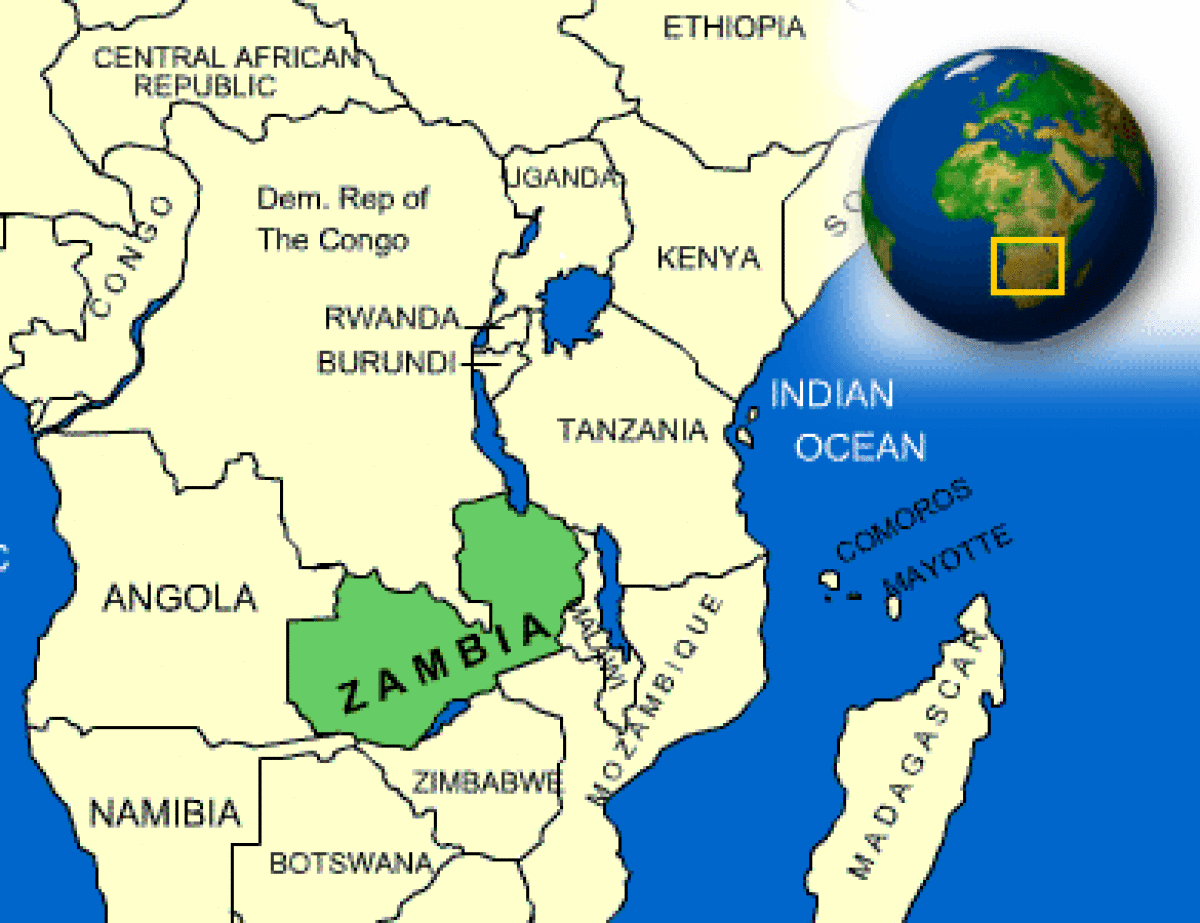
Where is Zambia located?
What countries border Zambia?
Zambia Weather
What is the current weather in Zambia?
Zambia Facts and Culture
What is Zambia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Zambians are known for their friendliness and courtesy. More
- Family: Zambians consider their children an investment in the future. Because the number of infant deaths is still high, most parents... More
- Personal Apperance: Second hand Western style clothing is popular. The term salaula means to rummage through a pile referring to the second... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the most popular sport. Both children and adults in Zambia enjoy playing a traditional African board game called... More
- Diet: The staple food in Zambia is a thick cornmeal mash called "nshima". Some Zambians feel that a meal is not... More
- Visiting: In Zambia, handshaking is common practice, and you should always use a person's professional name if known. Be sure to... More
Zambia Facts
What is the capital of Zambia?
| Capital | Lusaka |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Zambian Kwacha (ZMW) |
| Total Area |
290,586 Square Miles 752,618 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Africa, east of Angola, south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Language | English (official), - Bemba, Kaonda, Lozi, Lunda, Luvale, Nyanja, Tonga, and about 70 other indigenous languages. |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $4,300.00 (USD) |
Zambia Demographics
What is the population of Zambia?
| Ethnic Groups | African 98.7%, European 1.1%, other 0.2% |
| Nationality Noun | Zambian(s) |
| Population | 17,426,623 |
| Population - note | note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.89% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | LUSAKA (capital) 1.802 million |
| Urban Population | 39.200000 |
Zambia Government
What type of government does Zambia have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Hakainde HICHILEMA (since 24 August 2021); Vice President Mutale NALUMANGO (since 24 August 2021); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Hakainde HICHILEMA (since 24 August 2021); Vice President Mutale NALUMANGO (since 24 August 2021) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by president from among members of the National Assembly elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); last held on 12 August 2021 (next to be held in 2026) election results: 2021: Hakainde HICHILEMA elected president; percent of the vote - Hakainde HICHILEMA (UPND) 57.9%, Edgar LUNGU (PF) 37.3%, other 4.8% 2016: Edgar LUNGU re-elected president; percent of vote - Edgar LUNGU (PF) 50.4%, Hakainde HICHILEMA (UPND) 47.6%, other 2% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: only if at least one parent is a citizen of Zambia citizenship by descent only: yes, if at least one parent was a citizen of Zambia dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years for those with an ancestor who was a citizen of Zambia, otherwise 10 years residency is required |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 24 October (1964) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 24 August 1991, promulgated 30 August 1991 amendments: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly in two separate readings at least 30 days apart; passage of amendments affecting fundamental rights and freedoms requires approval by at least one half of votes cast in a referendum prior to consideration and voting by the Assembly; amended 1996, 2015, 2016; note - in late 2020, an amendment which would have altered the structure of the constitution was defeated in the National Assembly |
| Independence | 24 October 1964 (from the UK) |
Zambia Video
YouTube: CountryReports Zambia - A Historical Journey
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Zambia Geography
What environmental issues does Zambia have?
| Overview |
Zambia, in central southern Africa, is mostly a high plateau, 3,000 to 5,000 feet above sea level. Lusaka is one of the higher points in the country at 4200 ft. The highest point is Mwanda Peak at 7045ft on the border with Malawi. There are four major valleys: the Zambezi, the Kafue, the Luangwa and the Luapula. Zambia has several large lakes: man-made Kariba in the South, lakes Tanganyika and Mweru in the North, and Lake Bangweulu in the interior. Zambia is landlocked and has borders with Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Namibia, Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The protruding southeastern area of the DRC nearly bisects Zambia into two major geographic areas. The 90 mile-long corridor in the region known as the Copperbelt contains some of the world’s largest proven copper deposits. |
| Climate |
Zambia lies between 8 and 18 degrees south of the Equator. The pleasant climate rivals that of Southern California, having three seasons: the warm-wet season (December to April), the cool-dry season (May to August) and the hot-dry season (September to November). Humidity is quite low except during the rainy season, and the temperature rarely exceeds 95°F; it can get into the 40s during the winter months (June and July). Summer clothing is worn from mid-August to mid-May. Light woolens are useful in winter (mid-May to mid-August). Generally, summer evenings are cool, and winter days are sunny and warm. Annual rainfall during the rainy season averages 34 inches. At the season’s beginning and end, showers are brief. During January, however, heavier rains punctuated by thunderstorms often occur. Zambia’s vegetation is mostly savannah, with areas of tropical grassland and woodland. There are 19 national parks and 32 game management areas. The native fauna is classic big game found in Southern Africa (e.g., leopards and lions). Zambia has a great variety of birds, both resident and migrant, totaling more than 700 species. |
| Border Countries | Angola 1,110 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 1,930 km, Malawi 837 km, Mozambique 419 km, Namibia 233 km, Tanzania 338 km, Zimbabwe 797 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution and resulting acid rain in the mineral extraction and refining region; chemical runoff into watersheds; poaching seriously threatens rhinoceros, elephant, antelope, and large cat populations; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; lack of adequate water treatment presents human health risks |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly high plateau with some hills and mountains |
Zambia Economy
How big is the Zambia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Zambia had one of the world’s fastest growing economies for the ten years up to 2014, with real GDP growth averaging roughly 6.7% per annum, though growth slowed during the period 2015 to 2017, due to falling copper prices, reduced power generation, and depreciation of the kwacha. Zambia’s lack of economic diversification and dependency on copper as its sole major export makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in the world commodities market and prices turned downward in 2015 due to declining demand from China; Zambia was overtaken by the Democratic Republic of Congo as Africa’s largest copper producer. GDP growth picked up in 2017 as mineral prices rose. Despite recent strong economic growth and its status as a lower middle-income country, widespread and extreme rural poverty and high unemployment levels remain significant problems, made worse by a high birth rate, a relatively high HIV/AIDS burden, by market-distorting agricultural and energy policies, and growing government debt. Zambia raised $7 billion from international investors by issuing separate sovereign bonds in 2012, 2014, and 2015. Concurrently, it issued over $4 billion in domestic debt and agreed to Chinese-financed infrastructure projects, significantly increasing the country’s public debt burden to more than 60% of GDP. The government has considered refinancing $3 billion worth of Eurobonds and significant Chinese loans to cut debt servicing costs. |
| Industries | copper mining and processing, construction, foodstuffs, beverages, chemicals, textiles, fertilizer, horticulture |
| Currency Name and Code | Zambian Kwacha (ZMW) |
| Export Partners | South Africa 27.8%, Malawi 8.5%, Thailand 7.6%, Japan 7.5%, Saint Pierre and Miquelon 7.5%, China 5.2%, Egypt 5.2%, Netherlands 4.6% |
| Import Partners | South Africa 69.4%, US 3.3%, China 3.2% |
Zambia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Zambia?
Source: Google News
Zambia Travel Information
What makes Zambia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Zambia is a developing country in southern Africa with a representative government. Outside of Lusaka, Livingstone (Victoria Falls), and well-known game parks, tourist facilities are not fully developed.
Crime
Travel in many sections of Lusaka, Livingstone, and most other major cities, as well as in the major game parks, is generally safe during daylight hours. However, expatriates have been the victim of armed robberies in Livingstone, Copperbelt Province, and elsewhere. Though victims are seldom seriously injured, the incidents can be frightening and stolen property is rarely recovered. Carjacking remains an ongoing problem, especially in Lusaka and Livingstone. In most cases, carjackers will block the rear of a victim’s vehicle while it waits to pass through a security gate into a residence and then assailants will threaten the driver and take the car. In some cases, the victim has been held and assaulted. Drivers are advised to lock their car doors, close their windows, and remain vigilant when entering or exiting a residence.Travelers using public transportation or visiting high pedestrian traffic areas are advised to be vigilant against robbery and pick-pocketing. Vehicle thefts and burglaries occur throughout the country.
You should use caution when traveling near the border with Congo. Although rebel militias are no longer active in the Katanga province of Congo, armed criminal elements remain in the border area.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Zambia, you are subject to its laws. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning. It is illegal to take pictures of certain government structures, particularly presidential residences or offices, oil refineries, bridges, mines, railways, electrical power supply buildings, and military facilities. Often, these sites are not clearly marked and the first notification that a tourist would receive is a police officer demanding his/her camera memory card, film and/or camera. Authorities may also challenge photography of areas other than tourist attractions.In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit but still illegal in the United States; for example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is also a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Zambia, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what is legal and what is not legal wherever you travel.
Possession of more than 0.5 grams of an illegal substance can constitute drug trafficking in Zambia. The Zambian Drug Enforcement Commission (DEC) has detained a number of U.S. citizens for possession of antihistamines such as Benadryl and other over-the-counter medications, which contained small quantities of diphenhydramine, an active ingredient that is on Zambia’s list of controlled substances. Although unaware of these restrictions, U.S. citizens have been charged with drug-trafficking offenses, had their passports confiscated, and have been jailed. While government officials have told the Embassy that carrying such over-the-counter medications with a doctor’s prescription is permitted, U.S. citizens visiting Zambia should consider leaving such medications behind. When traveling with prescription medications, U.S. citizens should likewise carry a doctor’s prescription and ensure that the medication is in its original bottle. A complete list of controlled substances banned in Zambia is available via the U.S. Embassy website on the web page Living in Zambia. U.S. citizens carrying any of these banned drugs for medical purposes should contact the Government of Zambia’s Pharmaceutical Authority to request advance permission to bring the drugs into the country by emailing the Director General at pharmacy@pra.gov.zm or writing to: Director General Pharmaceutical Regulatory Authority, Box 31890 Lusaka. The office is located at Plot No 6903 Tuleteka Road, off Makish Road. Any U.S. citizen stopped by the Drug Enforcement Commission for possession of over-the-counter medications should contact the Embassy as soon as possible. Additional information about controlled substances may be found at the Zambian Drug Enforcement Commission website.
It is against both Zambian and U.S. law to buy, possess, or transport the following animal products: tortoise shells, rhino horns, elephant ivory, tusks of any animal, or any items made out of these materials. While many of these items are sold in open markets particularly aimed at foreign tourists, it remains the responsibility of the customer to ensure that he/she is not purchasing a prohibited item. The Zambian Wildlife Authority has screeners at international ports of entry/exit and WILL prosecute offenders to the fullest extent of the law with penalties ranging from large fines to five year prison sentences.
If you are arrested in Zambia, you should seek the assistance of an attorney. The Embassy maintains a list of attorneys in major cities, but cannot recommend the services of a particular lawyer.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Government hospitals and clinics are often understaffed and lack supplies. Private medical clinics in major cities can provide reasonable care in many cases, but major medical emergencies usually require medical evacuation to South Africa, Europe, or the United States. The nearest air ambulances are based in South Africa. In addition to purchasing medical insurance that covers medical evacuation (see below), U.S. citizens may wish to register with a medical rescue/ambulance service in Zambia, as this can facilitate quick action in an emergency. Some lodges in Zambia may do this on behalf of travelers automatically. Basic medical care outside of major cities is extremely limited. Throughout the country doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services. See the Embassy’s list of health care providers in Zambia, including ambulance service.Travelers should carry their prescription drugs and medications in the original labeled containers, as well as the written prescription from their physician. Travelers who cannot get a doctor’s note for their over-the-counter medications may wish to leave them behind or risk possible arrest. Refer to the section onCriminal Penaltiesabove for more information about over-the-counter medications.
Rabies, a preventable but fatal illness most often transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, is prevalent in Zambia. While rabies vaccine is available in some parts of Zambia, the post-exposure prophylaxis rabies immunoglobulin is NOT available in Zambia. You should consult with your health care professional about vaccination prior to your trip. If you have not been vaccinated and are bitten, post-exposure prophylaxis should be sought urgently outside Zambia. U.S. citizens in Zambia have been bitten by monkeys, baboons, dogs, and other animals which potentially carry the rabies virus.
Safety and Security
The U.S. Embassy recommends that travelers exercise caution when visiting Western Province. Relations between some residents and the government remain tense over rights under the Barotseland Agreement of 1964. In January 2011, protests in the provincial capital of Mongu and Limulunga turned violent resulting in two deaths, several injuries, and hundreds of arrests. The government of Zambia considers it treasonous for anyone to discuss the Barotseland Agreement or Barotseland autonomy/secession.Spontaneous demonstrations occasionally take place in Lusaka and elsewhere in the country. Remember, even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence. You should avoid the vicinity of demonstrations. You should also stay current with media coverage of local events and be aware of your surroundings at all times.
The Embassy has received several reports of the use and attempted use of “date rape” drugs on unsuspecting females in a variety of bars and restaurants. There are several “date rape” drugs on the market, and these are easily purchased or obtained in Zambia. Common symptoms of these drugs are: drunken feeling, loss of consciousness, memory problems, confusion, dizziness, excessive sweating, nausea, and loss of motor skills. Rapists use the drug to render a victim easier to attack. If you feel that you have been a victim of a "date rape" drug attack, seek medical attention immediately. The Embassy maintains a list of medical professionals.
The U.S. Embassy discourages travelers from driving off-road or on remote, lightly-used tracks near the borders with the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Congo-Kinshasa) and Angola as there may still be undetected land mines and unexploded ordnance. U.S. citizens who must drive in these areas are encouraged to drive in convoys and carry satellite telephones.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Zambia, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. In Zambia, vehicles drive on the left side of the road and vehicles in traffic circles travel clockwise. It is illegal to turn left on a red light. Driving on Zambian roads can be hazardous. Most roads do not have shoulders or sidewalks, forcing pedestrians and livestock to use the roadways both day and night. It is a traffic violation to splash a pedestrian when driving through water. While the main roads in Lusaka and the principal highways linking Lusaka with the major provincial capitals are generally maintained, many secondary roads are in poor repair. During the rainy season (end of October to mid-March), travelers who do not have a four-wheel drive vehicle will encounter problems driving on rural roads. Even in daylight, passing another vehicle can be particularly dangerous given the general condition of roads.Driving on Zambian roads can be hazardous. Most roads do not have shoulders or sidewalks, forcing pedestrians and livestock to use the roadways both day and night. It is a traffic violation to splash a pedestrian when driving through water. While the main roads in Lusaka and the principal highways linking Lusaka with the major provincial capitals are generally maintained, many secondary roads are in poor repair. During the rainy season (end of October to mid-March), travelers who do not have a four-wheel drive vehicle will encounter problems driving on rural roads. Even in daylight, passing another vehicle can be particularly dangerous given the general condition of roads.
Driving at night can be hazardous and is discouraged. Even in Lusaka there are few streetlights, and pedestrians on the edge of the road are difficult to see. When breakdowns occur, local drivers place a few branches behind the car to indicate trouble but these are difficult to see after dark. As a result, many drivers use their high beams at night to detect stopped vehicles and pedestrians but often fail to dim their high beams when approaching other cars. Cars with a non-functioning headlight are another hazard.
U.S. citizens have been involved in a number of serious car accidents. There are no emergency services for injured or stranded drivers. Car accident victims are vulnerable to theft by those who pretend to be helpful. It is advisable to have a cell phone when undertaking a trip outside of town, although some parts of the country do not yet have cell phone service.
City traffic is comprised mostly of cars and minibuses; motorcycles are rare. Some luxury buses travel between Lusaka and Livingstone and the Copperbelt. Minibuses serve as the primary means of inter-city travel in Zambia but are often overcrowded, poorly maintained, and seldom punctual. Drivers often pass using road shoulders or opposing traffic lanes and frequently stop with little or no warning to pick up or drop off passengers. If you hear sirens indicating an official motorcade while you are driving, you should come to a stop and, if possible, pull to the side of the road.
Seat belts are mandatory, as are helmets for motorcyclists. A child's seat is not mandatory by law but is essential for safeguarding children. Using a cell phone while operating a vehicle is illegal and carries a minimum fine equivalent to $60. The speed limit is 50 km/30 mph in Lusaka and 100 km/60 mph outside of city limits; however, speed limits are rarely respected, and most cars drive 80 km/50 mph in the city and 120 km/75 mph outside of town. Many vehicles operate at even faster speeds on the road from Lusaka to Livingstone.
If you are stopped by police while driving and asked to pay a fine, you should be provided an official receipt or directed to the nearest police station where you can make payment. Drivers under the influence of alcohol who are involved in accidents are tested at Lusaka's University Teaching Hospital (UTH) and then taken to court.
To take a vehicle into Zambia, you must obtain a temporary import permit (TIP) at the border, or, depending on the country of origin, a carnet de passage. If you are not the owner of the vehicle, you must have a letter from the owner authorizing the use of the vehicle in Zambia. You must also purchase third-party insurance at the border. Residents of Zambia should obtain a driver’s license after obtaining a residence or study permit. Cars must have small reflective stickers attached to the bumper (white on front, red on back), and drivers should always carry two reflective triangles (used to warn other drivers if your car breaks down). Traffic officer checkpoints are fairly frequent outside of urban centers and you risk a fine if found to be driving without reflective stickers, triangles, a spare tire, or non-working headlights or indicator lights.
