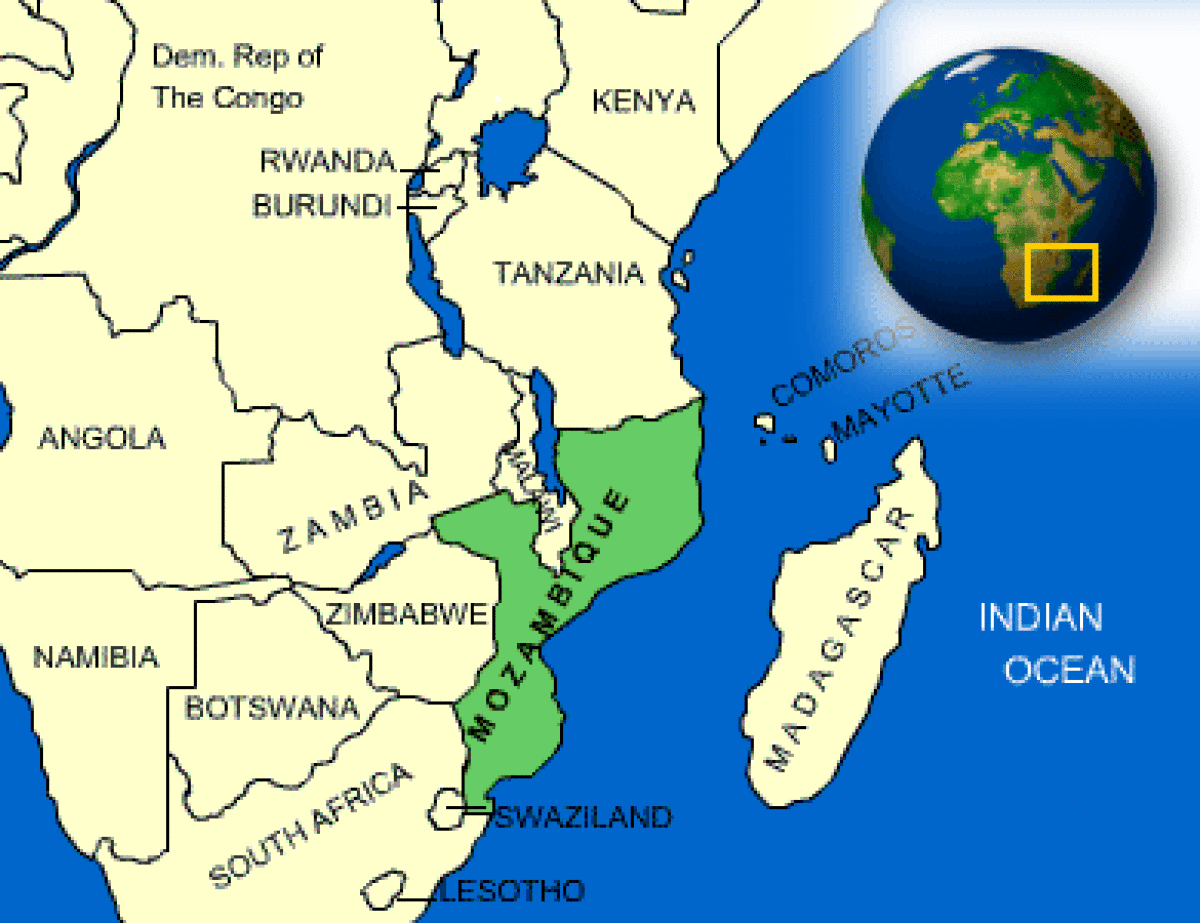
Where is Mozambique located?
What countries border Mozambique?
Mozambique Weather
What is the current weather in Mozambique?
Mozambique Facts and Culture
What is Mozambique famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Agriculture is the people's leading economic activity. Cashew trees and coconut palms grow throughout the country. Other farm products include... More
- Family: Mozambicans practice subsistence farming (farming that provides just enough for family needs). Men usually perform the initial plowing while women... More
- Personal Apperance: In Mozambique, clothing style can vary depending on region, climate, and occasion. Traditional attire often reflects the country's cultural diversity,... More
- Recreation: In Mozambique, recreation and sports are diverse and often reflect the country's cultural heritage, as well as its natural resources... More
- Diet: The diet in Mozambique is diverse and influenced by various factors such as geography, culture, and historical trade routes. It... More
- Food and Recipes: In Mozambique, like in many cultures, there are certain customs and etiquette practices associated with eating that reflect respect for... More
- Visiting: Understanding and respecting local customs when visiting people in Mozambique can enhance your cultural experience and strengthen your connections with... More
Mozambique Facts
What is the capital of Mozambique?
| Capital | Maputo |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Mozambican Metical (MZM) |
| Total Area |
308,641 Square Miles 799,380 Square Kilometers |
| Location | South-eastern Africa, bordering the Mozambique Channel, between South Africa and Tanzania |
| Language | Portuguese (official), indigenous dialects |
| GDP - real growth rate | 7% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $1,300.00 (USD) |
Mozambique Demographics
What is the population of Mozambique?
| Ethnic Groups | indigenous tribal groups 99.66% (Shangaan, Chokwe, Manyika, Sena, Makua, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08% |
| Nationality Noun | Mozambican(s) |
| Population | 30,098,197 |
| Population - note | note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.44% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MAPUTO (capital) 1.15 million; Matola 790,000 |
| Urban Population | 31.200000 |
Mozambique Government
What type of government does Mozambique have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Filipe Jacinto NYUSI (since 15 January 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Filipe Jacinto NYUSI (since 15 January 2015); Prime Minister Adriano Afonso MALEIANE (since 3 March 2022); note - President NYUSI removed Prime Minister Carlos Agostinho DO ROSARIO from office on 3 March 2022 as part of a cabinet reshuffle cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections/appointments: president elected directly by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for 2 consecutive terms); election last held on 15 October 2019 (next to be held on 9 October 2024); prime minister appointed by the president election results: 2019: Filipe NYUSI reelected president in first round; percent of vote - Filipe NYUSI (FRELIMO) 73.0%, Ossufo MOMADE (RENAMO) 21.9%, Daviz SIMANGO (MDM) 5.1% 2014: Filipe NYUSI elected president in first round; percent of vote - Filipe NYUSI (FRELIMO) 57.0%, Afonso DHLAKAMA (RENAMO) 36.6%, Daviz SIMANGO (MDM) 6.4% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Mozambique dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 25 June (1975) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1975, 1990; latest adopted 16 November 2004, effective 21 December 2004 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one third of the Assembly of the Republic membership; passage of amendments affecting constitutional provisions, including the independence and sovereignty of the state, the republican form of government, basic rights and freedoms, and universal suffrage, requires at least a two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly and approval in a referendum; referenda not required for passage of other amendments; amended 2007, 2018 |
| Independence | 25 June 1975 (from Portugal) |
Mozambique Video
YouTube: Unesco The Chopi Timbila
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Mozambique Geography
What environmental issues does Mozambique have?
| Overview | The Republic of Mozambique, 1,737-mile coastline stretches from the Rovuma River in the north, to Ponta de Ouro in the south. The country is mostly coastal lowlands, with uplands in the center, high plateaus (rising to 800 to 2,000 feet) in the northwest, and mountains (6,000 to 8,000 feet) in the west. The northern part of Mozambique is rugged, where mountains may reach a height of more than 8,000 feet. Africa’s fourth longest river, the Zambezi, divides Mozambique in half. |
| Climate | The climate in the plains and along the coast is warm and humid; the mountainous areas are cooler, although at times, equally wet. A hot, rainy season lasts from October to April. The rest of the year has a more moderate climate, with the coolest months in June and July. Rainfall is uneven and unpredictable; periodic droughts and floods occur. Mozambique experienced devastating floods in February and March 2000, causing loss of life and much destruction. |
| Border Countries | Malawi 1,569 km, South Africa 491 km, Swaziland 105 km, Tanzania 756 km, Zambia 419 km, Zimbabwe 1,231 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | a long civil war and recurrent drought in the hinterlands have resulted in increased migration of the population to urban and coastal areas with adverse environmental consequences; desertification; pollution of surface and coastal waters; elephant poaching for ivory is a problem |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in northwest, mountains in west |
Mozambique Economy
How big is the Mozambique economy?
| Economic Overview |
The economy of Mozambique is characterized by its diversity, natural resource wealth, and significant potential for growth. In recent years, the country's economy has been undergoing a period of transition and development, with key sectors including agriculture, mining, energy, tourism, and manufacturing. Agriculture plays a crucial role in Mozambique's economy, employing a large portion of the population and contributing to both domestic food security and export earnings. Cash crops such as cashew nuts, sugar, cotton, and tobacco are important for export, while subsistence farming remains prevalent in rural areas. Mining is another important sector, with Mozambique being rich in natural resources such as coal, natural gas, titanium, and gemstones. The discovery of vast natural gas reserves off the coast has attracted significant investment and has the potential to transform the country's economy in the coming years. Energy infrastructure development is a priority for Mozambique, with efforts focused on expanding electricity access and harnessing renewable energy sources. The construction of hydroelectric dams and investment in solar and wind power projects aim to address energy deficits and support economic growth. Tourism is emerging as a promising sector, with Mozambique's stunning coastline, wildlife reserves, and cultural heritage attracting increasing visitors. Infrastructure development and promoting ecotourism initiatives are key to realizing the sector's full potential. The Mozambican economy faces challenges including limited infrastructure, high levels of poverty and unemployment, vulnerability to climate change and natural disasters, and governance issues. Additionally, the country has faced setbacks such as debt distress and security concerns in certain regions. Mozambique's economy holds significant potential for growth and development, driven by its rich natural resources, strategic location, and ongoing efforts to improve infrastructure and attract investment. Continued investment in key sectors, diversification of the economy, and sustainable development policies are essential for unlocking Mozambique's economic potential and improving the livelihoods of its people. |
| Industries | food, beverages, chemicals (fertilizer, soap, paints), aluminum, petroleum products, textiles, cement, glass, asbestos, tobacco |
| Currency Name and Code | Mozambican Metical (MZM) |
| Export Partners | Belgium 42.4%, South Africa 17.6%, Zimbabwe 5.7%, Spain 5.4%, Portugal 4.4% |
| Import Partners | South Africa 30.4%, Portugal 6.1%, US 5.2%, India 4.2%, Australia 4.1% |
Mozambique News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Mozambique?
Source: Google News
Mozambique Travel Information
What makes Mozambique a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Mozambique is a developing country in southern Africa that has been steadily rebuilding its economy and civic institutions since ending a 16-year civil war in 1992. The country stabilized following Mozambique's first multi-party elections in October 1994, and the current president was reelected in October 2009. The next presidential elections will be held in 2014. Despite high economic growth rates in recent years, Mozambique remains among the world's poorest countries, with a GDP per capita of under $400. Facilities for tourism in Maputo, the capital city, are steadily improving but remain limited in other areas. Many goods and services have extremely limited availability. The official language is Portuguese, although English is spoken in many tourist areas, and in some rural areas only local languages are widely spoken.
Crime
Although the vast majority of visitors complete their travels in Mozambique without incident, the most serious threat facing U.S. citizens visiting Mozambique is crime. Street crimes, including mugging, purse-snatching, and pick-pocketing are common, both in Maputo and in secondary cities. Carjackings have become rare, but still do happen. Visitors must be vigilant when out in public areas and should not display jewelry or other items —even those of low value, like cell phones and personal music devices. Avoid isolated areas. Joggers and pedestrians have frequently been mugged, even during daylight hours. Visitors should take caution when walking at night, even in well-known tourist areas. Due to an increase in violent crime, pedestrian activity is discouraged on Maputo's Avenida Marginal between the Southern Sun hotel (formerly the Holiday Inn) and the Waterfront Restaurant.Mozambican police do not operate at the standard that U.S. citizens are accustomed to in the United States. Visitors should not expect the same level of police service.
Many airline trips from Mozambique to the United States, Europe, or African destinations transit Johannesburg, South Africa. Baggage pilferage is an ongoing problem at Johannesburg's Oliver Tambo International Airport. Travelers are encouraged to secure their luggage, use an airport plastic wrapping service, and avoid placing currency, electronics, jewelry, cameras, cosmetics, running shoes, or other valuables in checked luggage. Having a complete inventory of items placed in checked baggage can aid in processing a claim if theft does occur.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Mozambique, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods.Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Mozambique, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Persons violating Mozambican laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Mozambique are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Arrest notifications in Mozambique: While some countries will automatically notify the U.S. embassy if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the U.S. embassy as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are rudimentary, and most medical providers do not speak fluent English. Medicines are not always consistently available. There are both public and private medical facilities in the city of Maputo and most provincial capitals. All health care institutions and providers require payment at the time of service, and may even require payment before providing service. While some private clinics accept credit cards, many medical facilities do not. Doctors and hospitals outside Maputo generally expect immediate cash payment for health services. Outside of Maputo, available medical care ranges from very basic to nonexistent.
Safety and Security
Overland travel after dark is extremely dangerous due to the increased potential for vehicle hijacking. Visitors should be particularly vigilant when driving on the main thoroughfares connecting Mozambique and South Africa as incidents of vehicle theft, including assault and robbery, have been reported. U.S. government personnel who work at the U.S. Embassy in Mozambique are strongly discouraged from overland travel outside Maputo city limits after dark, and are encouraged to travel in convoys of two or more vehicles when outside of the city. They are prohibited from using “chapas” (local minibuses) due to frequent accidents involving these vehicles. Due to residual landmines, overland travelers are advised to remain on well-traveled roads or seek local information before going off-road outside of Maputo and other provincial capitals.Although demonstrations do occur in Mozambique, they are infrequent and there have been no recent demonstrations against U.S. interests. If any demonstrations do occur, they should be avoided.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Mozambique, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Mozambique is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Serious traffic accidents, one of the greatest threats to U.S. citizens in Mozambique, occur regularly throughout the country. Accidents involving drivers and pedestrians are common, sometimes resulting in pedestrian casualty. Pedestrians often walk in the road and may not be visible to motorists, especially at night. If a serious accident occurs, or if a driver hits a pedestrian, crowds quickly gather. Some drivers involved in accidents of this nature have felt threatened by the crowds and fled the accident scene. We urge any driver involved in an accident to report the accident to the nearest police station immediately and to contact the Embassy.
Drivers should obey police signals to stop at checkpoints, which are common throughout Mozambique. Foreigners visiting Mozambique for more than 90 days are required to have an International Driver’s License or to obtain a Mozambican driver’s license.
The main north-south thoroughfare is passable north of Maputo until the city of Caia (Sofala province), where vehicle passengers must disembark and cross the Zambezi River by ferryboat. On the north side of the river, the road continues to the Northern provinces. The road network connecting provincial capitals is in fair condition, but can be riddled with potholes and other obstacles.
The EN4 toll road between Maputo and South Africa is well-maintained. U.S. government personnel are prohibited from traveling outside cities after dark because of the increased risk of banditry, poor road conditions in some areas, poor maintenance of many vehicles in the country (e.g., no headlights or rear lights), as well as the threat imposed by livestock grazing on roadsides. Travel outside Maputo often requires a four-wheel drive vehicle, which creates an additional security risk since these vehicles are high-theft items. Public transportation is limited and often has poor safety standards.
The U.S. Embassy advises U.S. citizens not to use “chapas” (local minibuses) as a method of transportation due to frequent, often fatal accidents involving these vehicles. Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. We also suggest that travelers visit the web site of the Mozambique’s national tourist office and national authority responsible for road safety.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
