, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Macedonia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution.If Arrested: If you are arrested in Macedonia, Macedonian authorities are required to notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest.
Languages
The official language is Macedonian, which is written in a Cyrillic script. Albanian, Turkish, and Serbian are spoken widely. Sixty-seven per cent of the population in Macedonia are Macedonian, 22.9% are Albanian and there are between 2-3% Gypsy and Serb minorities.
Safety and Security
A small number of murders and armed robberies have occurred nationwide. None of these have targeted U.S. citizens or interests, but you should be aware of current events and your surroundings.Macedonia has not experienced any incidents of large-scale public violence in recent years, although there have been occasions where protest activity devolved into localized violent incidents. Public protests, demonstrations, and strikes in response to world or local events can sporadically occur in Macedonia. Traffic disruptions and police diversion of traffic often occurs in connection with these demonstrations, particularly near the center of Skopje. While the vast majority of demonstrations in Macedonia are peaceful, you should be aware that even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and possibly escalate into violence. You are urged to avoid demonstration areas if possible, and to exercise caution if traveling within the vicinity of any demonstrations. You should monitor media coverage to stay abreast of local events and should be aware of your surroundings at all times. Information regarding demonstrations in Macedonia can be found on the Embassy Skopje website. .
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
Driving safely in Macedonia requires excellent defensive driving skills. Many local drivers routinely ignore speed limits and other traffic regulations, such as stopping for red lights and stop signs. Drivers may make illegal left turns from the far right lane, or drive into oncoming lanes of traffic. The combination of speeding, unsafe driving practices, poor vehicle maintenance, the mixture of new and old vehicles on the roads, and poor lighting contributes to unsafe driving conditions. Drivers and passengers should always wear seatbelts in Macedonia. Pedestrians should exercise extreme caution when crossing the street, even when using crosswalks, as local drivers often do not slow down or stop for pedestrians.A valid U.S. driver's license and an International Driving Permit are required for U.S. citizens driving in Macedonia. Macedonians drive on the right side of the road. Speed limits are generally posted. Most major highways are in good repair, but many secondary urban and rural roads are poorly maintained and poorly lighted. Horse-drawn carts, livestock, dead animals, rocks, or other objects are sometimes found in the roadway. Some vehicles are old and lack standard front or rear lights. Secondary mountain roads can be narrow, poorly marked, and lacking guardrails, and may quickly become dangerous in inclement weather. Public transportation in Macedonia is dilapidated. Roadside emergency services are limited.
In case of emergency, drivers may contact the police at telephone 192, the Ambulance Service at telephone 194, and Roadside Assistance at telephone 196.
