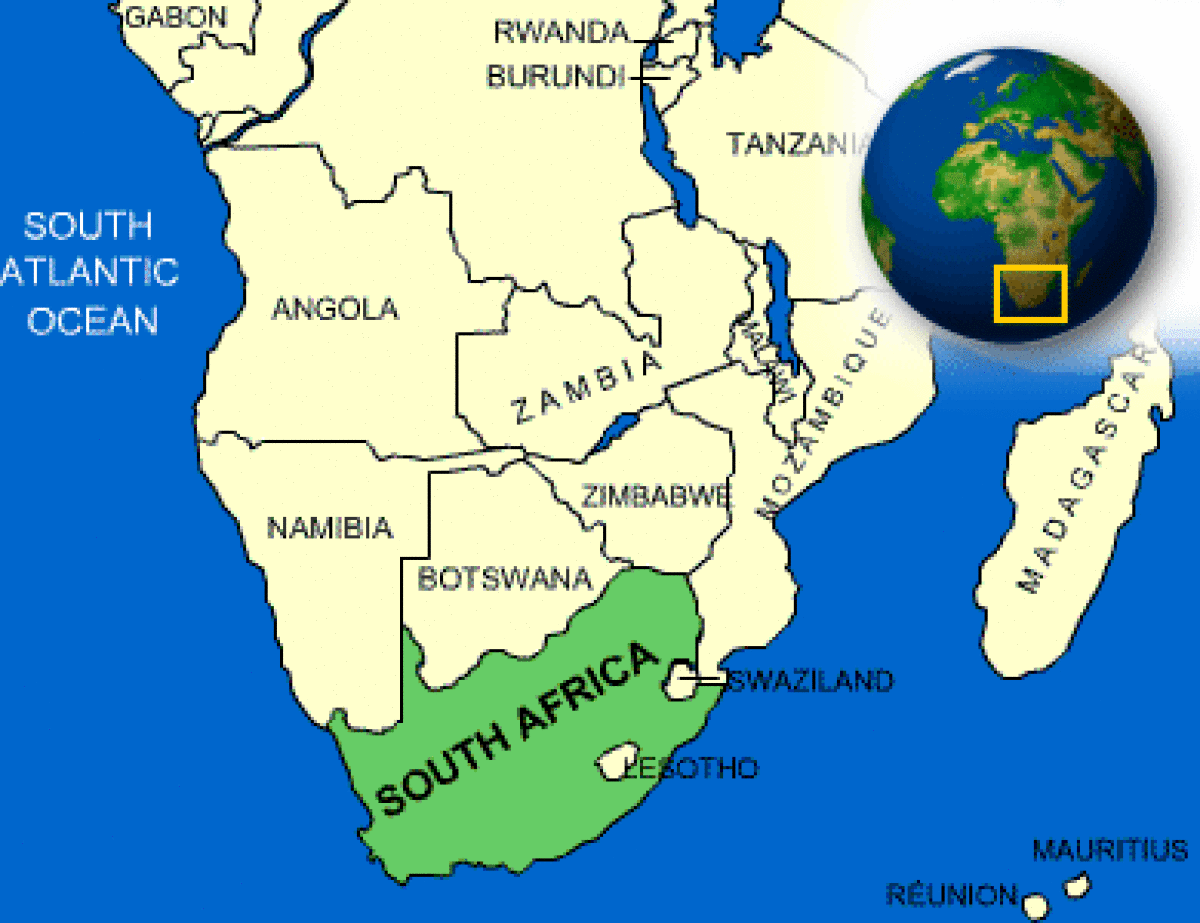
Where is South Africa located?
What countries border South Africa?
South Africa Weather
What is the current weather in South Africa?
South Africa Facts and Culture
What is South Africa famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Today’s South Africa and the attitudes of its people are both changing rapidly. Blacks generally value education as the key... More
- Family: Family life among the white population is similar to that of middle-class Europeans. Families are usually small and generally enjoy... More
- Personal Apperance: Male South Africans may wear shorts with knee socks rather than pants. Women usually wear comfortable dresses or long pants.... More
- Recreation: Soccer, rugby, and cricket are the most popular sports in South Africa. South Africans also enjoy tennis, field hockey,... More
- Diet: The South African diet is often determined by a person’s economic status. Beef, mutton, a variety of curries, green vegetables,... More
- Food and Recipes: The continental style of eating is generally observed by urban South Africans. In rural areas, people often eat with spoons... More
- Visiting: Visits are usually arranged in advance, but unannounced visits among relatives or friends are common. South Africans are generally hospitable... More
South Africa Facts
What is the capital of South Africa?
| Capital | Pretoria (administrative capital); Cape Town (legislative capital); Bloemfontein (judicial capital) |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Rand (ZAR) |
| Total Area |
470,691 Square Miles 1,219,090 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Africa, at the southern tip of the continent of Africa |
| Language | 11 official languages, including Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Pedi, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, Zulu |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $13,400.00 (USD) |
South Africa Demographics
What is the population of South Africa?
| Ethnic Group - note | Coloured is a term used in South Africa, including on the national census, for persons of mixed race ancestry who developed a distinct cultural identity over several hundred years |
| Ethnic Groups | Black African 81.4%, Coloured 8.2%, White 7.3%, Indian/Asian 2.7%, other 0.4% |
| Language - note | The languages spoken in South Africa are as diverse as its ethnic groups. Africans is the native tongue of about two-thirds of all whites and most of coloreds (8.6%), and English is the original language of most the whites (13.6%) and the Indians (2.6%). The black’s (75.2%) native tongues include a variety of Bantu languages, which are roughly divided into four language families: Nguni, Sotho, Tsonga or Shangana and Venda. |
| Languages | isiZulu or Zulu (official) 25.3%, isiXhosa or Xhosa (official) 14.8%, Afrikaans (official) 12.2%, Sepedi or Pedi (official) 10.1%, Setswana or Tswana (official) 9.1%, English (official) 8.1%, Sesotho or Sotho (official) 7.9%, Xitsonga or Tsonga (official) 3.6%, siSwati or Swati (official) 2.8%, Tshivenda or Venda (official) 2.5%, isiNdebele or Ndebele (official) 1.6%, other (includes South African sign language (official) and Khoi or Khoisan or Khoe languages) 2%; note - data represent language spoken most often at home |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: South African(s) adjective: South African |
| Population | 60,442,647 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.07% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 10.316 million Johannesburg (includes Ekurhuleni), 4.890 million Cape Town (legislative capital), 3.228 million Durban, 2.818 million PRETORIA (administrative capital), 1.296 million Port Elizabeth, 934,000 West Rand |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 68.8% of total population rate of urbanization: 1.72% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 29,664,388 female: 30,778,259 |
South Africa Government
What type of government does South Africa have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Matamela Cyril RAMAPHOSA (since 15 February 2018); Deputy President Paul MASHSATILE (since 7 March 2023); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government; Deputy President David MABUZA resigned 1 March 2023 head of government: President Matamela Cyril RAMAPHOSA (since 15 February 2018); Deputy President Paul MASHSATILE (since 7 March 2023) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 May 2019 (next to be held in 2024) election results: 2019: Matamela Cyril RAMAPHOSA (ANC) elected president by the National Assembly unopposed 2014: Jacob ZUMA (ANC) reelected president by the National Assembly unopposed |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Africa dual citizenship recognized: yes, but requires prior permission of the government residency requirement for naturalization: 5 year |
| National Holiday | Freedom Day, 27 April (1994) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest drafted 8 May 1996, approved by the Constitutional Court 4 December 1996, effective 4 February 1997 amendments: proposed by the National Assembly of Parliament; passage of amendments affecting constitutional sections on human rights and freedoms, non-racism and non-sexism, supremacy of the constitution, suffrage, the multi-party system of democratic government, and amendment procedures requires at least 75% majority vote of the Assembly, approval by at least six of the nine provinces represented in the National Council of Provinces, and assent of the president of the republic; passage of amendments affecting the Bill of Rights, and those related to provincial boundaries, powers, and authorities requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly, approval by at least six of the nine provinces represented in the National Council, and assent of the president; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 31 May 1910 (Union of South Africa formed from four British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State); 22 August 1934 (Status of the Union Act); 31 May 1961 (republic declared); 27 April 1994 (majority rule) |
South Africa Video
YouTube, Roman Dent South Africa Culture
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)South Africa Geography
What environmental issues does South Africa have?
| Overview |
South Africa lies at the southern tip of the African continent. South Africa has a narrow coastal zone and an extensive interior plateau with altitudes ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 feet above sea level. Lacking arterial rivers or lakes of significance, extensive water conservation and controls are necessary. South Africa is divided into nine provinces: the Western Cape, Eastern Cape, Northern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, Free State, Mpumalanga, Gauteng, Northwest and Limpopo Provinces. Both Pretoria and Johannesburg are situated on a high plateau in Gauteng Province. The surrounding countryside is characterized by relatively treeless, rolling hills. The Magaliesberg Mountain Range, more accurately described as a series of low rising hills, lies 30 miles to the north or northeast. The large Hartbeespoort Dam is located in this area. The more impressive Drakensberg Mountains are located 200 miles to the south, where peaks soar to 11,000 feet in neighboring Lesotho. The pine-studded Lebombo Mountains form the eastern boundary of the Johannesburg Consular District in Mpumalanga Province. Scenery in the Free State is flat, with a few buttes in the eastern part of the province. Bloemfontein is the provincial capital and the judicial capital of South Africa. The Western Cape has the widest range of scenic attractions, including the Mediterranean-like luxuriance of the Cape Peninsula, rolling uplands to the east, excellent surfing beaches, the majestic peaks of the Katberg, the placid lakes of the Wilderness on the south coast of the picturesque Garden Route, and the vast, arid distances of the Karoo to the north and east. |
| Climate |
South Africa has a moderate climate with sunny days and cool nights. The most southerly point has a mean yearly temperature of 61.8 degrees Fahrenheit, while Johannesburg, situated at 5,700 above sea level, has an annual mean of 60.8 degrees Fahrenheit. Pretoria, at 4,452 feet above sea level, is warmer with a mean annual temperature of 63.5 degrees Fahrenheit. The temperatures can be deceiving because of the very bright and dangerous high sun during most of the year, especially in the highveld areas. Although the country lies close to the Tropic of Capricorn, the high altitude of the inland areas results in a temperate climate in most of the country. In the Southern Hemisphere, seasons are opposite those of the Northern Hemispher-summer extends from October to March; winter from June to September. The rainy season in the Pretoria-Johannesburg area is during summer, and the temperature seldom rises above 90 degrees F, with cool nights. Winter is dry and cool with daily temperatures varying from as low as 30 degrees F during the night to as high as 75 degrees F during the day. Along the coastal area where Durban and Cape Town are located, heavier rainfall occurs during winter and spring, causing high humidity. Both cities experience strong winds - Durban from August through October and Cape Town throughout the year. The seasons are not pronounced but blend almost imperceptibly. For the most part, trees and shrubs remain green, with flowers blooming throughout the year. The highveld, which includes the Pretoria-Johannesburg area, remains dry and brown throughout much of the year. |
| Border Countries | Botswana 1,840 km, Lesotho 909 km, Mozambique 491 km, Namibia 967 km, Swaziland 430 km, Zimbabwe 225 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | lack of important arterial rivers or lakes requires extensive water conservation and control measures; growth in water usage outpacing supply; pollution of rivers from agricultural runoff and urban discharge; air pollution resulting in acid rain; soil erosion; desertification |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | vast interior plateau rimmed by rugged hills and narrow coastal plain |
South Africa Economy
How big is the South Africa economy?
| Economic Overview |
South Africa is a middle-income emerging market with an abundant supply of natural resources; well-developed financial, legal, communications, energy, and transport sectors; and a stock exchange that is Africa’s largest and among the top 20 in the world. Economic growth has decelerated in recent years, slowing to an estimated 0.7% in 2017. Unemployment, poverty, and inequality - among the highest in the world - remain a challenge. Official unemployment is roughly 27% of the workforce and runs significantly higher among black youth. Even though the country's modern infrastructure supports a relatively efficient distribution of goods to major urban centers throughout the region, unstable electricity supplies retard growth. Eskom, the state-run power company, is building three new power stations and is installing new power demand management programs to improve power grid reliability but has been plagued with accusations of mismanagement and corruption and faces an increasingly high debt burden. South Africa's economic policy has focused on controlling inflation while empowering a broader economic base; however, the country faces structural constraints that also limit economic growth, such as skills shortages, declining global competitiveness, and frequent work stoppages due to strike action. The government faces growing pressure from urban constituencies to improve the delivery of basic services to low-income areas, increase job growth, and provide university-level education at affordable prices. Political infighting among South Africa’s ruling party and the volatility of the rand risks economic growth. International investors are concerned about the country’s long-term economic stability; in late 2016, most major international credit rating agencies downgraded South Africa’s international debt to junk bond status. GDP and Growth: South Africa has the second-largest economy in Africa, after Nigeria. The country has faced economic challenges, including slow GDP growth, high unemployment rates, and inequality. Unemployment: Unemployment in South Africa has been persistently high, particularly affecting the youth. The country faces structural challenges in its labor market. Mining Sector: South Africa has rich natural resources, and historically, mining has been a significant contributor to its economy. It is a major producer of minerals like gold, platinum, and diamonds. Agriculture: Agriculture plays a crucial role in South Africa's economy, providing employment and contributing to food production. However, the sector faces challenges such as drought and land reform issues. Manufacturing: South Africa has a diverse manufacturing sector, producing goods ranging from automobiles to processed food. Manufacturing contributes to economic diversity and job creation. Financial Services: The financial services sector is well-developed, with Johannesburg being a major financial hub in Africa. The banking and financial industries are key contributors to the economy. Tourism: South Africa is a popular tourist destination, known for its natural beauty, wildlife, and cultural attractions. The tourism sector has been impacted by global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic. Infrastructure Challenges: South Africa faces challenges related to infrastructure, including electricity shortages and aging transport networks. These challenges can impact economic productivity. Government Debt: South Africa's government debt has been a concern, and fiscal challenges have been exacerbated by the need for increased spending during the COVID-19 pandemic. Land Reform and Agriculture Policies: Land reform policies have been a topic of discussion and debate, with efforts to address historical imbalances in land ownership. The impact of these policies on agriculture and the broader economy is closely watched. COVID-19 Impact: Like many countries, South Africa has faced economic challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lockdowns and disruptions to global trade have affected various sectors. Political Landscape: The political environment in South Africa has implications for economic policies and investor confidence. The country has experienced political changes, and the ruling African National Congress (ANC) has been in power since the end of apartheid. Renewable Energy Initiatives: South Africa has made strides in renewable energy, with projects focused on wind and solar power. The government aims to diversify the energy mix and reduce reliance on coal. Trade Relations: South Africa is an active participant in regional trade agreements, and it has trade relationships with countries worldwide. However, trade imbalances and external factors can impact the trade balance. |
| Industries | mining (world's largest producer of platinum, gold, chromium), automobile assembly, metalworking, machinery, textile, iron and steel, chemicals, fertilizer, foodstuffs |
| Currency Name and Code | Rand (ZAR) |
| Export Partners | UK 12.8%, US 12.7%, Germany 9.3%, Japan 8.9%, Italy 5.8% |
| Import Partners | Germany 15.5%, US 9.5%, UK 9.1%, Japan 5.8%, Saudi Arabia 5.3%, France 5%, China 4.9% |
South Africa News and Current Events
What current events are happening in South Africa?
Source: Google News
South Africa Travel Information
What makes South Africa a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
South Africa is a parliamentary democracy and is, in many respects, a developed country, although much of its population lives in poverty. All major urban areas have modern, world-class hotels and tourist facilities. Game parks and areas most often visited by tourists have a wide range of facilities. Food and water are generally safe, and a wide variety of consumer goods and pharmaceuticals is readily available. The capital is Pretoria, while the seat of parliament is located in Cape Town. Johannesburg is the financial capital and largest city in South Africa. Durban is home to Africa’s busiest port and is the number-one domestic tourist destination for South Africans.
Crime
The vast majority of visitors complete their travels in South Africa without incident. However, visitors should be aware that criminal activity is prevalent throughout the country and can be violent. The South African government has in place a number of strong anti-crime initiatives, but violent crimes, such as armed robbery, carjacking, mugging, "smash-and-grab" attacks on vehicles, and other criminal acts are still common and do affect visitors and resident U.S. citizens.Note: Visitors to the U.S. Embassy in Pretoria and U.S. Consulates General in Cape Town, Durban, and Johannesburg should be aware of the risk of muggings, several of which have occurred near U.S. diplomatic facilities. While measures have been taken to address concerns about potential muggings, visitors approaching U.S. government facilities should be aware of their personal security and carry as little money and valuables as possible.
Visitors and residents are advised of ongoing criminal activity involving organized crime gangs targeting individuals and commercial businesses at shopping centers and other public places. Once a victim has been identified, he/she may be followed back to his/her residence or hotel and robbed. Robberies often involve weapons; the use of force is used from the moment of attack and generally escalates greatly for those offering some form of resistance.
These gangs target people of opportunity and not always appearing to be affluent. Crime affects all sectors of society to include those driving expensive cars, wearing eye-catching jewelry, flashing large amounts of cash, and/or making high-value purchases. Criminals also gravitate towards “soft” targets - people who appear preoccupied and do not pay attention to their immediate surroundings. Visitors who believe they are being followed should travel directly to a police station or other public location of safety.
Cash-in-transit (armored vehicles) robberies remain common; tourists should try to avoid traveling near these vehicles and personnel during a cash delivery or pick-up, particularly at shopping centers or other public locations. Crimes against property, such as carjacking, have often been accompanied by violent acts, including murder, when victims resist or are slow to respond to attackers’ demands.
South Africa also has the highest reported occurrence of rape in the world. Foreigners are not specifically targeted, but several have been the victims of rape. Victims of violent crime, especially rape, are strongly encouraged to seek immediate medical attention, including antiretroviral therapy against HIV/AIDS. Questions about how to receive such treatment should be directed to the nearest U.S. consulate.
Criminal activity, such as assault, armed robbery, and theft, is particularly high in areas surrounding certain hotels and public transportation centers, especially in major cities. Theft of passports and other valuables is most likely to occur at airports, bus terminals, and train stations. A number of U.S. citizens have been mugged or violently attacked on commuter and metro trains, especially between Johannesburg and Pretoria.
In the Western Cape, police resources have been strained by continuing gang conflicts and vigilante violence in the low-income areas and informal settlements around Cape Town. People who are unfamiliar with the Cape Flats/Khayelitsha area, surrounding townships, and squatter camps should not visit these areas. Additionally, travelers should be aware that muggings have occurred along popular hiking routes on Table Mountain. Visitors to Table Mountain should be vigilant, hike in groups, and not carry/display valuables.
Crime in Durban remains high. Visitors should avoid traveling in the city center after dark, as well as all travel to the surrounding townships. The suburbs north and west of the city are generally considered to be safer than the city center, but all visitors should remain vigilant and exercise situational awareness at all times.
If confronted by an armed individual, you should immediately comply, and avoid making sudden movements. Any hesitation on your part could be perceived as a threat and may result in unnecessary violence.
ATMs: Criminals often loiter near ATMs, targeting persons withdrawing cash. A common scheme is the “Good Samaritan” fraud, where a criminal attempts to “help out” with a particular ATM transaction. Often the ATM in these situations has been tampered with to record the card information, and the “Good Samaritan” will then take the information and use it to withdraw cash later. This is a prevalent crime, and both residents and visitors have been targeted. Do not accept “assistance” from anyone, or agree to assist others with ATM transactions. Travelers should also try to avoid using ATMs after business hours, on the street, or in remote locations.
Criminals have also used commercial explosives to blow up ATMs in South Africa. ATM bombings have taken place in the early hours of the morning in remote or isolated areas, although some attacks have taken place at gas stations and shopping complexes.
Based on these threats, the following security precautions are recommended:
Avoid using ATMs in dark, remote, or isolated areas.
Never allow someone to assist you at the ATM, and never assist anyone else at the ATM, either.
ATMs located inside shopping malls, hotels, and banks are preferred since they are normally high-traffic areas, and are monitored by security guards and cameras.
Avoid using an ATM with a cord or any foreign object attached to it. If you notice a suspicious device on or alteration to an ATM, immediately leave the area, take cover, and notify the police. Shrapnel and debris from an explosion can travel long distances and cause serious injury or death.
Before withdrawing money, scan the area for any suspicious persons or activity. Should anyone approach you while you are withdrawing money, immediately cancel the transaction, remove your card, and leave the area.
Incidents of credit card fraud, counterfeit U.S. currency, and various check-cashing scams have also been reported. When giving your credit card to a store or restaurant employee for processing, do not let the card out of your sight. Most South African restaurants and gas stations have portable credit card machines that can be brought to your table or car.
Hotel Security: Thefts from hotel rooms throughout the country remain a concern. Travelers are strongly encouraged to make use of hotel-provided room safes or lock-boxes at the front desk for all valuables.
Financial and Romance Scams: Visitors should also beware of telephone, internet, and e-mail fraud schemes, which attempt to win the confidence of unsuspecting persons who are persuaded to enter into a romantic relationship via email, or to provide financial assistance, or to travel to South Africa and assist in a supposedly lucrative business venture. Since 2008, there have been several cases of U.S. citizens losing thousands of dollars and putting themselves in danger by responding to either romantic or financial scams (also known as “419 scams”). “Lonely hearts” scams are a common and growing problem, with “engagements” via internet used to lure victims into sending money to assist with supposed education, health or job problems. Victims have lost tens-of-thousands of dollars on these scams. If you are contacted by someone claiming to be a U.S. citizen you met on the internet or only know online asking you for financial assistance, instruct them to contact the nearest U.S. consulate. You should exercise extreme caution when sending funds to individuals overseas for any reason whether your relationship with them is of a business or personal nature. Some scam victims have traveled to South Africa only to lose more money, and in a few cases, to be physically attacked or kidnapped for ransom. Click to view the State Department’s financial scam web page. If you have lost money in a financial scam, please file a report with your local police and with the Internet Crime Complaint Center. Victims can also report Internet fraud to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) online or by phone, toll-free, at 1-877-FTC-HELP (1-877-382-4357).
To check on a business’s legitimacy while in the United States, contact the International Trade Administration, Room 3317, Department of Commerce, Washington, DC 20230, telephone: 1-800-USA-TRADE or 202-482-5149, fax: 202-482-5198. If you are abroad, contact the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Car Thefts and Carjacking: Carjacking and thefts from cars remain serious problems. Doors should remain locked and windows rolled up at all times. Motorists are urged to hide bags, cell phones, and other valuables from view at all times and to be extremely cautious when approaching intersections. “Smash-and-grab” robberies are common throughout South Africa, particularly in urban areas, at traffic lights, and at highway off-ramps. A criminal, sometimes posing as a vendor or beggar, will walk between lines of vehicles waiting at an intersection, surveying the contents for valuables. Once an item of value is identified, the perpetrator will quickly smash the window and grab the item off the seat before fleeing, often before the driver can determine what happened. In another scenario, an individual (or two working in tandem) may indicate to a driver an apparent flat tire or other problem and wait for the driver to pull over or exit the car before grabbing exposed valuables.
If you see a car pulled over to the side of the road do not stop to offer assistance, but rather call the police to report the vehicle’s location so that authorities can render assistance. You should avoid carrying anything of value inside the car (e.g., briefcases, purses, laptops, etc.) that could attract potential assailants. When parking your vehicle, use parking lots that are well-lit and have a security presence, and physically check that the vehicle is locked before you walk away. Criminals have perfected the technique of blocking the wireless alarm remote signal and either stealing the vehicle or waiting inside the vehicle for the driver to return in order to rob them.
Criminals, working in groups, have placed debris on the road (rocks, bricks, shards of metal, etc.) in an effort to puncture a vehicle’s tires. Another less-frequently used tactic is for criminals to throw rocks, bricks, paint, or eggs from freeway overpasses onto moving vehicles to damage cars and disorient drivers, forcing them to pull over. Other criminals hide along the road and rob the driver once he has pulled over to inspect the damage.
Airport Safety: Although infrequent, travelers leaving the airport have been targeted by criminals for robbery while en route to their hotels or places of residence. As such, all travelers should be extremely vigilant when leaving the airport and ensure that a reliable mode of transportation is used (such as arranging pick-up directly with a hotel, or using airport-approved modes of transport, such as Gautrain or official metered taxis from the taxi rank).
Concerted efforts have been made to reduce luggage theft and pilferage at O.R. Tambo International Airport (Johannesburg), with noticeable results. However, travelers are encouraged to lock their suitcases when possible and avoid placing valuables in checked baggage. A good practice, regardless of destination, is to make an inventory of items and contact your air carrier immediately if you experience a loss.
Criminals are known to also target travelers at ATMs in airports. Travelers should refer to the above section, “ATM Scams,” for security precautions at ATMs.
Firearms: Travelers to South Africa may not import or take in-transit any firearms or ammunition without a temporary import or in-transit permit issued by the South African Police Service. Information on how to obtain a permit for firearms for personal protection and hunting can be found at the South African Police Service’s Firearms website.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in South Africa you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. If you violate South Africa’s laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in South Africa are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Engaging in trafficking or sexual conduct with children or using/disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime, prosecutable in the United States. Please see our information on Criminal Penalties.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if U.S. citizens are arrested in South Africa, they should request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. consulate of the arrest, and to have communications forwarded to the nearest U.S. consulate. Notification by local authorities of U.S. citizens arrested in South Africa is rare. As such, U.S. citizens should request consular notification in the event that they are arrested.
Languages
isiZulu or Zulu (official) 25.3%, isiXhosa or Xhosa (official) 14.8%, Afrikaans (official) 12.2%, Sepedi or Pedi (official) 10.1%, Setswana or Tswana (official) 9.1%, English (official) 8.1%, Sesotho or Sotho (official) 7.9%, Xitsonga or Tsonga (official) 3.6%, siSwati or Swati (official) 2.8%, Tshivenda or Venda (official) 2.5%, isiNdebele or Ndebele (official) 1.6%, other (includes South African sign language (official) and Khoi or Khoisan or Khoe languages) 2%; note - data represent language spoken most often at home
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Private medical facilities are good in urban areas and in the vicinity of game parks, but they may be limited elsewhere. Pharmacies are well-stocked, and equivalents to most American medicines are available. However, travelers taking specific medications should bring an adequate supply for their entire stay and a prescription with them. Nearly all private South African hospitals are owned by one of the following three corporations:Life Health Care (http://www.lifehealthcare.co.za/),
NetCare ( http://www.netcare.co.za/live/netcare_index.php ), or
Mediclinic ( http://www.mediclinic.co.za/Pages/default.aspx ).
Information about locating private hospitals can be obtained by accessing these companies’ websites.
While most of South Africa is malaria-free, malaria risk exists throughout the year in rural low-altitude areas of Limpopo and Mpumalanga provinces, including Kruger National Park and neighboring game reserves. Risk also exists in the coastal lowlands of KwaZulu-Natal north of the Tugela River (including in Zululand, but excluding urban areas of Richards Bay). Risk is much lower from June to September. Visitors should prepare accordingly and use malaria prophylaxis and mosquito repellent. For information on malaria, its prevention, protection from insect bites, and anti-malarial drugs, please visit the CDC's malaria web page.
Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in South Africa.
Safety and Security
Anti-American violence is not typical in South Africa, although in the past there have been isolated incidents perpetrated by parties unhappy about U.S. foreign policy. Nevertheless, the Department of State remains concerned about the continued worldwide threat of terrorist attacks, demonstrations, and other violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests overseas. You are encouraged to review the most recent Worldwide Caution issued by the Department of State.Xenophobic Attacks: South Africa has seen a number of attacks directed at refugees or immigrants from other African nations in recent years. Many of the attacks were centered in Johannesburg and the province of Gauteng in low-income neighborhoods and informal settlements, but other incidents have taken place throughout the country. Many individuals have been killed in these incidents, including targeted victims as well as bystanders. While there have been no reports of U.S. citizens or other non-African visitors being targeted, these incidents of mob violence have sprung up quickly and proven difficult for local authorities to control. U.S. citizen residents and visitors are advised to listen to local media for reports of such incidents and to avoid areas (primarily--but not limited to--townships) where they may be likely to occur.
Public Disturbances and Strikes: Organized or wildcat labor strikes occur regularly in South Africa. Service delivery protests also occur frequently and are generally motivated by poor residents’ frustrations with shortfalls in public service deliveries. While both types of disturbances – labor strikes and service delivery protests – are generally localized and normally occur well away from typical tourist destinations, these disturbances can develop quickly, unpredictably, and occasionally turn violent. Use caution and steer clear of any area where protests, demonstrations, or other public disturbances are taking place. During strikes by public workers, access to government offices, public hospitals and schools may be difficult due to protests, and should be avoided if possible. South Africa has many private medical facilities/services that may not be impacted by public-service strikes.
Public Transportation: Public transportation accidents involving trains, buses, minibus taxis and private cars are a regular occurrence in South African and past incidents have resulted in deaths or serious injuries. In addition, minibus taxis and buses have been targeted by criminal elements for hijacking and robbery. Often, the safety and security standards on public transportation systems – especially in urban areas and townships - in South Africa are not on par with what travelers would expect in the United States. The use of individual metered taxis from established taxi companies and tour buses is recommended. The Gautrain, which travels between the airport and Johannesburg/Pretoria, is considered a very reliable and safe mode of transportation.
Game Park/Safari Safety: While visiting game parks and reserves, it is dangerous to leave your vehicle or otherwise be on foot, even in the presence of a guide. Several incidents of wild animal attacks on tourists in the region have resulted in deaths or serious injuries.
Ocean Safety: If visiting South Africa’s expansive coastline, be mindful of the possible presence of sharks when swimming or engaging in water sports. In 2012, at the Fish Hoek beach and other areas of the Cape Town and Western Cape coastlines and at Port St. John’s in the Eastern Cape, several people were attacked by sharks, and some of the attacks were fatal. When a shark is spotted close to the shore, local authorities will sound a warning siren to notify swimmers if lifeguards and shark spotters are on duty.
Tragic accidents can occur when swimming in the ocean or walking/climbing on shore areas that are not designated and lifeguard-patrolled beaches. Visitors from the United States and elsewhere have drowned when swimming in coastal waters, where riptides, tides and wave patterns can change unexpectedly and overwhelm even excellent swimmers. Do not swim alone in isolated beach areas. Do not dive into unknown bodies of water, as hidden rocks or shallow depths can cause serious injury or death.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning South Africa is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.South African law does not require an international driver’s license for U.S. citizen tourists who are licensed to drive in the United States and who are in South Africa for less than six months. A valid driver’s license from any U.S. state or territory that has the signature and photo of the driver is valid to drive in South Africa for stays of less than six months. However, while South African law does not require an international driver’s license, insurance companies for both long-term residents and rental car customers often require proof of a South African or international driver’s license in order to honor an insurance claim, even when such proof was not requested at the time the policy was secured.
Unlike the United States, where traffic moves on the right-hand side of the road, traffic in South Africa moves on the left, and the steering wheel is on the right-hand side of the car.
Deaths from road accidents are more than twice as high in South Africa as they are globally. According to published reports, the high incidence of mortality in these collisions is due to a combination of poor driving, limited enforcement of traffic laws, road rage, aggressive driving, distracted driving, and driving under the influence of alcohol.
Travelers should use caution at all times when driving, and especially avoid nighttime travel outside major cities. Road conditions are generally good in South Africa; however, excessive speed, poor lighting on rural roads, and insufficient regulatory control of vehicle maintenance and operator licensing have resulted in an increasing number of traffic fatalities. Drivers should also take care to avoid pedestrians crossing roads or major highways.
Traffic lights are frequently out of order. Please treat all intersections with malfunctioning traffic lights as a four-way stop.
Travelers are advised to carry mobile phones. Please note that texting or talking without a hands-free unit while driving is a violation of South African law. U.S. mobile phones may not work in South Africa, but rental mobile phones are widely available and may be rented from kiosks at major airports. The nationwide emergency number for the police is 10111, and the nationwide number for ambulance service is 10177. It is not necessary to dial an area code when calling these numbers.
Pedestrian Safety: Take extreme care when crossing streets. Collisions involving vehicles and pedestrians are all too common on South African roadways. Pedestrian deaths occur regularly, including four cases involving U.S. citizen victims since 2008. Drivers are often aggressive towards pedestrians and fail to yield the right-of-way, even in marked crosswalks. NOTE: The U.S. Embassy in Pretoria and Consulates General in Johannesburg, Cape Town, and Durban are located on busy city streets, and visitors should exercise caution when walking to and from these facilities.
