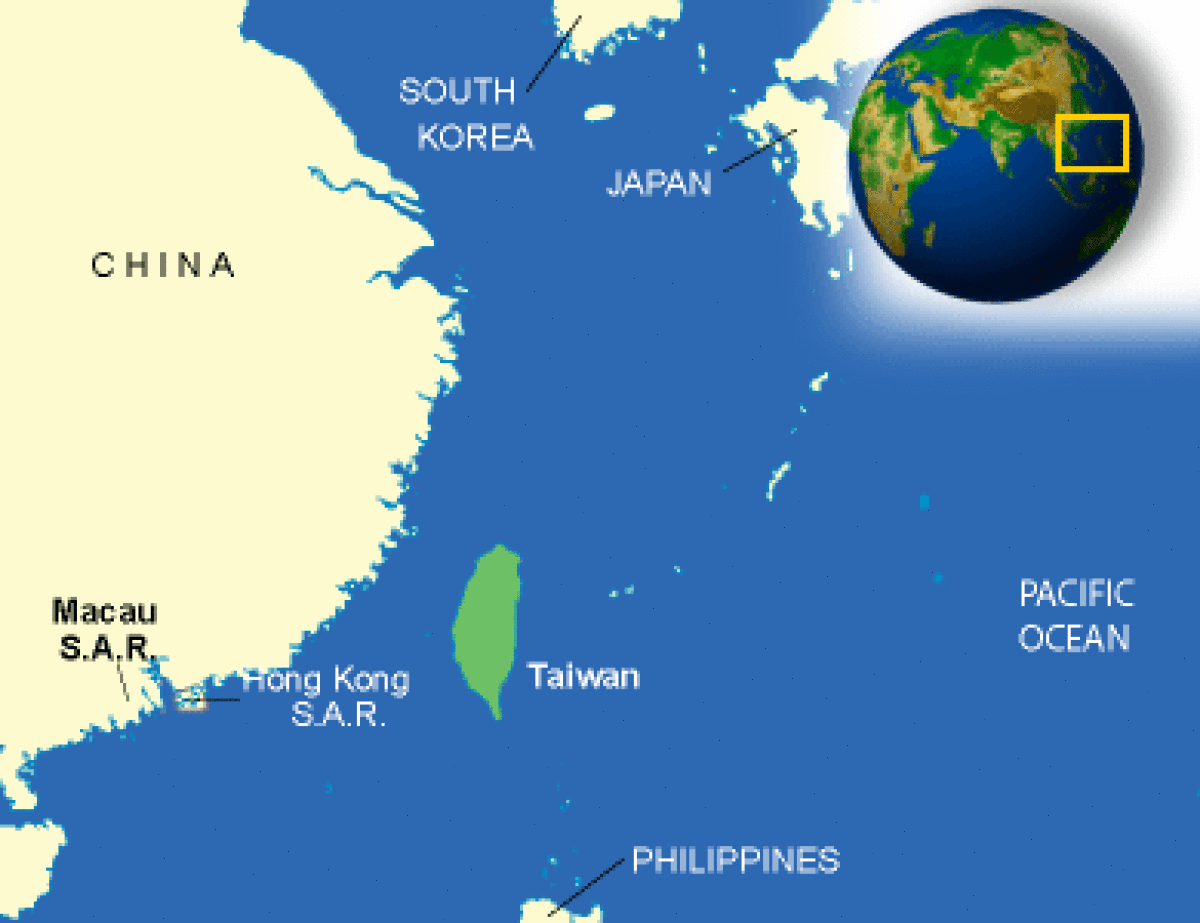
Where is Taiwan located?
What countries border Taiwan?
Taiwan Weather
What is the current weather in Taiwan?
Taiwan Facts and Culture
What is Taiwan famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Great importance on the concept of "face"." "Face" roughly equates to Western concepts of status and respect. Chinese people regard... More
- Family: The Taiwanese concept of family includes children, parents, extended family, elders, and ancestors. Taiwanese often live in small and crowded... More
- Personal Apperance: Western-Style clothing is common. A suit is the most appropriate attire for conducting business in Taiwan. In less formal situations,... More
- Recreation: Many Taiwanese enjoy golf, ping-pong, basketball, soccer, softball, and badminton. Health clubs and gyms are used regularly. Senior men... More
- Diet: Taiwanese cuisine is diverse and influenced by various cultures such as Chinese, Japanese, and indigenous Taiwanese cuisine. Here are some... More
- Food and Recipes: Mealtime customs in Taiwan: Sharing Food: One of the most important customs in Taiwanese mealtime is sharing food. Dishes are usually... More
- Visiting: First impressions are very important when dealing with Chinese people and a great deal of emphasis is placed upon the... More
- Dating: Customs and practices observed in Taiwanese society: Introduction through Friends: Many people in Taiwan prefer to meet potential partners through mutual... More
Taiwan Facts
What is the capital of Taiwan?
| Capital | Taipei |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | New Taiwan Dollar (TWD) |
| Total Area |
13,892 Square Miles 35,980 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Asia, islands bordering the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, South China Sea, and Taiwan Strait, north of the Philippines, off the southeastern coast of China |
| Language | Chinese: Mandarin (official), Taiwanese (Min), Hakka dialects |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $47,500.00 (USD) |
Taiwan Demographics
What is the population of Taiwan?
| Ethnic Groups | Taiwanese (including Hakka) 84%, mainland Chinese 14%, aborigine 2% |
| Nationality Noun | Chinese/Taiwanese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 23,603,049 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.27% |
| Urban Population | 0.000000 |
Taiwan Government
What type of government does Taiwan have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President TSAI Ing-wen (since 20 May 2016); Vice President LAI Ching-te (since 20 May 2020) head of government: Premier CHEN Chien-jen (President of the Executive Yuan) (since 31 January 2023); Vice Premier CHENG Wen-tsan (Vice President of the Executive Yuan) (since 31 January 2023) cabinet: Executive Yuan - ministers appointed by president on recommendation of premier elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 13 January 2024 (next to be held in 2028); premier appointed by the president; vice premiers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the premier election results: 2023: LAI Ching-te elected president; percent of vote - LAI Ching-te (DPP) 40.1%, HOU Yu-ih (KMT) 33.5%, KO Wen-je (TPP) 26.5%; note - LAI takes office on 20 May 2024 2020: TSAI Ing-wen reelected president; percent of vote - TSAI Ing-wen (DPP) 57.1%, HAN Kuo-yu (KMT) 38.6%, James SOONG (PFP) 4.3%; note - TSAI is the first woman elected president of Taiwan |
| Suffrage | 20 years of age; universal; note - in March 2022, the Legislative Yuan approved lowering the voting age to 18, but the change will require a constitutional amendment that must be submitted to a referendum |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Taiwan dual citizenship recognized: yes, except that citizens of Taiwan are not recognized as dual citizens of the People's Republic of China residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Republic Day (National Day), 10 October (1911); note - celebrates the anniversary of the Chinese Revolution, also known as Double Ten (10-10) Day |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1912, 1931; latest adopted 25 December 1946, promulgated 1 January 1947, effective 25 December 1947 amendments: proposed by at least one fourth of the Legislative Yuan membership; passage requires approval by at least three-fourths majority vote of at least three fourths of the Legislative Yuan membership and approval in a referendum by more than half of eligible voters; revised several times, last in 2005 |
Taiwan Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Taiwan Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Taiwan Geography
What environmental issues does Taiwan have?
| Overview |
Named "Ihla Formosa", or Beautiful Island, by the Portuguese, Taiwan is a land of contrasts. It has everything from industrial towns and cities to rural towns and spectacular mountain vistas, from centuries old Confucian ceremonies to modern music and chaotic traffic to friendly people willing to help a stranger. Taiwan is a small island 394 kilometers (245 miles) long and 144 kilometers (89.5 miles) wide at its broadest point, and includes a number of smaller islands. Foothills and mountains covering over two thirds of the island. Yu Shan (Jade Mountain), Taiwan's highest peak at 3952 meters, is taller than Japan's Mount Fuji. Taiwan is very active geologically, sitting as it does at the juncture of the Philippine and Eurasian tectonic plates. Steam vents and hot sulfur springs abound. Earthquakes are a common occurrence in Taiwan. |
| Climate |
The Tropic of Cancer bisects the island, so the climate is sub-tropical with temperatures ranging from 12 to 35 degrees Celsius (54-95 degrees Fahrenheit). Northern Taiwan has two long seasons (summer & winter) and two short seasons (spring and autumn). Spring, mid-March to mid-May, is mostly sunny and mild with brief spells of cloudy skies and rain showers. Spring's average daily temperature is 17-25C or 62-77F. Summer, mid-May through late September, is hot with an average rainfall of 10 inches a month, mostly from afternoon showers and thunderstorms. Autumn, late September to early November, is characterized by mild temperatures and afternoon showers. Winter, November through mid-April, is characterized by low cloud drizzle, fog, and occasional winds. The daily temperatures range between 17 - 24 degrees C (62-75F) in November, dropping to 12 - 19C (54 - 66F) in January and then rising to 14 - 22C (57 - 72F) in March. Occasionally, the temperature drops below 1OC (50F), especially in mountainous areas. The typhoon season usually starts in mid-June and lasts through October. An average of 12 typhoons form in the Western Pacific each year. The average daily temperature range in Taipei is 21 - 29C (70 - 84F) in May; 24 - 35C (75 - 95F) in July and August; 23 - 33C (73 - 91F) in September; and 20 - 27C (68 - 81F) in October. Kaohsiung enjoys a milder, drier winter than Taipei, but summer temperatures average about the same. As a result of its subtropical position and heavy rainfall, Taiwan's natural landscape is constantly green with varied hues of forest, shrubs, and coarse tropical grass. All but the peaks of the highest mountains are covered with vegetation. |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water supplies; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan's international status |
| Terrain | eastern two-thirds mostly rugged mountains; flat to gently rolling plains in west |
Taiwan Economy
How big is the Taiwan economy?
| Economic Overview |
Taiwan has a dynamic and export-oriented economy that ranks among the largest in Asia. Here is an overview of the Taiwanese economy: High-Tech Industry: Taiwan is renowned for its high-tech industry, particularly in the fields of semiconductors, electronics, and information technology. It is a global leader in the production of computer hardware, integrated circuits, and electronic components. Taiwan's technology companies, such as TSMC and Foxconn, play a crucial role in the global supply chain. Export-Oriented Economy: Taiwan is heavily reliant on exports and has a strong focus on international trade. Major export products include electronic components, machinery, chemicals, textiles, and plastics. The economy is highly integrated into global markets, with significant trading relationships with countries such as China, the United States, Japan, and Europe. SMEs and Entrepreneurship: Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of Taiwan's economy. The country has a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem, with a high number of startups and innovative ventures. SMEs contribute to job creation, innovation, and economic growth, particularly in sectors like technology, manufacturing, and services. Strong Financial Sector: Taiwan has a well-developed financial sector that supports economic activities. The banking system is sound, and there is an established stock market (Taiwan Stock Exchange) where many domestic and international companies are listed. The government has implemented policies to encourage the development of financial technology (FinTech) and digital payment systems. Economic Integration: While Taiwan is not a member of the United Nations, it maintains extensive economic ties with countries worldwide. It has signed free trade agreements (FTAs) with several nations and is an active participant in regional economic frameworks, such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). Economic Challenges: Taiwan faces several economic challenges, including an aging population, income inequality, and regional geopolitical tensions. The government is implementing measures to address these challenges, such as promoting innovation, investing in education and skills development, and diversifying trade partners. Resilience and Adaptability: Despite challenges, Taiwan's economy has demonstrated resilience and adaptability over the years. The country has successfully transitioned from labor-intensive industries to high-value manufacturing and knowledge-based sectors. Its ability to innovate, invest in research and development, and nurture human capital has been key to its economic success. |
| Industries | electronics, petroleum refining, chemicals, textiles, iron and steel, machinery, cement, food processing |
| Currency Name and Code | New Taiwan Dollar (TWD) |
| Export Partners | China 25.3%, US 20.5%, Japan 9.2% |
| Import Partners | Japan 24.2%, US 16.1%, China 7.1%, South Korea 6.9% |
Taiwan News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Taiwan?
Source: Google News
Taiwan Travel Information
What makes Taiwan a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Taiwan is a stable democracy with a strong and well-developed economy. Tourist facilities are widely available.
Crime
Although the overall violent crime rate in Taiwan is low, you should avoid high crime areas, namely areas where massage parlors, barbershops, and nightclubs operate as covers for prostitution and are often run by criminals. In contrast to these illegal fronts, ordinary barbershops and other legitimate businesses prominently advertise their services, and you can see the interiors through storefront windows. Illicit establishments generally do not advertise, and casual passersby cannot view their interiors. Several U.S. citizens have been assaulted in these establishments and in the areas near bar and nightclub districts. Taiwan’s public buses and subway are generally considered safe, but passengers in taxis – particularly women - should exercise caution when traveling alone in taxis late at night. In several parts of Taiwan, incidents of purse snatching by thieves on motorcycles have been reported. You should keep a photocopy of your passport, other identification, and credit cards in a safe place.Don't buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but you may also be breaking local law.
The emergency telephone number for Taiwan services (ambulance, fire, police) is 119. The number for police is 110. Victims of domestic violence or sexual assault may call 113. Taiwan Police also offers a 24 hour telephone line for foreigners in English: 0800-024-111.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Health facilities in Taiwan are adequate for routine and emergency medical treatment. Physicians are well trained and many have studied in the United States and speak English. State of the art medical equipment is available at many clinics and hospitals. Hospitals’ nursing services provide medication dispensing and wound care but generally not the daily patient maintenance functions found in U.S. hospitals. Taiwan regulations require ambulances to have emergency equipment and supplies and to be staffed by trained medical personnel (dial 119). For information on specific clinics and hospitals, please refer to AIT's website.You can find good information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s hotline for international travelers at 1-877-FYI-TRIP (1-877-394-8747), fax 1-888-CDC-FAXX (1-888-232-3299), or via the CDC’s website : http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/destinations/taiwan.htm Or Taiwan's CDC: http://www.cdc.gov.tw/mp.asp?mp=5
Safety and Security
Taiwan is a modern democracy with vibrant public participation. Political demonstrations are common, especially around election time. Since Taiwan democratized in the early 1990s, there have been very few cases of violence associated with political demonstrations. But even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational. You should avoid areas of demonstrations if possible and exercise caution if within the vicinity of any political demonstrations. The American Citizens Services Section of the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT) will post notices regarding demonstrations in Taiwan on the AIT website whenever it receives reliable information about them. In most cases, AIT will not send out a warden message when it has information on a planned demonstration.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While traveling abroad, you may find that road and driving conditions are significantly different from those in the United States. The information below concerning Taiwan is provided for general reference and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Roads in Taiwan's major cities are generally congested, and the many scooters and motorcycles that weave in and out of traffic make driving conditions worse. You should exercise caution when crossing streets because many drivers do not respect the pedestrian's right of way. Be especially cautious when driving on mountain roads, which are typically narrow, winding, poorly banked, and which may be impassable after heavy rains.
