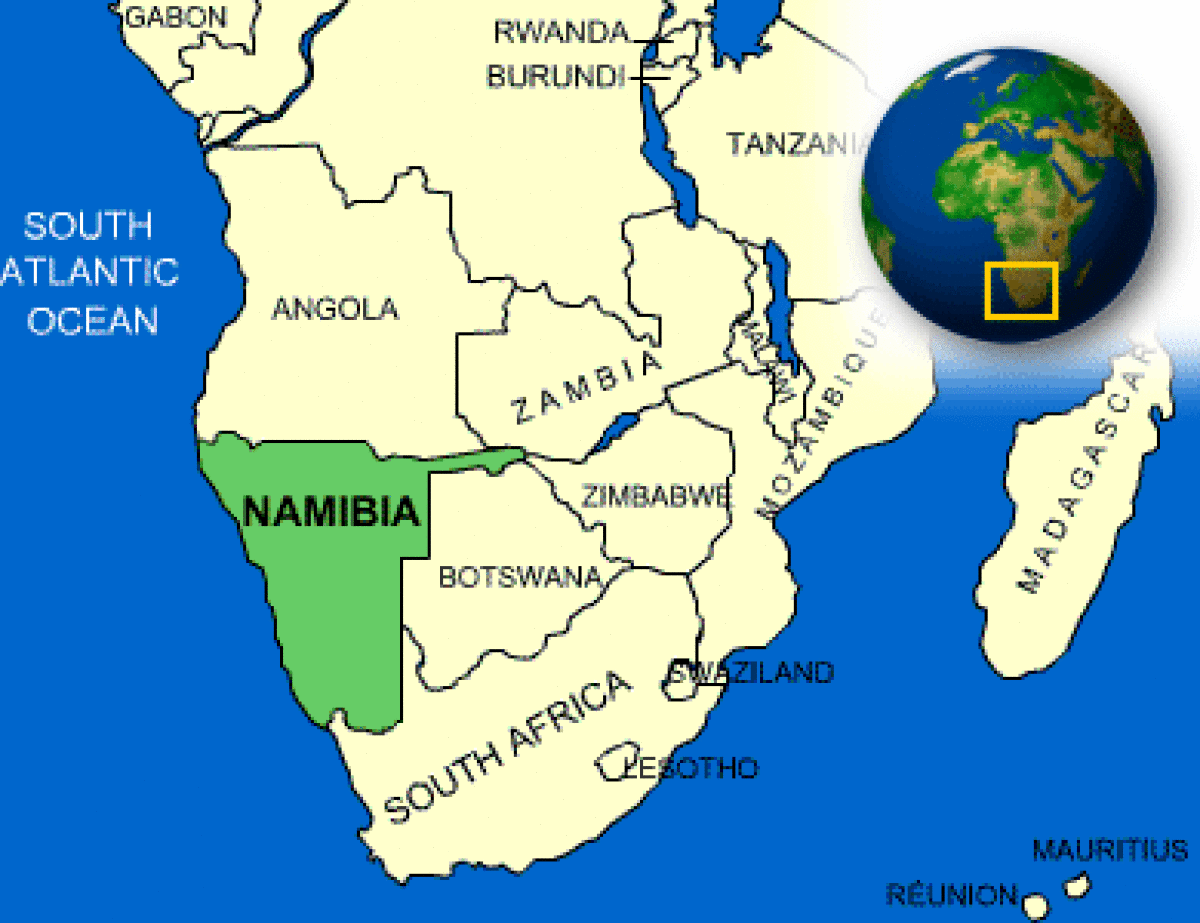
Where is Namibia located?
What countries border Namibia?
Namibia Weather
What is the current weather in Namibia?
Namibia Facts and Culture
What is Namibia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The majority of rural inhabitants in Namibia engage in fishing, crop cultivation, or livestock rearing to sustain their livelihoods. Their... More
- Family: In most Namibian cultures when a man dies his parents and siblings often inherit the property.The practice of having more... More
- Personal Apperance: In Namibia, clothing choices often depend on the region and the weather. Since Namibia has diverse climates ranging from desert... More
- Recreation: In Namibia, recreational activities encompass a diverse range of pursuits, catering to varied interests across its multicultural society. Sports hold... More
- Diet: In Namibia, the cuisine reflects a blend of indigenous traditions, colonial influences, and modern culinary trends. Staple foods include: 1. Maize... More
- Food and Recipes: Mealie (corn) is the staple Mealtime customs in Namibia can vary depending on cultural backgrounds and individual preferences, but there... More
- Visiting: Sure, here's a version without numbers: When visiting Namibia, it's important to respect local customs and traditions. Start by greeting people... More
Namibia Facts
What is the capital of Namibia?
| Capital | Windhoek |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Namibia Dollar (NAD) and South Afrtican Rand (ZAR) |
| Total Area |
318,259 Square Miles 824,292 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola and South Africa |
| Language | English 7% (official), Afrikaans common language of most of the population and about 60% of the white population, German 32%, indigenous languages: Oshivambo, Herero, Nama |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $11,300.00 (USD) |
Namibia Demographics
What is the population of Namibia?
| Ethnic Groups | black 87.5%, white 6%, mixed 6.5% |
| Nationality Noun | Namibian(s) |
| Population | 2,630,073 |
| Population - note | note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.75% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | WINDHOEK (capital) 380,000 |
| Urban Population | 38.400000 |
Namibia Government
What type of government does Namibia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Acting President Nangolo MBUMBA (since 4 February 2024); Acting Vice President Netumbo NANDI-NDAITWAHNOTE (since 4 February 2024); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government; President Hage GEINGOB died on 4 February 2024, and Vice President MBUMBA was sworn in to run the government until the next presidential election in November 2024 head of government: Acting President Nangolo MBUMBA (since 4 February 2024); Acting Vice President Netumbo NANDI-NDAITWAHNOTE (since 4 February 2024); Prime Minister Saara KUUGONGELWA-AMADHILA (since 21 March 2015); note - the prime minister is appointed by the president to coordinate the work of the cabinet, advise the president, and is second in line of succession if the president is unable to serve; note - President Hage GEINGOB died on 4 February 2024, and the Vice President MBUMBA was sworn in to run the government until the next presidential election in November 2024 cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from among members of the National Assembly elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 28 November 2019 (next to be held in November 2024) election results: 2019: Hage GEINGOB reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Hage GEINGOB (SWAPO) 56.3%, Panduleni ITULA (independent) 29.4%, McHenry VENAANI (PDM) 5.3%, other .9% 2014: Hage GEINGOB elected president in the first round; percent of vote - Hage GEINGOB (SWAPO) 86.7%, McHenry VENAANI (DTA) 5%, Hidipo HAMUTENYA (RDP) 3.4%, Asser MBAI (NUDO)1.9%, Henk MUDGE (RP) 1%, other 2% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Namibia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 21 March (1990) |
| Constitution |
history: adopted 9 February 1990, entered into force 21 March 1990 amendments: passage requires majority vote of the National Assembly membership and of the National Council of Parliament and assent of the president of the republic; if the National Council fails to pass an amendment, the president can call for a referendum; passage by referendum requires two-thirds majority of votes cast; amendments that detract from or repeal constitutional articles on fundamental rights and freedoms cannot be amended, and the requisite majorities needed by Parliament to amend the constitution cannot be changed; amended 1998, 2010, 2014 |
| Independence | 21 March 1990 (from South African mandate) |
Namibia Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Namibia Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Namibia Geography
What environmental issues does Namibia have?
| Overview |
Namibia is an arid country covering more than 320,000 square miles. The Caprivi Strip juts out to the northeast to touch both Zimbabwe and Zambia. Namibia has four distinct geographic regions. The Namib Desert forms a 50- to 70-mile wide belt along the entire coastline. A semiarid and mountainous plateau, varying in altitude from 3,000 to 6,000 feet, covers the central part of the interior and includes Windhoek, the capital city. The low-lying eastern and southeastern plains are extensions of the dry Kalahari Region of Botswana and South Africa. The northern, bush-covered plains include the relatively high rainfall areas of the Kavango and the eastern Caprivi. Windhoek, the capital, has a population of 282,300 and is at an altitude of 5,600 feet. The city itself is hilly and surrounded by sparsely vegetated mountains, creating a landscape that calls to mind Arizona or New Mexico. Indeed, with its bustling downtown commercial section, good-quality roads and public services, and trim residential areas, Windhoek proper could easily pass for a small, southwestern, American city. |
| Climate | Namibia’s climate is typical of a semi-desert and high plateau country, with hot days and cool nights. In mid-summer (December–February), daytime temperatures can exceed 100°F in lower elevations. In Windhoek, January average high temperatures are in the 90s. Winter (May–September) sees daytime highs of about 70°F; nights can be cold, dipping below freezing. Windhoek enjoys about 300 sunny days a year. Rains usually come from December through March, peaking in February, for a yearly average rainfall of 12–16 inches in Windhoek. The unrelenting dryness of the rest of the year makes the rains refreshing, welcome, and eagerly anticipated, turning the mountains surrounding Windhoek green for the brief summer months. |
| Border Countries | Angola 1,376 km, Botswana 1,360 km, South Africa 967 km, Zambia 233 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | very limited natural fresh water resources; desertification; wildlife poaching; land degradation has led to few conservation areas |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly high plateau; Namib Desert along coast; Kalahari Desert in east |
Namibia Economy
How big is the Namibia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Namibia's Economic Landscape: Opportunities and Challenges Nestled in the southwestern corner of Africa, Namibia has vast landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a promising economic outlook. Since gaining independence from South Africa in 1990, Namibia has made significant strides in developing its economy, yet it grapples with persistent challenges. Let's delve into the factors shaping Namibia's economic landscape. Economic Structure Namibia's economy is diverse, with sectors such as mining, agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing contributing significantly to its GDP. Mining, particularly diamond and uranium extraction, remains a cornerstone of the economy, accounting for a substantial portion of export earnings and government revenue. The country is also endowed with other mineral resources, including copper, gold, and zinc, contributing to its resilience in mining. Agriculture plays a vital role in Namibia's economy, employing a large portion of the population, particularly in rural areas. Livestock farming, including cattle, goats, and sheep, is the primary agricultural activity supported by a network of communal and commercial farms. However, the sector faces challenges such as erratic rainfall patterns, land degradation, and limited access to markets and financing, hindering its full potential. Tourism is another critical sector driving Namibia's economy, thanks to its breathtaking natural landscapes, including the iconic Namib Desert, Etosha National Park, and the Skeleton Coast. The sector has shown resilience despite occasional setbacks, contributing to foreign exchange earnings and employment opportunities. Challenges Facing Namibia's Economy While Namibia boasts a diverse economic base, it grapples with several challenges that impede its growth and development. Income inequality remains a pressing issue, with a significant portion of the population living in poverty, particularly in rural areas. Addressing this disparity requires targeted policies to improve access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities for all Namibians. Infrastructure deficits pose another challenge to Namibia's economic development. While the country has made investments in infrastructure projects, including road networks and ports, further upgrades and expansions are needed to support economic activities across the country. Improving infrastructure enhances connectivity and facilitates trade and investment, fostering economic growth. Furthermore, Namibia faces environmental challenges, including droughts and climate change, which impact agriculture, water resources, and biodiversity. Addressing these challenges requires sustainable development strategies that balance economic growth with environmental conservation and resilience-building measures. Opportunities for Growth Despite these challenges, Namibia remains well-positioned to capitalize on various economic growth and diversification opportunities. The country's strategic location as a gateway to southern Africa presents opportunities for trade and investment, particularly in the logistics and transportation sectors. Enhancing trade facilitation measures and infrastructure connectivity can further leverage Namibia's position as a regional trade hub. Moreover, Namibia has untapped potential in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power. Expanding renewable energy infrastructure reduces reliance on fossil fuels, creates employment opportunities, and promotes sustainable development. |
| Industries | meatpacking, fish processing, dairy products; mining (diamond, lead, zinc, tin, silver, tungsten, uranium, copper) |
| Currency Name and Code | Namibia Dollar (NAD) and South Afrtican Rand (ZAR) |
| Export Partners | EU 79%, US 4% |
| Import Partners | US 50%, EU 31% |
Namibia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Namibia?
Source: Google News
Namibia Travel Information
What makes Namibia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Namibia is a southern African country with a moderately developed economy. Facilities for tourism are good and generally improving in quality. The capital is Windhoek.
Crime
Crime is a serious concern in Namibia, but visitors who employ common-sense preventive measures normally enjoy an incident-free stay. Incidents of violent crime directed specifically against U.S. citizens or other foreigners are rare. The most common crimes are property-motivated crimes of opportunity, including pick-pocketing, purse snatching, vehicle theft, and vehicle break-ins. Such crimes most commonly occur in the central business districts of cities, or other areas frequently visited by foreign tourists, both at night and during the day.Basic precautions remain the best deterrents against becoming a victim. Be alert to your surroundings, avoid dark or isolated areas, don’t leave valuables in parked cars, and keep car doors locked and windows up while driving. Safeguard purses, wallets, and cellular phones while in public. Drivers should also exercise caution at rest stops between towns; whenever possible, avoid driving or making rest stops by the road at night.
Take special care when utilizing a taxi or other transportation service. Criminals posing as taxi drivers have occasionally robbed passengers in the past. The Namibia Bus and Taxi Association (NABTA) has taken steps to regulate taxi drivers by allocating registration numbers (one alphabetical designation followed by a two-digit number), which are prominently pasted on the doors and rear windscreens of legitimate taxis. Generally, travelers are more likely to find a legitimate taxi service if booked through a hotel rather than by flagging down a driver randomly on the street. Whatever your circumstance, be cautious and aware of your surroundings when utilizing taxi services; take note of the vehicle license and taxi registration numbers, as well as the name of your driver.
ATM and Credit Card Fraud is becoming more sophisticated and more common in Namibia. ATM users should be suspicious of any unknown person approaching while at an ATM, even if that person appears to be offering assistance. A variety of distraction schemes have been used to steal money or information from tourists at ATMs. Perpetrators may also use card-reading or card-trapping devices attached to ATMs to procure PIN codes or other important personal information. Carefully inspect an ATM before using it and, whenever possible, try to use ATMs which are enclosed and/or under guard.
While most business establishments deal honestly, some may have individual employees who use card-reading machines to steal information when patrons pay with a credit card. This can be done with hand-held devices in a matter of seconds. Whenever possible, pay with cash. If you must use a credit card, then it is best to observe the transaction closely as it is processed, and to ensure that the card is not taken out of your sight. Many banks and credit card companies have the capacity to send automatic “alerts” by e-mail or text message when a card has been used. Before traveling, inquire whether your bank or credit card issuer will provide such services.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, you may be breaking local law too.
The government has also begun to establish “Tourist Protection Units” (TPUs) which are mandated to carefully monitor criminal activity in areas frequented by tourists and to assist tourists victimized by crime. TPUs exist in Windhoek and in Swakopmund. If you are a victim of crime in one of these cities, please contact:
Windhoek Main Police Station
061-209-4339
Swakopmund Police Station
064-405-558
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Namibia, you are subject to its laws. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Namibia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.U.S. citizens should avoid purchasing diamonds and other protected resources outside of licensed retail establishments. The penalty for illegal dealing in diamonds in Namibia is stiff – up to U.S. $20,000 in fines or five years in prison – and the courts generally impose the maximum sentence. The purchase and exportation of other protected resources (for example, elephant ivory or hunting trophies from certain endangered species) may also be prohibited by Namibian, international, and/or U.S. law.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Namibia, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the U.S. Embassy.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Windhoek has a small number of private medical hospitals and clinics capable of providing emergency care and performing many routine procedures. Doctors – both general practitioners and specialists – as well as dentists generally have training and facilities that are comparable to U.S. standards. Facilities outside the capital vary widely. Several large towns have well-equipped facilities similar to those available in Windhoek, while smaller towns generally do not. Malaria is prevalent only in the north of the country. Malaria prophylaxis is not required in Windhoek, but is suggested for travel to the north.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens wishing to cross into neighboring countries (Angola, Botswana, South Africa, Zambia) from Namibia should do so only at official border crossing areas and should consult the State Department's Country Specific Information for information about entrance requirements for these countries.Though street demonstrations are rare in Namibia, U.S. citizens should avoid them when they occur. U.S. citizens traveling in Namibia are urged to contact the U.S. Embassy’s consular section in Windhoek for the latest safety and security information.
Stay up to date by bookmarking our Bureau of Consular Affairs website, which contains the current Travel Warnings and Travel Alerts as well as the Worldwide Caution. Follow us on Twitter and the Bureau of Consular Affairs page on Facebook as well, or you can download our free Smart Traveler App from iTunes or the Android market for travel information at your fingertips.
You can also call 1-888-407-4747 toll-free within the United States and Canada, or by calling a regular toll line, 1-202-501-4444, from other countries. These numbers are available from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
There is nobody better at protecting you than yourself. Take some time before travel to improve your personal security—things are not always as they are in the United States. Here are some useful tips for traveling safely abroad.
Cell phone coverage in Namibia is generally good in areas near main roads. Mobile phone users may call 112 in an emergency and will be connected to the appropriate service (e.g., police, hospital, etc.) It is not necessary to dial an area code when calling this number.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
The information below concerning Namibia is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.In Namibia, driving is done on the left-hand side of the road. Many of Namibia's rural roads are gravel. Although these roads are generally well maintained, controlling a vehicle on gravel is significantly more difficult than on pavement. Drivers should not drive in excess of 80km per hour (45 mph) on gravel roads, should reduce speed significantly for curves or turns, and should heed all warning signs. Hitting a sand patch or driving around a curve too fast can easily result in a rollover or spinout. Many accidents on gravel roads occur when tourists exceed safe speeds on corners or in areas recently damaged by rains. Visitors are reminded that motor vehicle accidents – often, single car accidents – are one of the primary causes of injury and death in Namibia, and drivers are therefore strongly urged to drive with caution.
For those driving outside the capital, distances between cities can be considerable, and often gasoline is only available at a few service stations along a route. Fuel availability can be affected by power outages as well. All travelers are encouraged to plan their route to ensure a sufficient supply of fuel, and to carry five liters of water per person when traveling on dirt roads to guard against dehydration if an accident should occur.
Turning at a red traffic light is not permitted in Namibia. Seat belts are required for all vehicle occupants. Motorcyclists are required by law to wear protective helmets. While child car seats are not required, they are recommended.It is an offense to use a mobile phone while driving. The traffic fine is the equivalent of approximately U.S. $200.
To drive legally while in Namibia, visitors staying more than 90 days need an international driving permit. International driving permits must be obtained prior to leaving the United States and are available from either the American Automobile Association or the American Automobile Touring Alliance. Short-term visitors do not need an international driving permit; a valid U.S. driver's license is sufficient.
Roads in Namibia are generally well maintained. However, few have shoulders or “pull-off” lanes for broken down vehicles. Wildlife wandering on roads is a special driving hazard in Namibia, especially at night. An encounter at high speeds with antelope or cattle can be fatal. The salt-surfaced roads at the coast can also be deceptively dangerous, especially when they have been made slick by morning or evening mist. Robberies have occurred at roadside "rest stops," so motorists are advised to take rest breaks in towns and/or at gasoline stations. Embassy Windhoek has a policy against its staff members driving after dark outside Windhoek. This is due to the dangers of other vehicles, gravel roads, intermittent flooding, crime, and animals on the main highways. U.S. citizen visitors to Namibia are encouraged to drive only during daylight hours.
Most major roads are undivided with one lane in each direction. Drivers should remain alert for passing vehicles and exercise caution when passing slow moving vehicles. Accidents involving drunk drivers are an increasing problem on major roads where there are high speed limits. Driving under the influence is illegal in Namibia. A charge of culpable homicide can be made against a driver involved in an accident resulting in death.
Roadside assistance and emergency medical services outside Windhoek may be unreliable or non-existent. Assistance on main roads that link Namibia's larger towns, however, is generally good due to high quality cell phone networks. Travelers with mobile phones may call 112 in an emergency and will be connected to the appropriate service (e.g. police, hospital etc.). Public transportation is not widely available outside the capital. Taxis and municipal buses are the only forms of public transportation in Windhoek. Schedules and routes are limited. Car rentals or radio taxis are generally the best means of transport but may be relatively expensive. The Embassy has received reports of foreign citizens being robbed by drivers of taxis hailed on the streets of Windhoek. The Embassy has not received any such reports regarding radio taxis.
Flashing of high beams and similar signals could mean anything from a friendly greeting to a warning. When encountering a motorcade, motorists are encouraged to make way immediately and follow promptly any instructions given by the officials present.
Because of the possibility of intoxicated and/or reckless drivers, sexual assault and/or robbery, the poor mechanical condition of some motor vehicles, and the high incidence of single-vehicle rollover accidents, U.S. citizens are urged to avoid hitchhiking in Namibia.
