Where is Sierra Leone located?
What countries border Sierra Leone?
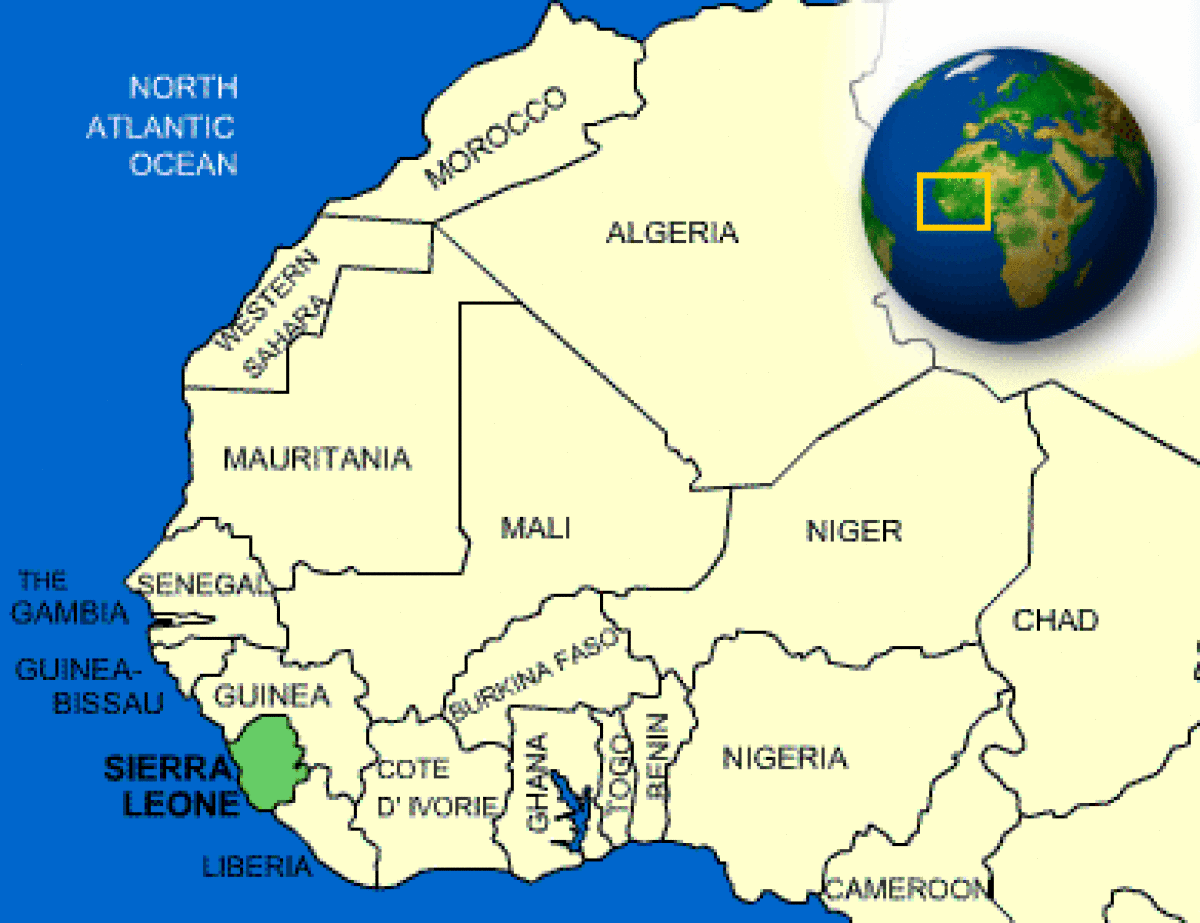
Sierra Leone Facts and Culture
What is Sierra Leone famous for?
-
Cultural Attributes: Sierra Leoneans are social people and enjoy joking and teasing. Common gestures include hand slapping and handshaking.
When a mate has... More - Family: For Sierra Leoneans, families consist of a father, a mother, and children. However, extended family is important. Family members are... More
- Personal Apperance: How people dress in Sierra Leone varies depending on location, occupation, occasion, and personal preference. Everyday Wear: In urban areas,... More
- Recreation: In Sierra Leone, recreational activities vary depending on location, socioeconomic status, and personal preferences. Football (Soccer): Football is the most... More
- Diet: In Sierra Leone, the local diet is diverse and influenced by the country's rich cultural heritage and natural resources. Here... More
- Food and Recipes: The largest meal is eaten at midday. The staple for the noon meal is foo-foo, a dough-like paste... More
- Visiting: When visiting Sierra Leone, it's important to be mindful of local customs and etiquette to show respect for the culture... More
- Dating: Dating customs in Sierra Leone can vary depending on factors such as urban versus rural settings, religious beliefs, and individual... More
Sierra Leone Facts
What is the capital of Sierra Leone?
| Capital | Freetown |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Leone (SLL) |
| Total Area |
27,699 Square Miles 71,740 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Liberia |
| Language | English (official, regular use limited to literate minority), Mende (principal vernacular in the south), Temne (principal vernacular in the north), Krio (English-based Creole, spoken by the descendants of freed Jamaican slaves who were settled in the Freetown area, a lingua franca and a first language for 10% of the population but understood by 95%) |
| GDP - real growth rate | -23.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $1,600.00 (USD) |
Sierra Leone Demographics
What is the population of Sierra Leone?
| Ethnic Groups | 20 native African tribes 90% (Temne 30%, Mende 30%, other 30%), Creole (Krio) 10% (descendants of freed Jamaican slaves who were settled in the Freetown area in the late-18th century), refugees from Liberia's recent civil war, small numbers of Europeans, |
| Nationality Noun | Sierra Leonean(s) |
| Population | 6,624,933 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.3% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | FREETOWN (capital) 941,000 |
| Urban Population | 39.200000 |
Sierra Leone Government
What type of government does Sierra Leone have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Julius Maada BIO (since 27 June 2023); Vice President Mohamed Juldeh JALLOH (since 27 June 2023); note - the president is chief of state, head of government, and Minister of Defense head of government: President Julius Maada BIO (since 27 June 2023); Vice President Mohamed Juldeh JALLOH (since 27 June 2023) cabinet: Ministers of State appointed by the president, approved by Parliament; the cabinet is responsible to the president elections/appointments: president directly elected by 55% in the first round or absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 24 June 2023 (next to be held in 2028) election results: 2023: Julius Maada BIO reelected president in first round; percent of vote - Julius Maada BIO (SLPP) 56.2%, Samura KAMARA (APC) 41.2%, other 2.6% 2018: Julius Maada BIO elected president in second round; percent of vote - Julius Maada BIO (SLPP) 51.8%, Samura KAMARA (APC) 48.2% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent or grandparent must be a citizen of Sierra Leone dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 27 April (1961) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest effective 1 October 1991 amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage of amendments requires at least two-thirds majority vote of Parliament in two successive readings and assent of the president of the republic; passage of amendments affecting fundamental rights and freedoms and many other constitutional sections also requires approval in a referendum with participation of at least one half of qualified voters and at least two thirds of votes cast; amended several times, last in 2016 |
| Independence | 27 April 1961 (from the UK) |
Sierra Leone Video
YouTube: IFCvideocasts Rebuilding Business and Investment in Post Conflict Sierra Leone
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Sierra Leone Geography
What environmental issues does Sierra Leone have?
| Overview | Roughly circular in shape, Sierra Leone has an area of 29,925 square miles; It is located on the West African coast between 7 and 10 degrees north of the Equator. Three main topographical regions run northwest to southwest, roughly parallel to the coast: a belt of mangrove swamps and white sand beaches, an area of low plains covered with secondary forest and cultivated land, and an easternmost region of high plateaus and mountains, some rising as high as 6,000 feet. The mountainous peninsula on which Freetown is located comprises a fourth distinct geographical region. |
| Climate |
The tropical climate has rainy and dry seasons, high temperatures, and almost constant humidity. The rainy season extends from May to November but is heaviest between July and September, when over half of the annual rainfall occurs. In Freetown, annual rainfall is 150 inches or more; inland areas receive less. The beginning and end of the rainy season are marked by frequent strong electrical storms, similar to those occurring during the hot summer months in the eastern U.S. Coastal temperatures during the rainy season range from a daily high of about 80°F. to a nightly low of about 76°F. Relative humidity in Freetown rarely falls below 80%, except when the harmattan reaches the coast. This current of dry, dusty air flows from the Sahara Desert toward the south and west, usually reaching Sierra Leone in December. During this season, which lasts through February, Freetown experiences its coolest weather. |
| Border Countries | Guinea 652 km, Liberia 306 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | rapid population growth pressuring the environment; overharvesting of timber, expansion of cattle grazing, and slash-and-burn agriculture have resulted in deforestation and soil exhaustion; civil war depleting natural resources; overfishing |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification |
| Terrain | coastal belt of mangrove swamps, wooded hill country, upland plateau, mountains in east |
Sierra Leone Economy
How big is the Sierra Leone economy?
| Economic Overview |
Sierra Leone's economy faced several challenges but also showed signs of resilience and potential for growth. GDP and Growth: Sierra Leone is classified as a low-income country, heavily reliant on agriculture, mining, and other natural resources. Its GDP growth has been volatile in recent years, influenced by factors such as global commodity prices, political stability, and external aid. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the economy was showing signs of recovery, with GDP growth projected to be around 5-6% in 2020 and beyond. Agriculture: Agriculture is a critical sector of the economy, employing the majority of the population and contributing significantly to GDP. The main agricultural products include rice, cassava, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, and various fruits and vegetables. However, the sector faces challenges such as low productivity, limited access to modern inputs and technology, and vulnerability to climate change and natural disasters. Mining and Natural Resources: Sierra Leone is rich in mineral resources, including diamonds, rutile, bauxite, gold, and iron ore. Mining plays a significant role in the economy, contributing to government revenue and foreign exchange earnings. Efforts have been made to improve transparency and governance in the mining sector, although challenges remain in terms of sustainable resource management and equitable distribution of benefits. Infrastructure and Energy: Sierra Leone faces significant infrastructure deficits, including inadequate road networks, limited access to electricity, and insufficient water and sanitation facilities. Improving infrastructure is essential for economic development and attracting investment in key sectors such as tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. Efforts are underway to expand access to energy through investments in renewable energy projects and infrastructure development. Foreign Aid and Investment: Sierra Leone relies heavily on foreign aid and investment to finance development projects and support social services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. The government has pursued policies to attract foreign investment, particularly in sectors such as mining, agriculture, and tourism. However, challenges such as corruption, bureaucracy, and inadequate infrastructure have hindered investment inflows. Social Challenges: Sierra Leone faces various social challenges, including high levels of poverty, unemployment, and inequality. Access to healthcare and education remains limited, particularly in rural areas. The country also continues to recover from the devastating effects of the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016, which had significant economic and social impacts. COVID-19 Pandemic: Like many countries, Sierra Leone has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has disrupted economic activities, led to job losses, and strained healthcare systems. Efforts to contain the spread of the virus have included lockdowns, travel restrictions, and vaccination campaigns, with varying degrees of success. |
| Industries | mining (diamonds); small-scale manufacturing (beverages, textiles, cigarettes, footwear); petroleum refining |
| Currency Name and Code | Leone (SLL) |
| Export Partners | Belgium 41.6%, Germany 31.7%, UK 4%, US 4% |
| Import Partners | Germany 26.1%, UK 10.7%, Netherlands 7.5%, US 5.7%, Cote d'Ivoire 4.9%, Italy 4.3% |
Sierra Leone News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Sierra Leone?
Source: Google News
Sierra Leone Travel Information
What makes Sierra Leone a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Sierra Leone is a developing country in western Africa still recovering from a ten-year civil war that ended in 2002. English is the official language, but Krio, an English-based language, is widely used. Tourist facilities in the capital, Freetown, are limited; elsewhere, they are rudimentary or nonexistent.
Crime
Entrenched poverty in Sierra Leone has led to criminality. Visitors and resident U.S. citizens have experienced armed mugging, assault, and burglary. Petty crime and pick-pocketing of wallets, cell phones, and passports are very common especially on the ferry to and from Lungi International Airport as well as in the bars, restaurants, and nightclubs in the Lumley Beach and Aberdeen areas of Freetown. The majority of these crimes against U.S. citizens are non-violent confrontations characterized as crimes of opportunity (i.e., pick-pocketing, theft of unattended possessions in public places or hotel rooms, bag snatching, and financial confidence scams). Law enforcement authorities usually respond to crimes slowly, if at all. Police investigative response is often incomplete and does not provide support to victims. Inefficiency and corruption are serious problems at all levels within the government of Sierra Leone. U.S. citizens traveling to or residing in Sierra Leone should maintain a heightened sense of awareness of their surroundings to help avoid becoming victims of crime.Home invasions, especially targeting westerners, are extremely common in Sierra Leone. Most residential break-ins are perpetrated by small groups of well-organized, armed bandits equipped with tools. These criminals are motivated, intrepid, and aggressive. They do not fear confrontation and are often armed with machetes or homemade firearms. They often use stealth techniques to enter a residence, such as taking advantage of a rainstorm to mask their movements, sneaking past a sleeping guard, cutting through roofs, or tunneling under walls. Expatriates are frequent targets due to their perceived wealth.
Over the past, the U.S. Embassy has received several reports of crime perpetrated on westerners driving vehicles. In each case, cars were stopped in traffic or moving slowly when thieves reached in open windows or opened unlocked doors to steal purses, telephones, and a variety of other valuables from the unsuspecting motorist. Thefts tended to occur on poorly maintained roads requiring slow speed and elaborate maneuvering around potholes and drainage canals. Criminals also threw rocks and caused diversions to distract drivers while simultaneously entering the passenger side of the vehicle to steal property. Specifically, thieves have targeted Signal Hill Road (near the UNIPSIL Headquarters) in Western Freetown because it is a high-traffic area with poor road conditions, lack of street lights, and heavy foliage. For more information about driving safety, see the Embassy’s Security Messages for U.S. Citizens here.
The Embassy also receives regular reports from U.S. citizens investing in Sierra Leone who have been victims of fraud, often in the mining industry. While law enforcement authorities have been involved in investigating the cases, many remain unresolved. Investors are urged to proceed cautiously when engaging in business transactions with individuals presenting themselves as legitimate diamond or gold dealers. It is not uncommon for registered diamond or gold dealers to target foreigners using sophisticated financial scams resulting in significant financial loss.
Business fraud is rampant and the perpetrators often target foreigners, including U.S. citizens. Schemes previously associated with Nigeria are now also prevalent in Sierra Leone, and pose a danger of grave financial loss. Typically these scams begin with unsolicited communication (usually e-mails) from strangers who promise quick financial gain, often by transferring large sums of money or valuables out of the country, but then require a series of "advance fees" to be paid, such as fees for legal documents or taxes. The final payoff does not exist; the purpose of the scam is simply to collect the advance fees. A common variation is the scammer’s claim to be a refugee or émigré of a prominent West African family, or a relative of a present or former political leader who needs assistance in transferring large sums of cash. Still other variations appear to be legitimate business deals that require advance payments on contracts. Sometimes victims are convinced to provide bank account and credit card information and financial authorization that is used to drain their accounts, incur large debts against their credit, and take their life savings.
The best way to avoid becoming a victim of advance-fee fraud is common sense – if a proposition looks too good to be true, it probably is. You should carefully check and research any unsolicited business proposal before committing any funds, providing any goods or services, or undertaking any travel. It is virtually impossible to recover money lost through these scams. Please see the Department of State’s brochure on International Financial Scams for more information.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Sierra Leone, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport with you or if you take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some activities that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.If you break local laws in Sierra Leone, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not wherever you go. Persons violating Sierra Leone laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Sierra Leone are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Sierra Leone fall critically short of U.S and European standards. There are no 911 equivalent ambulance services in Sierra Leone. Trauma care is extremely limited, and local hospitals should only be used in the event of an extreme medical emergency. Blood transfusions can be life-threatening rather than life-saving due to lack of screening and poor quality control. Many primary health care workers, especially in rural areas, lack adequate professional training. Instances of misdiagnosis, improper treatment, and the administration of improper drugs have been reported. Quality and comprehensive medical services are very limited in Freetown, and are almost nonexistent for all but the most minor treatment outside of the capital. Medicines are in short supply and due to inadequate diagnostic equipment, lack of medical resources, and limited medical specialty personnel, complex diagnosis, and treatment are unavailable. Life-threatening emergencies often require evacuation by air ambulance at the patient's expense.Visitors with serious health concerns, e.g., diabetes, heart disease, asthma, or who are on blood thinners (with the exception of aspirin) are discouraged from traveling to Sierra Leone.
All visitors traveling to Sierra Leone must have current vaccinations prior to arrival in Freetown. These include, but are not limited to, tetanus, yellow fever, polio, meningitis, typhoid, hepatitis A and B, and rabies. The cholera vaccine is not required. The International Certificate of Vaccinations yellow card should be hand-carried as proof of current yellow fever inoculation.
Visitors should begin taking malaria prophylaxis two weeks prior to arrival, and hand-carry enough medication for the duration of their visit. It is mandatory that visitors bring their own supply of medications.
The quality of medications in Sierra Leone is inconsistent and counterfeit drugs remain a problem. Local pharmacies are generally unreliable. In the event medications are needed, such as over-the-counter medication, antibiotics, allergy remedies, or malaria prophylaxis, travelers may contact the U.S. Embassy's American Citizen Services (ACS) Unit to receive general information about reliable pharmacies. ACS maintains a list of physicians, clinics, and pharmacies as provided by the Embassy Health Unit.
Gastrointestinal diseases, malaria, and HIV pose serious risk to travelers in Sierra Leone. Lassa Fever is endemic in Eastern Province. Since sanitary conditions in Sierra Leone are poor and refrigeration is unreliable, use caution when eating uncooked vegetables, salads, seafood, or meats at restaurants and hotels. Only bottled water should be consumed. In the past, even some bottled water was found to be contaminated by bacteria. Swimming in the ocean is safe, but swimming in rivers is not.
Safety and Security
Security in Sierra Leone has improved significantly since the end of the civil war in 2002. The United Nations Peacekeeping Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL) withdrew in December 2005 and Sierra Leone resumed responsibilities for its own security. The Sierra Leonean police are working to improve its professionalism and capabilities, but these fall short of U.S. standards in response time, communications, and specialty skills.Areas outside Freetown lack most basic services. U.S. Embassy officials are free to travel throughout Sierra Leone. Travelers are urged to exercise caution especially when venturing beyond the capital. Road conditions are hazardous and serious vehicle accidents are common. Travel outside the capital after dark is not allowed for U.S. Embassy officials and should be avoided by all travelers. Emergency response to vehicular and other accidents ranges from slow to nonexistent.
There are occasional unauthorized, possibly armed, roadblocks outside Freetown, where travelers might be asked to pay a small amount of money to the personnel manning the roadblock. Because many Sierra Leoneans outside of Freetown speak broken English or Krio, it can be difficult for foreigners to communicate their identity. Public demonstrations are rare, but can turn violent. U.S. citizens are advised to avoid large crowds, political rallies, and street demonstrations. You should maintain security awareness at all times. In addition, you should carry a means of communication at all times (fully charged cell phone with emergency contacts).
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Sierra Leone is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Most main roads in Freetown are narrow and paved, but have potholes. Extremely narrow unpaved side streets are generally navigable. Most roads outside Freetown are unpaved and are generally passable with a four-wheel drive vehicle. However, certain stretches of mapped road are often impassable during the rainy season, which usually lasts from May to September. During the rainy season, add several hours to travel time between Freetown and outlying areas. There is a major road repair and resurfacing program going on throughout the country that is slowly improving the quality of roads. Public transport (bus or group taxi) is erratic, unsafe, and not recommended. Pick pocketing is common in public taxis and mini-buses. U.S. Embassy officials are prohibited from using public transportation except for taxis that operate in conjunction with an approved hotel and that are rented on a daily basis.
Many vehicles on the road in Sierra Leone are unsafe. Accidents resulting from the poor condition of these vehicles, including multi-vehicle accidents, are common. Many drivers on the road in Sierra Leone are inexperienced and often drive without proper license or training. Serious accidents are common, especially outside of Freetown, where the relative lack of traffic allows for greater speeds. The chance of being involved in an accident increases greatly when traveling at night, and U.S. Embassy officials are not authorized to travel outside of major cities after dark.
