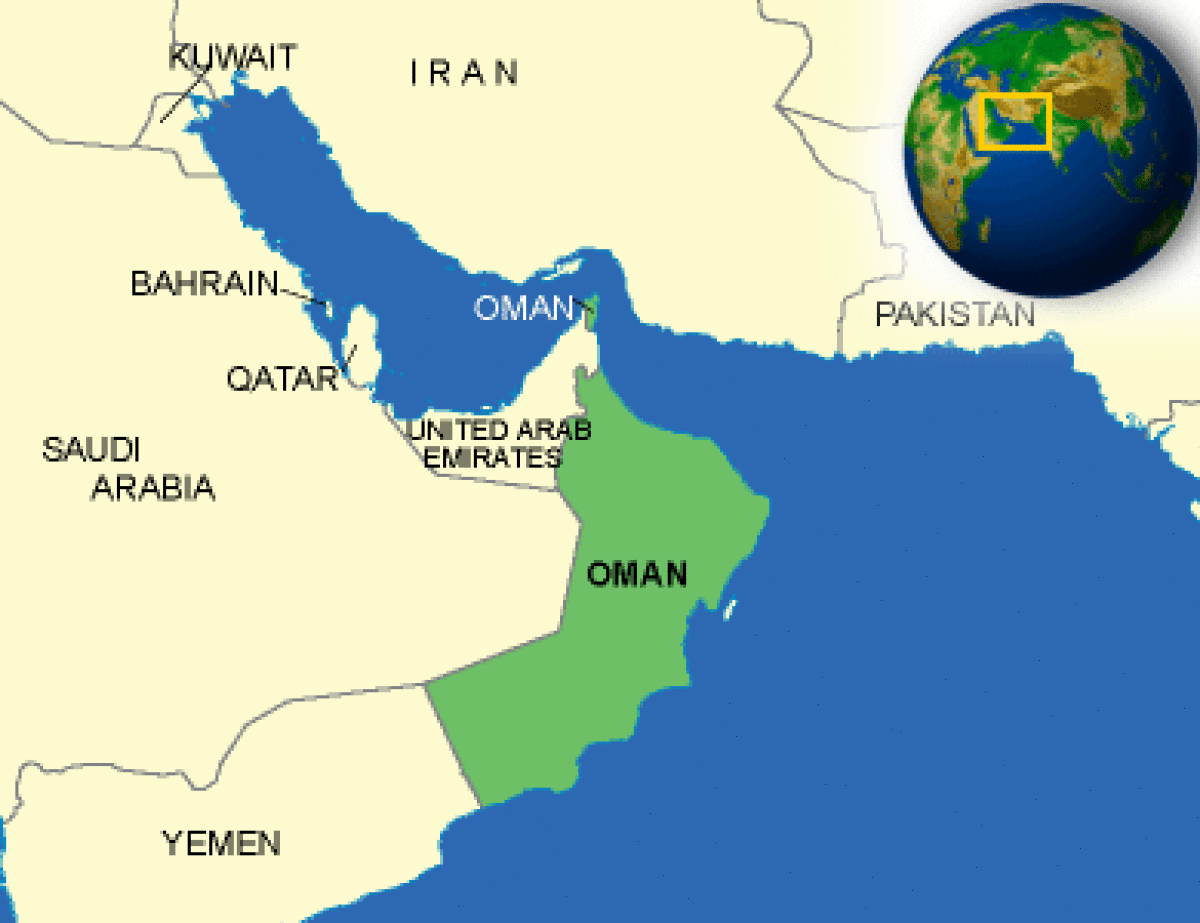
Where is Oman located?
What countries border Oman?
Oman Weather
What is the current weather in Oman?
Oman Facts and Culture
What is Oman famous for?
- Family: Omanis are tribal people and the family is the center of their life. The woman's role is domestic while the men's... More
- Personal Apperance: Omani men wear the traditional dishdasha, an ankle-length robe. On their heads they wear a skullcap or turban. Omani women wear... More
- Recreation: Camel racing and horse racing are popular sports. Hockey and target shooting are also popular. The Boy and Girl Scouts... More
- Food and Recipes: Rice, dates, fish, fruit and meat are staple foods. Omanis eat their meals on the floor or ground, the dishes... More
Oman Facts
What is the capital of Oman?
| Capital | Muscat |
| Government Type | absolute monarchy |
| Currency | Omani Rial (OMR) |
| Total Area |
119,498 Square Miles 309,500 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Middle East, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, between Yemen and UAE |
| Language | Arabic (official), English, Baluchi, Urdu, Indian dialects |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $46,200.00 (USD) |
Oman Demographics
What is the population of Oman?
| Ethnic Groups | Arab, Baluchi, South Asian (Indian, Pakistani, Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi), African |
| Nationality Noun | Omani(s) |
| Population | 4,664,844 |
| Population - note | note: immigrants make up over 40% of the total population, according to UN data |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.06% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MUSCAT (capital) 743,000 |
| Urban Population | 73.400000 |
Oman Government
What type of government does Oman have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Sultan and Prime Minister HAITHAM bin Tarik Al Said (since 11 January 2020); note - the monarch is both chief of state and head of government head of government: Sultan and Prime HAITHAM bin Tarik Al Said (since 11 January 2020) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the monarch |
| Suffrage | 21 years of age; universal; note - members of the military and security forces by law cannot vote |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Oman dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: unknown |
| National Holiday | National Day, 18 November; note - celebrates Oman's independence from Portugal in 1650 and the birthday of Sultan QABOOS bin Said al Said, who reigned from 1970 to 2020 |
| Constitution |
history: promulgated by royal decree 6 November 1996 (the Basic Law of the Sultanate of Oman serves as the constitution); amended by royal decree in 2011 amendments: promulgated by the sultan or proposed by the Council of Oman and drafted by a technical committee as stipulated by royal decree and then promulgated through royal decree; amended by royal decree 2011, 2021 |
| Independence | 1650 (expulsion of the Portuguese) |
Oman Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Oman Geography
What environmental issues does Oman have?
| Overview | Oman occupies the southeastern corner of the Arabian Peninsula. Oman has three distinct topographical regions. The first consists of two flat, relatively fertile coastal strips up to 20 miles wide: one in the north stretching from the Muscat capital area to the border with the U.A.E., and one surrounding the southern city of Salalah. The second feature includes two mountainous regions: one in the north with elevations ranging from several hundred feet to the craggy peaks of Jebel Akhdar at 10,000 feet, and the other bordering the Salalah Plain in the south. Both are deeply scarred throughout by dry streambeds called "wadis." The third feature is sandy wasteland, mainly in the Rub Al Khali (Empty Quarter) along the border with Saudi Arabia. |
| Climate | Oman’s climate is one of the hottest in the world. Temperatures reach 130°F in the summer from April to October and rarely drop below 65°F in the cooler season from November to March. Average annual rainfall measures only 4 or 5 inches and occurs during December into April. Despite limited rainfall, however, humidity averages 65% to 80%. Summer monsoons create a tropical climate in the south. |
| Border Countries | Saudi Arabia 676 km, UAE 410 km, Yemen 288 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | rising soil salinity; beach pollution from oil spills; very limited natural fresh water resources |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | central desert plain, rugged mountains in north and south |
Oman Economy
How big is the Oman economy?
| Economic Overview |
Oman is heavily dependent on oil and gas resources, which can generate between and 68% and 85% of government revenue, depending on fluctuations in commodity prices. In 2016, low global oil prices drove Oman’s budget deficit to $13.8 billion, or approximately 20% of GDP, but the budget deficit is estimated to have reduced to 12% of GDP in 2017 as Oman reduced government subsidies. As of January 2018, Oman has sufficient foreign assets to support its currency’s fixed exchange rates. It is issuing debt to cover its deficit. Oman is using enhanced oil recovery techniques to boost production, but it has simultaneously pursued a development plan that focuses on diversification, industrialization, and privatization, with the objective of reducing the oil sector's contribution to GDP. The key components of the government's diversification strategy are tourism, shipping and logistics, mining, manufacturing, and aquaculture. Muscat also has notably focused on creating more Omani jobs to employ the rising number of nationals entering the workforce. However, high social welfare benefits - that had increased in the wake of the 2011 Arab Spring - have made it impossible for the government to balance its budget in light of current oil prices. In response, Omani officials imposed austerity measures on its gasoline and diesel subsidies in 2016. These spending cuts have had only a moderate effect on the government’s budget, which is projected to again face a deficit of $7.8 billion in 2018. |
| Industries | crude oil production and refining, natural gas production, construction, cement, copper |
| Currency Name and Code | Omani Rial (OMR) |
| Export Partners | Japan 22.1%, South Korea 19.9%, China 15.2%, Thailand 12.6%, Taiwan 5.5%, Singapore 4.7%, US 4.4% |
| Import Partners | UAE 27.6%, Japan 16.7%, UK 7.4%, US 6.9%, Germany 5% |
Oman News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Oman?
Source: Google News
Oman Travel Information
What makes Oman a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Sultanate of Oman, a land of great natural beauty on the southeast corner of the Arabian Peninsula, has a long and proud heritage. Oman has seen rapid economic and social development in the past four decades. A monarchy governed by Sultan Qaboos bin Said, the country has a bicameral representative body (the lower house of which is directly elected), which provides the government with advice and is empowered to draft and review legislation. While Oman is traditionally Islamic and Islam is the state religion, Omanis have for centuries lived with people of other faiths. Non-Muslims are free to worship at churches and temples built on land donated by the Sultan. The economy is largely dependent on the production and export of oil and natural gas, but is becoming increasingly diversified. Excellent tourist facilities are available in the major cities of Muscat, Salalah, Sohar, and Nizwa, and can increasingly be found elsewhere in the country.
Crime
The incidence of street crime is low in Oman; violent crime is rare by U.S. standards, but can occur. Crimes of opportunity remain the most likely to affect visitors. Visitors to Oman should, therefore, take normal precautions, such as avoiding travel in deserted or unfamiliar areas and after dark. Visitors should also protect personal property from theft. In particular, valuables and currency should not be left unsecured in hotel rooms. Common sense and caution are always the best methods for crime prevention.Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Oman, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Oman, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.Persons violating Oman's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Oman are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Oman prohibits pornographic materials and firearms. Local law limits each traveler to two bottles of alcohol. Items subject to confiscation at the airport due to content considered culturally inappropriate include, but are not limited to, compact discs, digital video discs, and video and audiocassettes. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender travelers should review the LGBT Travel Information page.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that Omani police and prison officials notify the U.S. Embassy as soon as you are arrested or detained.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
There are a number of modern medical facilities in Oman. Local medical treatment varies from quite good to inadequate, depending in large part on location. Many Western pharmaceuticals can be found in Oman. Hospital emergency treatment is available. Doctors and hospitals often expect cash payment for health services.
Safety and Security
There have been no instances in which U.S. citizens or facilities in Oman have been subject to terrorist attacks; however, the Department of State remains concerned about the possibility of terrorist attacks against U.S. citizens and interests throughout the region. U.S. citizens in Oman are urged to maintain a high level of security awareness. The State Department suggests that all U.S. citizens in Oman maintain an unpredictable schedule and vary travel routes and times whenever possible. U.S. citizens are also urged to treat mail or packages from unfamiliar sources with suspicion. Unusual mail or packages should be left unopened and reported to local authorities. U.S. citizens with security concerns are encouraged to contact local authorities and the Consular Section of the U.S. Embassy in Muscat.Spontaneous and/or planned public demonstrations take place throughout the country from time to time in response to world events or local developments. Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can escalate into violence. U.S. citizens should remain attuned to readily available English and/or Arabic-language media outlets and avoid public demonstrations.
The United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) has advised that elevated regional tensions have increased the risk of maritime attacks being conducted by extremists to vessels operating in the Gulf of Oman, North Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden, and the Bab el Mandeb regions.
MARAD recommends vessels at anchor, operating in restricted maneuvering environments, or at slow speeds should be especially vigilant, and report suspicious activity. U.S. flag vessels that observe suspicious activity in the area are advised to report such suspicious activity or any hostile or potentially hostile action to COMUSNAVCENT battlewatch captain at phone number 011-973-1785-3879. All suspicious activities and events should also be reported to the U.S. Coast Guard National Response Center at the following toll-free telephone: 1-800-424-8802, direct telephone 202-267-2675, or TDD 202-267-4477.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
Road conditions, lighting, and traffic safety in cities and on major highways are good. The condition of rural roads varies from good to poor. Travel between cities, especially at night, may be dangerous due to poor or no lighting, wandering livestock, and speeding drivers. The safety of public transportation is generally good. Taxis, mini vans, and small buses may swerve to the side of the road to pick up passengers with little notice or regard for other vehicles.Local Laws and Practices: Traffic laws in Oman are strictly enforced and the consequences for violating them may be severe by U.S. standards. For example, running a red light results in a mandatory, non-bailable detention period of 48 hours, followed by confiscation of one's driver's license, vehicle registration, and car registration plate until the Omani judicial process is concluded, which may take as long as several months. Other common traffic violations that carry strict penalties, up to and including jail sentences, fines, and/or deportation, include: driving without a license, driving under the influence of alcohol, failure to wear a seat belt, talking on cellular telephones (other than using hands-free technology) while driving, speeding excessively, overtaking another vehicle, screeching a car's tires or failing to keep one's car clean. In the event of a traffic violation and fine, drivers should cooperate with police officers and should not attempt to pay or negotiate payment at the time of the traffic stop.
U.S. citizens considering driving in Oman are advised to familiarize themselves with the Royal Oman Police (ROP)'s procedures for road and traffic accidents (RTA) to reduce traffic jams, which are available on the ROP web site under “Minor Road Traffic Accidents.” Note: Minor RTA are accidents causing minor damage to one or more vehicles that do not result in injuries, deaths, or material damage to public/private properties. Parties involved in such accidents should immediately move their vehicles to the side of the road.
U.S. citizens involved in accidents outside the Muscat area are advised not to move their vehicles from the accident location until the ROP gives them permission; moving a vehicle may be interpreted as an admission of guilt.
The use of European-style traffic circles is prevalent in Oman. However, unlike European traffic practice, the driver on the inside lane always has priority. A driver flashing his/her high beams is generally asking for a chance to pass. Turning right on a red traffic signal is prohibited.
Visitors should not drive without a valid license. Short-term visitors in possession of a valid U.S. driver's license may drive rental vehicles, but residents must have an Omani driver's license. To obtain an Omani license, a U.S. citizen must have a U.S. license that has been valid for at least one year or must take a driving test. Visitors hiring rental cars should insure the vehicles adequately against death, injury and loss or damage. Residents may insure their vehicles outside the Sultanate; however, third party liability insurance must be purchased locally.
Emergency Services: A modern ambulance service using U.S. equipment and staff trained in the United States was instituted in 2004 and has been assessed as very good. It serves most of the country. For all traffic-related emergencies, the Royal Oman Police can be contacted by dialing "9999."
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
