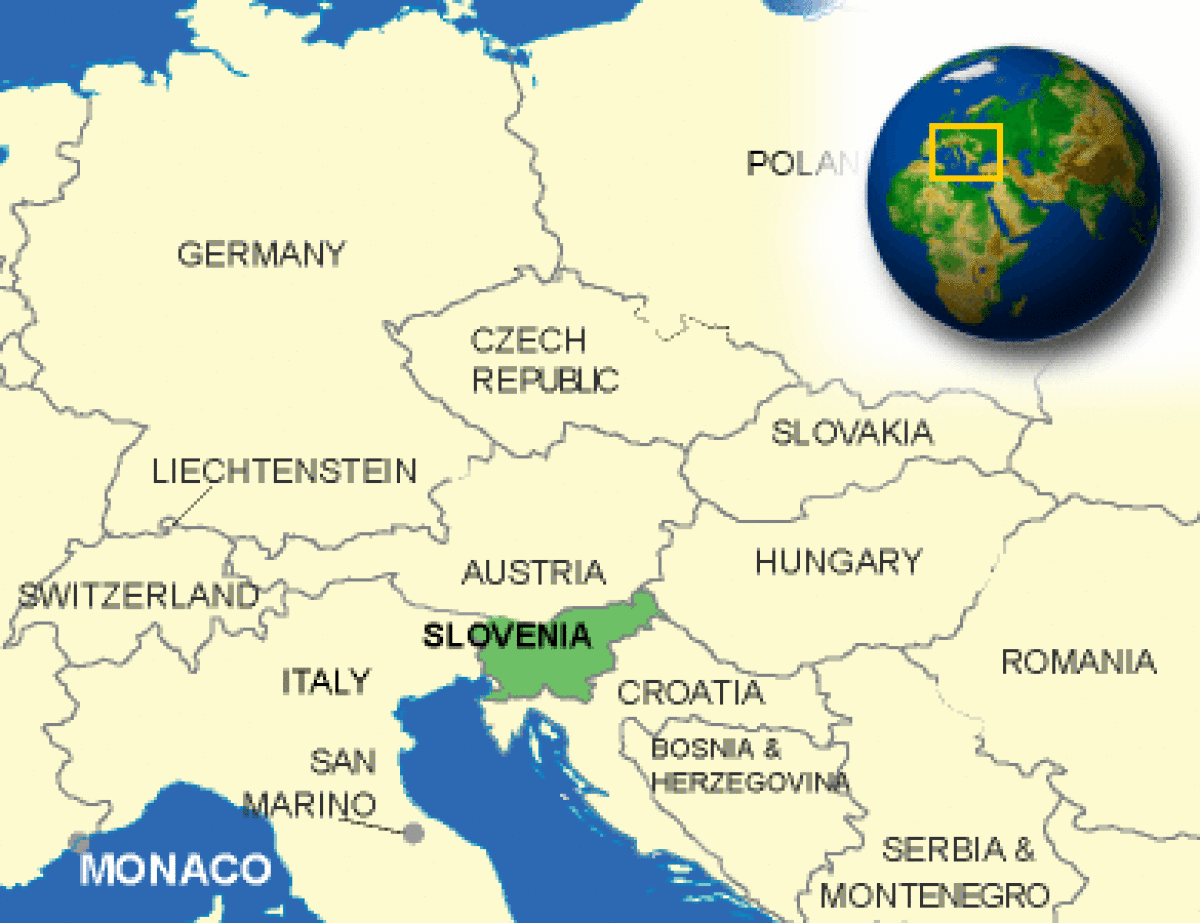
Where is Slovenia located?
What countries border Slovenia?
Slovenia Weather
What is the current weather in Slovenia?
Click for weather forecast
Slovenia Facts and Culture
What is Slovenia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Slovenes appear reserved at first but are very friendly upon acquaintance. They place a high value on their relationships with... More
- Family: The living arrangements and family size are changing. Ten years ago, it was common for two or three generations to... More
- Personal Apperance: Grooming in public is important to Slovenes. Contemporary Western styles are worn. People wear furs to keep warm, including a... More
- Recreation: Slovenes like outdoor recreation such as hiking, biking, swimming, horseback riding and fishing. In winter they ski and skate. Skis... More
- Diet: The many influences on Slovenian cuisine include Italian, Austrian, south Slavic, and Hungarian cooking traditions. A typical meal may consist... More
- Food and Recipes: Traditionally, Slovenes eat in continental style, with the fork in the left hand and the knife in the right. Breakfast... More
- Visiting: While family and friends enjoy visiting, it is customary to call ahead. It is prevalent to invite friends to the... More
- Dating: Young people often go out to movies, fairs, and dances. They may visit museums, parks, sporting events or walk in... More
Slovenia Facts
What is the capital of Slovenia?
| Capital | Ljubljana |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
7,827 Square Miles 20,273 Square Kilometers |
| Location | south Central Europe, Julian Alps between Austria and Croatia |
| Language | Slovenian 92%, Serbo-Croatian 6.2%, other 1.8% |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $30,900.00 (USD) |
Slovenia Demographics
What is the population of Slovenia?
| Ethnic Groups | Slovene 92%, Croat 1%, Serb 0.5%, Hungarian 0.4%, Bosniak 0.3%, other 5.8% (1991) |
| Languages | The official language is Slovene, a Slavic language. The language has a special language construct that indicates two people or things, separate to singular and plural. Slovene uses Roman characters, but excludes q,w,and x. The oldest documents preserved date back to 1000 AD. Slovene resisted the pressure to "Germanize" the language. The next most used language is English. |
| Nationality Noun | Slovene(s) |
| Population | 2,102,678 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.21% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | LJUBLJANA (capital) 273,000 |
| Urban Population | 49.900000 |
Slovenia Government
What type of government does Slovenia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Natasa PIRC MUSAR (since 23 December 2022); note - PIRC MUSAR is Slovenia's first female president head of government: Prime Minister Robert GOLOB (since 1 June 2022) cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, elected by the National Assembly elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second consecutive term); election last held on 23 October 2022 with a runoff on 13 November (next to be held in 2027); following National Assembly elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually nominated prime minister by the president and elected by the National Assembly election results: 2022: Natasa PIRC MUSAR elected president in second round: percent of vote in first round - Anze LOGAR (SDS) 34%, Natasa PIRC MUSAR (independent) 26.9%, Milan BRGLEZ (SD) 15.5%, Vladimir PREBILIC (independent) 10.6%, Sabina SENCAR (Resni.ca) 5.9%, Janez CIGLER KRALJ (NSi) 4.4%, other 2.7%; percent of vote in second round - Natasa PIRC MUSAR 53.9%, Anze LOGAR 46.1%; Robert GOLOB (GS) elected prime minister on 25 May 2022, National Assembly vote - 54-30 2017: Borut PAHOR reelected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Borut PAHOR (independent) 47.1%, Marjan SAREC (Marjan Sarec List) 25%, Romana TOMC (SDS) 13.7%, Ljudmila NOVAK (NSi) 7.2%, other 7%; percent of vote in second round - Borut PAHOR 52.9%, Marjan SAREC 47.1% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Slovenia; both parents if the child is born outside of Slovenia dual citizenship recognized: yes, for select cases residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years, the last 5 of which have been continuous |
| National Holiday | Independence Day/Statehood Day, 25 June (1991) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1974 (preindependence); latest passed by Parliament 23 December 1991 amendments: proposed by at least 20 National Assembly members, by the government, or by petition of at least 30,000 voters; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; referendum required if agreed upon by at least 30 Assembly members; passage in a referendum requires participation of a majority of eligible voters and a simple majority of votes cast; amended several times, last in 2016 |
| Independence | 25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia) |
Slovenia Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Slovenia Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Slovenia Geography
What environmental issues does Slovenia have?
| Overview |
Slovenia is a central European country with a surface area of 12,153 square miles. To the southwest, Slovenia has a 28-mile coastline on the Adriatic Sea. There are basically six topographies: the Alps, including the Julian Alps, the Kamnik-Savinja Alps, the Karavanke chain and the Pohorje Massif to the north and northeast; the pre-Alpine hills of Idrija, Cerkno, Skofja Loka and Posavje spreading across the entire southern side of the Alps; the Dinaric karst (a limestone region of underground rivers, gorges, and caves) below the hills and encompassing the "true" or "original" Karst Plateau (from which all karst regions around the world take their name) between Ljubljana and the Italian border; the Slovenian Littoral, 28 miles of coastline along the Adriatic Sea; the "lowlands," comprising about one-fifth of the territory in various parts of the country; and the essentially flat Pannonian Plain to the east and northeast. Slovenia is predominantly hilly or mountainous; about 90% of the surface is more than 700 feet above sea level. Forest, some of it virgin, covers just under half of the country, making Slovenia one of the greenest countries in the world. Agricultural land (fields, orchards, vineyards, pastures, etc.) account for 43% of the total. Major rivers are the Drava, Sava (which meets the Danube in Belgrade), Soca, and Mura. |
| Climate |
Slovenia is temperate with four seasons, but the topography creates three individual climates. The northwest has an Alpine climate with strong influences from the Atlantic and abundant precipitation. Temperatures in the Alpine valleys are moderate in summer but cold in winter. The coast and a large part of Primorska as far as the Soca Valley has a Mediterranean climate with warm sunny weather much of the year and mild winters. Most of eastern Slovenia has a Continental climate with hot summers and cold winters. The average temperature in July is 68-75 °F in the interior while on the coast it is around 82-85 °F. Ljubljana sits in a valley, and often has fog or rain covering the city. Slovenia gets most of its rain in the spring (May and June) and autumn (October and November). January is the coldest month with an average temperature of 30°F, and July is the warmest, with an average temperature of 70°F. The mean average temperature in Ljubljana is 50°F. Average annual precipitation is 31 inches in the east and 117 inches in the northeast, on account of heavier snowfall. |
| Border Countries | Austria 330 km, Croatia 670 km, Italy 232 km, Hungary 102 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Sava River polluted with domestic and industrial waste; pollution of coastal waters with heavy metals and toxic chemicals; forest damage near Koper from air pollution (originating at metallurgical and chemical plants) and resulting acid rain |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | a short coastal strip on the Adriatic, an alpine mountain region adjacent to Italy and Austria, mixed mountains and valleys with numerous rivers to the east |
Slovenia Economy
How big is the Slovenia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Slovenia is considered one of the wealthier and more advanced economies in Central and Eastern Europe. Its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita is above the European Union average. The country has experienced moderate economic growth in recent years. 3. Trade and Exports: Slovenia's economy highly depends on foreign trade. The country exports various goods, including machinery, pharmaceuticals, electrical equipment, vehicles, and chemicals. Key trading partners include other European Union countries, especially Germany, Italy, and Austria. 4. Tourism: Tourism is a significant contributor to Slovenia's economy. The country is known for its picturesque landscapes, including the Julian Alps, lakes, and historic cities. Ljubljana, the capital, is also a popular tourist destination. 5. Banking and Finance: Slovenia has a well-developed banking sector. The country went through a banking crisis in the 2010s, leading to reforms and restructuring in the financial sector. The banking system has stabilized, and efforts have been made to enhance transparency and improve regulations. 6. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Slovenia has attracted foreign direct investment, particularly in the automotive, pharmaceutical, and information technology sectors. The government has implemented reforms to improve the business environment and encourage foreign investment. 7. Challenges: Despite its economic strengths, Slovenia faces challenges, including an aging population, which can impact labor market dynamics and public finances. Structural reforms have been introduced to address these challenges and enhance competitiveness. 8. Eurozone Member: Slovenia adopted the euro (EUR) as its official currency in 2007 and is a member of the Eurozone. This provides stability for trade and financial transactions with other Eurozone countries. 9. Innovation and Technology: Slovenia has been promoting innovation and technology. It has a growing tech sector, and initiatives are underway to support research and development activities. 10. Fiscal Policy: Slovenia has pursued prudent fiscal policies, but managing public finances remains important. The government has worked on reducing the budget deficit and public debt. |
| Industries | ferrous metallurgy and aluminum products, lead and zinc smelting, electronics (including military electronics), trucks, electric power equipment, wood products, textiles, chemicals, machine tools |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 24.7%, Italy 12.1%, Croatia 8.7%, Austria 7.1%, France 6.7%, Bosnia and Herzegovina 4.5% |
| Import Partners | Germany 19.2%, Italy 17.9%, France 10.2%, Austria 8.3% |
Slovenia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Slovenia?
Source: Google News
Slovenia Travel Information
What makes Slovenia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Slovenia is a parliamentary democracy and a member of the European Union. Tourist facilities are widely available throughout the country. Slovenian is the official language; English is not widely spoken outside of major cities and tourist attractions.
Crime
Slovenia’s overall crime rate is low and violent crimes are relatively uncommon. Most crimes tend to be directed towards obtaining personal property, such as purse snatching, pick-pocketing, and residential and vehicle break-ins. Visitors should take normal security precautions and report any incidents to the local police.Vehicle break-in/theft is a continuing problem in Slovenia. You should always lock your vehicles, use vehicle anti-theft devices, park in well-lighted areas, and if possible, secure vehicles in residential or hotel garages. To guard against residential burglaries, it is advisable to implement preventative security measures such as rolling down shutters and locking windows and doors when not at home and keeping garage doors closed.
We urge U.S. citizens to exercise caution with so-called "gentlemen's clubs." A few such establishments have presented foreign customers with grossly inflated bar bills, sometimes in the thousands of dollars, and threatened those customers who refuse to pay.
Incidents of violent crime, while still relatively infrequent, are possible. U.S. citizens have reported incidents of sexual assault in at least one nightclub in recent years. Use caution when accepting open drinks at bars or clubs, and don’t leave your drinks unattended.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Slovenia, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. If you break local laws in Slovenia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not in countries where you will be traveling. And certain crimes may result in you being prosecuted both in a foreign country and in the United States. For instance, engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography is illegal in Slovenia and these actions are also prosecutable in the United States. Persons violating Slovenian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Slovenia are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Slovenia, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the Embassy to your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the Embassy.
Languages
The official language is Slovene, a Slavic language. The language has a special language construct that indicates two people or things, separate to singular and plural. Slovene uses Roman characters, but excludes q,w,and x. The oldest documents preserved date back to 1000 AD. Slovene resisted the pressure to "Germanize" the language. The next most used language is English.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Adequate medical care is readily available. Travelers to Slovenia may obtain a list of English-speaking physicians on the U.S. Embassy’s website. Antibiotics, as well as other U.S.-equivalent prescription medications are available at local pharmacies. In Slovenia all medications, including drugs considered over-the-counter and first aid supplies, are dispensed through pharmacies (called “lekarna”). Please see the Embassy’s website for a list of pharmacies open 24 hours.Persons who engage in outdoor activities may wish to take a vaccine to prevent tick-borne encephalitis.
Safety and Security
While Slovenia has not had any incidents of international or indigenous terrorism, it shares open borders with three Schengen Zone neighbors. This allows for the possibility of terrorist groups entering/exiting the country with anonymity. We remind U.S. citizens to remain vigilant with regard to their personal security and to exercise caution while traveling in Slovenia.While civil disorder is rare in Slovenia, there are occasional strikes, protests, and other public demonstrations. Protests in Ljubljana are usually held in areas around Kongresni Trg (Congress Square), opposite the Slovenian Parliament, and, sometimes, near the U.S. Embassy. While most demonstrations are peaceful and not anti-American in nature, some participants have occasionally expressed anti-U.S. sentiments. As all demonstrations can potentially turn confrontational or even violent, U.S. citizens are urged to avoid these events whenever possible, and to exercise caution when in the vicinity of any such gathering. For additional information, we encourage U.S. citizens to check the Embassy’s website or call the Embassy at 386-1-200-5595 (200-5556 after hours and on weekends/holidays).
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Slovenia, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Slovenia is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Driving: Slovenia has a well-developed road network that is safe for travel. Highways connect to neighboring cities and countries, and are clearly marked; road signs and traffic rules are consistent with those used throughout Europe. As the number of cars in Slovenia continues to rise, roads are becoming more heavily congested during the weekends and during rush hours. Parking is difficult and can be expensive in the center of Ljubljana. Third-party liability insurance is required for all vehicles; coverage is purchased locally. Travelers driving rented automobiles from Croatia into Slovenia are generally able to purchase Slovene insurance at the border. However, at the smaller border crossings or during peak travel times, it can take several hours to arrange such coverage. Travelers should be alert to aggressive drivers both in cities and on highways. Many of the serious accidents in Slovenia occur as a result of high-speed driving. Emergency roadside assistance and towing services is available by dialing 1987. Dial 112 for an ambulance or fire brigade, and 113 for police. By Slovenian law, the maximum legal blood-alcohol limit for drivers is 0.05.
Traffic moves on the right. The speed limit is 50kph/30 mph in most urban areas and 130 kph/80 mph on expressways (the avtocesta). Motorists are required to have their headlights on during the daytime; drivers and passengers alike must wear seat belts; motorcyclists and their passengers must wear approved helmets. The use of hand-held cellular telephones while driving is prohibited in Slovenia and turning right on red is not allowed.
Between November 15th and March 15th, the use of winter tires is mandated by law. All-season tires are permitted if they carry the MS mark and have at least 4 mm of tread. In addition, local police may require chains in heavy snow. Failure to possess the proper tires/chains may result in a substantial fine and the suspension of the cited vehicle's use. Insurance may be deemed void if a vehicle which is involved in an accident between November 15 and March 15 is not fitted with winter tires.
Vignettes: Highway vignettes (which are purchased in the form of windshield stickers) are obligatory for all passenger vehicles using expressways in Slovenia. A one-year vignette costs EUR 95, a monthly vignette costs EUR 30, and a weekly vignette costs EUR 15. For motorcycles, a one-year vignette is EUR 47.50, a half-year vignette is EUR 25, and a weekly vignette is EUR 7.50. One of the most common problems faced by U.S. citizens visiting Slovenia is being pulled over on a highway for driving without a vignette. Drivers without a vignette may be fined between EUR 300-800 and must also immediately purchase a vignette. Simply buying a vignette and placing it on the dashboard is not sufficient – the vignette must be permanently affixed to the windshield of the vehicle. Vignettes can be purchased in Slovenia at gas stations, newsstands, automobile clubs, post offices (Posta Slovenije), and some toll stations, As well as at some gas stations in neighboring countries.
Driver’s licenses: U.S. citizens visiting or residing in Slovenia must be in possession of both a valid U.S. driver’s license and an International Driver’s License in order to drive legally in Slovenia. This combination of U.S. and an International Driver’s Licenses is valid for a maximum of one year, after which time individuals are required to obtain a Slovenian driver’s license. Two automobile associations are authorized by the U.S. Department of State to issue International Driver’s Licenses: the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (through the National Auto Club ).
Current information about traffic and road conditions is available in English from the Automobile Association of Slovenia by calling (01) 530-5300 and from the Traffic Information Center for Public Roads.
Taxis: While Ljubljana's taxis are generally safe, clean, and reliable, taxi drivers at the airport, some hotels, and main railway stations have been known to overcharge tourists by shutting off their meters. When using a taxi, you should first ask about the rate and check to see that the meter is running during the journey.
Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Also, we suggest that you visit the website of Slovenia's national tourist office and the Slovenian Roads Agency.
Bicycling: Bicycling is popular in Slovenia, and cities have well-developed bicycling networks, with marked bicycle lanes along most roads. Slovenia has more rules governing cyclists than the United States, and police are authorized to ticket cyclists who do not follow them. There are special rules regarding children and bicycles. Please visit Slovenia’s Bicycle Safety page for a list of rules and advice for cyclists.
