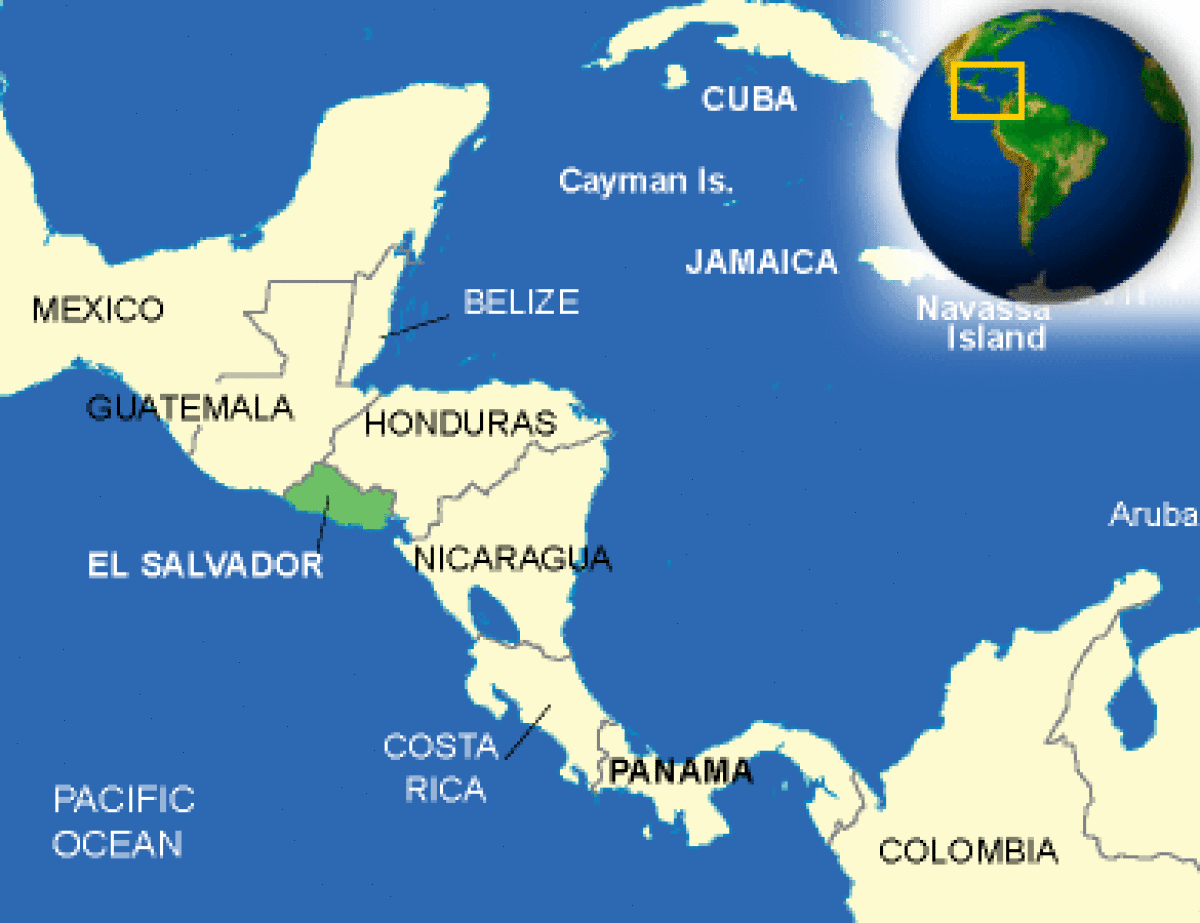
Where is El Salvador located?
What countries border El Salvador?
El Salvador Weather
What is the current weather in El Salvador?
El Salvador Facts and Culture
What is El Salvador famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Salvadorans work hard. They are very creative when it comes to finding a way to make money. They do not... More
- Family: Family structure and its traditions are different for people living in the city and for people living in towns, or... More
- Personal Apperance: Climate in El Salvador is tropical, and that dictates the type of clothes worn by its inhabitants. In urban areas,... More
- Recreation: Football soccer is, by far, the most played sport in the country. It is the unofficial national sport, played by... More
- Diet: The national dish in El Salvador is the "pupusa". A pupusa is a stuffed grilled tortilla. This tortilla is about... More
- Food and Recipes: It is polite for guests to try some of every dish that is served. Leaving a little food on the... More
- Visiting: When a friend or relative is invited over to someone's house, it is customary for the person being invited to... More
- Dating: In past generations, when two young adults, male and female, were attracted to each other, and wanted to make official... More
El Salvador Facts
What is the capital of El Salvador?
| Capital | San Salvador |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| Total Area |
8,124 Square Miles 21,041 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central America, bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Guatemala and Honduras |
| Language | Spanish, Nahua (among some Amerindians) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $8,900.00 (USD) |
El Salvador Demographics
What is the population of El Salvador?
| Ethnic Groups | Mestizo 86.3%, White 12.7%, Indigenous 0.2% (includes Lenca, Kakawira, Nahua-Pipil), Black 0.1%, other 0.6% |
| Languages | Spanish (official), Nawat (among some Indigenous) |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Salvadoran(s) adjective: Salvadoran |
| Population | 6,628,702 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.34% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 1.116 million SAN SALVADOR (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 75.4% of total population rate of urbanization: 1.33% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 3,172,244 female: 3,456,458 |
El Salvador Government
What type of government does El Salvador have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Acting President Claudia Juana RODRÍGUEZ DE GUEVARA (since 1 December 2023); note - parliament granted a six-month leave of absence to President Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez and Vice President Félix Augusto Antonio ULLOA Garay (to allow them to participate in the 4 February 2024 presidential election) and approved the appointment of Claudia Juana RODRÍGUEZ DE GUEVARA as acting president from 1 December 2023 to 1 June 2024, when election winner Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez will be sworn in for a second term head of government: Acting President Claudia Juana RODRÍGUEZ DE GUEVARA (since 1 December 2023) cabinet: Council of Ministers selected by the president elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a single 5-year term; election last held on 4 February 2024 (next to be held in 2029) election results: 2024: Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez reelected president - Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez (Nuevas Ideas) 84.7%, Manuel FLORES (FMLN) 6.4%, Joel SANCHEZ (ARENA) 5.6%, Luis PARADA (NT) 2%, other 1.3%; note he will be inaugurated on 1 June 2024 2019: Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez elected president - Nayib Armando BUKELE Ortez (GANA) 53.1%, Carlos CALLEJA Hakker (ARENA) 31.7%, Hugo MARTINEZ (FMLN) 14.4%, other 0.8% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 15 September (1821) |
| Constitution |
history: many previous; latest drafted 16 December 1983, enacted 23 December 1983 amendments: proposals require agreement by absolute majority of the Legislative Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly; constitutional articles on basic principles, and citizen rights and freedoms cannot be amended; amended 2003, 2009, 2014 |
| Independence | 15 September 1821 (from Spain) |
El Salvador Video
Geography Now- YouTube Geography Now! El Salvador!
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)El Salvador Geography
What environmental issues does El Salvador have?
| Overview |
El Salvador, with an area of 8,260 square miles, is the smallest independent state in Central America. El Salvador is rectangular in shape, 60 miles wide and 160 miles long. El Salvador has 350 rivers. The largest, the Rio Lempa, flows 150 miles from northern to central El Salvador, forming one of the most important Pacific watersheds in Latin America. It is El Salvador's only navigable river. The land is 90% volcanic in origin, and many places still bear the scars. The country’'s topography is rough and irregular from continuous volcanic activity, accounting for El Salvador’s rich soil. Two volcanic mountain ranges, a central one parallel to the Pacific and a northern one along the border with Honduras, run across almost the entire length of the country. The two ranges divide El Salvador into three distinct and progressively higher zones. The plains along the Pacific Ocean are at sea level; the central plateau is 2,000 feet above sea level; and the northern highlands rise more than 3,000 feet. Although the central plateau represents only 25% of the total area, it contains the heaviest concentration of population and the largest cities. |
| Climate |
El Salvador's tropical climate has pronounced wet and dry seasons. The dry season, "verano" or summer, from December to April is dusty, especially in rural areas. The hottest months of the year, March and April, immediately precede the rainy season, "invierno" (winter). During the May-November rainy season, mornings are usually clear, with heavy rains in early evening and at night. Thunder and strong winds occasionally accompany the rain, and some June and September mornings are overcast. Occasional 2- to 3-day rainy spells occur. The average annual rainfall is 66 inches. The three geographic zones have distinct climatic characteristics. The narrow coastal belt is a hot tropical savanna with lush vegetation and temperatures that average 80°F. The central highlands, where San Salvador lies, are slightly cooler, with an average temperature of 73°F. San Salvador's temperatures range from 50°F to 90°F throughout the year. Incoming polar air infrequently causes cold nights and even frost. The highlands in the extreme north of El Salvador are consistently cool. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions have littered El Salvador's history. Earthquakes ranging from 6.5 to 7.9 on the Richter Scale have struck the country at least 15 times since 1700. The most serious recent earthquakes occurred on January 13 and February 13, 2001. Although damage in San Salvador was slight, schools, hospitals, businesses, and public buildings throughout the country were damaged or destroyed. These two powerful quakes resulted in 1,300 deaths and left more than one million homeless. Infrastructure damages are estimated at $1.6 billion, or 12% of the country's GDP. Of the volcanoes located within the metropolitan area of San Salvador, Volcano San Salvador erupted last in 1917 and Volcano Ilopango in 1879. Although hurricanes do not usually threaten El Salvador directly, strong Caribbean storms can generate heavy winds and rains. Hurricane Mitch hit El Salvador in November 1998, generating extreme rainfall which caused widespread flooding. |
| Border Countries | Guatemala 203 km, Honduras 342 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution; contamination of soils from disposal of toxic wastes |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea |
| Terrain | mostly mountains with narrow coastal belt and central plateau |
El Salvador Economy
How big is the El Salvador economy?
| Economic Overview |
El Salvador, the smallest country in Central America, has an economy characterized by agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Despite its small size, the country has made significant strides in economic growth and development. However, it faces numerous challenges, including poverty, violence, and the need for diversification. This article delves into the key aspects of El Salvador's economy, the challenges it faces, and the opportunities for future growth. Key Economic Sectors Agriculture Agriculture remains an important sector in El Salvador, employing a significant portion of the population. Key agricultural products include coffee, sugar, corn, and seafood. Coffee, in particular, has historically been a major export commodity, though its relative importance has declined due to market volatility and competition. The government has been working to modernize agriculture, improve productivity, and support small farmers through various programs and initiatives. Manufacturing and Industry The manufacturing sector in El Salvador includes textiles, apparel, food processing, and electronics. The country's participation in the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) has boosted its manufacturing exports to the United States. The textile and apparel industry is a significant employer, benefiting from preferential trade agreements and foreign investment. However, the sector faces challenges such as global competition and the need for technological upgrades. Services The service sector is the largest contributor to El Salvador's GDP, with significant growth in banking, finance, retail, and tourism. Remittances from Salvadorans living abroad, particularly in the United States, play a crucial role in the economy, accounting for a substantial portion of household incomes. The financial services sector has been expanding, with efforts to enhance financial inclusion and digital banking. Tourism Tourism is a growing sector, with the government promoting El Salvador as a cultural, historical, and eco-tourism destination. The country's scenic beaches, archaeological sites, and vibrant culture attract visitors worldwide. However, safety concerns and infrastructure limitations have been challenges to fully capitalizing on the tourism potential. Economic Challenges Poverty and Inequality Poverty and inequality remain significant challenges in El Salvador. Despite economic growth, a large portion of the population lives in poverty, with limited access to education, healthcare, and social services. Addressing these issues requires comprehensive social policies, investments in human capital, and efforts to create more inclusive economic opportunities. Violence and Security Issues High levels of violence and crime, driven by gang activities, have been a major impediment to economic development. The government has implemented various security measures and programs to combat violence, but sustained efforts and international cooperation are needed to create a safer environment conducive to investment and growth. Economic Diversification El Salvador's economy is relatively concentrated in a few sectors, making it vulnerable to external shocks. Diversifying the economy by developing new industries, such as technology and renewable energy, is essential for long-term stability and growth. Encouraging innovation, supporting entrepreneurship, and attracting foreign investment are critical components of this strategy. Infrastructure and Investment Inadequate infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications, challenges economic development. Improving infrastructure is vital for enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and attracting investment. The government has been working on infrastructure projects and seeking international partnerships to address these gaps. Recent Developments and Future Prospects Bitcoin Adoption In 2021, El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender. The government aims to promote financial inclusion, attract investment, and boost the economy through cryptocurrency adoption. This initiative has garnered global attention and has the potential to transform the country's financial landscape, though it also comes with risks and uncertainties. Economic Reforms The government has implemented economic reforms to improve the business environment, enhance transparency, and attract foreign investment. These reforms include tax incentives, regulatory simplification, and measures to combat corruption. Strengthening institutions and governance is crucial for sustaining these reforms and ensuring long-term economic stability. Green Economy and Sustainability El Salvador is increasingly focusing on sustainable development and the green economy. Efforts to promote renewable energy, protect natural resources, and mitigate climate change are integral to this strategy. The country invests in solar and wind energy projects, reforestation programs, and sustainable agriculture practices to build a more resilient and environmentally friendly economy. Conclusion El Salvador's economy is at a pivotal point, facing significant challenges and presenting numerous opportunities for growth and development. Addressing poverty, violence, and economic diversification is essential for creating a more prosperous and inclusive society. By embracing innovation, fostering sustainable development, and enhancing the business environment, El Salvador can pave the way for a brighter economic future. As the country navigates these economic waters, the potential for transformation and progress remains promising. |
| Industries | food processing, beverages, petroleum, chemicals, fertilizer, textiles, furniture, light metals |
| Currency Name and Code | US Dollar (USD) |
| Export Partners | US 47.1%, Honduras 13.9%, Guatemala 13.6%, Nicaragua 6.6%, Costa Rica 4.5% |
| Import Partners | US 39.4%, Guatemala 9.6%, China 8.1%, Mexico 7.4%, Honduras 5.7% |
El Salvador News and Current Events
What current events are happening in El Salvador?
Source: Google News
El Salvador Travel Information
What makes El Salvador a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
El Salvador is a democratic country with a developing economy. Tourism facilities are not fully developed. The capital is San Salvador, accessible by El Salvador's International Airport at Comalapa. The U.S. dollar has been the primary currency in El Salvador since 2001, and the economy is fully dollarized. U.S. citizens traveling with U.S. dollars should not exchange them for colones.
Crime
The Department of State considers El Salvador a critical crime threat country which means that conditions exist such that a continuous serious threat for crime, forced entries, and assaults on residents are common. In 2011, El Salvador had the second highest murder rate in the world, at 71 per 100,000 people (by comparison, the murder rate in Massachusetts, with a similar geographical area and population, was 2.6 per 100,000). In 2012, a truce between El Salvador’s two principal street gangs may have contributed to a decline in the homicide rate. According to Salvadoran police statistics, the number of murders for 2012 decreased by 41% from 2011. However, the sustainability of the decline is unclear. In addition, the number of reported robberies, assaults, rapes, and missing persons showed significant increases in 2012, and most of these crimes go unsolved.U.S. citizens do not appear to be targeted based on their nationality. However, 26 U.S. citizens have been murdered in El Salvador since January 2010. During the same time period, 274 U.S. citizens reported having their passports stolen. Armed robberies of climbers and hikers in El Salvador’s national parks is common, and the Embassy strongly recommends engaging the services of a local guide certified by the national or local tourist authority when hiking in back country areas, even within the national parks. In 2000, the National Civilian Police (PNC) established a special tourist police force (POLITUR) to provide security and assistance to tourists, as well as protection for the cultural heritage of El Salvador. It has officers located in 19 tourist destinations.
A majority of serious crimes in El Salvador are never solved; only 6 of the 26 murders of U.S. citizens since January 2010 have resulted in convictions. El Salvador’s current conviction rate for all crimes is five percent. The Government of El Salvador lacks sufficient resources to properly investigate and prosecute cases and to deter violent crime. While several of the PNC’s investigative units have shown great promise, routine street level patrol techniques, anti-gang, and crime suppression efforts are limited. Equipment shortages (particularly radios, vehicles, and fuel) further limit their ability to deter or respond to crimes effectively.
Transnational criminal organizations conduct narcotics, arms trafficking, and other unlawful activities throughout the country and use violence to control drug trafficking routes and carry out other criminal activity. Other criminals, acting both individually and in gangs, commit crimes such as murder-for-hire, carjacking, extortion, armed robbery, rape, and other aggravated assaults. According to Salvadoran government figures, out of a population of roughly six million people, there are some 40,000 known gang members from several gangs including the Mara Salvatrucha (MS-13) and Eighteenth Street (M18) gangs. Gang members are quick to engage in violence if confronted.
Extortion is a particularly serious and common crime in El Salvador. Many extortion attempts are no more than random cold calls that originate from imprisoned gang members using cellular telephones, and the subsequent threats against the victim are made through social engineering and/or through information obtained about the victim’s family. U.S. citizens who are visiting El Salvador for extended periods may be at higher risk for extortion demands. While reported rates of extortion have dropped in the last two years, recent reports show that there is an increase in the level of violence associated with extortion cases, including media reports of extortion victims and witnesses being killed. Many extortion cases are not reported for fear of reprisal and lack of faith in the ability of the government to protect the victims. Criminals have ready access to firearms and shootouts are not uncommon. Foreigners, however, may not carry guns even for their own protection without first obtaining firearms licenses from the Salvadoran government. Failure to do so will result in the detention of the bearer and confiscation of the firearm, even if it is licensed in the United States.
Travelers should remain in groups and avoid remote or isolated locations in order to minimize their vulnerability. Travelers should also avoid displaying or carrying valuables in public places. Passports and other important documents should not be left in private vehicles. Armed assaults and carjackings take place both in San Salvador and in the interior of the country, but are especially frequent on roads outside the capital where police patrols are scarce. Criminals have been known to follow travelers from the El Salvador International Airport to private residences or secluded stretches of road where they carry out assaults and robberies. Armed robbers are known to shoot if the vehicle does not come to a stop. Criminals often become violent quickly, especially when victims fail to cooperate immediately in surrendering valuables. Frequently, victims who argue with assailants or refuse to give up their valuables are shot. Kidnapping for ransom continues to occur, but has decreased in frequency since 2001. U.S. citizens in El Salvador should exercise caution at all times and practice good personal security procedures throughout their stay.
Armed holdups of vehicles traveling on El Salvador's roads are common, and we encourage U.S. citizens to remain aware of their surroundings. The U.S. Embassy warns its personnel to drive with their doors locked and windows raised, to avoid travel outside of major metropolitan areas after dark, and to avoid travel on unpaved roads at all times because of criminal assaults and lack of police and road service facilities. Travelers with conspicuous amounts of luggage, late-model cars, or foreign license plates are particularly vulnerable to crime, even in the capital.
Travel on public transportation, especially buses, both within and outside the capital, is risky and not recommended. The Embassy advises official visitors and personnel to avoid using mini-buses and regular buses and to use only radio-dispatched taxis or those stationed in front of major hotels.
U.S. citizens using banking services should be vigilant while conducting their financial exchanges either inside local banks or at automated teller machines (ATMs). There have been several reports of armed robberies in which victims appear to have been followed from the bank after completing their transactions. U.S. citizens have also been victimized at well known restaurants, hotels, and retailers within San Salvador. The Embassy has noticed a recent trend in credit card cloning and similar fraud. Credit card fraud can be difficult to recover from and can adversely affect your credit score and financial health. Using a credit card is safer than using an ATM card or Debit card to pay. With ATM or Debit cards, the money is transferred out of the account at the very moment of the transaction, and it is usually not recoverable or contestable.
For your security we recommend the following to avoid becoming a victim of credit card fraud: notify the card issuer of your travel plans, check your statements frequently, limit the number of credit cards you have and/or carry with you, limit the locations that you regularly use your card(s), maintain direct visual contact with their credit cards at all times, and shred all receipts. If you become a victim of credit card fraud, contact your bank’s fraud hotline and cancel your card immediately. They will ask you for information and will usually then send you an affidavit to sign, affirming you did not make the charges.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking the local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in El Salvador, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning for not having your passport with you. In other places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but are still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law. For example, buying pirated goods, engaging in sexual conduct with children, or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in El Salvador, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating El Salvador’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in El Salvador are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Prison and detention center conditions are harsh and dangerous. Overcrowding constitutes a serious threat to prisoners’ health and lives. In many facilities, provisions for sanitation, potable water, ventilation, temperature control, and lighting are inadequate or nonexistent.
While some countries automatically notify the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested, that might not always be the case. To ensure the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Guns: El Salvador has strict laws requiring a locally obtained license to possess or carry a firearm in the country. The Embassy strongly advises persons without a Salvadoran firearms license not to bring guns into the country or use a firearm while in El Salvador. The Embassy cannot intervene in the judicial process when a U.S. citizen is charged with a firearms or any other type of violation. Convictions for possessing an unlicensed firearm can carry a prison sentence of three to five years.
Languages
Spanish (official), Nawat (among some Indigenous)
Medical Facilities and Health Information
There are few private and no public hospitals with an environment that would be acceptable to visiting U.S. citizens. The Embassy recommends that these hospitals be used only for emergency care to stabilize a condition prior to returning to the United States for definitive evaluation and treatment. Private hospitals and physicians expect up-front payment (cash or, for hospitals, credit card) for all bills as there are no hospitals or medical offices who will bill U.S. insurance companies.Priority Ambulance (011-503-2264-7911) is the only private ambulance service with a fleet of vehicles in San Salvador that has trained personnel and medical equipment to manage emergencies. The response time is often less than ideal because of the heavy traffic in San Salvador. Therefore, whenever possible, people should transport themselves directly to the hospital by private vehicle.
Pharmacies are plentiful, but not all medicines found in the United States are available in El Salvador. Medicines often have a different brand name and are frequently more expensive than in the United States. We recommend that U.S. citizens traveling to El Salvador carry an adequate supply of any medication they require in its original container, which should be clearly labeled. A copy of the prescription from your doctor will be helpful in the event that it is requested by immigration or customs authorities.
No specific vaccinations are required for entry into El Salvador from the United States. Travelers coming from countries where yellow fever is endemic must have had a yellow fever vaccination in order to enter the country. For more information, visit El Salvador’s Immigration web site.
You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) website. For information about outbreaks of infectious diseases abroad, consult the World Health Organization (WHO) website, which contains additional health information for travelers, including detailed country-specific health information.
Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in El Salvador. For further information, please consult the CDC’s information on Tuberculosis.
Tap water is not safe to drink in El Salvador, and the Embassy advises official visitors and personnel to use either bottled water or to disinfect tap water using the guidelines suggested at the CDC website.
Safety and Security
Most travelers to El Salvador experience no safety or security problems, but the criminal threat in El Salvador is critical and a Travel Warning for El Salvador was issued on August 9, 2013. Random and organized violent crime is endemic throughout El Salvador. U.S. citizens are not normally singled out based on their nationality, but are subject to the same threats as all other persons in El Salvador. See the section below on crime for additional related information.Political or economic issues in the country may give rise to demonstrations, sit-ins, or protests at any time or place, but these activities occur most frequently in the capital or on its main access roads. U.S. citizens are cautioned to avoid areas where demonstrations are being held and to follow local news media reports or contact the U.S. Embassy for up-to-date information.
Strong undertows and currents can make swimming at El Salvador's Pacific Coast beaches extremely dangerous for even strong and experienced swimmers. Since 2008, twelve U.S. citizens have drowned while swimming in Salvadoran waters. Lifeguards are not present at beaches and lakes and access to medical resources in these areas is limited.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in El Salvador, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning El Salvador is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Major highways and thoroughfares are among the best in Central America, but road conditions throughout El Salvador are not up to U.S. standards. Even within the city of San Salvador, it is not uncommon to see missing manhole covers and large objects in the roadway marking the danger. Road travel at night is particularly dangerous outside the capital as there are few road lights and many vehicles lack adequate safety lighting or reflectors. The Embassy advises against driving outside the capital during night time or periods of low visibility. Mini-buses, regular buses, and taxis are often poorly maintained. Drivers are frequently untrained and unlicensed, and generally do not adhere to traffic rules and regulations.
Because of inconsistent enforcement of traffic laws in El Salvador, drivers must make an extraordinary effort to drive defensively. Passing on blind corners or across several lanes of traffic is commonplace. Two lane traffic circles are common in El Salvador and can be especially dangerous to navigate as it is generally understood that the traffic in the inside lane has right of way.
Although the law in El Salvador requires all parties involved in a vehicle accident to stay at the scene until the police respond, it is not unusual in minor traffic accidents for both parties to simply drive away especially if one or both drivers are uninsured. Salvadoran law requires that the driver of a vehicle that injures or kills another person must be arrested and detained until a judge can determine responsibility for the accident. This law is uniformly enforced.
Visitors to El Salvador may drive on their U.S. driver’s license for up to 30 days. After that time, a visitor is required to obtain a Salvadoran license.
Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Also, we suggest that you visit the web site of El Salvador’s national tourist office and the national authority responsible for road safety. Further information on traffic and road conditions is available in Spanish from Automovil Club de El Salvador (ACES).
