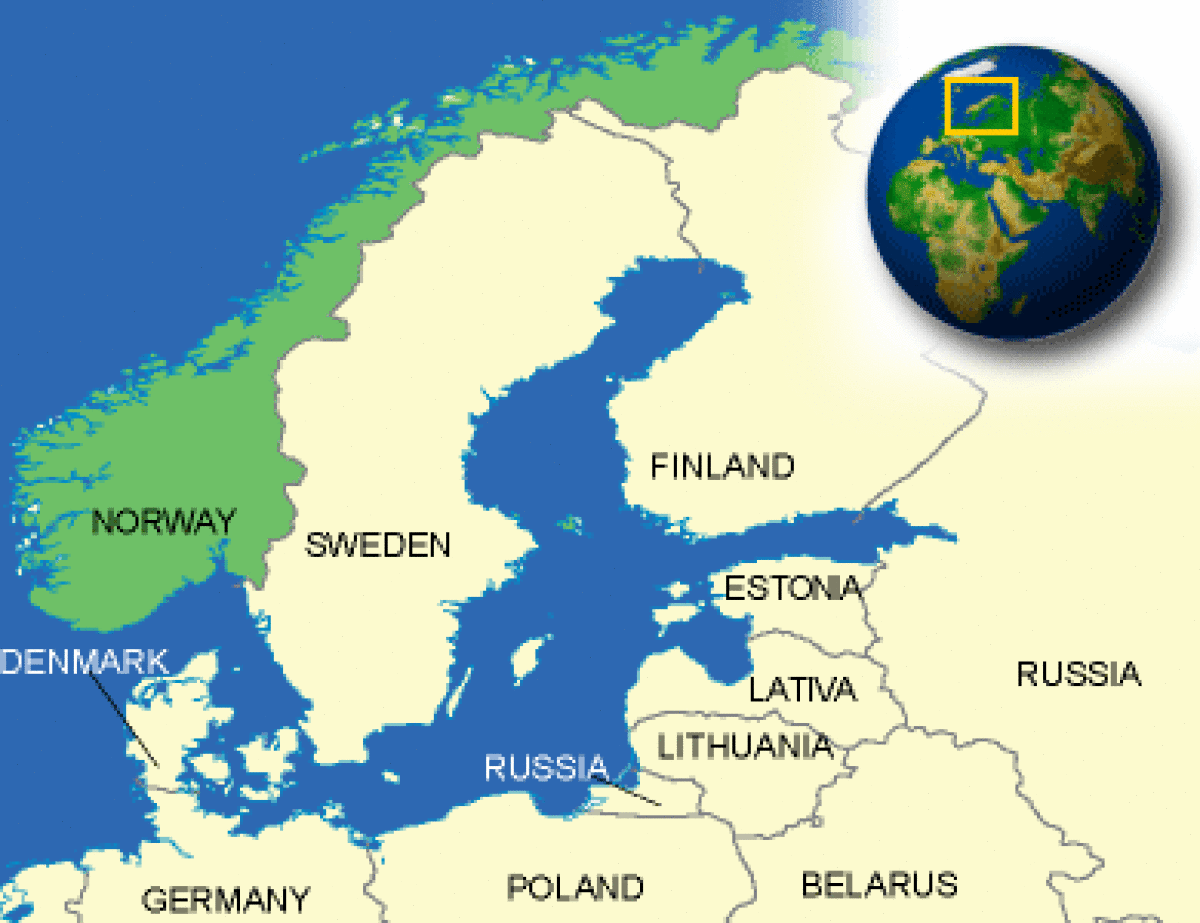
Where is Norway located?
What countries border Norway?
Norway Weather
What is the current weather in Norway?
Norway Facts and Culture
What is Norway famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Norwegians cherish their freedom and independence. Although the country has a king, his role is mainly ceremonial. Norway's love of... More
- Family: In many families both parents work, but family relationships are very important. Families in Norway are usually small, often with... More
- Personal Apperance: Norwegian clothing style can vary depending on location, weather, occasion, and personal preference. However, there are some general trends and... More
- Recreation: Soccer, Handball, and Gymnastics are the sports played by kids, usually on sports teams; school teams are rare. Kids also... More
- Diet: Norwegian cuisine is influenced by its geography, climate, and cultural traditions. Seafood: With its long coastline and abundant fjords, seafood... More
- Food and Recipes: Norwegians typically eat four meals a day. Frokost (Breakfast) is usually eaten at home and may consist of porridge or... More
- Visiting: Norwegians feel they have a “border” around their heads that is about three feet, which is their “intimate zone,” which... More
Norway Facts
What is the capital of Norway?
| Capital | Oslo |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Norwegian Krone (NOK) |
| Total Area |
125,020 Square Miles 323,802 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden |
| Language | Bokmal Norwegian (official), Nynorsk Norwegian (official) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 0.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $68,400.00 (USD) |
Norway Demographics
What is the population of Norway?
| Ethnic Groups | Norwegian, Sami 20,000 |
| Nationality Noun | Norwegian(s) |
| Population | 5,467,439 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.33% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | OSLO (capital) 915,000 |
| Urban Population | 79.400000 |
Norway Government
What type of government does Norway have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King HARALD V (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince HAAKON MAGNUS (son of the monarch, born 20 July 1973) head of government: Prime Minister Jonas Gahr STORE (since 14 October 2021) cabinet: Council of State appointed by the monarch, approved by Parliament elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following parliamentary elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch with the approval of the parliament |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Norway dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | Constitution Day, 17 May (1814) |
| Constitution |
history: drafted spring 1814, adopted 16 May 1814, signed by Constituent Assembly 17 May 1814 amendments: proposals submitted by members of Parliament or by the government within the first three years of Parliament's four-year term; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of a two-thirds quorum in the next elected Parliament; amended over 400 times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 7 June 1905 (union with Sweden declared dissolved); 26 October 1905 (Sweden agreed to the repeal of the union); notable earlier dates: ca. 872 (traditional unification of petty Norwegian kingdoms by HARALD Fairhair); 1397 (Kalmar Union of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden); 1524 (Denmark-Norway); 17 May 1814 (Norwegian constitution adopted); 4 November 1814 (Sweden-Norway union confirmed) |
Norway Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Norway Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Norway Geography
What environmental issues does Norway have?
| Overview | Located in northwestern Europe on the Scandinavian Peninsula, Norway is a picturesque country bounded on the west by the North Atlantic and the North Sea and on the east by Sweden, Finland, and Russia. Norway covers 150,000 square miles, including Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands, with landscape ranging from farms and fields to forests, lakes, plateaus, glaciers, and the highest peak in northern Europe. The jagged coastline stretches 1,625 miles when measured in a straight line and a staggering 13,125 miles including the ins and outs of the fjords. Although small in population, Norway is one of the largest European countries in area. |
| Climate |
Many people expect Norway's climate to be bitterly cold. The latitude of the country certainly suggests this would be true. The Arctic Circle cuts through Norway about halfway up the length of the country. Oslo lies in the southern part of the country but is at the same latitude as Anchorage, Alaska. Hammerfest, on the northern tip of the Norwegian mainland, is the world's most northerly town. Still, the climate of cities along the Norwegian coast is much milder than might be expected at such northerly latitudes, even during midwinter, because of the warming effect of the Gulf Stream. Summer in the southern part of the country can last from early May to late August or, in a bad year, for only a week in late June. There are about 20 hours of daylight during June and July in Oslo. (Note: In northern Norway, the midnight sun shines for nearly two months during this period!) Summer days rarely get warmer than 80 F and can be quite cool in the 50s and 60s. Winter brings only about six hours of daylight in Oslo and none in areas north of the Arctic Circle. Snow brightens the landscape considerably, even during the shortest days. However, some people find the darkness oppressive. Norwegians seem to have found numerous ways to combat the depression of winter such as utilizing the many (often lit) cross-country trails and downhill slopes within the Oslo city limits or keeping things cozy and bright inside, using lots of candlelight for cheer and warmth. |
| Border Countries | Finland 729 km, Sweden 1,619 km, Russia 196 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | water pollution; acid rain damaging forests and adversely affecting lakes, threatening fish stocks; air pollution from vehicle emissions |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | glaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic tundra in north |
Norway Economy
How big is the Norway economy?
| Economic Overview |
Norway boasts a robust and stable economy largely driven by its abundant natural resources, particularly oil and gas. It also has a well-developed welfare state and a high standard of living. Oil and Gas Sector: Norway is one of the world's largest exporters of oil and natural gas, and its economy has historically been heavily reliant on revenues from these resources. However, given the volatility of commodity prices and the increasing focus on renewable energy, the government has been working to diversify the economy to reduce its dependency on oil and gas. Welfare State: Norway has a comprehensive welfare system, including universal healthcare, free education (including higher education), and generous social security benefits. These programs contribute to a high standard of living and low levels of income inequality, but they also impose a significant financial burden on the government. Strong Fiscal Position: Norway has accumulated substantial financial reserves thanks to its oil wealth, primarily through its Government Pension Fund Global (commonly known as the Norwegian Oil Fund). This sovereign wealth fund is one of the largest in the world and is designed to support future generations when oil revenues decline. The prudent management of these funds has helped Norway maintain a strong fiscal position. Diversification Efforts: Norway has been actively diversifying its economy by recognizing the risks associated with overreliance on oil and gas. Investments have been made in renewable energy, technology, and aquaculture industries. The government has also encouraged innovation and entrepreneurship through various policies and initiatives. Stable Macroeconomic Environment: Norway's macroeconomic environment is stable, characterized by low inflation, low unemployment rates, and sound fiscal management. The Norwegian krone (NOK) is a freely floating currency, and the country is committed to maintaining price stability. Challenges and Concerns: Despite its economic strengths, Norway faces several challenges. These include an aging population, which puts pressure on the welfare system, and the need to transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly economy. Additionally, the country must navigate the geopolitical and economic uncertainties of Brexit, global trade tensions, and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. International Trade: Norway is a member of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and the European Economic Area (EEA), which provides access to the European single market. It also has significant trade relationships with countries outside of Europe, particularly in the energy sector. |
| Industries | petroleum and gas, food processing, shipbuilding, pulp and paper products, metals, chemicals, timber, mining, textiles, fishing |
| Currency Name and Code | Norwegian Krone (NOK) |
| Export Partners | UK 19.4%, Germany 12.4%, France 11.5%, Netherlands 9.3%, US 8.6%, Sweden 7.3% |
| Import Partners | Sweden 15.7%, Germany 13.4%, Denmark 8.1%, UK 7.4%, US 6.2%, France 4.8%, Netherlands 4.8% |
Norway News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Norway?
Source: Google News
Norway Travel Information
What makes Norway a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Norway is a highly developed, stable democracy with a modern economy. The cost of living in Norway is high; tourist facilities are well-developed and widely available.
Crime
Norway has a relatively low level of crime in comparison to the United States and Western European countries with large populations. The most likely forms of crime, especially in the Oslo metropolitan area, include residential and office burglaries and petty thefts. In Oslo and the other major urban areas, crime has been centered in the inner city and high transit areas. As in any other location, especially in urban areas, you should exercise basic security awareness. Although rare, violent and weapons-related crimes are growing in frequency and receive intense media coverage. These crimes usually occur in areas known to have drug trafficking and gang problems, such as certain parts of eastern Oslo. Reports have shown an increase in rape in Norway, mainly in downtown Oslo, with areas such as Grünerlokka being an area of particular concern. You should be aware that instances of pick-pocketing and petty theft are common in major tourist areas, hotel lobbies, train and transit stations, and surrounding areas. The Oslo Central train station is an especially popular area for pick-pockets and bag snatchers.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Norway, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties will vary from country to country. This can be especially true in countries such as Norway which may seem similar to the United States, yet travelers may not be aware of subtle legal and cultural differences. Norwegian family law, for example, can be very different from that in the United States, so visitors and long-term residents are encouraged to familiarize themselves with this law to avoid potential problems. There are also some things that might be legal in Norway, but are illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods in Norway. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. While you are overseas, you may be subject to both U.S. and local laws. If you do something illegal in Norway, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not at your destination.While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are widely available and of high quality, but may be limited outside the larger urban areas. The remote and sparse populations in northern Norway and the dependency on ferries to cross fjords of western Norway may affect transportation and ready access to medical facilities. The U.S. Embassy in Oslo maintains a list of emergency medical and dental clinics in major cities.
Safety and Security
In July 2011, Norway suffered two sequential terrorist attacks by a right-wing extremist against government buildings in Oslo and a youth camp, leaving 77 dead. In a separate case in September 2012, Norwegian courts upheld the convictions of two men resident in Norway suspected of planning attacks and having links to al-Qaida. Like other countries in the Schengen area, Norway's open borders with its Western European neighbors also allow the possibility of terrorists entering/exiting the country with anonymity. Be vigilant with regard to your personal security.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Norway, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Public transportation in Norway is generally safe, and the maintenance and condition of urban roads is generally good. Rural road conditions are fair and the availability of roadside assistance is limited. Most roadways beyond the city limits of Oslo and other major cities tend to be simple two-lane roads. In mountainous areas of Norway, the roads tend to be narrow and winding, and have many tunnels. The northerly latitude can cause road conditions to vary greatly, depending on weather and time of year. Many mountain roads are closed due to snow from late fall to late spring. The use of winter tires is mandatory on all motor vehicles from November to April.Norwegian law requires that drivers always use headlights when driving. Norwegian law also requires drivers to yield to vehicles coming from the right. In some, but not all, instances, major roads with “right of way” are marked. Seatbelts are mandatory for drivers and passengers. It is illegal to use a hand-held cell phone while driving; violators risk a fine of 1,300 kroner (approximately $215).
Norway has some of Europe’s strictest laws on driving under the influence of alcohol; they prescribe heavy penalties for drivers convicted of having very low blood-alcohol levels. Frequent road checks with mandatory breathalyzer tests and the promise of stiff jail sentences encourage alcohol-free driving. The maximum legal blood alcohol content level for driving a car in Norway is .02 per cent.
Automatic cameras placed by the police along roadways help to maintain speed limits, which are often lower than in other European countries. Fines – and sometimes even jail time – are imposed for violations.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
