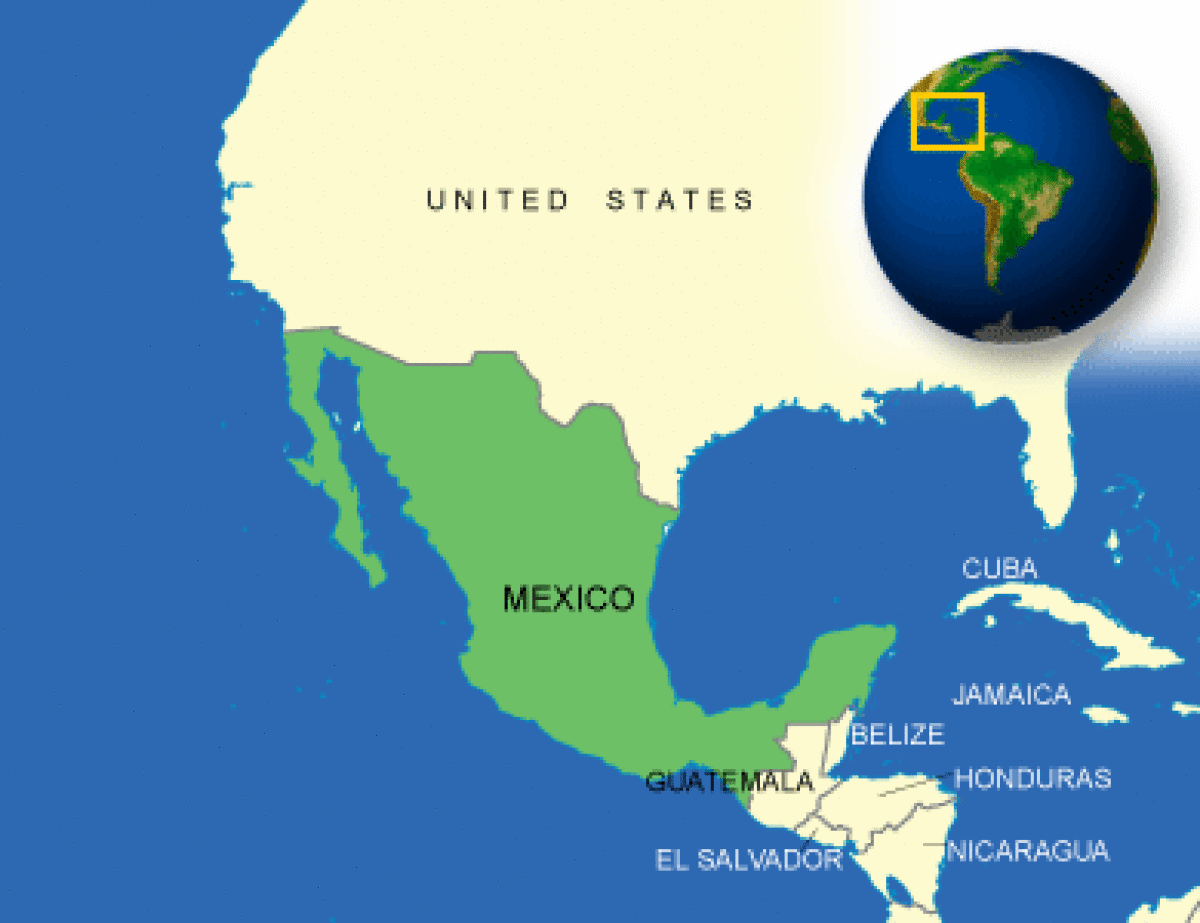
Where is Mexico located?
What countries border Mexico?
Mexico Weather
What is the current weather in Mexico?
Mexico Facts and Culture
What is Mexico famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Generally, Mexicans feel individuals are more important than schedules. The Mexican people are generally proud of their country. A wealthy... More
- Family: Mexican families are usually large (three or more children). Families that live in urban areas usually have smaller families. ... More
- Personal Apperance: Most Mexicans wear clothing that is also common in other Western countries, especially in urban areas. But there are also... More
- Recreation: Children love to play Soccer (Futbol) and you can see them in schools, streets, and parks. Also, but to a... More
- Diet: Staple foods include corn, beans, rice, and chillies. They are combined with spices, vegetables, and meats or fish in daily... More
- Food and Recipes: When eating, both hands are kept above the table. Guests do not leave directly after the meal but stay for... More
- Visiting: Mexicans are very accommodating. Visitors are usually welcomed and served refreshments even though they arrive unannounced. It is impolite to... More
- Dating: When dating, a young man frequently meets a young woman at a prearranged place, rather than at her home. Parental... More
Mexico Facts
What is the capital of Mexico?
| Capital | Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico) |
| Government Type | federal presidential republic |
| Currency | Mexican Peso (MXN) |
| Total Area |
758,445 Square Miles 1,964,375 Square Kilometers |
| Location | North America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, between Belize and the United States and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Guatemala and the United States |
| Language |
Spanish only 92.7%, Spanish and indigenous languages 5.7%, indigenous only 0.8%, unspecified 0.8% Note: indigenous languages include various Mayan, Nahuatl, and other regional languages |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $18,500.00 (USD) |
Mexico Demographics
What is the population of Mexico?
| Ethnic Group - note | Mexico does not collect census data on ethnicity |
| Ethnic Groups | Mestizo (Indigenous-Spanish) 62%, predominantly Indigenous 21%, Indigenous 7%, other 10% (mostly European) |
| Languages | Spanish only 93.8%, Spanish and indigenous languages 5.4%, indigenous only 0.6%, unspecified 0.2%; note - indigenous languages include various Mayan, Nahuatl, and other regional languages |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Mexican(s) adjective: Mexican |
| Population | 130,739,927 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.72% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 22.281 million MEXICO CITY (capital), 5.420 million Guadalajara, 5.117 million Monterrey, 3.345 million Puebla, 2.626 million Toluca de Lerdo, 2.260 million Tijuana |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 81.6% of total population rate of urbanization: 1.4% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 63,899,138 female: 66,840,789 |
Mexico Government
What type of government does Mexico have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Claudia SHEINBAUM Pardo (since 1 October 2024) head of government: President Claudia SHEINBAUM Pardo (since 1 October 2024) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a single 6-year term; election last held on 2 June 2024 (next to be held in 2030) election results: 2024: Claudia SHEINBAUM Pardo elected president; percent of vote - Claudia SHEINBAUM Pardo (MORENA) 59.4%, Xóchitl GÁLVEZ Ruiz (PAN) 27.9%, Jorge Álvarez MÁYNEZ (MC) 10.4%, other 2.3% 2018: Andrés Manuel LÓPEZ OBRADOR elected president; percent of vote - Andrés Manuel LÓPEZ OBRADOR (MORENA) 53.2%, Ricardo ANAYA Cortés (PAN) 22.3%, José Antonio MEADE Kuribreña (PRI) 16.4%, Jaime RODRÍGUEZ Calderón 5.2% (independent), other 2.9% 2012: Enrique PEÑA NIETO elected president; percent of vote - Enrique PEÑA NIETO (PRI) 38.2%, Andrés Manuel LÓPEZ OBRADOR (PRD) 31.6%, Josefina Eugenia VÁZQUEZ Mota (PAN) 25.4%, other 4.8% note: the president is both chief of state and head of government |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: not specified residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 16 September (1810) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest approved 5 February 1917 amendments: proposed by the Congress of the Union; passage requires approval by at least two thirds of the members present and approval by a majority of the state legislatures; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 16 September 1810 (declared independence from Spain); 27 September 1821 (recognized by Spain) |
Mexico Video
YouTube: Expoza Travel Mexico Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Mexico Geography
What environmental issues does Mexico have?
| Overview |
Mexico is located in North America. It borders the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico between Belize and the United States and borders the North Pacific Ocean between Guatemala and the United States. Its land mass covers approximately 1.9 million sq. km and has approximately 9,330 sq. km of beachfront property. With a climate that varies from tropical to desert, the terrain ranges from high rugged mountains to low coastal plains and high plateaus to desert. Its lowest elevation point is Laguna Salada at 10 meters. The highest point is the Volcano, Pico de Orizaba, at 5,700 meters. Mexican natural hazards include tsunamis on the Pacific coast, volcanoes and destructive earthquakes at the center and south, and hurricanes on the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean coasts. |
| Climate | With a climate that varies from tropical to desert, the terrain ranges from high rugged mountains to low coastal plains and high plateaus to desert. Mexican natural hazards include tsunamis on the Pacific coast, volcanoes and destructive earthquakes at the center and south, and hurricanes on the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean coasts. |
| Border Countries | Belize 250 km, Guatemala 962 km, United States 3,141 km |
| Environment - Current Issues |
Scarcity of hazardous waste disposal facilities; rural to urban migration; natural freshwater resources scarce and polluted in the north, inaccessible and poor quality in the center and extreme southeast; raw sewage and industrial effluents polluting rivers in urban areas; deforestation; widespread erosion; desertification; deteriorating agricultural lands; serious air and water pollution in the national capital and urban centers along US-Mexico border; land subsidence in Valley of Mexico caused by groundwater depletion Note: the government considers the lack of clean water and deforestation national security issues |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | High, rugged mountains; low coastal plains; high plateaus; desert |
Mexico Economy
How big is the Mexico economy?
| Economic Overview |
Mexico's $2.4 trillion economy – the 11th largest in the world - has become increasingly oriented toward manufacturing since the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) entered into force in 1994. Per capita income is roughly one-third that of the United States; income distribution remains highly unequal. Mexico has become the United States' second-largest export market and third-largest source of imports. In 2017, two-way trade in goods and services exceeded $623 billion. Mexico has free trade agreements with 46 countries, putting more than 90% of its trade under free trade agreements. In 2012, Mexico formed the Pacific Alliance with Peru, Colombia, and Chile. Mexico's current government, led by President Enrique PEÑA NIETO, has emphasized economic reforms, passing and implementing sweeping energy, financial, fiscal, and telecommunications reform legislation, among others, with the long-term aim to improve competitiveness and economic growth across the Mexican economy. Since 2015, Mexico has held public auctions of oil and gas exploration and development rights and for long-term electric power generation contracts. Mexico has also issued permits for private sector import, distribution, and retail sales of refined petroleum products in an effort to attract private investment into the energy sector and boost production. Since 2013, Mexico’s economic growth has averaged 2% annually, falling short of private-sector expectations that President PEÑA NIETO’s sweeping reforms would bolster economic prospects. Growth is predicted to remain below potential given falling oil production, weak oil prices, structural issues such as low productivity, high inequality, a large informal sector employing over half of the workforce, weak rule of law, and corruption. Mexico’s economy remains vulnerable to uncertainty surrounding the future of NAFTA — because the United States is its top trading partner and the two countries share integrated supply chains — and to potential shifts in domestic policies following the inauguration of a new president in December 2018. |
| Industries | Food and beverages, tobacco, chemicals, iron and steel, petroleum, mining, textiles, clothing, motor vehicles, consumer durables, tourism |
| Currency Name and Code | Mexican Peso (MXN) |
| Export Partners | United States 78% |
| Import Partners | United States 49.7%, China 14.9%, Japan 4.7% |
Mexico News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Mexico?
Source: Google News
Mexico Travel Information
What makes Mexico a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Mexico is a Spanish-speaking country about three times the size of Texas, consisting of 31 states and one federal district. The capital is Mexico City. Mexico has a rapidly developing economy, ranked by the World Bank as the thirteenth-largest in the world in terms of GDP. The climate ranges from tropical to arid, and the terrain consists of coastal lowlands, central high plateaus, deserts, and mountains of up to 18,000 feet.Many cities throughout Mexico are popular tourist destinations for U.S. citizens and in 2013 U.S. citizens continued to account for the largest foreign tourist population visiting Mexico. Travelers should note that location-specific information contained below is not confined solely to those cities identified, but can reflect conditions throughout Mexico. Although the majority of visitors to Mexico thoroughly enjoy their stay, a small number experience difficulties, and serious inconveniences.
Crime
Crime in Mexico continues to occur at a high rate and can often be violent. Street crime, ranging from pick-pocketing to armed robbery, is a serious problem in most major cities. Carjacking is also common (see the Travel Warning for Mexico on the U.S. Department of State website for more specific information). The homicide rates in parts of Mexico have risen sharply in recent years, driven largely by violence associated with transnational criminal organizations. The Mexican government makes a considerable effort to protect foreign visitors traveling to major tourist destinations. As a result, resort areas and tourist destinations in Mexico generally do not see the levels of violence and crime reported in the northern border region and in areas along major trafficking routes. Nevertheless, crime and violence are still serious problems. While most victims of violence are individuals associated with criminal activity, the security situation poses serious risks for anyone, including U.S. citizens. U.S. citizen victims of crime in Mexico are encouraged to report incidents to the nearest police headquarters and to the nearest U.S. consular office.The Mexican government has taken significant steps to strengthen its law enforcement capabilities at the federal level. However, state and local police forces continue to suffer from a lack of training and funding and are a weak deterrent to criminals, often armed with superior weapons. In some areas, municipal police are widely suspected of colluding with organized crime. In others, police officers are specifically targeted by criminal organizations. Because of the dangerous situation in which police officers operate, all travelers are advised to take a non-threatening posture when interacting with police and to cooperate with police instructions. We further advise travelers to avoid any areas where law enforcement operations are being carried out.
Pirated Merchandise: Counterfeit and pirated goods are widely available in Mexico. Their sale is largely controlled by organized crime. Purchase for personal use is not criminalized in Mexico; however, bringing these goods back to the United States may result in forfeitures and/or fines.
Personal Property: Travelers should always leave valuables and irreplaceable items in a safe place, or avoid bringing them at all. Visitors are encouraged to make use of hotel safes, avoid wearing expensive jewelry, clothing, or accessories, and carry only the cash or credit cards that will be needed on each outing. There have been significant numbers of incidents of pickpocketing, purse snatching, and hotel-room theft. Public transportation is a particularly popular place for pickpockets.
Do not leave valuables in rental vehicles, even when locked. Some travelers have had their passports stolen from their bags at airports. Remember to secure your passport within a zipper pocket or other safe enclosure so that it cannot be easily removed from your person or your luggage. Be vigilant of your passport even after passing through security and while waiting in a departure lounge to board your flight.
Business travelers should be aware that theft can occur even in apparently secure locations. Theft of items such as briefcases and laptops occurs frequently at Mexico City's Benito Juárez International Airport and at business-class hotels. Passengers arriving at Mexican airports who need to obtain pesos should use the exchange counters or ATMs in the arrival/departure gate area, where access is restricted, rather than changing money after passing through Customs, where they can be observed by criminals. A number of U.S. citizens have been arrested for passing on the counterfeit currency they had earlier received in change. If you receive what you believe to be a counterfeit banknote, bring it to the attention of Mexican law enforcement.
Personal Safety: Visitors should be aware of their surroundings at all times, even when in areas generally considered safe. Women traveling alone are especially vulnerable and should exercise caution, particularly at night. Some U.S Citizens have reported being sexually assaulted, robbed of personal property, or abducted and then held while their credit cards were used at various businesses or Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs). Individuals who have been targeted were often walking alone in isolated locations. Be very cautious in general when using ATMs in Mexico. If you must use an ATM, it should be accessed only during the business day at large protected facilities (preferably inside commercial establishments, rather than at glass-enclosed, highly visible ATMs on streets). Travelers to remote or isolated hunting or fishing venues should be aware that they may be some distance from appropriate medical services, banking facilities (such as ATMs), and law enforcement or consular assistance in an emergency.
Kidnapping: Kidnapping, including the kidnapping of U.S. citizens, continues to occur. So-called express kidnappings, i.e., attempts to get quick cash in exchange for the release of an individual, have occurred in almost all of Mexico's large cities and appear to target not only the wealthy but also the middle class. Kidnappings are largely crimes of opportunity, increasingly carried out by younger, less "professional" criminals, and are more violent than in the past. The National Citizens' Observatory, a think tank, reported on June 27, 2013, that kidnappings in Mexico increased by 17 percent in the first quarter of 2013 compared with the last quarter of 2012. The Mexican government had reported a decline in kidnappings until it stopped publishing statistics on this category of crime in April 2013. Review the sections above on personal property and personal safety for common sense actions you can take to reduce the risk of becoming a victim.
A common scam throughout Mexico is ‘virtual' kidnapping, a confidence scam in which a telephone caller contacts a family member of an alleged victim, typically speaking in a distraught voice in a ploy to elicit information about a family member and then use this knowledge to demand ransom for the release of the alleged victim. Other types of ‘virtual' kidnappings include communicating via text message only from stolen or lost cell phones, or convincing individuals to isolate themselves in an effort to extort money from their families. Information that can be used against victims may also be obtained from social networking websites. Calls are often placed by prison inmates using smuggled cellular phones. In the event of such a call, it is important to stay calm, as the vast majority of these calls are hoaxes. Do not reveal any personal information and try to speak with the victim to corroborate his/her identity. Any kidnapping, real or virtual, should be reported to the police as well as to the Embassy or nearest consulate.
Credit/Debit Card "Skimming": Exercise caution when utilizing credit or debit cards. There have been reports of instances in which U.S. citizens in Mexico have had their card numbers "skimmed" and the money in their debit accounts stolen or their credit cards fraudulently charged. ("Skimming" is the theft of credit card information by an employee of a legitimate merchant or bank, manually copying down numbers or using a magnetic stripe reader, or using a camera and skimmer installed in an ATM machine.) In addition to skimming, the risk of physical theft of credit or debit cards also exists. To prevent such theft, the Embassy recommends that travelers keep close track of their personal belongings and that they only carry what they need. Most restaurants and other businesses will bring the credit card machine to your table so that you can keep the card in your possession at all times. If travelers choose to use credit cards, they should regularly check their account status to ensure there are no unauthorized transactions.
Buses and Public Transportation: Whenever possible, visitors should travel by bus only during daylight hours and only by first-class conveyance. Although there have been several reports of bus hijackings and robberies on toll roads, buses on toll roads have experienced a markedly lower rate of incidents than (second and third-class) buses that travel the less secure "free" highways. Although the police have made progress in bringing this type of crime under control, armed robberies of entire busloads of passengers still occur, including recent armed robberies of local commuter buses traveling within Mexico City. There was one recent incident involving the placement of contraband under a bus seat of an unwitting U.S. citizen passenger. Be sure to check around and under your seat and immediately report any items that do not belong to you. Metro (subway) robberies are frequent in Mexico City, especially during peak travel times. If riding the metro or the city bus system, U.S. citizens should take extreme care with valuables and belongings.
Taxis: Robberies and assaults on passengers in "libre" taxis (that is, taxis not affiliated with a taxi stand) are frequent and violent in Mexico, with passengers subjected to beating, shooting, and sexual assault. U.S. citizens visiting Mexico should avoid taking any taxi not summoned by telephone or contacted in advance. When in need of a taxi, telephone a radio taxi or "sitio" (regulated taxi stand – pronounced "C-T-O"), and ask the dispatcher for the driver's name and the taxi's license plate number. Ask the hotel concierge or other responsible individual to write down the license plate number of the cab you are taking. Avoid "libre" taxis and the Volkswagen beetle taxis altogether. Although "libre" taxis are more convenient and less expensive, these are not as well regulated, may be unregistered, and are potentially more dangerous. U.S. Embassy employees in Mexico City are prohibited from using "libre" taxis, or any taxis hailed on the street, and are authorized to use only "sitio" taxis.
Passengers arriving at any airport in Mexico should take only authorized airport taxis after pre-paying the fare at one of the special booths located and well-publicized inside the airport.
Harassment/Extortion: In some instances, U.S. citizens have become victims of harassment, mistreatment, and extortion by alleged Mexican law enforcement, immigration, and other officials. Mexican authorities have cooperated in investigating such cases, but one must have the officer's name, badge number, and patrol car number to pursue a complaint effectively. Please note this information if you have a problem with the police or other officials. In addition, tourists should be wary of persons representing themselves as police officers or immigration, or other officials. When in doubt, ask for identification. Be aware that offering a bribe to a public official to avoid a ticket or other penalty is a crime in Mexico.
One extortion technique, known as the " grandparent scam ", involves calls placed by persons alleging to be attorneys or U.S. Government employees claiming that a person's relative – nearly always a purported grandchild - has been in a car accident in Mexico and has been arrested/detained. The caller asks for a large sum of money to ensure the subject's release. When the recipient of the call checks on their family member, they discover that the entire story is false. If the alleged detainee cannot be located in the U.S. and the family has reason to believe that the person did, in fact, travel to Mexico, contact the U.S. Embassy or nearest U.S. Consulate for assistance in determining if they have been detained by authorities. Further information on international financial scams is available on our website.
Beware of possible scams involving inflated prices for tourist-related goods and services and avoid patronizing restaurants and other service providers that do not have clearly listed prices. You should check with your hotel for the names of reputable establishments and service providers in the area. When using credit cards for payment you should try to maintain direct visibility of the person swiping the card in the machine to protect against credit card skimming.
Sexual Assault: Rape and sexual assault continue to be serious problems in resorts and other areas. Many of these incidents occur at night or during the early morning hours, in hotel rooms, or on deserted beaches. Acquaintance rape is a serious problem. Hotel workers, taxi drivers, and security personnel have been implicated in many cases. Women should avoid being alone, particularly in isolated areas and at night. It is imperative that victims file a police report, which should include a rape "kit" exam, against the perpetrator(s) as soon as possible at the nearest police station. There have been several cases where the victim traveled back to the U.S. without filing a police report or undergoing a rape exam; their attempts to document their case, later on, did not carry weight with local Mexican authorities.
Some bars and nightclubs, especially in resort cities such as Cancún, Acapulco, Mazatlán, Cabo San Lucas, and Tijuana, can be havens for drug dealers and petty criminals. Interaction with such individuals may put a traveler at risk. There have been instances of contamination or drugging of drinks to gain control over the patron.
See the information under "Special Circumstances" below regarding Spring Break in Mexico if you are considering visiting Mexican resort areas between February and April when thousands of U.S. college students traditionally arrive in those areas. Additional information designed specifically for traveling students is also available on the U.S. goverment's Students Abroad website.
Transnational Crime in Mexico: Mexican transnational criminal organizations (TCOs) are engaged in a violent struggle to control trafficking routes and other criminal activity. Recent attacks and persistent security concerns have prompted the U.S. Embassy to urge U.S. citizens to defer nonessential travel to certain areas in Mexico, and to advise U.S. citizens residing or traveling in those areas to exercise extreme caution. For updated and more detailed information on these areas and the threats involved, please refer to the Travel Warning for Mexico on the U.S. State Department's website.
TCOs have increasingly targeted unsuspecting individuals, who cross the border on a regular and predictable basis traveling between known destinations, as a way to transport drugs to the U.S. They affix drugs to the undercarriage of the traveler's car while it is parked in Mexico. Once in the U.S., members of the organization remove the packages while the vehicle is unattended. If you are a frequent border crosser, you should vary your routes and travel times as well as closely monitor your vehicle to avoid being targeted.
Criminal Penalties
While in a foreign country, an individual is subject to that country's laws and regulations, which can differ significantly from those in the United States – and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. The trial process and typical investigation/prosecution timeline in Mexico are significantly different and longer from that in the United States, and procedures may vary from state to state. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Mexican laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Mexico are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. If you break local laws in Mexico, your U.S. citizenship will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is illegal wherever you go. If arrested in Mexico, a U.S. citizen must go through the foreign legal process including possible charge or indictment, prosecution, possible conviction and sentencing, and any appeals process. Within this framework, U.S. consular officers provide certain services to U.S. citizens and their families, including information about local attorneys, and advocacy to ensure fair and humane treatment.Sexual Crimes: Sexual exploitation of children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. Soliciting the sexual services of a minor is illegal in Mexico, and is punishable by imprisonment. The Mexican government has announced an aggressive program to discourage sexual tourism. Police authorities in the state of Baja California recently began enforcement of anti-pedophile legislation.
Firearms Penalties: Illegal firearms trafficking from the United States into Mexico is a major problem and the Mexican government has strict laws prohibiting the importation of weapons. The Department of State warns all U.S. citizens against taking any firearm or ammunition into Mexico. Entering Mexico with a firearm, certain types of knives, or even a single round of ammunition is illegal, even if the weapon or ammunition is taken into Mexico unintentionally. The Mexican government strictly enforces laws restricting the entry of firearms and ammunition along all land borders and at airports and seaports and routinely x-rays all incoming luggage. U.S. citizens entering Mexico with a weapon or any amount of ammunition at all, even accidentally, generally are detained for at least a few days which can result in arrests, convictions, and long prison sentences. Travelers are strongly advised to thoroughly inspect all belongings prior to travel to Mexico to avoid the accidental import of ammunition or firearms. For more information visit the websites of the Mexican Secretary of Defense and Mexican Customs.
The process for temporarily importing a hunting weapon or ammunition into Mexico is complicated and, if handled incorrectly can result in imprisonment and confiscation of the weapon and any ammunition. The U.S. Embassy in Mexico recommends prospective hunters obtain the services of a licensed shooting or hunting club for help in importing any firearm or ammunition, which require separate permits. Prohibited weapons and calibers are all those identified by Mexican law as reserved for "the exclusive use of the Mexican military." These prohibited weapons and calibers include full-auto and semi-auto handguns larger than .380, revolvers .357 Magnum and larger, rifles larger than .30 caliber, and shotguns larger than 12ga or with a barrel shorter than 25 inches. Allowed handgun calibers are .380 auto, .38, and .22. Allowed long guns are rifles no larger than .30 caliber, and 12-, 20-, and 410-gauge shotguns with barrels longer than 25 inches. For more information about importing hunting weapons or ammunition into Mexico, contact the ANGADI (Asociación Nacional de Ganaderos Diversificados Criadores de Fauna) at info@anggadi.org.mx.
Vessels entering Mexican waters with firearms or ammunition on board must have a permit previously issued by the Mexican Embassy or a Mexican consulate. Mariners do not avoid prosecution by declaring their weapons at the port of entry. Before traveling, mariners who have obtained a Mexican firearm permit should contact Mexican port officials to receive guidance on the specific procedures used to report and secure weapons and ammunition.
Drug Penalties and Prescription Medications: Penalties for drug offenses are strict, and convicted offenders can expect large fines and jail sentences of up to 25 years. The purchase of controlled medications requires a prescription from a licensed Mexican physician. Some Mexican doctors have been arrested for writing prescriptions without due cause. In those instances, U.S. citizens who purchased the medications have been held in jail for months waiting for the Mexican judicial system to make a decision on their case. Marijuana prescriptions (or "medical marijuana") are not valid in Mexico. Individuals in possession of a state medical marijuana license should remember that the license is not valid outside of the borders of that state, and bringing marijuana into Mexico – even if it is accompanied by a prescription – is considered international drug trafficking, a serious federal offense. The Mexican list of controlled medications differs from that of the United States, and Mexican public health laws concerning controlled medications are unclear and often enforced selectively. To determine whether a particular medication is controlled in Mexico or requires a prescription from a Mexican doctor for purchase, please consult the website of the Mexican Federal Commission for Protection against Health Risks (Comisión Federal para la Protección contra Riesgos Sanitarios - COFEPRIS).
The U.S. Embassy cautions that possession of any amount of prescription medication brought from the United States, including medications to treat HIV, and psychotropic drugs such as Valium, can result in arrest if Mexican authorities suspect abuse, or if the quantity of the prescription medication exceeds the amount required for several days' use. Individuals are advised to carry a copy of the prescription. If significant quantities of the medication are required, individuals should carry a doctor's letter explaining that the quantity of medication is appropriate for their personal medical use.
Buying Prescription Drugs: Any drug classified by the Mexican government as a controlled medicine, including antibiotics, cannot be purchased in Mexico without a Mexican prescription. The prescription must be written by a physician who is federally registered. Purchasing a controlled medicine without a valid prescription in Mexico is a serious crime for both the purchaser and the seller. Purchasing a controlled medicine with a U.S. prescription is not sufficient and is also illegal, regardless of what the Mexican pharmacy may be willing to sell to the purchaser. By law, Mexican pharmacies cannot honor foreign prescriptions. U.S. citizens have been arrested and their medicines confiscated by authorities when their prescriptions were written by a licensed U.S. physician and filled by a licensed Mexican pharmacist. There have been cases of U.S. citizens buying prescription drugs in border cities only to be arrested soon after or have money extorted by criminals impersonating police officers. Those arrested are often held for the full 48 hours allowed by Mexican law without charges being filed, then released. During this interval, the detainees are often asked for bribes or are solicited by attorneys who demand large fees to secure their release, which will normally occur without any intercession as there are insufficient grounds to bring criminal charges against the individuals. In addition, U.S. law enforcement officials believe that as many as 25 percent of the medications available in Mexico are counterfeit and substandard. Such counterfeit medications may be difficult to distinguish from real medications and could pose serious health risks to consumers. The importation of prescription drugs into the United States can be illegal in certain circumstances. U.S. law generally permits persons to enter the United States with only an immediate supply (i.e., enough for about one month) of prescription medication.
Criminal Penalties for Possession: Mexico has new laws that have been touted by the press as making the possession of drugs for personal use legal. Many of the allowable amounts are much less than what has been reported by the news media. Additionally, the new drug laws include stiffer penalties for many drug offenses, and the sale and distribution of drugs continues to be illegal in Mexico. U.S. citizens traveling to Mexico should review this information to avoid possible prosecution under Mexican law.
Importing Medicines into Mexico: Medications for personal use are not subject to duty when hand-carried into Mexico. Individuals are advised to carry a copy of their prescriptions in the event they are asked to prove that the medicines are for personal use. To ship (import) prescription medication into Mexico for personal use, a foreigner must obtain a permit from the Mexican Health Department prior to importing the medicine into Mexico. For a fee, a customs broker can process the permit before the Mexican authorities on behalf of an individual. If using the services of a customs broker, it is advisable to agree upon the fees before telling the broker to proceed. Current listings of local customs brokers (agencias aduanales) are available in the Mexico City yellow pages.
Arrests and Notifications: The Mexican government is required by international law to notify the U.S. Embassy or the nearest U.S. consulate promptly when a U.S. citizen is arrested if the arrestee so requests. In practice, however, depending on where the arrest takes place, this notification can be months late, or may never occur at all, limiting the assistance the U.S. Government can provide. U.S. citizens should promptly identify themselves as such to the arresting officers and should request that the Embassy or nearest consulate be notified immediately. Also see the "grandparent scam," described above in the Harassment/Extortion section, in which a U.S. citizen is alleged to be detained by authorities in Mexico in an attempt to get relatives in the United States to wire money. Confirm an alleged detention or arrest with the Embassy or consulate before taking any other action.
Prison Facilities: Prison conditions in Mexico can be extremely poor. In many facilities, food is insufficient in both quantity and quality, and prisoners must pay for adequate nutrition from their own funds. Many Mexican prisons provide sub-standard medical care, and prisoners with urgent medical conditions may receive only a minimum of attention. U.S. citizens who are incarcerated in Mexico are sometimes forced to pay hundreds and even thousands of dollars in "protection money" to fellow prisoners. From 2009 through 2012, 29 U.S. citizen deaths in Mexican prisons have been reported, including at least 9 apparent homicides.
Prisoner Treatment/Interrogations: Mexico is a party to several international anti-torture conventions, and both the Mexican Constitution and Mexican law prohibit torture. However, U.S. citizens have reported being beaten, sexually assaulted, and subjected to severe interrogation techniques while in the custody of Mexican security forces. In its annual report, Mexico's National Commission on Human Rights documents cases of Mexican security forces seeking to obtain information through torture. Convictions for torture or for any alleged abuses by security forces are rare.
Languages
Spanish only 93.8%, Spanish and indigenous languages 5.4%, indigenous only 0.6%, unspecified 0.2%; note - indigenous languages include various Mayan, Nahuatl, and other regional languages
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical care can be found in major cities. Excellent health facilities are available in Mexico City, but training and availability of emergency responders may be below U.S. standards. Care in more remote areas is limited. Standards of medical training, patient care, and business practices vary greatly among medical facilities in beach resorts throughout Mexico. In recent years, some U.S. citizens have complained that certain healthcare facilities in beach resorts have taken advantage of them by overcharging or providing unnecessary medical care. A significant number of complaints have been lodged against some of the private hospitals in the Cabo San Lucas area, including complaints about price gouging and various unlawful and/or unethical pricing schemes and collection measures. Additionally, U.S. citizens should be aware that many Mexican facilities require payment ‘up front' prior to performing a procedure. Hospitals in Mexico do not accept U.S. domestic health insurance or Medicare/Medicaid and will expect payment via cash, credit, debit card, or bank transfer. Elective medical procedures may be less expensive than in the United States, but providers may not adhere to U.S. standards. Additionally, visitors are cautioned that facilities may lack access to sufficient emergency support. The U.S. Embassy encourages visitors to obtain as much information about the facility and the medical personnel as possible when considering surgical or other procedures, and when possible patients should travel with a family member or another responsible party.In addition to other publicly available information, U.S. citizens may click on the map of U.S. consular operations in Mexico to link to the nearest Embassy or consulate's website which contains lists of doctors or hospitals. Before beginning international travel, U.S. citizens may wish to obtain emergency medical evacuation insurance, check with their healthcare providers to see if the cost of medical treatment outside the U.S. is covered, and inquire about the reimbursement process.
Procedures after the Death of a U.S. Citizen in Mexico: When a United States citizen dies in Mexico, it is critical that the next of kin act promptly to contract with a Mexican funeral home to help carry out funeral arrangements, including the return of the deceased's remains to the U.S., if desired. The next of kin must also provide documents establishing the identity of both the next of kin and the decedent. Common documents used for this purpose are passports, and government-issued photo identification such as a driver's license, birth certificates, and marriage certificates. The next of kin is responsible for all costs associated with the funeral home, and/or shipment of remains or personal effects.
The Embassy or Consulate in the district where the U.S. citizen died can provide a list of funeral homes and location-specific requirements in the Consular District. Although Embassy staff members may not make funeral and other arrangements, staff can help locate and notify the next of kin of their loved one's passing, inform families about the Mexican legal requirements for claiming a loved one's remains, and assist in shipping personal effects to the United States. The U.S. Embassy and its Consulates also prepare a Consular Report of Death of a U.S. Citizen Abroad, based on the local Mexican death certificate. The Consular Report of Death Abroad may be used in most legal proceedings in the United States as proof of death overseas. To prepare this document, Embassy staff will need original evidence of U.S. citizenship of the decedent and the original Mexican death certificate.
Water Quality: In many areas in Mexico, tap water is unsafe and should be avoided. Bottled water and beverages are safe, although, visitors should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Ice may also come from tap water and should be avoided. Visitors should exercise caution when buying food or beverages from street vendors.
The quality of water along some beaches in or near Acapulco or other large coastal communities may be unsafe for swimming because of contamination. Swimming in contaminated water may cause diarrhea and/or other illnesses. Mexican government agencies monitor water quality in public beach areas but their standards and sampling techniques may differ from those in the United States.
Altitude: In high-altitude areas such as Mexico City (elevation 7,600 feet or about 1/2 mile higher than Denver, Colorado), most people need a short adjustment period. Symptoms of a reaction to high altitude include a lack of energy, shortness of breath, occasional dizziness, headache, and insomnia. Those with heart problems should consult their doctor before traveling. Air pollution in Mexico City and Guadalajara is severe, especially from December to May, and combined with high altitude could affect travelers with underlying respiratory problems.
Safety and Security
All travelers to Mexico should review the Department of State's Travel Warning for Mexico which provides updated and detailed information about security issues affecting the country on a state-by-state basis. Millions of U.S. citizens visit Mexico safely each year. However, crime and violence, much of it fueled by transnational criminal activity, affect many parts of the country, including both urban and rural areas. Visitors should remain alert and be aware of their surroundings at all times, particularly when visiting areas identified in the Travel Warning with special advisories. In its efforts to combat violence, the Mexican government has deployed federal police and military troops to various parts of the country. Government checkpoints, often staffed by military personnel, have been erected in many parts of the country, especially, but not exclusively near the border. U.S. citizens are advised to cooperate with personnel at government checkpoints when traveling on Mexican highways.Demonstrations are common and occur in all parts of the country, both urban and rural. Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence. Demonstrators in Mexico may block traffic on roads, including major arteries, or take control of toll booths on highways. U.S. citizens are urged to avoid areas of demonstrations and to exercise caution if in the vicinity of any protests. Travelers should avoid participating in demonstrations and other activities that might be deemed political by the authorities as the Mexican Constitution prohibits political activities by foreigners; such actions may result in detention and/or deportation.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
Continued concerns regarding criminal activity on highways along the Mexican border (which includes placement of illegal checkpoints and the murder of persons who did not stop and/or surrender their vehicles) have prompted the U.S. Mission in Mexico to impose certain restrictions on U.S. government employees transiting the area. Effective July 15, 2010, Mission employees and their families may not travel by vehicle across the U.S.-Mexico border to or from any post in the interior of Mexico. This policy also applies to employees and their families transiting Mexico to and from Central American posts. This policy does not apply to employees and their family members assigned to border posts (Tijuana, Nogales, Ciudad Juarez, Nuevo Laredo, and Matamoros), although they may not drive to interior posts as outlined above. Travel is permitted between Hermosillo and Nogales, but not permitted from Hermosillo to any other interior posts.While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Mexico is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance. Public transportation vehicles, specifically taxis and city buses, often do not comply with traffic regulations, including observing speed limits and stopping at red lights.
Driving and Vehicle Regulations: U.S. driver's licenses are valid in Mexico. Mexican law requires that only owners drive their vehicles, or that the owner is inside the vehicle. If not, the vehicle may be seized by Mexican customs and will not be returned under any circumstances. The Government of Mexico strictly regulates the entry of vehicles into Mexico. Traffic laws in Mexico are sporadically enforced and therefore often ignored by drivers, creating dangerous conditions for drivers and pedestrians. Driving under the influence of alcohol is illegal in all parts of Mexico. Using a mobile device (such as a cell phone) is also prohibited while driving in many parts of Mexico, including Mexico City, and violators may be fined.
Insurance: Mexican insurance is required for all vehicles, including rental vehicles. Mexican auto insurance is sold in most cities and towns on both sides of the border. U.S. automobile liability insurance is not valid in Mexico, nor is most collision and comprehensive coverage issued by U.S. companies. Motor vehicle insurance is considered invalid in Mexico if the driver is found to be under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Road Emergencies and Automobile Accidents: Motor vehicle accidents are a leading cause of death for U.S. citizens in Mexico. Motorists should exercise caution and remain alert on all Mexican roads. If you have an emergency while driving, the equivalent of "911" in Mexico is "066", but this number is not always answered. If you are driving on a toll highway (or "cuota"), or any other major highway, you may contact the Green Angels (Angeles Verdes), a fleet of trucks with bilingual crews. The Green Angels may be reached directly at (01) (55) 5250-8221. If you are unable to call them, pull off to the side of the road and lift the hood of your car; chances are that they will find you.
If you are involved in an automobile accident, you may be taken into police custody until it can be determined who is liable and whether you have the ability to pay any penalty. If you do not have Mexican liability insurance, you may be prevented from departing the country even if you require life-saving medical care, and you are almost certain to spend some time in jail until all parties are satisfied that responsibility has been assigned and adequate financial satisfaction received. Drivers may face criminal charges if injuries or damages are serious.
Road Safety: Avoid driving on Mexican highways at night. Even multi-lane expressways in Mexico often have narrow lanes and steep shoulders. Single-vehicle rollover accidents involving U.S. citizens are common, often resulting in death or serious injury to vehicle occupants. Use extreme caution when approaching towns, driving on curves, and passing large trucks. All vehicle occupants should use seatbelts at all times. Criminal assaults have occurred on highways throughout Mexico; travelers should exercise extreme caution at all times and should use toll ("cuota") roads rather than the less secure "free" ("libre") roads whenever possible. Always keep car doors locked and windows up while driving, whether on the highway or in town. While in heavy traffic, or stopped in traffic, leave enough room between vehicles to maneuver and escape, if necessary. In addition, U.S. citizens should not hitchhike or accept rides from or offer rides to strangers anywhere in Mexico. Please refer to the Road Safety Overseas section on the U.S. State Department website for more information.
Vehicular traffic in Mexico City is restricted in order to reduce air pollution. The restriction is based on the last digit of the vehicle license plate. This applies equally to permanent, temporary, and foreign (U.S.) plates. For additional information, refer to the Hoy No Circula website (Spanish only) maintained by the Mexico City government.
In recent years, moped rentals have become very widespread in Cancún and Cozumel, and the number of serious moped accidents has risen accordingly. Most operators carry no insurance and do not conduct safety checks. The U.S. Embassy recommends avoiding operators who do not provide a helmet with the rental. Some operators have been known to demand fees many times in excess of damages caused to the vehicles, even if renters have purchased insurance in advance. Vacationers at other beach resorts have encountered similar problems after accidents involving rented jet skis. There have been cases of mobs gathering to prevent tourists from departing the scene and to intimidate them into paying exorbitant damage claims.
For additional information in English concerning Mexican driver's permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, mandatory insurance, etc., please telephone the Mexican Secretariat of Tourism (SECTUR) at 1-800-44-MEXICO (639-426). Travelers can also consult MexOnline for further information regarding vehicle inspection and importation procedures. For detailed information in Spanish only, visit Mexican Customs' website Importación Temporal de Vehículos ("Temporary Importation of Vehicles"). Travelers are advised to consult with the Mexican Embassy or the nearest Mexican consulate in the United States for additional, detailed information prior to entering Mexico.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
