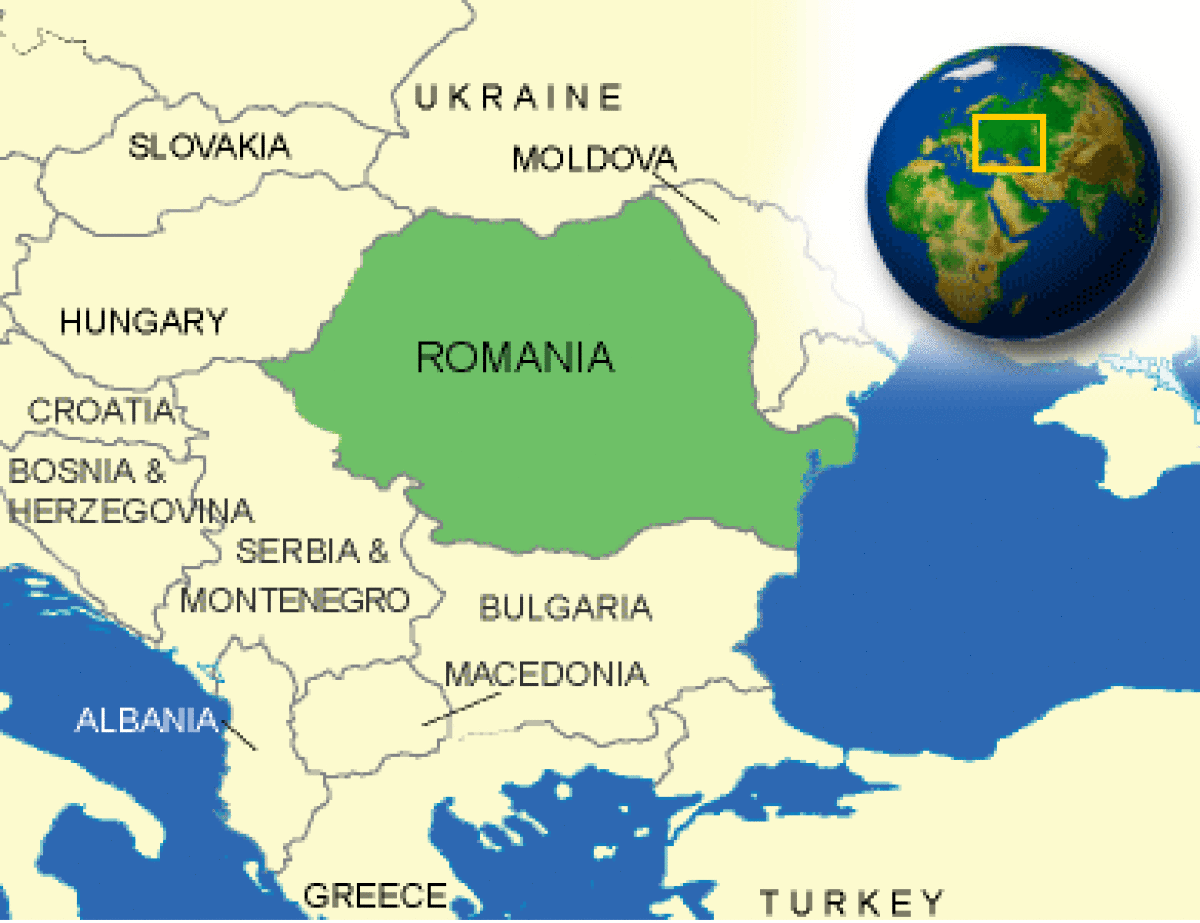
Where is Romania located?
What countries border Romania?
Romania Weather
What is the current weather in Romania?
Romania Facts and Culture
What is Romania famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The conflicting attitudes about the future of the nation have led to violence, instability, and the rise of dangerous tensions... More
- Family: The father maintains a dominant role in the family. Most women work outside the home, but they remain responsible for... More
- Personal Apperance: Few Romanians have the means to buy fashionable clothing. People generally dress conservatively in public. The elderly are more likely... More
- Recreation: Children start playing sports early, usually gymnastics, volleyball, handball, and skating, depending on their school. Some people enjoy open-air activities like... More
- Diet: Lunch is the main meal of the day and generally consists of soup, meat, potatoes, bread, and vegetables. Pastries are... More
- Food and Recipes: The continental style of eating is used. Both hands (not elbows) are kept above the table during a meal. ... More
- Visiting: Guests are usually offered tea, coffee, or wine. When invited to dinner, it is considered polite for the guest to... More
- Dating: Couples in rural areas marry relatively early and follow local and ethnic customs regarding courtship and marriage. In the past,... More
Romania Facts
What is the capital of Romania?
| Capital | Bucharest |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Leu (RON) |
| Total Area |
92,043 Square Miles 238,391 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Bulgaria and Ukraine |
| Language | Romanian (official), Hungarian, German |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $20,600.00 (USD) |
Romania Demographics
What is the population of Romania?
| Ethnic Groups | Romanian 89.5%, Hungarian 6.6%, Roma 2.5%, Ukrainian 0.3%, German 0.3%, Russian 0.2%, Turkish 0.2%, other 0.4% |
| Languages | The Germans and Hungarians speak their native ethnic tongues. The Roma speak Romany. |
| Nationality Noun | Romanian(s) |
| Population | 21,302,893 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.27% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | BUCHAREST (capital) 1.937 million |
| Urban Population | 52.800000 |
Romania Government
What type of government does Romania have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Klaus Werner IOHANNIS (since 21 December 2014) head of government: Prime Minister Marcel CIOLACU (since 15 June 2023); Deputy Prime Ministers Sorin GRINDEANU (since 25 November 2021) and Hunor KELEMEN (since 23 December 2020) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 10 November 2019 with a runoff on 24 November 2019 (next to be held in November 2024); prime minister appointed by the president with consent of Parliament election results: 2019: Klaus IOHANNIS reelected president in second round; percent of vote - Klaus IOHANNIS (PNL) 66.1%, Viorica DANCILA (PSD) 33.9% 2014: Klaus IOHANNIS elected president in second round; percent of vote - Klaus IOHANNIS (PNL) 54.4%, Victor PONTA (PSD) 45.6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Romania dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Unification Day (unification of Romania and Transylvania), 1 December (1918) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 21 November 1991, approved by referendum and effective 8 December 1991 amendments: initiated by the president of Romania through a proposal by the government, by at least one fourth of deputies or senators in Parliament, or by petition of eligible voters representing at least half of Romania’s counties; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by both chambers or – if mediation is required - by three-fourths majority vote in a joint session, followed by approval in a referendum; articles, including those on national sovereignty, form of government, political pluralism, and fundamental rights and freedoms cannot be amended; amended 2003 |
| Independence | 9 May 1877 (independence proclaimed from the Ottoman Empire; 13 July 1878 (independence recognized by the Treaty of Berlin); 26 March 1881 (kingdom proclaimed); 30 December 1947 (republic proclaimed) |
Romania Video
YouTube: TrekkingThePlanet The Painted Monasteries of Romania
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Romania Geography
What environmental issues does Romania have?
| Overview |
The Republic of Romania is the 12th largest country in Europe. It occupies the greater part of the lower basin of the Danube River system and the hilly eastern regions of the middle Danube Basin. Its 91,700 square miles make it similar in size to the United Kingdom and the State of Oregon. Some consider Romania to be a "Latin Island," because it is bordered by two seas: one real, the Black Sea to which Romania owes its 150 miles of coastline and the other, the sea of non-Latin countries with which it shares its other borders. The country is almost equally divided geographically into mountains, plains, hills, and plateaus. Apart from a stretch of tableland near the Black Sea coast, Romania's mountainous sector is part of the rugged Carpathian chain. |
| Climate | Romania has a continental climate, particularly in the Old Kingdom (east and south of the Carpathians). A long, and occasionally harsh, winter (December-March), a hot summer (May-August), and a prolonged autumn (September-November) are the principal seasons. The average daily minimum temperature for Bucharest (February) is 28.6ºF, and the average daily maximum (August) is 95ºF. Rainfall, heaviest from April through July, averages 5 inches in June. |
| Border Countries | Bulgaria 608 km, Hungary 443 km, Moldova 450 km, Serbia and Montenegro 476 km, Ukraine (north) 362 km, Ukraine (east) 169 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | soil erosion and degradation; water pollution; air pollution in south from industrial effluents; contamination of Danube delta wetlands |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | central Transylvanian Basin is separated from the Plain of Moldavia on the east by the Carpathian Mountains and separated from the Walachian Plain on the south by the Transylvanian Alps |
Romania Economy
How big is the Romania economy?
| Economic Overview |
Overview of the Romanian economy: Market Economy: Romania has a developing market economy. Since the fall of communism in 1989, the country has undergone significant economic reforms to transition from a centrally planned economy to a market-based one. Diverse Sectoral Composition: The Romanian economy is diversified, with key sectors including services, industry, agriculture, and construction. Services contribute the most to the GDP, followed by industry and agriculture. Industry: Romania has a strong industrial base, with sectors like automotive, machinery, IT, and textiles playing significant roles. The automotive industry, in particular, has been a major driver of exports and foreign direct investment. Agriculture: Agriculture is an important sector, especially in rural areas. Romania has fertile land and favorable climatic conditions for agriculture. Key products include cereals, vegetables, fruits, and livestock. Exports: Romania has a relatively open economy that focuses on exports. Key export products include machinery, equipment, vehicles, electronics, textiles, and agricultural products. Other EU countries, especially Germany, Italy, and France, are the country's main trading partners. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Foreign investment has played a significant role in Romania's economic development since the 1990s. FDI inflows are attracted by factors such as a skilled workforce, competitive labor costs, strategic location, and EU membership. Challenges: Despite progress, Romania faces several economic challenges. These include corruption, an inefficient public sector, bureaucracy, infrastructure deficits, emigration of skilled workers, regional disparities, and a high level of informal economic activities. European Union Membership: Romania joined the European Union (EU) in 2007, which has brought both benefits and challenges. EU membership has provided access to funding, trade opportunities, and support for reforms. However, it has also required compliance with EU regulations and standards. COVID-19 Pandemic: Like many countries, Romania's economy has been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Measures such as lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing have affected various sectors, including tourism, retail, and hospitality. Government Policies: The Romanian government has implemented various economic policies to stimulate growth, attract investment, improve infrastructure, and address structural issues. However, there is ongoing debate about the effectiveness of these policies and the pace of reforms. |
| Industries | textiles and footwear, light machinery and auto assembly, mining, timber, construction materials, metallurgy, chemicals, food processing, petroleum refining |
| Currency Name and Code | Leu (RON) |
| Export Partners | Italy 25.2%, Germany 15.6%, France 7.6%, UK 5.8%, US 4.3%, Turkey 4.1% |
| Import Partners | Italy 20.8%, Germany 14.9%, Russia 7.2%, France 6.4% |
Romania News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Romania?
Source: Google News
Romania Travel Information
What makes Romania a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Romania is a republic and a member of both NATO and the European Union. The country has a market-oriented economy with developed tourist facilities in the capital, Bucharest, and facilities of varying quality throughout the rest of the country.
Crime
While most crimes in Romania are nonviolent, crimes do occur in which people do get hurt and even severely injured, especially at nightclubs and bars. Reports of sexual assault are uncommon; however, to be safe, be vigilant, especially at night and in situations involving alcohol. Although racial prejudice exists in Romania, especially toward those who look like Roma (“gypsies”), hate crimes are rare.Crimes against tourists, such as robbery, pick pocketing, and confidence schemes remain problematic. Organized groups of thieves and pickpockets, sometimes including minors, operate in train stations and on trains, subways, and buses in major cities. A number of thefts and assaults have occurred on overnight trains, including thefts from passengers in closed compartments. The U.S. Embassy recommends using the highest class available for train travel, and traveling with at least one other person. Avoid leaving your personal belongings unattended; stow them securely out of sight if leaving them in a parked car.
Credit card and internet fraud remain among the most common crimes affecting foreigners in Romania. Romania is largely a "cash-only" economy. While an increasing number of businesses accept credit cards, you may wish to use cash for goods and services rendered due to the risk of credit card fraud. Vendors, including restaurant staff, have been known to misuse credit card information by making illegal purchases on a customer's account. There are an increasing number of Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs) located throughout major cities, and sophisticated identity theft rings target them. Try to use ATMs located inside banks and check for any evidence of tampering before use. Be cautious when using publicly available internet terminals, such as in internet cafes, as sensitive personal information, account passwords, etc. may be compromised.
You should be alert to money exchange schemes targeting travelers. Some of these ploys have become sophisticated, involving individuals posing as plainclothes policemen who approach you, flashing a badge, and asking for your passport and wallet. If presented with a situation like this, you should insist on the presence of a uniformed police officer and request that any problem be resolved at a police station.
You should be cautious about entering into contracts with Romanian groups and/or organizations. There have been a number of incidents in which such contracts have not been honored. As a result, the U.S. Embassy recommends that all contracts entered into by foreigners are reviewed by a Romanian attorney. The Romanian legal system is difficult for foreigners to navigate, making the assistance of a local attorney nearly essential.
You should be very careful about developing relationships with individuals known only through contact over the Internet. Professional thieves in Romania commonly target U.S. citizens by contacting them through chat rooms or personal advertisements. They generally identify themselves as young Romanian women and develop a "relationship" with their victims over time. Requests for money may not begin for six months or longer when a fictional child becomes ill, a job is lost; a business needs start-up cash, etc. While numerous variations of this scam exist, money extortion remains the ultimate goal. If you believe you may have fallen victim to this kind of scam, contact American Citizens Services at the U.S. Embassy. Romanian authorities may be reluctant to prosecute these crimes unless you can show that coercion was used or a significant amount of your money was stolen.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, but by buying them you may be breaking local law too.
Criminal Penalties
While traveling or living in Romania, you are subject to Romanian laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Romanian laws and legal systems can be vastly differentthan our own. Criminal penalties may vary as well. Please see the Embassy’s legal information for more details about Romanian law and penalties. Please also note the Embassy’s judicial assistance information for more information about the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in force between Romania and the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you engage in sexual conduct with children or use or disseminate child pornography. Under Romanian law, engaging in sexual conduct with a minor under the age of 15, or a minor between the ages of 15 and 18 where the adult has abused the minor's trust or had influence/authority over the minor, is a crime punishable with a 3-10 year prison sentence. Engaging in illicit sexual conduct with someone who has a physical or psychological disability is punishable with a 3-12 year prison sentence. Distribution of obscene materials depicting minors is a crime punishable with a 1-5 year prison sentence. Prostitution is illegal in Romania, regardless of the age of the participants.Penalties for the possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Romania are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
If Arrested: If you are arrested in Romania, Romanian authorities are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the embassy. A consular officer from the embassy will visit you, but will not be able to get you out of jail; you will need to consult an attorney. A list of English speaking attorneys can be found on the embassy’s website The Romanian authorities will provide you with an attorney and translator if you cannot afford one.
Languages
The Germans and Hungarians speak their native ethnic tongues. The Roma speak Romany.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in Romania is generally not up to Western standards and basic medical supplies are limited, especially outside major cities. Some medical providers that meet Western quality standards are available in Bucharest and other cities but can be difficult to locate. Sanitary conditions in hospitals are variable. Nursing care and assistance from orderlies is often lacking in hospitals. Families often provide basic assistance to hospitalized relatives that U.S. citizens generally expect the hospital to provide. Travelers seeking medical treatment should choose their provider carefully.Most prescription drugs and over-the-counter medication are available in Romania but may be sold under different brand names. Specific individual drugs may not be available due to differences in laws and regulations. Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Romania.
Response times for emergency services vary widely depending on the region of the country and the nature of the emergency. Romania has helicopter services available for the most critical medical evacuation situations.
Safety and Security
Romania remains largely free of terrorist incidents. The Romanian equivalent to the “911” emergency line is 112. English-speaking operators are available.Prior police notice is required for public demonstrations, and police oversight is routinely provided. The ongoing financial crisis and resulting austerity measures have increased the occurrences of strikes and public demonstrations in Romania, especially in Bucharest. To date, protests have remained peaceful. However, even demonstrations that are meant to be peaceful can become violent and unpredictable; you should avoid them if at all possible. Be alert and aware of your surroundings and pay attention to what the local news media has to say. Information on specific demonstrations can be found on the Embassy website’s Demonstration Notices page.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Romania, you will encounter road conditions that significantly differ from those in the United States. Traffic accidents are arguably the single most dangerous threat for U.S. citizens visiting Romania. The World Economic Forum ranks Romania 142 out of 144 states for road quality, with a limited number of freeways and infrequent passing lanes. While major streets in larger cities and major inter-city roads are generally in fair to good condition, many secondary roads are in poor repair, unpaved, badly lighted, narrow, and lacking marked lanes. According to the European Union Road Federation, Romania has the highest per vehicle rate of traffic fatalities of any country in the EU. It is essential to practice defensive driving techniques if you choose to drive in Romania.Roads, especially in the mountains, can be particularly dangerous when wet or covered with snow or ice. Winter snow removal, even in cities and on major highways, can be intermittent. Pedestrians, animals, cyclists, and horse-drawn carts share many roads with motor vehicles and it can be extremely difficult to see, particularly at night in rural areas. Parked vehicles often block sidewalks, forcing pedestrians to walk in the streets. Maintain vigilance when driving to avoid hitting those who are walking in the streets. Cross the street only at crosswalks, and always look both ways before crossing. Crosswalks are generally poorly marked and may be ignored by drivers even if there is a traffic light.
Romanian traffic laws are very strict. The traffic police can confiscate any form of a driver's license or permit for 1-3 months and request payment of fines at the time of the infraction; this includes minor infractions such as failing to yield to pedestrians at crosswalks. There is zero tolerance for driving under the influence of alcohol. Police are required to give all drivers involved in an accident breathalyzer tests on the scene. Refusal to take a breathalyzer test will result in criminal penalties regardless of whether or not alcohol was involved. Driving under the influence of alcohol or causing an accident resulting in injury or death may result in imprisonment.
U.S. driver's licenses are only valid in Romania for up to 90 days. Before the 90-day period has expired, U.S. citizens must either obtain an international driving permit in addition to their U.S. driver's license or a Romanian driver's license. Wearing a seat belt is mandatory. Children under 12 years of age may not be transported in the front seat.
Unless otherwise marked with road signs, speed limits are as follows:
Intercity traffic on highways
130 km/hr for cars and motorcycles (80 miles/hr)
110 km/hr for vans (65 miles/hr)
Urban traffic - 50 km/hr (30 miles/hr)
Express and European roads
100 km/hour for cars and motorcycles (60 miles/hr)
90 km/hour for vans (55 miles/hr)
All other roads
90 km/hr for cars and motorcycles (55 miles/hr)
80 km/hr for vans (50 miles/hr)
Motor vehicles with trailers, and drivers with less than one year of driving experience have speed limits 20 km/hr (or 12 miles/hr) slower than those listed above.The host country authority responsible for road safety is the Traffic Police of the Romanian Ministry of Interior. You can reach emergency roadside help and information for vehicle assistance and towing services by dialing 9271. For ambulance services, fire brigade, or police dial 112.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
