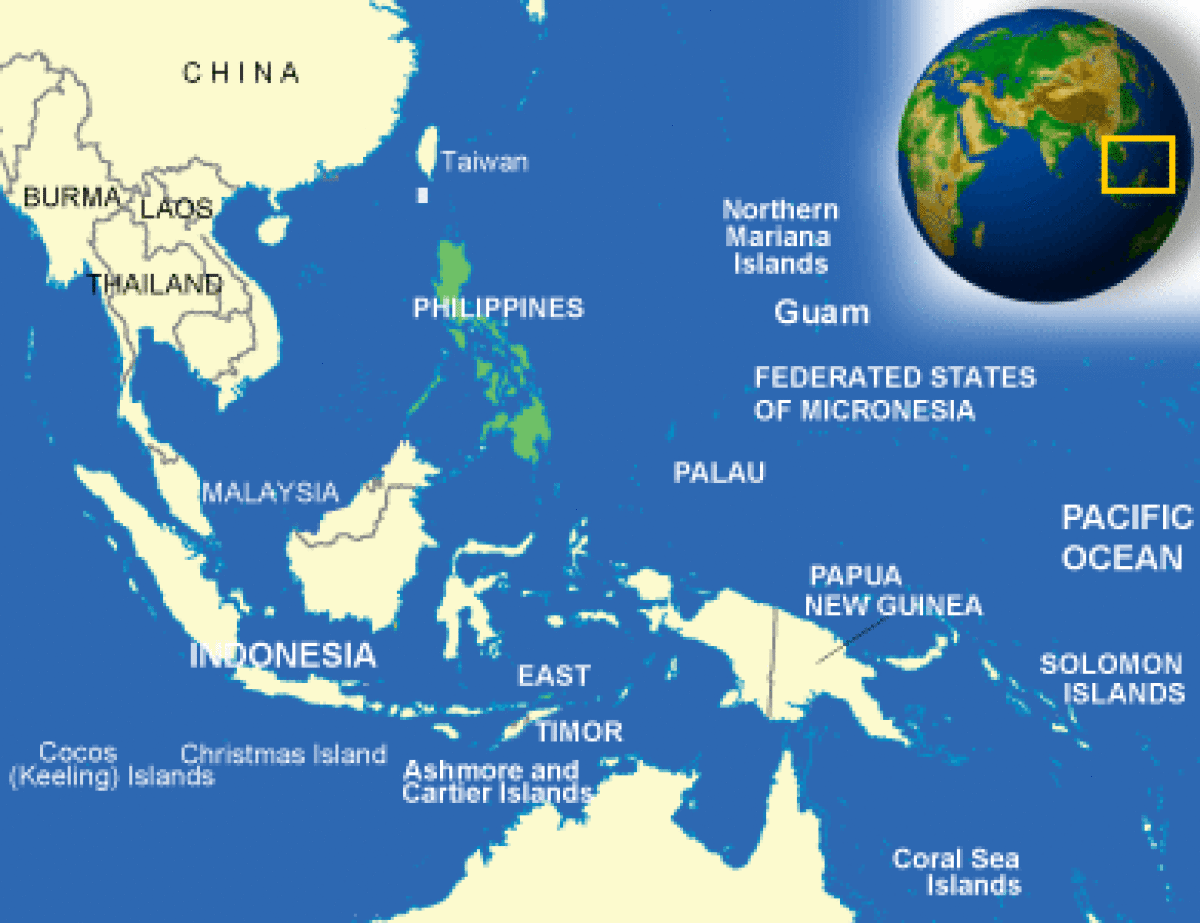
Where is Philippines located?
What countries border Philippines?
Philippines Weather
What is the current weather in Philippines?
Philippines Facts and Culture
What is Philippines famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Filipinos are sensitive people. Insincerity is easily detected and can ruin a relationship. Individualism is less important than the family.... More
- Family: The average Filipino family is large, often with four or more children. Professionally and otherwise, Filipino women generally enjoy equality... More
- Personal Apperance: As elsewhere in the world, clothing trends in the Philippines have somewhat conformed to Western standards, with a few exceptions.... More
- Recreation: Teenagers form peer groups called barkadas, a kind of friendship club that is essential to their lives. Each barkada is... More
- Diet: Rice is the staple food in the Filipino diet. It is prepared in various tasty ways and is often included... More
- Food and Recipes: The conversation is casual during meals. The best way for a guest to compliment a meal is to eat heartily.... More
- Visiting: Hospitality is important to Filipinos. Guests are made to feel at ease and should, in turn, be tactful and sincere.... More
- Dating: In urban areas, dating habits are similar to Western styles. Group dating begins in the early teens. The groom and... More
Philippines Facts
What is the capital of Philippines?
| Capital | Manila |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Philippines Peso (PHP) |
| Total Area |
115,830 Square Miles 300,000 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of Vietnam |
| Language | two official languages - Filipino (based on Tagalog) and English; eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and Pangasinense |
| GDP - real growth rate | 6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $7,500.00 (USD) |
Philippines Demographics
What is the population of Philippines?
| Ethnic Groups | Christian Malay 91.5%, Muslim Malay 4%, Chinese 1.5%, other 3% |
| Languages | There are two official languages in the Philippines, Pilipino and English. English is used for business, government, and education from the fourth grade through college. Pilipino, which is based mostly on Tagalog, which is the language spoken in central Luzon. Pilipino is referred to as Tagalog by most people. |
| Nationality Noun | Filipino(s) |
| Population | 109,180,815 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.84% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MANILA (capital) 11.862 million; Davao 1.565 million; Cebu City 855,000; Zamboanga 884,000 |
| Urban Population | 48.800000 |
Philippines Government
What type of government does Philippines have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Ferdinand "BongBong" MARCOS, Jr. (since 30 June 2022); Vice President Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (since 30 June 2022); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Ferdinand "BongBong" MARCOS, Jr. (since 30 June 2022); Vice President Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (since 30 June 2022) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with the consent of the Commission of Appointments, an independent body of 25 Congressional members including the Senate president (ex officio chairman), appointed by the president elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on separate ballots by simple majority popular vote for a single 6-year term; election last held on 9 May 2022 (next to be held on 9 May 2028) election results: 2022: Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. elected president; percent of vote - Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. (PFP) 58.7%, Leni ROBREDO (independent) 27.9%, Manny PACQUIAO (PROMDI) 6.8%, other 6.6%; Sara DUTERTE-Carpio elected vice president; percent of vote Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (Lakas-CMD) 61.5%, Francis PANGILINAN (LP) 17.8%, Tito SOTTO 15.8%, other 4.9% 2016: Rodrigo DUTERTE elected president; percent of vote - Rodrigo DUTERTE (PDP-Laban) 39%, Manuel "Mar" ROXAS (LP) 23.5%, Grace POE (independent) 21.4%, Jejomar BINAY (UNA) 12.7%, Miriam Defensor SANTIAGO (PRP) 3.4%; Leni ROBREDO elected vice president; percent of vote Leni ROBREDO (LP) 35.1%, Bongbong MARCOS (independent) 34.5%, Alan CAYETANO 14.4%, Francis ESCUDERO (independent) 12%, other 4% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Philippines dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 12 June (1898); note - 12 June 1898 was date of declaration of independence from Spain; 4 July 1946 was date of independence from the US |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest ratified 2 February 1987, effective 11 February 1987 amendments: proposed by Congress if supported by three fourths of the membership, by a constitutional convention called by Congress, or by public petition; passage by either of the three proposal methods requires a majority vote in a national referendum; note - the constitution has not been amended since its enactment in 1987 |
| Independence | 4 July 1946 (from the US) |
Philippines Video
YouTube: ClubTravelie Manila, the Pearl of the Orient
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Philippines Geography
What environmental issues does Philippines have?
| Overview |
The Philippines is composed of 7,107 separate islands (7,106 during high tide), only 880 of which are inhabited. The three major geographical areas in the Philippines are the large island of Luzon in the north, which includes Manila; the large island of Mindanao in the south; and the group of islands lying between them, known as the Visayas. The three stars on the Philippine flag symbolize these three areas. The island geography of the Philippines includes about 21,000 miles of natural coastline. Much of the coastal area is rugged and irregular, punctuated by numerous natural harbors and picturesque coves. The Philippines also has some of the most spectacular beaches to be found in the South Pacific. Sites that would live up to anyone's fantasy of a pristine South Pacific paradise of white sand beaches and crystal blue waters, they are a popular destination for tourists from around the world. Unfortunately, the heavy pollution and rocky coastline of Manila Bay render the metro Manila area itself unsuited for leisurely Sundays at the beach. The interior of the country is generally mountainous, with several mountain peaks reaching almost 10,000 feet. In addition, the Philippines has extensive fertile plains along the coast and in the center of the country. It also features lush and scenic rolling hills, with rich valleys crossed by rivers. There are numerous volcanoes in the country, and some are frequently active. The most recent and infamous example was the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo on June 12, 1991, which was the largest volcanic eruption of the century. The Mt. Pinatubo eruption permanently altered the topography of northern Luzon and continues to cause flood control problems. Minor earth tremors occur frequently. In 1969 and 1970, major earthquakes hit Manila, resulting in moderate damage and some loss of life. In January 1982, an earthquake measuring 6.8 on the Richter scale hit Northern Bicol. In August 1983, an earthquake measuring 5.7 occurred in Ilocos Norte. Both caused extensive property damage and loss of life. On July 16, 1990, one of the largest and most destructive earthquakes ever to hit the Philippines struck in Central Luzon. At its epicenter near Cabanatuan, it measured 8.0 on the Richter scale. This "killer earthquake" caused great destruction and loss of life in Baguio and some other cities of Central Luzon but did not seriously damage Manila. The Philippines is a country rich with unique tropical rain forests and coral reefs. It has been referred to as the Galapagos Islands times ten. It hosts more than 510 species of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians that exist nowhere else on earth. The country is also on the East Asian Migratory Flyway for birds that travel from the south pole to the north pole and back again each year. The Olango Island Wildlife Sanctuary, just minutes from Cebu City, has won international ecotourism awards for its educational tours and conservation efforts. Scuba diving and snorkeling on the biologically diverse coral reefs are also popular activities, with good resorts and coral reefs within driving distance from Manila. Less than 18% of the land area remains covered by forests-only about 5 million hectares. And only 800,000 hectares of this forest is considered old growth forest. These natural resources provide the basis for food security and employment for millions of Filipinos. |
| Climate |
The Philippines has a tropical climate, but it is marginally less hot and humid than many tropical countries for most of the year. Although the sun shines almost year round, there are slight seasonal variations in the weather. The dry summer season, which runs from about late April to early June is hot and humid and with little rainfall. The typhoon season runs from June to September, with frequent drenching rains that can temper the heat somewhat but also preclude any outdoor activities. The downpours are often limited in duration, but the resulting flash floods can create chaos by blocking streets, stranding motorists, and bringing the already congested traffic of Manila to a virtual standstill. The most pleasant season follows the rainy season, from November until March. During this time of year, mornings can be fresh, and even the midday temperatures remain bearable, with frequent breezes that temper the heat. The temperature range in Manila is relatively narrow, with minimum temperatures in the mid-70s and highs in the mid-90s, and an annual mean of about 80°F. Average relative humidity ranges from 69% in April to 84% in August or September. Baguio, the original summer capital of the Philippines, is located 155 miles north of Manila at an altitude of about 5,000 feet. The climate varies between the dry and the very wet season, each lasting about six months. The dry season runs from December to May, with temperatures ranging from the 50s and 60s at night to highs in the mid-80s during the day. Baguio averages 176 inches of rainfall a year, about half of which falls in July and August alone. The rains begin tapering off in September and are light in October and November. |
| Environment - Current Issues | uncontrolled deforestation especially in watershed areas; soil erosion; air and water pollution in major urban centers; coral reef degradation; increasing pollution of coastal mangrove swamps that are important fish breeding grounds |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants |
| Terrain | mostly mountains with narrow to extensive coastal lowlands |
Philippines Economy
How big is the Philippines economy?
| Economic Overview |
The Philippine economy is characterized by a diverse range of sectors contributing to its growth, including agriculture, manufacturing, services, and increasingly, information technology and business process outsourcing (IT-BPO). GDP Growth: The Philippine economy has been experiencing steady growth over the past few years, although it faced challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, the Philippines consistently posted GDP growth rates averaging around 6%, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in Asia. Services Sector: The services sector is a significant driver of the Philippine economy, contributing the largest share to GDP. This includes IT-BPO, tourism, retail, and financial services. The IT-BPO industry, in particular, has been a major contributor to economic growth, leveraging the country's skilled English-speaking workforce. Remittances: The Philippines receives a substantial amount of remittances from overseas Filipino workers (OFWs), particularly from countries like the United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. These remittances play a crucial role in supporting household consumption and driving domestic demand. Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector is another important contributor to the Philippine economy, encompassing industries such as electronics, automotive, and food processing. The government has been implementing initiatives to attract more investment in manufacturing and improve competitiveness. Agriculture: Agriculture remains a significant sector, employing a large portion of the population, particularly in rural areas. However, it has faced challenges such as land reform issues, natural disasters, and low productivity. Efforts to modernize the sector and improve productivity are ongoing. Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure development has been a priority for the Philippine government, with ambitious plans aimed at improving connectivity, transportation, and logistics across the archipelago. Projects such as roads, bridges, airports, and seaports are underway to support economic growth and development. Challenges: Despite its growth potential, the Philippine economy faces various challenges, including income inequality, poverty, corruption, and bureaucratic red tape. Addressing these challenges is crucial for sustaining inclusive growth and development. Government Policies: The government has been implementing various policies and reforms to promote investment, improve the business climate, and boost economic competitiveness. These include tax reforms, ease of doing business initiatives, and initiatives to attract foreign direct investment. Regional Disparities: There are significant regional disparities in the Philippine economy, with the capital region of Metro Manila and surrounding areas experiencing faster growth compared to rural and less developed regions. Efforts to promote more inclusive growth and development are needed to address these disparities. |
| Industries | electronics assembly, textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, wood products, food processing, petroleum refining, fishing |
| Currency Name and Code | Philippines Peso (PHP) |
| Export Partners | US 24.7%, Japan 15%, Netherlands 8.7%, Taiwan 7.1%, Singapore 7%, Hong Kong 6.7%, Malaysia 4.7% |
| Import Partners | US 20.6%, Japan 20.4%, South Korea 7.8%, Singapore 6.5%, Taiwan 5%, Hong Kong 4.5% |
Philippines News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Philippines?
Source: Google News
Philippines Travel Information
What makes Philippines a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Philippines is an emerging economy with a democratic system of government. Located in Southeast Asia, the country is an archipelago consisting of more than 7,100 islands, of which more than 800 are inhabited. The major island groupings are Luzon in the north, where the capital, Manila, is located; the Visayas in the center; and Mindanao in the south. Tourist facilities are available within population centers and the main tourist areas. English is widely spoken in the Philippines, and most signs are in English.
Crime
Crime is a significant concern in Manila. As a rule of thumb, U.S. citizens should exercise good judgment and remain aware of their surroundings. Reports of confidence games (con games), pick pocketing, Internet scams, and credit/ATM card fraud are common. U.S. citizens should be wary of unknown individuals who attempt to befriend them, especially just after their arrival in the country. It is best not to accept food, drink, or rides in private vehicles from strangers, even if they appear to be legitimate. There have been several cases of solo travelers meeting people on Roxas Boulevard in downtown Manila, striking up a conversation, developing a relationship, and then being invited to a tourist destination outside of Manila under the guise of meeting their Philippine family. The travelers are taken to the area and, typically, during a meal are given a substance that knocks them unconscious. They are then robbed of valuables, including their ATM cards, which are then used to drain their bank accounts. While U.S. citizens are not typically targeted, kidnappings and violent assaults do occur in the Manila area.Taxis are the recommended form of public transportation. The following safeguards are important: do not enter a taxi if it has already accepted another passenger and always request that the driver use the meter to record your fare. If the driver is unwilling to comply with these requests, wait for another cab. It is also a good idea to make a mental note of the license plate number of the cab, or text it to someone, should there be a problem. There have been several instances of travelers arriving at the Manila international airport and, shortly after they leave the airport area in a taxi or private vehicle, their vehicle is stopped, typically by an intentional rear-end collision, and the travelers are robbed. When driving in the city, make certain that vehicle doors are locked and the windows are rolled up. For both safety and security reasons, avoid all other forms of public transportation, such as the light rail system, buses, and “jeepneys.”
You should also be vigilant when using credit and debit cards. One common form of credit/ATM card fraud involves an illicit electronic device attached to ATM card readers that retrieves and records information, including the PIN, from a card's magnetic strip. The information is then used to make unauthorized purchases. To limit your vulnerability to this scam, never let your card out of your sight. Avoid ATMs with unusual coverings attached to the card receiver. When using an ATM, be aware of your surroundings. Avoid ATM locations in dimly lit areas. Be careful to prevent observation by others when entering your PIN code. A continuing problem is the commercial scam or sting that attempts to sell or to seek negotiation of fraudulent U.S. securities. Visitors and residents should be wary when presented with supposed Federal Reserve Notes or U.S. securities for sale or negotiation.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in the Philippines, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. Criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in the Philippines, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.U.S. citizens should also be aware of a recent statement by the Bureau of Immigration (BI) regarding the participation of foreigners in demonstrations in the Philippines. In the statement, the BI advised foreigners against participating in public protests or political rallies since this activity may be considered a violation of the terms of admission to the Philippines. Foreign nationals who participate in these activities may be detained and deported for violating Philippine immigration laws.
Persons violating the Philippines’ laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession of, use of, or trafficking in illegal drugs in the Philippines are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. If a traveler is found to have any amount of drugs on his or her person, or nearby, when arriving at or departing from the Philippines, he or she will be charged with trafficking. This offense is non-bailable, and the maximum penalty is life imprisonment. There have been instances where persons carrying controlled substances (e.g., medical marijuana or morphine) as well as a doctor’s prescription for the substance were charged with drug possession because they did not possess the proper prior clearance from the Philippine government before entry.
If you are arrested in the Philippines, authorities of the Philippines are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request that the police or prison officials notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest.
Languages
There are two official languages in the Philippines, Pilipino and English. English is used for business, government, and education from the fourth grade through college. Pilipino, which is based mostly on Tagalog, which is the language spoken in central Luzon. Pilipino is referred to as Tagalog by most people.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical care is available in major cities in the Philippines, but even the best hospitals may not meet the standards of medical care, sanitation, and facilities provided by hospitals and doctors in the United States. Medical care is limited in rural and more remote areas.Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost several or even tens of thousands of dollars. Most hospitals will require a down payment of estimated fees in cash at the time of admission. In some cases, public and private hospitals have withheld lifesaving medicines and treatments for non-payment of bills. Hospitals also frequently refuse to discharge patients or release important medical documents until a bill has been paid in full. A list of doctors and medical facilities in the Philippines is available from the U.S. Embassy in Manila.
You can find good information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website. For information about outbreaks of infectious diseases abroad, consult the World Health Organization (WHO) website. The WHO website also contains additional health information for travelers, including detailed country-specific health information.
In the past, the Philippines has seen outbreaks of dengue and schistosomiasis. The CDC website has additional information about both diseases.
Schistosomiasis is transmitted by waterborne larvae and is endemic in the Philippines. The disease presents a risk on Mindanao, Bohol, and Samar, as well as the provinces of Sorsogon (the southern tip of Luzon Island) and eastern Mindoro Island. Travelers should avoid freshwater exposure in these areas.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens contemplating travel to the Philippines should carefully consider the risks to their safety and security while there, including the risk of terrorism. The southern island of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago are of particular security concern. Travelers should defer all travel to the Sulu Archipelago and should exercise extreme caution on the island of Mindanao. For further information regarding the continuing threats due to terrorist and insurgent activities in the Philippines, see the Travel Warning for the Philippines.Terrorist groups, such as the Abu Sayyaf Group and Jema’ah Islamiyah, as well as groups that have broken away from the more mainstream Moro Islamic Liberation Front, have carried out bombings resulting in deaths, injuries, and property damage; they have also taken hostages. The city of Zamboanga suffered widespread devastation in September 2013 during a deadly confrontation between Philippine public security forces and rogue fighters of the Moro National Liberation Front. Separately, bombings in central and western areas of Mindanao have targeted bus terminals, public buildings, public markets, and local festivals. While those responsible do not appear to have targeted foreigners, travelers should remain vigilant and avoid congregating in public areas. Official U.S. government visitors and Embassy employees must seek special permission for travel to Mindanao or the Sulu Archipelago. When traveling in Mindanao, U.S. official travelers attempt to lower their profile, limit their length of stay, and exercise extreme caution. Some foreigners who reside in or visit western and central Mindanao hire their own private security personnel.
Kidnap-for-ransom gangs operate in the Philippines and have targeted foreigners, including Filipino-Americans. Such gangs are especially active in the Sulu Archipelago, and a number of foreigners have been kidnapped there in recent years.
Occasionally, the U.S. Embassy is the target of planned and/or spontaneous demonstrations. While Philippine security forces generally prevent such demonstrators from reaching the Embassy, in rare instances protestors have made their way successfully to the Embassy perimeter. In such instances, Embassy security authorities may take appropriate measures to safeguard personnel and visitors, including restricting access to the compound. U.S. citizens or other individuals having business at the Embassy should keep this in mind and be prepared to defer their business until any such situation is resolved.
U.S. citizens in the Philippines are advised to monitor local news broadcasts and consider the level of preventive security when visiting public places, especially when choosing hotels, restaurants, beaches, entertainment venues, and recreation sites.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in the Philippines, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning the Philippines is provided for general reference only and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Travel within the Philippine archipelago is possible by boat, plane, bus, or car. Few U.S. citizens rent cars to drive, as the roads are more crowded and drivers are less disciplined than those in the United States. It is particularly dangerous to drive off the national highways and paved roads, especially at night, and you should avoid doing so. There have been five major inter-island ferryboat accidents in the last two years, one with significant loss of life. The safety record is such that U.S. government employees are advised not to take inter-island ferry boat services unless they are the only means of transportation available. There have also been a series of bus accidents as a result of poor bus maintenance. U.S. citizens are advised to avoid overcrowded or unsafe transport and to exercise caution in planning travel by inter-island ferryboats or other public conveyances.
For specific information concerning Philippine driver's permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, and mandatory insurance, please contact the Philippine Embassy in Washington, DC, at tel. (202) 467-9300 or one of the Philippine consulates in the United States (Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, and San Francisco).
