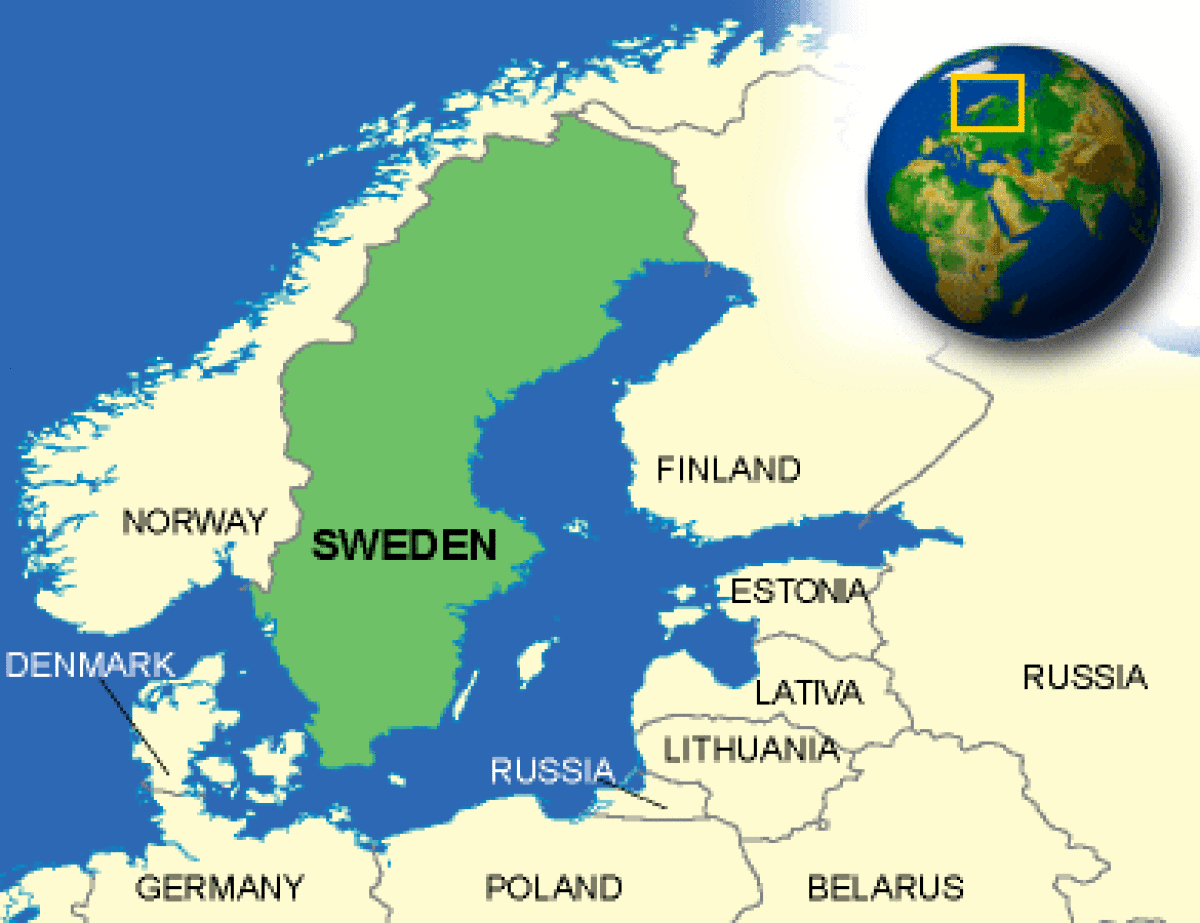
Where is Sweden located?
What countries border Sweden?
Sweden Weather
What is the current weather in Sweden?
Sweden Facts and Culture
What is Sweden famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Life in Sweden is greatly influenced by its geographic location and climate. Much of the country experiences long, dark winters... More
- Family: About 80 percent of Sweden's people live in urban areas, the remaining 20 percent are scattered across the land in... More
- Personal Apperance: Swedes wear warm conservative European fashions. Swedish folk costumes consist of white blouses, vests, and long dark skirts often with... More
- Recreation: Singing in choirs is Sweden's most popular hobby. Popular sports include fotboll (FOOT boll) or soccer, skiing, tennis, golf, swimming,... More
- Diet: The Swedish diet is known for its emphasis on fresh, locally sourced ingredients, simplicity, and a balance of flavors. While... More
- Food and Recipes: For breakfast, one might eat fil (a kind of yogurt), knäckebröd (crisp bread) with margarine, and coffee. They might also have a... More
- Visiting: A host usually offers something to drink to their guests. Usually, people invite others over for an evening meal. ... More
- Dating: In Sweden, dating is generally characterized by egalitarian values and a casual approach. Here are some aspects of dating in... More
Sweden Facts
What is the capital of Sweden?
| Capital | Stockholm |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Swedish Krona (SEK) |
| Total Area |
173,859 Square Miles 450,295 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway |
| Language | Swedish |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $48,000.00 (USD) |
Sweden Demographics
What is the population of Sweden?
| Ethnic Groups | indigenous population: Swedes and Finnish and Sami minorities; foreign-born or first-generation immigrants: Finns, Yugoslavs, Danes, Norwegians, Greeks, Turks |
| Languages | The numbers in Swedish and in English are very similar. If, for example, you want to say 31 you just take the word for 30, "trettio", and the word for 5, "fem", and put them together to make "trettiofem". This works in exactly the same way as it does in English. Sweden uses the Roman alphabet with three extra letters. å ö ä. Some words are the same in English and Swedish for example "man" and "person" are the same. |
| Nationality Noun | Swede(s) |
| Population | 10,202,491 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.18% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | STOCKHOLM (capital) 1.385 million |
| Urban Population | 85.200000 |
Sweden Government
What type of government does Sweden have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King CARL XVI GUSTAF (since 15 September 1973); Heir Apparent Princess VICTORIA Ingrid Alice Desiree (daughter of the monarch, born 14 July 1977) head of government: Prime Minister Ulf KRISTERSSON (since 18 October 2022); Deputy Prime Minister Ebba BUSCH (since 18 October 2022) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually becomes the prime minister |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Sweden; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen of Sweden and the father unknown dual citizenship recognized: no, unless the other citizenship was acquired involuntarily residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | National Day, 6 June (1983); note - from 1916 to 1982 this date was celebrated as Swedish Flag Day |
| Constitution |
history: Sweden has four fundamental laws which together make up the Constitution: The Instrument of Government (several previous; latest 1974); The Act of Succession (enacted 1810; changed in 1937 and 1980); The Freedom of the Press Act (many previous; latest in 1949); The Fundamental Law on Freedom of Expression (adopted 1991) amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage requires simple majority vote in two consecutive parliamentary terms with an intervening general election; passage also requires approval by simple majority vote in a referendum if Parliament approves a motion for a referendum by one third of its members; the results of such a referendum are only binding if a majority vote against the proposal; there has not been a referendum on constitutional matters; The Instrument of Government - amended several times, last in 2018; The Act of Succession - changed in 1937, 1980; The Freedom of the Press Act - amended several times, last in 2019; The Fundamental Law on Freedom of Expression - amended several times, last in 2023 |
| Independence | 6 June 1523 (Gustav VASA elected king of Sweden, marking the abolishment of the Kalmar Union between Denmark, Norway, and Sweden) |
Sweden Video
YouTube: Top 10 Places Top 10 Beautiful Places to Visit in Sweden
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Sweden Geography
What environmental issues does Sweden have?
| Overview | Sweden is bounded on the west by Norway and an arm of the North Sea, on the north by Norway and Finland, and on the east and south by the Baltic Sea. The country is long and narrow, encompassing an area of 174,000 square miles. In the northwest are mountains, and lakes abound throughout Sweden. To the south and east are forests, fertile valleys, and plains. Along Sweden’s rocky coast, interspersed with bays and inlets, are many islands, the largest of which are Gotland and Öland. |
| Climate | Despite its northern latitude, Sweden’s climate is not excessively cold due to the proximity of the Gulf Stream and the Baltic Sea. The mean annual temperature is 48 degrees F. Stockholm is situated at approximately the same latitude as Juneau, Alaska. During most of December and early January, the sun does not rise before 9 a.m. and sets as early as 2:30 p.m. Snow usually falls in January, February, and March. The average temperature range for January is 27° F to 30° F. Spring comes late, with snow possible even in May. By June, daylight is almost continuous, and the vegetation is luxuriant. In July, the average temperature range is 57° F to 72° F. Many firms close down for the month so that the entire staff can take vacation. The average annual rainfall in Stockholm is 22 inches. It rains an average of 164 days a year. |
| Border Countries | Finland 586 km, Norway 1,619 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | acid rain damage to soils and lakes; pollution of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly flat or gently rolling lowlands; mountains in west |
Sweden Economy
How big is the Sweden economy?
| Economic Overview |
Sweden is known for its highly developed mixed economy and strong welfare state. Strong Economy: Sweden boasts a high standard of living and a strong economy. It is the largest economy in Scandinavia and ranks among the top countries globally in terms of GDP per capita. Key sectors of the Swedish economy include manufacturing, services, innovation, and exports. Export-Oriented: Sweden has a robust export-oriented economy. Major exports include machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and electrical equipment. Well-known Swedish companies such as Volvo, IKEA, Ericsson, and H&M contribute significantly to the country's export success. Innovation and Technology: Sweden has a reputation for innovation and technological advancements. The country invests heavily in research and development (R&D) and promotes a supportive environment for entrepreneurship and startups. It is home to successful tech companies, including Spotify, Skype, and Klarna. Well-Developed Welfare State: Sweden has a comprehensive welfare system that provides a high level of social security. It offers universal healthcare, generous parental leave, free education up to the university level, and strong social safety nets. The welfare state is funded through high taxes and contributions from individuals and businesses. Strong Focus on Sustainability: Sweden places a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. The country has made significant strides in renewable energy, waste management, and sustainable transportation. It aims to be one of the world's first fossil fuel-free nations. Stable Macroeconomic Policies: Sweden maintains a stable and well-managed economy. The government follows prudent fiscal policies, and the central bank, Sveriges Riksbank, focuses on maintaining price stability. This stability contributes to investor confidence and economic growth. Active Labor Market: Sweden has a highly skilled and educated workforce. The labor market operates with a combination of flexibility and worker protection. Labor unions play a significant role in negotiating wages and working conditions. Open to Global Trade: Sweden is an active participant in global trade. It is a member of the European Union (EU) but has not adopted the euro and uses the Swedish Krona (SEK) as its currency. The country has trade agreements with numerous countries and is known for its commitment to free trade. Strong Social Partnership: The Swedish model is characterized by a strong social partnership between employers, employees, and the government. This collaboration contributes to labor market stability, cooperative wage-setting, and social harmony. |
| Industries | iron and steel, precision equipment (bearings, radio and telephone parts, armaments), wood pulp and paper products, processed foods, motor vehicles |
| Currency Name and Code | Swedish Krona (SEK) |
| Export Partners | US 11.6%, Germany 10.1%, Norway 9%, UK 8.2%, Denmark 5.9%, Finland 5.5%, Netherlands 5.3%, France 5.1%, Belgium 4.7% |
| Import Partners | Germany 18.5%, Denmark 8.8%, UK 8.6%, Norway 8.2%, Netherlands 6.7%, France 5.4%, Finland 5.2%, US 5% |
Sweden News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Sweden?
Source: Google News
Sweden Travel Information
What makes Sweden a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Sweden is a highly developed, stable democracy with a modern economy. Swedish is the official language, but English is well-spoken throughout the country.
Crime
Sweden has a low crime rate, though violent crime does occur on occasion. Most crimes involve the theft of personal property from cars or residences or in public areas. Pickpockets and purse-snatchers are becoming more prevalent. Many U.S. citizens fall victim to these highly-skilled thieves, especially at the main train stations in Stockholm and Gothenburg, and while riding the bus or train to and from airports. Do not put any bags containing valuables, such as your passport, down on the ground. Thieves particularly like computer bags. Pickpockets and purse-snatchers often work in pairs or groups so one can distract the victim while the other grabs the items; often, they operate in or near major tourist attractions such as Stockholm's Old Town, and also at restaurants, amusement parks, museums, bars, public transportation, including airports. Hotel breakfast rooms and lobbies attract professional, well-dressed thieves who blend in with guests and target purses and briefcases left unguarded by unsuspecting tourists and business travelers. Don’t leave your valuables in parked vehicles.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Sweden, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Sweden are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. There is no bail system in Sweden, and U.S. citizens who are arrested may be held in custody until the trial is complete. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Sweden, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not at your destination.Arrest notifications in host country: While some countries will automatically notify the U.S. Embassy if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the U.S. Embassy as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Languages
The numbers in Swedish and in English are very similar. If, for example, you want to say 31 you just take the word for 30, "trettio", and the word for 5, "fem", and put them together to make "trettiofem". This works in exactly the same way as it does in English. Sweden uses the Roman alphabet with three extra letters. å ö ä. Some words are the same in English and Swedish for example "man" and "person" are the same.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in Sweden is comparable to that found in the United States. The Swedish medical system is state-run, so instead of visiting a local private general practitioner, you can visit a local medical center or clinic, called an "Akutmottagning" or "Vardcentral." You should be prepared to present your passport. The Swedish medical system does not cover people who don’t live in Sweden; nonresidents are expected to pay their own medical costs. In case of a medical emergency, use the emergency telephone number "112" to contact the appropriate emergency service.If you have special needs, you should consult your personal physician and take appropriate precautions, including bringing adequate supplies of necessary medication. You can bring medicines into the country as long as they are intended for a medical reason and your personal use. Medications categorized as narcotics may only be brought into the country to cover your personal use for a maximum of five days, three weeks, or three months,depending on the type, and must be accompanied by a note from your medical doctor stating why you need them. Class II and Class III narcotics may only be brought into Sweden to cover your personal use for a maximum of five days each time you enter Sweden. Medications categorized Class IV and Class V narcotics may be brought into the country to cover your personal use for three weeks, however if you are a foreign resident and in Sweden only temporarily, you may bring enough for the duration of your stay in Sweden, up to a maximum of three months. To find out the classification of your medication contact the Medical Products Agency in Sweden.
In addition, stringent Swedish customs regulations prohibit travelers from receiving drugs from abroad after having arrived in the country. You may find local physicians reluctant to prescribe equivalent quantities or dosages. Prescriptions are dispensed at pharmacies called "Apotek" in Swedish. Most pharmacies are open only during normal shopping hours, but major cities will have a 24-hour pharmacy.
Safety and Security
Sweden has been subject to terrorist incidents in the recent past, and the potential for a terrorist incident remains. Like other countries in the Schengen area, Sweden's open borders with its Western European neighbors allow the possibility of terrorist groups to enter and exit the country with anonymity. You should remain vigilant and exercise caution.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Sweden, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. You can use a valid U.S. driver's license while visiting Sweden, but you must be at least 18 years old to drive. Driving is on the right in Sweden as in the United States. Road signs use standard international symbols and Swedish text. Many urban streets have traffic lanes reserved for public transportation only. Swedish roads are comparable to those in the United States, though secondary roads may be less heavily traveled. The secondary routes often narrow to two lanes with a wider shoulder. Slower vehicles are expected to move onto the shoulder to allow faster moving vehicles to pass. All vehicles on the road must have their headlights turned on, no matter the time of day. You must use snow tires between December 1 and March 31, and you should be experienced driving on ice and snow, if you are going to drive in the winter. Gas stations in rural areas can be far apart. Some gas stations are unattended and require a credit card with a chip to purchase fuel; some U.S. banks will issue this type of card upon request. You must use seat belts, and children under the age of seven must be seated in approved child or booster seats. The maximum speed limit is 110 kilometers per hour (approximately 66 miles per hour). Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs, including prescription drugs, is considered a very serious offense. The maximum legal blood-alcohol level is .02-- much lower than in the United States. Swedish police often conduct alcohol tests on roads and highways. The rules are strictly enforced and fines can be severe, including possible jail sentences.Public transport in Sweden is the recommended method of travel. Passenger trains, intercity buses, and airplanes provide regular service over longer distances. Public transportation in urban centers includes buses, subways, trams, suburban trains, and taxis. Taxis are more expensive than in major U.S. cities. Most local residents use public transport in Stockholm, as parking can be hard to find and expensive. The bus, train, and subway systems are considered safe. Cyclists are common on many roads, especially in urban areas.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
