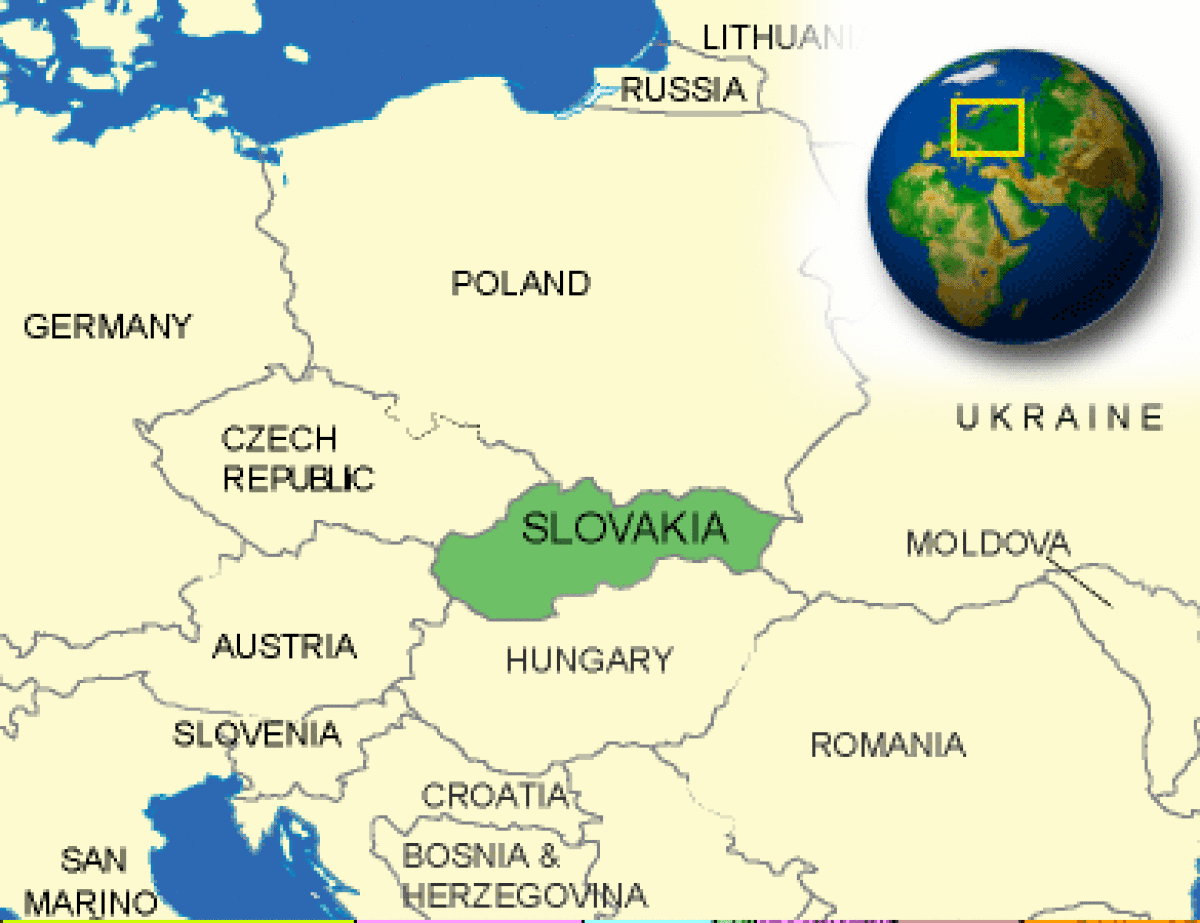
Where is Slovakia located?
What countries border Slovakia?
Slovakia Weather
What is the current weather in Slovakia?
Slovakia Facts and Culture
What is Slovakia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Slovaks are proud of their rich cultural heritage. Slovaks are usually outgoing and value good humor and hard work. They... More
- Family: Typical Slovak families have two or three children. While most women hold jobs outside the home and comprise 47 percent... More
- Personal Apperance: Clothing in urban areas is fashionable, while older, rural people remain more conservative. Businessmen wear suits, and women and girls... More
- Recreation: Ice hockey and soccer are the most popular team sports. Slovaks enjoy skiing, snowboarding, and ice skating in winter. The Poprad-Tatry... More
- Diet: Among the most famous Slovak foods are rezen (breaded steak), potatoes, rice, dumplings, pasta, and sauce. The national dish is... More
- Food and Recipes: Slovaks eat in continental style. Three meals are consumed each day. Breakfast consists of bread and rolls, sliced meat or... More
- Visiting: Impromptu visits are typical, but only between close friends and family members. Guests remove hats and shoes in the home;... More
- Dating: Popular dating activities include dancing and going to the movies and theater. Men marry between the ages of 23 and... More
Slovakia Facts
What is the capital of Slovakia?
| Capital | Bratislava |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
18,932 Square Miles 49,035 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Europe, south of Poland |
| Language | Slovak (official), Hungarian |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $29,500.00 (USD) |
Slovakia Demographics
What is the population of Slovakia?
| Ethnic Groups | Slovak 85.7%, Hungarian 10.6%, Roma 1.6% (the 1992 census figures underreport the Gypsy/Romany community, which is about 500,000), Czech, Moravian, Silesian 1.1%, Ruthenian and Ukrainian 0.6%, German 0.1%, Polish 0.1%, other 0.2% (1996) |
| Languages | Slovaks speak Slovak. Hungarian is the second most commonly spoken language, especially in the south. German is widely understood, while English is the language of choice to study in school. The Slovak Republic was formed at the time of the division of the Czech Republic in 1993. |
| Nationality Noun | Slovak(s) |
| Population | 5,440,602 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.09% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | BRATISLAVA (capital) 434,000 |
| Urban Population | 54.700000 |
Slovakia Government
What type of government does Slovakia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Zuzana CAPUTOVA (since 15 June 2019) head of government: Prime Minister Robert FICO (since 25 October 2023); Deputy Prime Ministers Robert KALINAK, Denisa SAKOVA, Tomas TARABA, and Peter KMEC (all since 25 October 2023) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election first round 23 March 2024 with a runoff on 6 April 2024 (next to be held in 2029); following National Council elections (every 4 years), the president designates a prime minister candidate, usually the leader of the party or coalition that wins the most votes, who must win a vote of confidence in the National Council election results: 2024: Peter PELLEGRINI elected president in the second round; percent of vote in first round - Ivan KORCOK (independent) 42.5%; Peter PELLEGRINI (Hlas-SD) 37%; Stefan HARABIN (independent) 11.7%, other 8.8%; percent of vote in second round Peter PELLEGRINI (Hlas-SD) 53.1%; Ivan KORCOK (independent) 46.9%; PELLEGRINI will takeoffice on 15 June 2024 2019: Zuzana CAPUTOVA elected president in second round; percent of vote - Zuzana CAPUTOVA (PS) 58.4%, Maros SEFCOVIC (independent) 41.6% 2014: Andrej KISKA elected president in second round; percent of vote - Andrej KISKA (independent) 59.4%, Robert FICO (Smer-SD) 40.6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Slovakia dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Constitution Day, 1 September (1992) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous (preindependence); latest passed by the National Council 1 September 1992, signed 3 September 1992, effective 1 October 1992 amendments: proposed by the National Council; passage requires at least three-fifths majority vote of Council members; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia) |
Slovakia Video
YouTube: Mr History A Super Quick History of Slovakia
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Slovakia Geography
What environmental issues does Slovakia have?
| Overview |
Slovakia, located in the very heart of Europe, has an area of 18,859 square miles (48,845 square kilometers). The terrain includes the high Carpathian Mountains (The Tatras) in the north, the low Carpathian mountains in the center, the foothills to the west, and the Danube River Basin in the south. Slovakia is mostly mountainous; approximately 80% of the territory is 750 meters or more above sea level. The highest point is Gerlachovský Peak, 2,655 meters above sea level. Slovakia is a land of beautiful, wide valleys, which were created by the Váh, Nitra, and Hron Rivers. Most of the land is drained by the Danube, the largest river in Slovakia, which empties into the Black Sea, and its tributaries (Morava, Váh, Hron and others). The Dunajec River drains a smaller part of Slovakia; it is a tributary of the Visla, which empties into the Baltic Sea. The longest river in Slovakia is the Váh, which is 242 miles (390 kilometers). In the eastern part of the country lie the woodlands of the Carpathian Mountains. The breadbasket of Slovakia, the Podunajska Plain, lies further south along the Danube River. In the woodland regions oak, birch and spruce grow abundantly up to the tree line. Mountain pine and alpine vegetation grow above the tree line. Because the country lies on the crossroads of several different plant systems, unique flora abound. The entire territory of Slovakia is rich in fauna and most animal species live in the mountainous woodland regions. |
| Climate |
The climate in Slovakia is a mixture of continental and ocean climates and has four distinct seasons. The mountain regions affect the weather much more than the geographical location of the country. The warmest and driest regions are the southern Slovak plains and the Eastern Slovak lowlands where the average temperature is 10 degrees C and average annual precipitation is approximately 500 mm. In the High Tatras the average temperature is 3 degrees C and annual precipitation is 2,000 mm. The coldest month is January; the warmest is July. During winter the temperatures in the mountain valleys are substantially lower than on the mountain peaks, and temperature inversions are quite common. Bratislava is moderately dry with average temperatures ranging from –1 degree C to –4 degrees C in January and from 19.5 degrees C to 20.5 degrees C in July. The maximum daily temperature in July is approximately 32 degrees C. Annual rainfall varies from 61 to 101 cm. Bratislava ranks among the warmest places in Slovakia. During the winters in Bratislava the sun rises at 7:30 and sets about 16:00. The skies are often overcast, and snow and ice storms occur. During the summer, sunrise is before 5:00 and sunset is about 21:00. |
| Border Countries | Austria 91 km, Czech Republic 215 km, Hungary 677 km, Poland 444 km, Ukraine 97 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution from metallurgical plants presents human health risks; acid rain damaging forests |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | rugged mountains in the central and northern part and lowlands in the south |
Slovakia Economy
How big is the Slovakia economy?
| Economic Overview |
A general economic overview of Slovakia. Please note that economic conditions can change, and checking more recent sources for the latest information is advisable. As of that time: 1. Economic Structure: Slovakia has a market-oriented economy and is part of the European Union and the Eurozone, using the euro (EUR) as its official currency. The country underwent significant economic reforms after gaining independence in 1993, transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a more open and market-oriented system. 2. GDP and Growth: Slovakia has experienced relatively strong economic growth, driven by foreign direct investment (FDI), manufacturing, and exports. Industries like automotive manufacturing, electronics, and machinery have played a crucial role in the country's economic development. 3. Automotive Industry: The automotive sector is a crucial driver of Slovakia's economy. The country has become a significant hub for automobile production, with several international automotive companies having manufacturing plants in Slovakia. 4. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Slovakia has attracted significant foreign direct investment, particularly in manufacturing. The business-friendly environment, skilled workforce, and strategic location within Europe have contributed to FDI inflows. 5. Export-Oriented Economy: Slovakia has an export-oriented economy, focusing on machinery, vehicles, electrical machinery, and pharmaceuticals. The country's geographical location in the heart of Europe facilitates trade with other European countries. 6. European Union Membership: Slovakia's membership in the European Union has provided access to a larger market and opportunities for economic integration. It has also benefited from EU structural funds. 7. Unemployment and Labor Market: Unemployment rates in Slovakia have generally decreased, but challenges such as skills mismatches persist. The labor market is dynamic, and efforts are made to address workforce development needs. 8. Challenges: Slovakia faces challenges related to regional disparities, with differences in economic development between the capital city, Bratislava, and other regions. Strengthening innovation and research and development efforts is an ongoing goal to enhance the country's competitiveness. 9. Banking and Finance: Slovakia has a stable banking sector, and the country's financial institutions are integrated into the broader European financial system. 10. Renewable Energy: Slovakia has tried diversifying its energy sources, focusing on increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix. 11. Tourism: While not as prominent as in some other European countries, tourism is growing in Slovakia, driven by its historical sites, natural beauty, and cultural attractions. |
| Industries | metal and metal products; food and beverages; electricity, gas, coke, oil, nuclear fuel; chemicals and manmade fibers; machinery; paper and printing; earthenware and ceramics; transport vehicles; textiles; electrical and optical apparatus; rubber products |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 26%, Czech Republic 15.2%, Italy 10.8%, Austria 7.7%, Hungary 5.5%, Poland 5.3%, France 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Germany 22.6%, Czech Republic 15.1%, Russia 12.5%, Italy 6.9%, France 4.4%, Austria 4.2% |
Slovakia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Slovakia?
Source: Google News
Slovakia Travel Information
What makes Slovakia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Slovakia is a markedly developed European nation and a member of the Schengen travel area and the Euro zone. Some tourist facilities are not as developed as those found in Western Europe, particularly outside the major cities, and some goods and services common in other European countries are occasionally unavailable in Slovakia. The official language is Slovak; English is not widely spoken outside of tourist destinations.
Crime
Police forces suffer from a lack of manpower, resources, and equipment. Local police do not usually speak English. Western visitors, especially short-term visitors such as tourists and students, are the primary foreign targets of street crime. The majority of street crime is non-violent. The most common crimes reported include pick-pocketing and cell phone and bag/purse theft, particularly during the summer months. Other crimes reported in the past include the less common robbery, and drugging and robbing of unsuspecting victims at nightspots and bars. Most thefts reported by U.S. citizens occur at crowded tourist sites (such as Bratislava’s Old Town area) or on public buses, trams, or trains. Thieves in Slovakia often work in groups or pairs. In most cases, one thief distracts the victim, another performs the robbery, and a third person hands off the stolen item to a nearby accomplice. Groups of street children are known to divert tourists’ attention so that a member of their group can pickpocket the tourists while they are distracted.Foreigners and minorities, particularly non-white individuals, have been victims of racially motivated incidents in Slovakia, and may be especially subject to various types of harassment, such as verbal abuse.
Both indigenous and foreign organized crime groups are well established in Slovakia. They do not target U.S. citizens or other foreign individuals and tend to coexist peacefully in tourist districts so as not to scare away tourist dollars. Though not common, violent incidents sometimes do occur.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, but you will be breaking local law too.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Slovakia, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States; for instance, engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. While you are overseas, U.S. laws don’t apply. If you do something illegal in Slovakia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know the laws of the country you are visiting. Driving under the influence is not allowed under Slovak law; the permissible blood alcohol level is zero, and driving while intoxicated is a crime. If stopped, a driver who is found operating a vehicle while intoxicated will experience a trip to the police station at a minimum.Taking photographs of security/military installations (for example, military bases, government buildings, nuclear power plants, etc.) is prohibited in Slovakia. If you violate this law, authorities may confiscate the film, issue a reprimand or fine, or even expel you from the country. Serious cases may be reported to and handled by local and/or military police.
Everyone in Slovakia over 15 years of age, including U.S. citizen visitors, is required by law to carry a passport at all times. It is not sufficient to carry a photocopy of the passport, although we recommend that you keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place. The police have the right to ask U.S. citizens for identification, and only a passport showing legal entry and/or legal residency status is adequate evidence.
A document other than a passport may not be considered sufficient proof of identity and legal status in Slovakia. If you are asked for your passport with residency permit and you do not have it, you risk a spot fine and/or detention by the police.
If you are arrested in Slovakia, authorities are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest.
Languages
Slovaks speak Slovak. Hungarian is the second most commonly spoken language, especially in the south. German is widely understood, while English is the language of choice to study in school. The Slovak Republic was formed at the time of the division of the Czech Republic in 1993.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are available in Slovakia, although the quality and availability varies within the country. For any emergency, including a medical emergency, call 112 within Slovakia free of charge. An English-speaking dispatcher should be available. According to the level of the medical emergency, the dispatcher may send an ambulance, which may be medically equipped and staffed by paramedics or a physician if the patient’s condition warrants it. Only a limited number of doctors speak English. Doctors and hospitals expect cash payment for health services unless the patient can present an insurance number from the Slovak National Insurance Company. This includes ambulance service, for which the cost begins at 120 euro for those without local Slovak health insurance. Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost tens of thousands of dollars or more. Medical prescriptions issued in the United States are not valid in Slovakia. If a prescription is needed, a local doctor must issue it. Medicines are generally available locally at pharmacies, where customers ask the pharmacist for every product including over-the-counter medicines; if they are not available under the U.S. drug name, you should consult the pharmacist or a local doctor for a local substitute. The Ministry of Health administers the use of medicines, and medicine brought into Slovakia for personal use may be subject to comparison against the list of those authorized for use in Slovakia.
Safety and Security
Civil disorder is rare in Slovakia, although strikes and demonstrations may occur. You should be vigilant in protecting your security, bearing in mind that even demonstrations meant to be peaceful may turn violent. Avoid street demonstrations whenever possible.Slovakia remains largely free of terrorist incidents. However, like other countries in the Schengen area, Slovakia’s open borders with its neighbors (except for Ukraine) allow for the possibility of terrorist groups entering/exiting the country without the knowledge of Slovak police.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Slovakia, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.Roads in Slovakia typically are safe and well maintained. Four-lane highways exist in and around Bratislava. However, most roads outside of developed areas are two lanes only, and aggressive drivers attempting to pass at unsafe speeds pose a serious hazard. Due to poor lighting and narrow, winding roads, we do not recommend nighttime driving outside of built-up areas.
Slovakia commonly receives heavy snow from November through March. Snow removal is not adequate on rural roads. Roads in the mountainous northern part of the country are particularly prone to hazardous conditions during winter months. Winter tires are required by law when there are snowy conditions, and chains are necessary in certain mountainous areas.
In Slovakia, vehicles travel on the right side of the road. Headlights must be used at all times (day and night) throughout the year. The maximum legal speed on highways is 130 kilometers per hour (78 mph). On smaller roads, the maximum speed is 90 kph (54 mph). The limit in towns is 50 kph (31 mph). It is strictly prohibited to use cellular phones while driving. Safety reflection vests and first aid kits must be located in each vehicle. Seat belts are compulsory and baby car seats are required for all children less than 36 kg (80 lbs).
Driving under the influence of alcohol is a crime under Slovak law. The blood alcohol tolerance level is zero percent. Penalties for drivers involved in car accidents involving injury or death are decided by a court of law. Penalties for minor offenses are not generally large, but foreigners are sometimes targeted for additional sums. If you suspect this has occurred, you should ask for a written receipt and note the name and number of the traffic officer imposing the fine.
A highway user decal is required for travel on most major roads outside of Bratislava. The decal is valid for the calendar year, and is available at gas stations, post offices, and some newspaper kiosks. Short-term stickers are available and are valid for seven days or for one month.
Taxi companies generally provide reliable, safe, and economical services. Avoid independent cabs that do not prominently display a company name. Taxis sometimes overcharge in areas frequented by tourists. You can expect higher charges when you randomly stop a cab on the street. Radio-dispatched taxis are often much more reliable and less expensive.
Buses, trolleybuses, and trams are mechanically safe and generally reliable, but there have been reports of thefts on city transportation or of harassment by the transport police. On public transportation you must have a time-ticket validated after entering the vehicle (valid for 15 or 60 minutes), or a prepaid zone ticket (valid for 24 hours, 48 hours, 3 days, 7 days, 1 month, 3 months, or 1 year). Different ticket validities and fees apply in towns outside of Bratislava. Children from 6 to 15 years of age pay reduced fares. Passengers who are traveling without a valid ticket will be fined by the ticket inspector. The ticket inspector must have an identification card and must provide a receipt for the fine. More information is provided in English on the Bratislava city transport website.
A motorcycle driver’s license and helmet are required to operate a motorized two-wheeled vehicle. Small motorcycles are not allowed on highways. All traffic regulations apply.
Tourists intending to drive in Slovakia are required to have an International Driving Permit. A U.S. driver’s license alone is not sufficient to drive in Slovakia; it must be accompanied by an International Driving Permit, which you can get in the United States from the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance. U.S. citizens who are not residents of Slovakia may drive with a valid U.S. state license, if accompanied by a valid International Driving Permit, for a maximum of 6 months.
If you do not have a U.S. state driver’s license, you may apply for a Slovak driver’s license at the Dopravny Inspektorat in the district of your place of residence in Slovakia. Completion of the regular driving course and a written examination (in Slovak) are required for issuance of a Slovak driver’s license. For specific information concerning a Slovak driver’s permit, vehicle inspection, road tax, and mandatory insurance, contact the Slovak Embassy in Washington, D.C.
U.S. citizens who are long-term residents in Slovakia and are in possession of a U.S. state driver’s license must apply for exchange of a U.S. state driver’s license for a Slovak driver’s license. Conditions for the exchange are set by the Law on Road Traffic effective from February 2009. Under the law, the issuing country must be a member either of the Geneva Convention (the United States ratified the Convention in 1950) or Vienna Convention on Road Traffic.
The law requires residents of Slovakia who hold U.S. state driver’s licenses to apply for exchange of their license within 60 days of the time period starting 185 days after the day their residency permit was issued. The applications are filed with the Dopravny Inspektorat at the district police department in the place of residency in Slovakia. The Slovak license is issued in the EU format and may be used in all EU countries.
