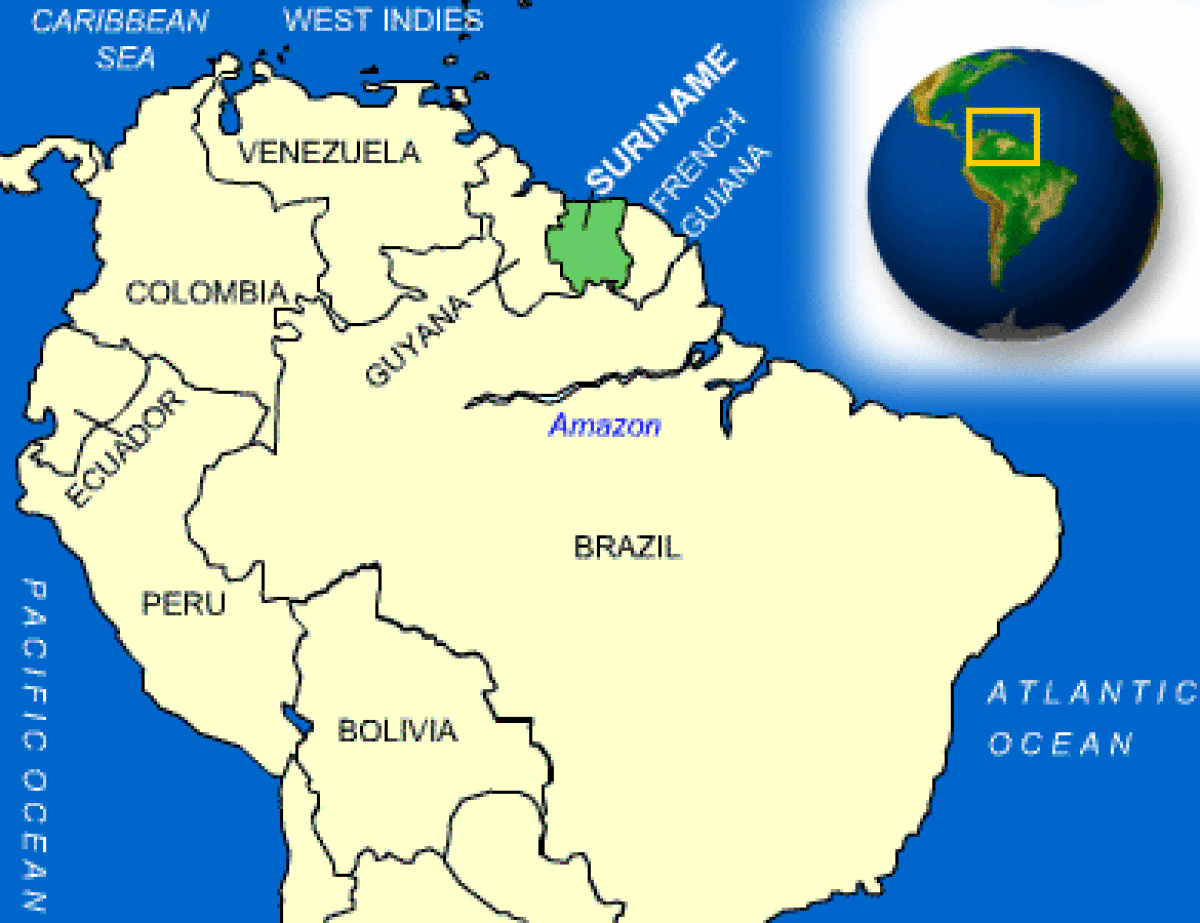
Where is Suriname located?
What countries border Suriname?
Suriname Weather
What is the current weather in Suriname?
Suriname Facts and Culture
What is Suriname famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Suriname is a culturally diverse country located on the northeastern coast of South America. Its population is composed of various... More
- Family: For some groups, child care is handled by one parent at a time. Children spend the first five to six years with... More
- Personal Apperance: In Suriname, the traditional attire varies among the different ethnic groups and is often worn during special occasions and cultural... More
- Recreation: In Suriname, there are various recreational activities enjoyed by its residents. Outdoor Exploration: Suriname's abundant natural beauty provides opportunities for... More
- Diet: Rice is a staple food along with cassava, sweet potatoes, plantains, chicken, and seafood. Favorite meals include Moksie alesie... More
- Food and Recipes: Mealtime customs in Suriname can vary depending on the cultural background of the individuals involved. Suriname is known for its... More
- Visiting: To not be considered rude, anyone visiting a friend is expected to visit everyone they know in the same neighborhood. More
- Dating: In Suriname, dating rituals can vary depending on cultural backgrounds, personal preferences, and individual circumstances. Courtship: Traditional courtship practices, such... More
Suriname Facts
What is the capital of Suriname?
| Capital | Paramaribo |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Suriname Guilder (SRG) |
| Total Area |
63,251 Square Miles 163,820 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana |
| Language | Dutch (official), English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes called Taki-Taki, is native language of Creoles and much of the younger population and is lingua franca among others), Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Javanese |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $16,700.00 (USD) |
Suriname Demographics
What is the population of Suriname?
| Ethnic Groups | Hindustani (also known locally as ""East Indians""; their ancestors emigrated from northern India in the latter part of the 19th century) 37%, Creole (mixed white and black) 31%, Javanese 15%, ""Maroons"" (their African ancestors were brought to the count |
| Nationality Noun | Surinamer(s) |
| Population | 609,569 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.15% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | PARAMARIBO (capital) 278,000 |
| Urban Population | 69.700000 |
Suriname Government
What type of government does Suriname have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI (since 16 July 2020); Vice President Ronnie BRUNSWIJK (since 16 July 2020); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI (since 16 July 2020); Vice President Ronnie BRUNSWIJK (since 16 July 2020) cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly; president and vice president serve a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 13 July 2020 (next to be held in May 2025) election results: 2020: Chandrikapersad SANTOKHI elected president unopposed; National Assembly vote - NA |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Suriname dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 25 November (1975) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1975; latest ratified 30 September 1987, effective 30 October 1987 amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the total membership; amended 1992 |
| Independence | 25 November 1975 (from the Netherlands) |
Suriname Video
YouTube: Geography Nuts SURINAME | Country Profile - South America Country Profile | Overview of Suriname
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Suriname Geography
What environmental issues does Suriname have?
| Overview |
Suriname lies on the northeast coast of South America, bordered by French Guiana in the east, Brazil in the south, and by Guyana in the west. Most of the country's 220-mile shoreline on the Atlantic Ocean consists of mud flats and mangrove swamp. Parts of Suriname's boundaries with French Guiana and Guyana are in dispute. Suriname has a land area of 63,000 square miles (163,000 sq. km.). Most Surinamers, however, live in the 1,900-square-mile narrow coastal plain about 50 KM wide in and around the major population centers of Paramaribo (250,000), Moengo and Nieuw Nickerie (38,000). Suriname's coastal area is mostly flat. Hills and low mountains reach a maximum height of about 4,000 feet (1,230 meters) in the heavily forested interior. Between these two zones lie the savanna lands, 30-40 miles wide. Large rivers and streams flow through Suriname from south to north, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean. Although they provide major transportation routes between the coast and the interior, the number of rivers has proved a historical hindrance to east-west land transportation. |
| Climate |
Suriname's climate is tropical, hot and humid year-round. Daytime temperatures in Paramaribo average 75°F to 90°F. Temperatures in the interior, not moderated by the steady coastal breezes, are generally higher. Seasons are distinguished mainly by more or less rain, with annual rainfall averaging 87 inches. Indeed, locals will tell you that the four seasons of Suriname are: 1) Little Rainy Season (December to February); 2) Little Dry Season (March to April); 3) Big Rainy Season (May to August); and Big Dry Season (September to November). The hottest months of the year are September and October when temperatures average 90 �F (32 �C). Suriname lies outside hurricane and earthquake zones. Parts of Paramaribo experience heavy flooding. Isolated flooding occurs on some city streets and in low-lying areas of Paramaribo for up to 24 hours at a time. |
| Border Countries | Brazil 597 km, French Guiana 510 km, Guyana 600 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | deforestation as timber is cut for export; pollution of inland waterways by small-scale mining activities |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps |
Suriname Economy
How big is the Suriname economy?
| Economic Overview |
Economic overview of Suriname: Economy and GDP: Suriname's economy is classified as an upper-middle-income economy. Its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is primarily driven by the extractive industries, including mining and oil production. Other important sectors include agriculture, manufacturing, construction, and services. Natural Resources: Suriname is rich in natural resources, including bauxite, gold, oil, and hardwood forests. These resources play a significant role in the country's economy, attracting foreign investments and generating export revenues. Mining Sector: Suriname has a well-developed mining sector, with bauxite being its most significant mineral export. Bauxite mining and alumina production are key contributors to the country's economy and provide employment opportunities. Gold mining is also a prominent industry, with Suriname being one of the top gold producers in South America. Oil and Energy Sector: Suriname has recently emerged as an oil-producing nation. Significant offshore oil discoveries have led to the development of oil fields, attracting international oil companies and investment. The oil sector has the potential to significantly impact Suriname's economy in the coming years. Agriculture: Agriculture plays an important role in Suriname's economy, employing a significant portion of the population. Key agricultural products include rice, bananas, citrus fruits, vegetables, and shrimp. The government has made efforts to promote sustainable agriculture and expand export opportunities for agricultural products. Services Sector: The services sector is an important contributor to Suriname's economy. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including trade, transportation, finance, tourism, and telecommunications. The government has been focusing on diversifying the services sector to reduce reliance on extractive industries. Infrastructure and Investment: Suriname has been investing in infrastructure development to support economic growth. Improvements in transportation, energy, telecommunications, and ports are crucial for attracting investments, enhancing trade, and fostering economic development. Challenges: Suriname faces several economic challenges, including high public debt, inflation, and unemployment. The country is working towards fiscal consolidation, promoting sustainable economic growth, and attracting foreign investment through policy reforms and initiatives. Regional Integration: Suriname is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Union of South American Nations (UNASUR). Regional integration and cooperation play a role in facilitating trade, investment, and economic development in Suriname. |
| Industries | bauxite and gold mining, alumina production, oil, lumbering, food processing, fishing |
| Currency Name and Code | Suriname Guilder (SRG) |
| Export Partners | US 25.7%, Norway 20.4%, France 8.3%, Trinidad and Tobago 6.5%, Canada 6.1%, Iceland 6.1%, Netherlands 5.7% |
| Import Partners | US 22.7%, Netherlands 16.1%, China 12.3%, Trinidad and Tobago 11.4%, France 7.6%, Japan 6%, Netherlands Antilles 4.5% |
Suriname News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Suriname?
Source: Google News
Suriname Travel Information
What makes Suriname a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Republic of Suriname is a developing country located on the northern coast of South America. Tourist facilities are available in the capital city of Paramaribo, but are less developed and in some cases non-existent in the country's rugged jungle interior. Dutch is the national language, but most Surinamese in Paramaribo speak English; accordingly most tourist arrangements can be made in English. Tourist arrangements for the interior should be made ahead of time.
Crime
Criminal activity throughout the country has shown a slight increase since September 2010 and travelers, including U.S. citizens, may be viewed as targets of opportunity. Burglary, armed robbery, and violent crime occur with some frequency in Paramaribo and in outlying areas. Pick-pocketing and robbery are common in the major business and shopping districts of the capital. Visitors should avoid wearing expensive or flashy jewelry and should not display large amounts of money in public.There have been several reports of criminal incidents in the vicinity of the major tourist hotels. Night walks, outside the immediate vicinity of the hotels, are not recommended, especially if you are alone. Visitors should specifically avoid the Palm Garden area (“Palmentuin” in Dutch) after dark, as there is no police presence and it is commonly the site of criminal activity.
Theft from vehicles is infrequent, but does occur, especially in areas near the business district. Drivers are cautioned not to leave packages and other belongings in plain view in their vehicles. There have been a few reports of carjackings within Paramaribo, mainly in residential areas. When driving, car windows should be closed and doors locked. The use of public minibuses is discouraged, due to widespread unsafe driving and poor maintenance. Taxis in Suriname are not clearly identified; they do not display the “Taxi” sign. As there are no meters in the taxis, you should verify the price before entering the taxi. The Embassy recommends that you use hotel concierge taxis.
Travel to the interior is usually trouble-free, but there have been reports of tourists being robbed. Police presence outside Paramaribo is minimal, and banditry and lawlessness are occasionally of concern in the cities of Albina and Moengo, and the district of Brokopondo, as well as along the East-West Highway between Paramaribo and Albina, and the Afobakka Highway in the district of Para. There have been reports of attempted and actual carjackings committed by gangs along the East-West Highway. If you plan on traveling to the interior, you are advised to make use of well-established tour companies for a safer experience.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, you may be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Suriname, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In Suriname you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings, particularly government buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. If suspected of driving under the influence and caught in an accident, the Surinamese Police may not be able to measure the alcohol level on the scene; they will take you to the nearest medical center to measure blood alcohol content. You will be held by the police for up to six hours until the results of your blood alcohol content are determined.There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in Suriname is a crime, which is also prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Suriname, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Suriname, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. Embassy, which for Suriname is located in the capital city, Paramaribo.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care, including emergency medical care, is limited in many areas and does not meet U.S. standards. There is one public emergency room in Paramaribo, and only a small ambulance fleet providing emergency transport with limited first response capabilities. The emergency room has no neurosurgeon, and other medical specialists may not always be available. In general, hospital facilities are not air conditioned, although private rooms with individual air conditioning are available at extra cost and on a space-available basis. Emergency medical care outside Paramaribo is limited, and is virtually non-existent in the interior of the country.The yellow fever vaccine is recommended for all travelers over 9 months of age. Rabies risk is present; all dog and bat bites or scratches should be taken seriously and post-exposure prophylaxis sought. Insect precautions are recommended. Due to the presence of Schistosomiasis in some of the freshwater bodies, avoidance of freshwater exposure is recommended.
Safety and Security
Demonstrations are not common in Suriname. If they occur, they will take place primarily in the capital or secondary cities, and are usually peaceful, but U.S. citizens traveling to or residing in Suriname should take common-sense precautions and avoid large gatherings or other events where crowds have congregated to demonstrate or protest. Travelers proceeding to the interior may encounter difficulties due to limited infrastructure and limited presence of government authority. Limited transportation and communications may hamper the ability of the U.S. Embassy to assist in an emergency situation.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Suriname, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Traffic moves on the left in Suriname; left-hand-drive (U.S. style) vehicles also are allowed on the road. Excessive speed, unpredictable driving habits by both vehicles and motorcyclists/bicycles, unusual right of way patterns, poorly maintained roads, and a lack of basic safety equipment on many vehicles are daily hazards on Surinamese roads. Seatbelts have been required for all automobile passengers since January 2007, and drivers must use a hands-free device if using a mobile phone while driving; driving while talking on cell phones is illegal in Suriname. Visitors are encouraged to use automobiles equipped with seatbelts and to avoid the use of motorcycles or scooters. An international driver's license is necessary to rent a car. Visitors renting a car in Suriname should be aware that child seats are required by law.The major roads in Paramaribo are usually paved, but are not always well maintained. Large potholes are common on city streets, especially during the rainy season, which lasts from approximately mid-November to January, and from April to July (rainy seasons can differ from year to year by as much as six weeks). Roads often are not marked with traffic lines. Many main thoroughfares do not have sidewalks, forcing pedestrians, motorcycles and bicycle traffic to share the same space.
The East-West Highway, a paved road that stretches from Nieuw Nickerie in the west to Albina in the east, runs through extensive agricultural areas; it is not uncommon to encounter slow-moving farm traffic or animals on the road. Travelers should exercise caution when driving to and from Nieuw Nickerie at night due to poor lighting and sharp road turns without adequate warning signs. There are few service stations along the road, and western-style rest stops are non-existent. The road is not always well maintained, and during the rainy season, large and sometimes impassable sinkholes develop along the road. Police recommend that you check with the police station in Albina for the latest safety information regarding travel between Paramaribo and Albina.
Roads in the interior are sporadically maintained dirt roads that pass through rugged, sparsely populated rain forest. Some roads are passable for sedans in the dry season, but deteriorate rapidly during the rainy season. Interior roads are not lit and there are no service stations or emergency call boxes. Bridges in the interior are in various states of repair. You are advised to consult with local sources, including The Foundation for Nature Conservation in Suriname, or STINASU, at telephone (597) 421-683 or 476-579, or with their hotels regarding interior road conditions before proceeding.
For specific information concerning Surinamese driving permits, vehicle inspection, road tax and mandatory insurance, please contact the Embassy of Suriname in Washington, D.C. or the Consulate of Suriname in Miami.
