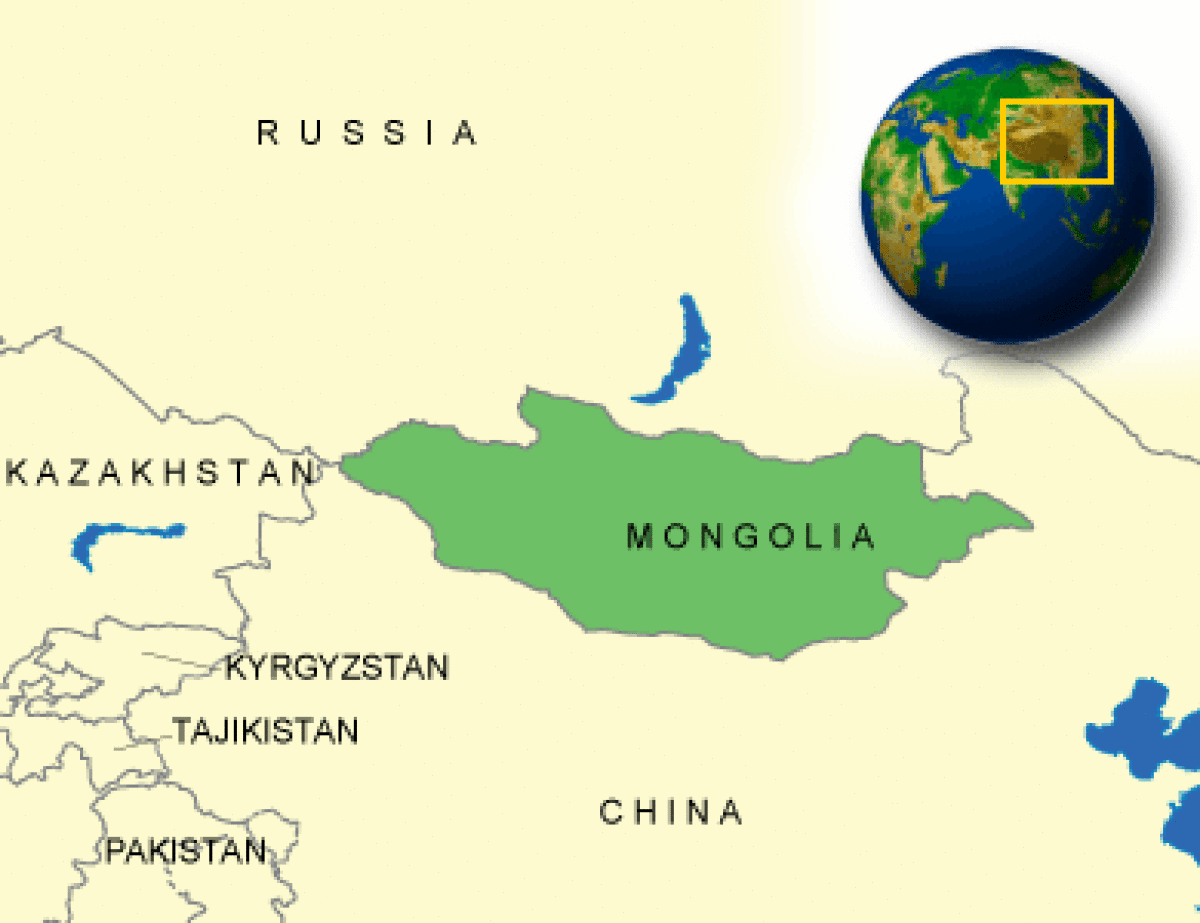
Where is Mongolia located?
What countries border Mongolia?
Mongolia Weather
What is the current weather in Mongolia?
Mongolia Facts and Culture
What is Mongolia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Most people are working to earn money. If people have money, they can put food on the table and gain... More
- Family: Many people are changing from the traditional nomadic lifestyle to city living. About half of the country's population now lives... More
- Personal Apperance: On a typical day, Mongolians wear what Europeans and Americans wear, jeans, jacket, sweater, and t-shirt. Mongolian traditional dress clothes... More
- Recreation: The three main sports are horse racing, archery and wrestling. The archery target is made of woven leather rings. Men... More
- Diet: Traditional Mongolian diet is heavily influenced by the nomadic lifestyle and the harsh climate of the region. Here are some... More
- Food and Recipes: A typical family eats three meals a day: breakfast, lunch, and dinner. There are no standard mealtimes for most people.... More
- Visiting: When guests leave Mongolians shake hands and if they know them well, they hug and kiss them. More
Mongolia Facts
What is the capital of Mongolia?
| Capital | Ulaanbaatar |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Mongolia Tughrik (MNT) |
| Total Area |
603,905 Square Miles 1,564,116 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern Asia, between China and Russia |
| Language | Khalkha Mongol 90%, Turkic, Russian |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $12,500.00 (USD) |
Mongolia Demographics
What is the population of Mongolia?
| Ethnic Groups | Mongol (predominantly Khalkha) 85%, Turkic (of which Kazakh is the largest group) 7%, Tungusic 4.6%, other (including Chinese and Russian) 3.4% |
| Nationality Noun | Mongolian(s) |
| Population | 3,168,026 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.44% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | ULAANBAATAR (capital) 1.184 million |
| Urban Population | 68.500000 |
Mongolia Government
What type of government does Mongolia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Ukhnaagiin KHURELSUKH (since 25 June 2021) head of government: Prime Minister Luvsannamsrai OYUN-ERDENE (since 27 January 2021); Deputy Prime Ministers Sainbuyen AMARSAIKHAN (since 8 September 2022) and Chimed KHURELBAATAR (since 5 January 2023) cabinet: directly appointed by the prime minister following a constitutional amendment ratified in November 2019; prior to the amendment, the cabinet was nominated by the prime minister in consultation with the president and confirmed by the State Great Hural (parliament) elections/appointments: presidential candidates nominated by political parties represented in the State Great Hural and directly elected by simple majority popular vote for one 6-year term; election last held on 9 June 2021 (next to be held in 2027); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition is usually elected prime minister by the State Great Hural election results: 2021: Ukhnaagiin KHURELSUKH elected president in first round; percent of vote - Ukhnaagiin KHURELSUKH (MPP) 68%, Dangaasuren ENKHBAT (RPEC) 20.1%, Sodnomzundui ERDENE (DP) 6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: both parents must be citizens of Mongolia; one parent if born within Mongolia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Naadam (games) holiday (commemorates independence from China in the 1921 Revolution), 11-15 July; Constitution Day (marks the date that the Mongolian People's Republic was created under a new constitution), 26 November (1924) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 13 January 1992, effective 12 February 1992 amendments: proposed by the State Great Hural, by the president of the republic, by the government, or by petition submitted to the State Great Hural by the Constitutional Court; conducting referenda on proposed amendments requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the State Great Hural; passage of amendments by the State Great Hural requires at least three-quarters majority vote; passage by referendum requires majority participation of qualified voters and a majority of votes; amended 1999, 2000, 2019, 2023; note - an amendment passed in a referendum held in May 2023 increased the seats in the State Great Hural from 76 to 126 |
| Independence | 29 December 1911 (independence declared from China; in actuality, autonomy attained); 11 July 1921 (from China) |
Mongolia Video
YouTube: Unesco Mongol Biyelgee: Mongolian traditional folk dance
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Mongolia Geography
What environmental issues does Mongolia have?
| Overview |
Mongolia is a large and sparsely populated country landlocked between China and Russia. Mongolia is the 6th largest country in Asia and 18th largest in the world. The capital, Ulaanbaatar, is over 4,000 feet above sea level. The country is divided into three basic zones: the Gobi, a vast, dry grassland in the east and south; the low Hangai mountains in the north and northwest; and the high Altai Mountains of the west and northwest. Mongolia’s most scenic lake is Lake Hovsgol located in the Altai, where elevations range up to 15,000 feet. There are three major river systems: the Tuul, which runs through Ulaanbaatar; the Orhon, which combines with the Tuul and flows into Lake Baikal in Russia; and the Selenge in the northeast. |
| Climate | Because of the elevation and distance from any ocean or sea, Mongolia has a harsh continental climate. Marked seasonal, even daily, changes in temperature, numerous high-pressure systems, and severe cold occur most of the year. A remarkably sunny country, Mongolia enjoys 250 sunny days a year, often with clear cloudless skies, making even the coldest temperatures more tolerable. |
| Border Countries | China 4,677 km, Russia 3,485 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | limited natural fresh water resources in some areas; the policies of former Communist regimes promoted rapid urbanization and industrial growth that had negative effects on the environment; the burning of soft coal in power plants and the lack of enforcement of environmental laws severely polluted the air in Ulaanbaatar; deforestation, overgrazing, and the converting of virgin land to agricultural production increased soil erosion from wind and rain; desertification and mining activities had a deleterious effect on the environment |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | vast semidesert and desert plains, grassy steppe, mountains in west and southwest; Gobi Desert in south-central |
Mongolia Economy
How big is the Mongolia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Despite its small population and landlocked geography, Mongolia's economy has seen significant growth and transformation in recent decades, driven primarily by its mining sector and strategic location as a gateway between Asia's economic powerhouses. The Mining Boom Mongolia's economy has been deeply influenced by its abundance of natural resources, particularly coal, copper, gold, and rare earth minerals. The mining sector has experienced a boom in recent years, attracting significant foreign investment and contributing substantially to the country's GDP. Projects such as the Oyu Tolgoi copper-gold mine, operated by multinational companies including Rio Tinto, have become major drivers of economic growth and export revenues. Challenges and Opportunities While the mining sector has propelled Mongolia's economic expansion, it also presents challenges and vulnerabilities. The country's heavy reliance on mineral exports makes its economy susceptible to fluctuations in global commodity prices. Moreover, issues such as environmental concerns, infrastructure deficits, and regulatory uncertainties have posed challenges to sustainable mining development. To mitigate these challenges and diversify its economy, Mongolia has been actively pursuing economic reforms and seeking to attract investment in other sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy. Efforts to improve infrastructure, enhance governance, and strengthen institutions are crucial for fostering a more resilient and inclusive economy. Strategic Positioning Mongolia's strategic location between China and Russia offers unique opportunities for trade and investment. As China continues to expand its Belt and Road Initiative, Mongolia stands to benefit from increased connectivity and trade linkages with its neighbors. Moreover, initiatives such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) and the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor provide avenues for regional cooperation and economic integration. Challenges Ahead Despite its economic potential, Mongolia faces several challenges on its path to sustainable development. Income inequality, especially between urban and rural areas, remains a pressing issue, requiring targeted policies to promote inclusive growth and poverty reduction. Moreover, the country's dependence on natural resources underscores the importance of prudent resource management, environmental protection, and diversification strategies. |
| Industries | construction materials; mining (coal, copper, molybdenum, fluorspar, and gold); oil; food and beverages; processing of animal products |
| Currency Name and Code | Mongolia Tughrik (MNT) |
| Export Partners | China 41.4%, US 31.7%, Russia 9.2%, South Korea 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Russia 34.4%, China 20.1%, South Korea 12.4%, Japan 6.2%, Germany 4.3%, Hong Kong 4.1% |
Mongolia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Mongolia?
Source: Google News
Mongolia Travel Information
What makes Mongolia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Mongolia is a vast country of mountains, lakes, deserts, and grasslands. It is approximately the size of Alaska. Since 1990, Mongolia has been successfully transitioning into a parliamentary democracy. Economic reforms continue, although the country’s development will depend on considerable infrastructure investment, particularly in the mining, energy, transportation, and communication sectors. You should be aware that shortcomings in these areas could affect your travel plans.
Crime
Street crime is common in Mongolia, particularly in Ulaanbaatar, the capital. Most of the street crime is non-violent, but violent incidents do occur regularly. The most common crimes against foreigners are pickpocketing and bag snatching. There are reports of organized groups operating in open areas, usually after dark, surrounding, grabbing, and choking an individual in order to search his or her pockets. Thieves have also cut victims’ bag straps and clothing in attempts to reach wallets, cell phones, and other valuables. If you detect pickpocket attempts, you should not confront the thieves, since they may become violent. It is best not to walk alone through Ulaanbaatar after dark.Inter-racial couples are targeted for assault. The perpetrators usually target foreign men with local women. These assaults range from organized attacks by nationalist groups to spontaneous incidents in bars.
Since the spring of 2010, the U.S. Embassy has received an increased number of reports of apparently xenophobic attacks against foreign nationals.These attacks occurred without provocation, and robbery was not the motive. Attackers targeted the victim(s) based solely on their ethnicity or perceived foreign nationality. Some of these attacks were directed against U.S. citizens.
Additionally, nationalist groups frequently mistake Asian-Americans for ethnic Chinese or Koreans and may attack without warning or provocation. Asian-Americans should exercise caution at all times when walking the streets of Ulaanbaatar.
In general, you should be extremely cautious at these locations:
Chinggis Khan International Airport in Ulaanbaatar: Organized groups frequently target tourists for robbery and pickpocketing at this airport.
The State Department Store and the area around the Circus: Organized pickpocket gangs target tourists at the entries/exits/elevators of the store and in surrounding areas, along Peace Avenue, and down to the Circus.
Naran Tuul Covered Market: Organized criminal groups target foreigners for robbery and pickpocketing.
You should also be careful in crowded public areas, such as open-air markets, the Central Post Office, and the Gandan Monastery.
In addition, you should be alert for potential criminal activity when you use public transportation or taxis. There have been several reports of foreigners being robbed and/or assaulted while riding in taxis. You may wish to ask your hotel, a restaurant, or store to make taxi arrangements for you. Also, you may wish to request that a native speaker write your destination address in Mongolian, since most cab drivers do not speak English. Private unmarked cars often act as taxis in Mongolia; their availability is high, but their consistency of performance, fare, and safety is low. You should not use unmarked taxis. If you find a cab driver whom you like (English speaker, trustworthy, clean car, etc.), request his mobile phone number for future use.
Crime rises sharply before, during, and after the Naadam Summer Festival in July, throughout the summer tourist season, and during and after Tsagaan Sar, the Winter Festival, in January or February.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegged items illegal in the United States, but you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Mongolia, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. Criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Mongolia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.If you are arrested in Mongolia, Mongolian authorities are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should ask the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. embassy of your arrest. You may need to make repeated requests to authorities to speak to a consular officer. Authorities may be unaware of your rights to consular access.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Mongolia are very limited and do not meet most Western standards, especially for emergency health care. Many brand-name Western medicines are unavailable. The majority of medical facilities are located in Ulaanbaatar and are extremely limited or non-existent outside of Ulaanbaatar. Specialized emergency care for infants and the elderly is not available. Doctors and hospitals usually expect immediate payment in cash for health services.Sanitation in some restaurants, particularly outside of Ulaanbaatar, is inadequate. Stomach illnesses are frequent. You should drink bottled water and use other routine safety measures to protect your health. Severe air pollution is a serious problem during the winter months, and travelers with breathing or other health problems should plan accordingly. Infectious diseases, such as plague and meningococcal meningitis, are present at various times of the year. Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Mongolia. For further information, please consult the CDC's information on TB . Local hospitals generally do not contact the Embassy about ill or injured U.S. citizens in their care. If you need assistance from the Embassy, you should ask the doctor or hospital to contact the U.S. Embassy in Ulaanbaatar. See our website for a list of medical facilities in Ulaanbaatar.
Safety and Security
There have been no significant acts of terrorism or extremism in Mongolia, and there are no regions of instability in the country. However, you are advised to avoid all protests, including political protests and street demonstrations that occur occasionally in Ulaanbaatar, since demonstrations may become violent at any time.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Mongolia, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Mongolia is provided for general reference only and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Driving in Ulaanbaatar can be extremely difficult due to poorly maintained streets, broken traffic lights, poor street lighting, a shortage of traffic signs, and undisciplined pedestrians. The knowledge and skills of the driving population have not kept pace with the dramatic growth in the number of automobiles on the streets in recent years. There are few paved roads outside of the capital and no street lights, and driving outside of Ulaanbaatar after dark is unsafe. For specific information concerning Mongolian drivers permits, vehicle inspection, road tax and mandatory insurance, contact the Embassy of Mongolia at 2833 M Street NW, Washington, DC 20007, telephone (202) 333-7117.
There are many metered taxis in Ulaanbaatar. There are a few car rental companies, but safety and maintenance standards are uncertain, so rental vehicles should be used with caution. Local tourist companies can provide cars with drivers. Public transportation within the capital is widespread, cheap, and generally reliable, but it is also extremely crowded, so pickpocketing can occur.
