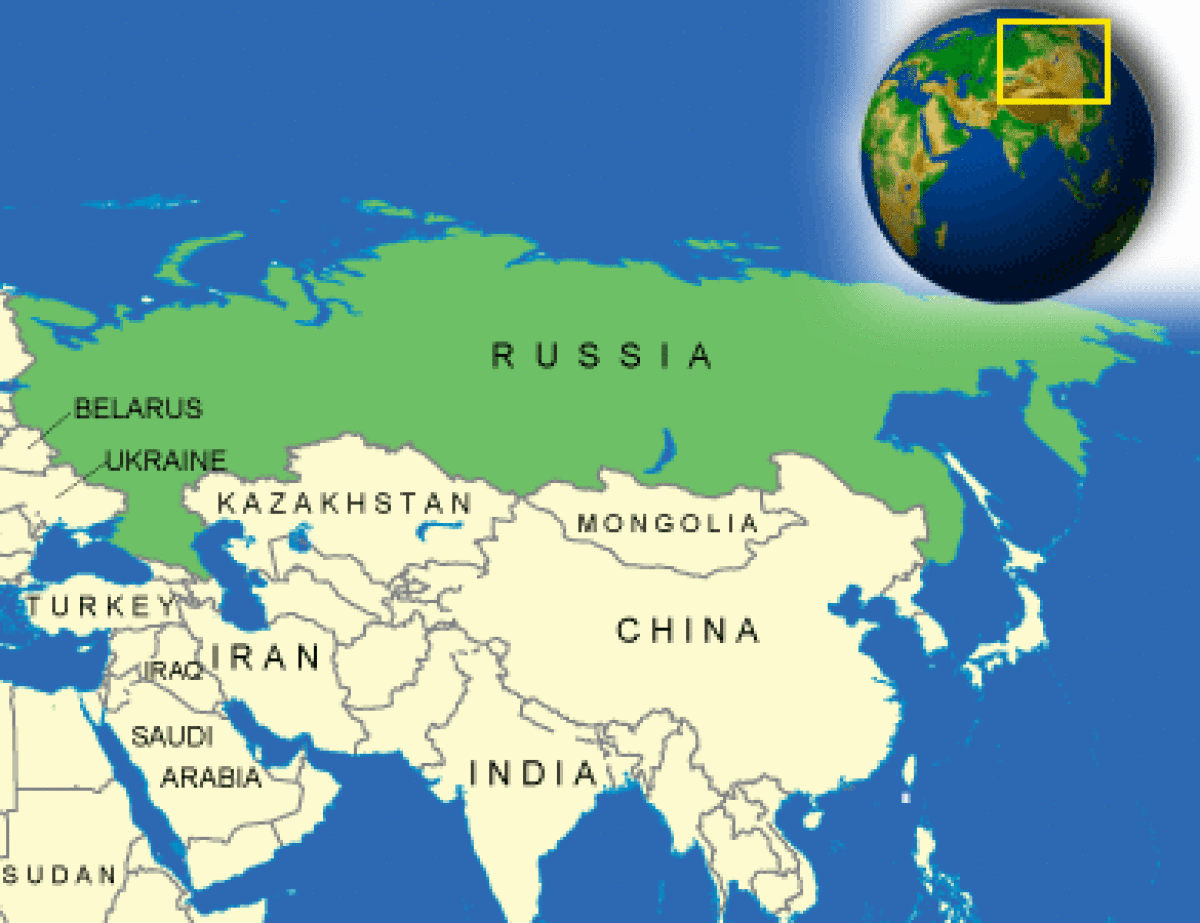
Where is Russia located?
What countries border Russia?
Russia Weather
What is the current weather in Russia?
Russia Facts and Culture
What is Russia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Much has been said about the purported fatalism and inertia of the Russian people. This is not born out of... More
- Family: Because housing is difficult to obtain, young couples often live with their parents for some time. It is the standard... More
- Personal Apperance: Russian clothing styles are essentially the same as in Europe, but the younger generation follows the latest trends, and the... More
- Recreation: Organized sports play an essential part in the daily life of most Russian citizens. Many physical training clubs, sports halls,... More
- Diet: Common Russian foods include borsch (cabbage soup with beets), pirozhki (a small oblong pie filled with a variety of ingredients... More
- Food and Recipes: Eating with a fork in the left hand and a knife in the right is standard, but many people use... More
- Visiting: Russians have special rituals for greeting guests. It is considered bad luck to greet a guest while standing in the... More
- Dating: When dating young people, usually go to a movie or walk. They may go to a bar or eating establishment... More
Russia Facts
What is the capital of Russia?
| Capital | Moscow |
| Government Type | semi-presidential federation |
| Currency | Russian Ruble (RUR or RUB) |
| Total Area |
6,601,631 Square Miles 17,098,242 Square Kilometers |
| Location | North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean |
| Language | Russian (official), many minority languages |
| GDP - real growth rate | -3.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $23,700.00 (USD) |
Russia Demographics
What is the population of Russia?
| Ethnic Group - note | nearly 200 national and/or ethnic groups are represented in Russia's 2010 census |
| Ethnic Groups | Russian 77.7%, Tatar 3.7%, Ukrainian 1.4%, Bashkir 1.1%, Chuvash 1%, Chechen 1%, other 10.2%, unspecified 3.9% |
| Language - note | Russian is the official language in the country. It is a European language belonging to the Slavonic group of languages. This group includes Ukrainian, Belorussian, Serbian, Czech and Polish. The Russian alphabet uses the Cyrillic, which consists of thirty-three letters; this alphabet is related to but quite distinct from the Roman (Latin) alphabet. Standard Russian is spoken throughout the territory, with regional differences in pronunciation and vocabulary. |
| Languages | Russian (official) 85.7%, Tatar 3.2%, Chechen 1%, other 10.1%; note - data represent native language spoken |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Russian(s) adjective: Russian |
| Population | 140,820,810 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.49% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 12.680 million MOSCOW (capital), 5.561 million Saint Petersburg, 1.695 million Novosibirsk, 1.528 million Yekaterinburg, 1.292 million Kazan, 1.251 million Nizhniy Novgorod |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 75.3% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.11% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.) |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 65,496,805 female: 75,324,005 |
Russia Government
What type of government does Russia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Vladimir Vladimirovich PUTIN (since 7 May 2012); no vice president position head of government: Premier Mikhail Vladimirovich MISHUSTIN (since 16 January 2020); First Deputy Premier Andrey Removich BELOUSOV (since 21 January 2020); Deputy Premiers Yuriy TRUTNEV (since 31 August 2013), Tatiana Alekseyevna GOLIKOVA (since 18 May 2018), Dmitriy Yuriyevich GRIGORENKO, Viktoriya Valeriyevna ABRAMCHENKO, Aleksey Logvinovich OVERCHUK, Marat Shakirzyanovich KHUSNULLIN, Dmitriy Nikolayevich CHERNYSHENKO (all since 21 January 2020), Aleksandr NOVAK (since 10 November 2020), Denis Valentinovich MANTUROV (since 15 July 2022) cabinet: the government is composed of the premier, his deputies, and ministers, all appointed by the president; the premier is also confirmed by the Duma elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 6-year term (2020 constitutional amendments allow a second consecutive term); election last held on 15 to 17 March 2024 (next to be held 2030) election results: 2024: Vladimir PUTIN reelected president; percent of vote - Vladimir PUTIN (independent) 88.5%, Nikolay KHARITONOV (Communist Party) 4.4%, Vladislav DAVANKOV (New People party) 3.9%, Leonid SLUTSKY (Liberal Democrats) 3.2% 2018: Vladimir PUTIN reelected president; percent of vote - Vladimir PUTIN (independent) 77.5%, Pavel GRUDININ (CPRF) 11.9%, Vladimir ZHIRINOVSKIY (LDPR) 5.7%, other 4.9%; Mikhail MISHUSTIN (independent) approved as premier by Duma; vote - 383 to 0 2012: Vladimir PUTIN elected president; percent of vote - Vladimir PUTIN (United Russia) 63.6%, Gennadiy ZYUGANOV (CPRF) 17.2%, Mikhail PROKHOROV (CP) 8%, Vladimir ZHIRINOVSKIY (LDPR) 6.2%, Sergey MIRONOV (A Just Russia) 3.9%, other 1.1%; Dmitriy MEDVEDEV (United Russia) approved as premier by Duma; vote - 299 to 144 note: there is also a Presidential Administration that provides staff and policy support to the president, drafts presidential decrees, and coordinates policy among government agencies; a Security Council also reports directly to the president |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Russia dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 3-5 years |
| National Holiday | Russia Day, 12 June (1990); note - commemorates the adoption of the Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous (during Russian Empire and Soviet era); latest drafted 12 July 1993, adopted by referendum 12 December 1993, effective 25 December 1993 amendments: proposed by the president of the Russian Federation, by either house of the Federal Assembly, by the government of the Russian Federation, or by legislative (representative) bodies of the Federation's constituent entities; proposals to amend the government’s constitutional system, human and civil rights and freedoms, and procedures for amending or drafting a new constitution require formation of a Constitutional Assembly; passage of such amendments requires two-thirds majority vote of its total membership; passage in a referendum requires participation of an absolute majority of eligible voters and an absolute majority of valid votes; approval of proposed amendments to the government structure, authorities, and procedures requires approval by the legislative bodies of at least two thirds of the Russian Federation's constituent entities; amended several times, last in 2020 (major revisions) |
| Independence | 25 December 1991 (from the Soviet Union; Russian SFSR renamed Russian Federation); notable earlier dates: 1157 (Principality of Vladimir-Suzdal created); 16 January 1547 (Tsardom of Muscovy established); 22 October 1721 (Russian Empire proclaimed); 30 December 1922 (Soviet Union established) |
Russia Video
Expedia- YouTube Moscow Vacation Travel Guide | Expedia
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Russia Geography
What environmental issues does Russia have?
| Overview |
The Russian Federation is physically the largest country in the world, covering 17 million square kilometers or 1.8 times the size of the United States. The territory of the Russian Federation covers 11 time zones and stretches 6,000 miles from east to west. It has a population of about 147.5 million. Politically, the Russian Federation is a union of 89 constituent republics, regions, and territories that enjoy varying degrees of economic and political independence from the central government located in the capital, Moscow. Moscow is the largest city in Russia and is located west of the great Russian plain on the banks of the Moscow River at 37°73' E and 55°45' N. The city is built on several low hills varying from 25 feet to 815 feet above sea level. St. Petersburg, Russia's second largest city and the former imperial capital, is located on a flat plain at the mouth of the Neva River on the Gulf of Finland at 55°57' N and 30°20' E. Established in 1703, the city is built on a series of 101 islands, and is laced by canals and various streams of the Neva. Yekaterinburg, Russia's third largest city with an estimated population of 1.5 million, is located near the center of Russia, at the crossroads between Europe and Asia. Founded in 1723, Yekaterinburg today is the seat of the government for the Sverdlovsk region, which contains numerous heavy industries, mining concerns, and steel factories. In addition, Yekaterinburg is a major center for industrial research and development as well as home to numerous institutes of higher education, technical training, and scientific research. Vladivostok, the largest city in the Russian Far East and home to the Russian Pacific fleet, is an important center for trade with the Pacific Rim countries. Closed to foreigners from 1958 to 1992, the city now is home to many foreign businesses and consulates. |
| Climate |
Climate ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia, subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north; winters vary from excellent along the Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia. In Moscow, Snow begins in October and continues periodically through April, although snowfall in May is not unusual. Annual rainfall averages 21 inches, with the heaviest rains falling between May and October. Prevailing winds are southerly and southwesterly. Due to Moscow's northern location, daylight varies from 7 hours in December to 17 1/2 hours in June. The average temperature in June and July is 66°F, but the summer temperatures frequently reach the low 90s. In the winter, the temperature may fall to minus 40°F, but the average December and January temperature is 14°F. Though Moscow's winter air is usually dry, the wind chill factor makes the temperature feel much colder. The climate in St. Petersburg is milder than in Moscow but is damp and misty. Average temperatures are 64°F in July and 17°F in January. St. Petersburg is famous for its "white nights," which occur in June when the sun shines for nearly 19 hours and sunset only brings semidarkness. The climate in Vladivostok is milder than in many other Russian cities due to its location on the Pacific Ocean. Winter temperatures range between -68°F and 25°F. |
| Border Countries | Azerbaijan 284 km, Belarus 959 km, China (southeast) 3,605 km, China (south) 40 km, Estonia 290 km, Finland 1,313 km, Georgia 723 km, Kazakhstan 6,846 km, North Korea 17.5 km, Latvia 292 km, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 227 km, Mongolia 3,441 km, Norway 196 km, Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 432 km, Ukraine 1,576 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution from heavy industry, emissions of coal-fired electric plants, and transportation in major cities; industrial, municipal, and agricultural pollution of inland waterways and seacoasts; deforestation; soil erosion; soil contamination from improper application of agricultural chemicals; scattered areas of sometimes intense radioactive contamination; groundwater contamination from toxic waste; urban solid waste management; abandoned stocks of obsolete pesticides |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Sulfur 94 |
| Terrain | broad plain with low hills west of Urals; vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia; uplands and mountains along southern border regions |
Russia Economy
How big is the Russia economy?
| Economic Overview |
The Russian economy is one of the world's largest and most resource-rich economies, with a diverse industrial base that includes energy, manufacturing, agriculture, and technology sectors. Its primary industries include oil, natural gas, metals, and minerals, which contribute significantly to export revenues. However, the economy is heavily reliant on the energy sector, particularly oil and gas exports, making it vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices. In recent years, Russia has faced economic challenges, including international sanctions, geopolitical tensions, and structural inefficiencies. These factors, coupled with low oil prices and weak domestic demand, have hindered economic growth. The Russian government has implemented various policies to diversify the economy, boost innovation, and attract foreign investment. Additionally, efforts have been made to reduce dependence on imports and promote import substitution to strengthen domestic industries. Despite these challenges, Russia remains a major player in the global economy, with a skilled workforce, advanced technological capabilities, and vast natural resources. Moving forward, the Russian government aims to modernize infrastructure, improve the business climate, and foster innovation to ensure sustainable economic growth and stability. |
| Industries | complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries including radar, missile production, and advanced electronic components, shipbuilding; road and rail transportation equipment; communications equipment; agricultural machinery, tractors, and construction equipment; electric power generating and transmitting equipment; medical and scientific instruments; consumer durables, textiles, foodstuffs, handicrafts |
| Currency Name and Code | Russian Ruble (RUR or RUB) |
| Export Partners | Netherlands 12.2%, China 6.4%, Italy 5.6%, Germany 4.6%, Poland 4.2% |
| Import Partners | China 15.5%, Germany 10%, Ukraine 6.6%, Italy 4.3% |
Russia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Russia?
Source: Google News
Russia Travel Information
What makes Russia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Russia is a vast and diverse nation that continues to evolve politically, economically, and socially. Most U.S. citizens find their stay in Russia both exciting and rewarding, but travel and living conditions in Russia contrast sharply with those in the United States. Major urban centers show tremendous differences in economic development compared to rural areas. While good tourist facilities exist in Moscow, St. Petersburg, and some other large cities, they are not developed in most of Russia, and some of the goods and services taken for granted in other countries are not yet available. Russian visa requirements are complex, and U.S. citizens must take care they do not unintentionally violate entry and exit regulations. Travel to the North Caucasus region of Russia is dangerous; the Department of State recommends that U.S. citizens do not travel to Chechnya and the rest of the North Caucasus region, including Mt. Elbrus. When traveling in Russia, U.S. citizens are subject to Russian law, and may not enjoy the same legal protections they have in the United States.
Crime
Incidents of unprovoked, violent harassment against racial and ethnic minorities regularly occur throughout the Russian Federation. The U.S. Embassy Moscow and Consulates General continue to receive reports of U.S. citizens victimized in violent attacks by "skinheads" or other extremists. Travelers are urged to exercise caution in areas frequented by such individuals and wherever large crowds have gathered. U.S. citizens most at risk are those of African, South Asian, or East Asian descent, or those who, because of their complexion, are perceived to be from the Caucasus region or the Middle East. These U.S. citizens are also at risk for harassment by police authorities.While visiting Russia, be alert to your surroundings. In large cities, take the same precautions against assault, robbery, or pickpockets that you would take in any large U.S. city: keep wallets in inner front pockets, carry purses tucked securely under arms, wear the shoulder strap of cameras or bags across the chest, walk away from the curb, and carry purses and other bags away from the street. The most vulnerable areas include underground walkways, the subway, overnight trains, train stations, airports, markets, tourist attractions, and restaurants. Foreigner travelers who have been drinking alcohol are especially vulnerable to assault and robbery in or around nightclubs or bars, or on their way home. Some travelers have been drugged at bars, while others have taken strangers back to their lodgings, where they were drugged, robbed and/or assaulted.
Internet Dating Schemes: Reports of fraud committed against U.S. citizens by internet correspondents professing love and romantic interest are common. Typically, the correspondent asks the U.S. citizen to send money or credit card information for living expenses, travel expenses, or "visa costs." The nature of the internet means that you cannot be sure of the real name, age, marital status, nationality, or even gender of the correspondent. We have received many reports of citizens losing thousands of dollars through such scams. Never send money to anyone you have not met in person. Please review our information on Internet Dating Schemes.
Turkey Drop Scam: A common street scam in Russia is the "turkey drop" in which an individual "accidentally" drops money on the ground in front of an intended victim, while an accomplice either waits for the money to be picked up, or picks up the money him/herself and offers to split it with the pedestrian. The individual who dropped the currency then returns, aggressively accusing both of stealing the money. This confrontation generally results in the theft of the pedestrian's money. Avoidance is the best defense. Do not get trapped into picking up the money, and walk quickly away from the scene.
Drug Crimes: The Russian media report that the drug GHB is reportedly gaining popularity in local nightclubs, under the names butyrate or oxybutyrate. This drug can also cause amnesia, loss of consciousness, and/or extreme intoxication when mixed with alcohol, and death. The drug, typically in the form of a capful of liquid mixed with a beverage, gained notoriety in the United States after incidents of date-rape and death. In many cases, stolen credit cards are used immediately. Victims of credit card or ATM card theft should report the theft to the credit card company or issuing bank immediately.
Back to Top
Crimes Involving Public Transportation/Highway Crime: Travelers should be vigilant in bus and train stations and when taking other public transportation. Bogus trolley inspectors, whose aim is to extort a bribe from individuals while checking for trolley tickets, are also a threat.
Travelers have generally found it safer to travel in groups organized by reputable tour agencies. We discourage the use of unmarked taxis, as passengers have been victims of robbery, kidnapping, extortion, and theft. Criminals use these unmarked taxis to rob passengers, and often wait outside bars or restaurants to find travelers who have been drinking and are more susceptible to robbery. Robberies may also occur in taxis shared with strangers. Although there are few registered taxi services in Russia, you should always use authorized services when arriving at a major airport.
To avoid highway crime, try not to drive at night, especially when alone, and do not sleep in your vehicle on the side of the road. Do not pick up hitchhikers; they pose a threat to your physical safety and put you in danger of arrest for unwittingly transporting narcotics.
Back to Top
Crimes Involving Businesses: Extortion and corruption are common in the business environment. Business disputes may involve threats of violence and even acts of violence. Organized criminal groups, and occasionally even local police, target foreign businesses in many cities and have been known to demand protection money. Small businesses are particularly vulnerable. Please report all extortion attempts to the Russian authorities and inform consular officials at the U.S. Embassy in Moscow or the nearest Consulate General.
Certain activities that are considered normal business activities in the United States and other countries are either illegal under the Russian legal code or are considered suspect by the Federal Security Service (FSB). There are particular risks involved in any commercial activity with the Russian military-industrial complex, including research institutes, design bureaus, production facilities or other high technology, and government-related institutions. Any misunderstanding or dispute in such transactions can attract the involvement of the security services and lead to investigation or prosecution for espionage. Rules governing the treatment of information remain poorly defined.
Airport Scams: Traveler's should be cautious when traveling in any of Russia's airports. There have been instances where U.S. citizens and other foreigners have been targeted. These scams usually involve a friendly stranger, who will ask you to watch his/her bag or purse, and then leave and either contact the police or return with someone appearing to be a policeman/woman. The bag may contain drugs or other illegal items. The perpetrators then extort money or other valuables to avoid hassles with the police. Travelers should never accept or agree to watch a bag that belongs to a stranger.
Personal Privacy: Travelers should be aware that in 1995, the Russian Federal Law on Operational Search Activity passed, in conjunction with Order No. 130 by the Minister of Information Technology and Communications (July 25, 2000), the "System for Operative Investigative Activities." Commonly known as "SORM," this law permits the monitoring, retention and analysis of all data that traverses Russian communications networks, including fax transmissions, telephone calls, internet browsing and e-mail messaging. U.S. citizens should be cognizant of this law when using any of these means of communication.
It is not uncommon for foreigners in general to become victims of harassment, mistreatment, and extortion by law-enforcement and other officials. Police do not need to show probable cause in order to stop, question, or detain individuals. If stopped, obtain the officer's name, badge number, and patrol car number, and note where the stop happened, as this information assists local officials in identifying the perpetrators. Authorities are concerned about these incidents and have cooperated in investigating such cases. U.S. citizens should always report harassment or crimes to the U.S. Embassy in Moscow or the nearest U.S. Consulate General.
Criminal Penalties
While traveling in Russia, you are subject to its laws. This is true even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from those in the United States and criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but are still considered illegal in the United States. For example, U.S. citizens can be prosecuted under U.S. law if they buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or the use and/or dissemination of child pornography in a foreign country is also a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Russia, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Therefore, it is very important to know what is legal and what is not legal in the country you are visiting.
Languages
Russian (official) 85.7%, Tatar 3.2%, Chechen 1%, other 10.1%; note - data represent native language spoken
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in most localities is below Western standards due to shortages of medical supplies, differing practice standards and the lack of comprehensive primary care. Those facilities in Moscow and St. Petersburg with higher standards do not necessarily accept all cases. Access to these facilities usually requires cash or credit card payment at Western rates at the time of service. The U.S. Social Security Medicare Program does not provide coverage for hospital or medical costs in Russia. Elderly travelers and those with existing health problems may be at risk. We do not recommend elective surgeries requiring blood transfusions and/or non-essential blood transfusions due to uncertainties surrounding the local blood supply. Most hospitals and clinics in major urban areas have adopted the use of disposable IV supplies, syringes, and needles as standard practice. However, travelers to remote areas might consider bringing a supply of sterile, disposable syringes and corresponding IV supplies. We recommend travelers do not visit tattoo parlors or piercing services due to the risk of infection.Outbreaks of diphtheria and hepatitis A have been reported throughout the country, even in large cities such as Moscow and St. Petersburg. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend up-to-date tetanus and diphtheria immunizations before traveling to Russia and neighboring countries. Typhoid can be a concern for those who plan to travel extensively in the region. Cases of cholera have rarely been reported throughout the area. Travelers can reduce the risk of exposure to infectious and noxious agents by drinking bottled water and using bottled water for food or drink preparation. Tap water is generally unsafe to drink outside of Moscow. Tuberculosis is also an increasingly serious health concern in Russia. For further information about tuberculosis, please consult the CDC's information on Tuberculosis.
HIV infection rates have risen markedly in recent years. While most prevalent among intravenous drug users, prostitutes and their clients, the HIV/AIDS rate in the general population is increasing. Reported cases of syphilis are much higher than in the United States, and some sources suggest that gonorrhea and chlamydia are also more prevalent in Russia than in Western Europe or the United States.
Travelers may obtain information on vaccinations and other health precautions, such as safe food and water precautions and insect bite protection, from the CDC hotline for international travelers at 1-877-FYI-TRIP (1-877-394-8747) or via the CDC website. For information about outbreaks of infectious diseases abroad, consult the infectious diseases section of the World Health Organization (WHO) website. The WHO website also contains additional health information for travelers, including detailed country-specific health information.
Alternative Medical Treatments: Foreigners occasionally travel to Russia to receive medical treatment that is more expensive or prohibited in the United States, including stem-cell therapy and surrogate birthing. These treatments may involve considerable risks. Standards of infection control in both surgical and postoperative care may be inadequate. Patients undergoing treatment often develop secondary infections that cannot be handled by the facilities offering the procedures, and must be admitted to local hospitals of uncertain quality. In these cases, the patient is responsible for all additional costs, including repatriation back to the United States.
Safety and Security
Due to continued civil and political unrest throughout much of the North Caucasus region of Russia, the Department of State continues to warn U.S. citizens against travel to Chechnya and all other areas of the North Caucasus, including North Ossetia, Ingushetia, Dagestan, Stavropol, Karachayevo-Cherkessiya, and Kabardino-Balkariya. The U.S. Government's ability to assist U.S. citizens who travel to the North Caucasus region is extremely limited. Due to ongoing security concerns, U.S. Government travel to the region is also very limited. Throughout the region, local criminal gangs have kidnapped foreigners, including U.S. citizens, for ransom. There have also been several kidnappings of foreigners and Russian citizens working for media and non-governmental organizations in the region. U.S. citizens have disappeared in Chechnya and remain missing. Close contacts within the local population does not guarantee safety. U.S. citizens residing in these areas should depart immediately.Terrorism: Acts of terrorism, including bombings and hostage takings, continue to occur in Russia, particularly in the North Caucasus region. However, in the past several years, Moscow and St. Petersburg have also been the targets of terrorist attacks. Additionally, between October 15 – December 30, 2013 there were three suicide bombings targeting public transportation in the city of Volgograd, two of which occurred during the same 24-hour period. Other bombings have occurred at Russian government buildings, airports, hotels, tourist sites, markets, entertainment venues, schools, and residential complexes, and on public transportation including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights. Extremist groups occasionally threaten to set off bombs in market areas of major cities that are operated largely by migrant workers. Large-scale public events also present an attractive target for terrorists. There is no indication that U.S. institutions or citizens have been targets, but there is a general risk of U.S. citizens becoming victims of indiscriminate terrorist attacks. U.S. citizens in Russia should be aware of their personal surroundings and follow good security practices. U.S. citizens are urged to remain vigilant and exercise good judgment and discretion when using any form of public transportation. When traveling, U.S. citizens may wish to provide a friend, family member, or coworker a copy of their itinerary.
In the event the U.S. Government receives information of any specific and credible threat, the Department of State will immediately provide information to the public.
Demonstrations: U.S. citizens should avoid public demonstrations, whether properly authorized or not, and avoid any large crowds and public gatherings that lack enhanced security measures. Occasional peaceful demonstrations taking place near the U.S. Embassy do not generally interfere with public services, but U.S. citizens should avoid them when possible. Travelers should also exercise a high degree of caution and remain alert when patronizing restaurants, casinos, nightclubs, bars, theaters, etc., especially during peak hours of business.
Mt. Elbrus: Mt. Elbrus has become an increasingly popular destination for adventure travelers wishing to climb the highest mountain in Europe. However, the security situation in the regions surrounding the mountain remains highly unstable. The U.S. Embassy recommends against attempting to climb Mt. Elbrus, as it can only be done by passing close to volatile and insecure areas of the North Caucasus region.
Stay informed about the security of the area by bookmarking our Bureau of Consular Affairs website, which contains current Travel Warnings, Travel Alerts, and Country Specific Information, as well as the Worldwide Caution.
If you do not have Internet access, call us for updates --1-888-407-4747 toll-free in the United States and Canada, or from elsewhere on a regular toll line at 1-202-501-4444. You can also call the U.S. Embassy in Moscow at 7-495-728-5577.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
You may encounter road conditions and driver safety norms that differ significantly from those in the United States. As a pedestrian, exercise great care near traffic, as vehicles frequently fail to yield to pedestrians. In some areas of Russia, roads are practically nonexistent. When driving, adhere to all local driving regulations, as they are strictly enforced and violators are subject to severe legal penalties. Russia practices a zero-tolerance policy with regard to alcohol consumption prior to driving. The maximum punishment is a two-year suspension of a driver's license. Authorities may detain an intoxicated driver until they determine that he or she is sober.Avoid excessive speed and, if possible, do not drive at night, particularly outside of major cities. In rural areas, it is not uncommon to find livestock crossing roadways at any given time. Construction sites or stranded vehicles are often unmarked by flares or other warning signals. Sometimes cars have only one working headlight and many cars lack taillights. Bicycles seldom have lights or reflectors. Due to these road conditions, be prepared for sudden stops at any time. Learn about your route from an auto club, guidebook, or government tourist office. Some routes have heavy truck and bus traffic, while others have poor or nonexistent shoulders; many are one-way or do not permit left turns. In addition, some of the newer roads have very few restaurants, motels, gas stations, or auto repair shops along their routes. For your safety, have your vehicle serviced and in optimum condition before you travel. It is also wise to bring an extra fan belt, fuses, and other spare parts. In the Russian Far East most vehicles are right-side drive, affording the drivers limited visibility on two-lane roads.
If you are involved in an automobile accident while in Russia, leave your car in the location where the accident occurred and wait for local officials to arrive. Do not move your car from the location where the accident occurred or you may be held liable even if you are not at fault. Drivers may have to wait several hours for local police to arrive at the scene.
Temporary visitors to Russia may drive for up to 60 days with a valid U.S. driver's license and a notarized Russian translation. Tourists may also use International Driving Permits issued by the American Automobile Association or the American Automobile Touring Alliance to drive in Russia. Russian law requires foreigners on business or employment visas or with permanent residence status to have a Russian driver's license. In order to obtain this license one has to take the appropriate exams in Russian. Travelers may not use a U.S. driver's license in place of a Russian license. Travelers without a valid license are often subject to prolonged stops by police.
Drivers must carry third-party liability insurance under a policy valid in Russia. U.S. automobile liability insurance is not valid in Russia, nor are most collision and comprehensive coverage policies issued by U.S. companies. A good rule of thumb is to buy coverage equivalent to that which you carry in the United States.
Roadside checkpoints are commonplace and are ostensibly in place to detect narcotics, alien smuggling, and firearms violations. However, traffic police sometimes use these checkpoints to extract cash "fines."
