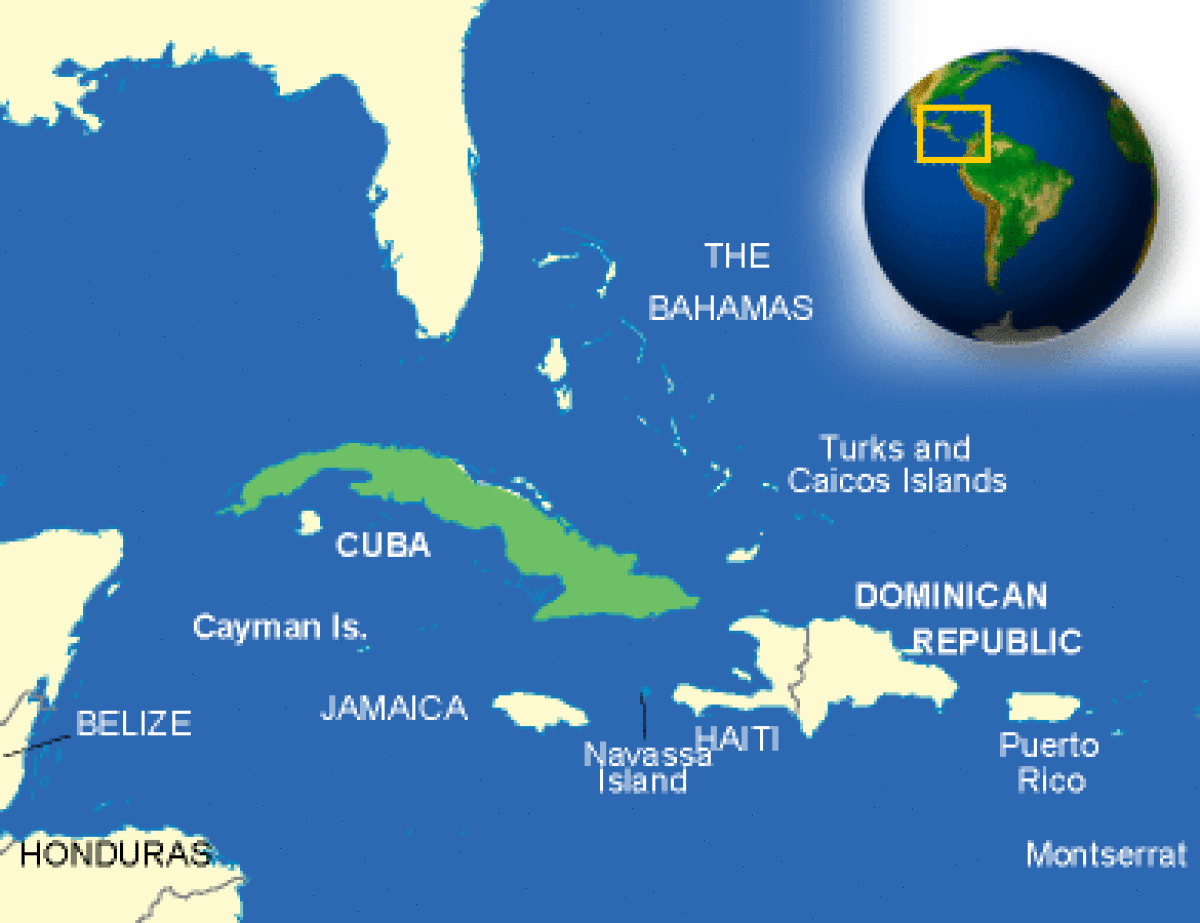
Where is Cuba located?
What countries border Cuba?
Cuba Weather
What is the current weather in Cuba?
Cuba Facts and Culture
What is Cuba famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Cubans are a generous, resourceful, and cheerful people. Daily life is challenged by economic and political problems. Nevertheless,... More
- Family: Very few new homes have been built in Cuba since the early sixties, therefore it is not unusual for three... More
- Personal Apperance: Casual dress and lightweight slacks are the norm during the day with more formal wear in the evenings. Shorts are... More
- Recreation: Baseball “pelota” is Cuba's favorite sport. Baseball was brought to Cuba in the 19th century by North Americans. Cubans also... More
- Diet: Traditional Cuban cuisine is called criollo. Traditional Cuban cooking uses hints and blends of Spanish, Afro-Caribbean, Portuguese, French, Arabic, and... More
- Visiting: It is customary to bring either wine or a small gift for the hosts. More
Cuba Facts
What is the capital of Cuba?
| Capital | Havana |
| Government Type | Communist state |
| Currency | Cuban pesos (CUP) |
| Total Area |
42,803 Square Miles 110,860 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, 150 km south of Key West, Florida |
| Language | Spanish (official) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $11,600.00 (USD) |
Cuba Demographics
What is the population of Cuba?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent racial self-identification from Cuba's 2012 national census |
| Ethnic Groups | White 64.1%, Mulatto or mixed 26.6%, Black 9.3% |
| Languages | Spanish (official) |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Cuban(s) adjective: Cuban |
| Population | 10,966,038 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.17% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 2.149 million HAVANA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 77.5% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.19% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 5,441,507 female: 5,524,531 |
Cuba Government
What type of government does Cuba have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (since 19 April 2018); Vice President Salvador Antonio VALDES Mesa (since 10 October 2019) Head of government: Prime Minister Manuel MARRERO Cruz (since 21 December 2019); Deputy Prime Ministers Ramiro VALDES Menendez, Ines Maria CHAPMAN Waugh, Jorge Luis TAPIA Fonseca, Alejandro GIL Fernandez, Ricardo CABRISAS Ruiz (since 21 December 2019), and Jorge Luis PERDOMO DI-LELLA (since 20 April 2021) Cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the president and appointed by the National Assembly Elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 19 April 2023 (next to be held in 2028) Election results: 2023: Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (PCC) reelected president; percent of National Assembly vote - 97.7%; Salvador Antonio VALDES Mesa (PCC) reelected vice president; percent of National Assembly vote - 93.4% 2018: Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez (PCC) elected president; percent of National Assembly vote - 98.8%; Salvador Antonio VALDES Mesa (PCC) elected vice president; percent of National Assembly vote - 98.1% Note - on 19 April 2018, DIAZ-CANEL succeeded Raul CASTRO as president of the Councils of State and Ministers; on 10 October 2019 he was elected to the newly created position of President of the Republic, which replaced the position of President of the Councils of State and Ministers |
| Suffrage | 16 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: yes Citizenship by descent only: yes Dual citizenship recognized: no Residency requirement for naturalization: unknown |
| National Holiday | Triumph of the Revolution (Liberation Day), 1 January (1959) |
| Constitution |
History: several previous; the latest drafted on 14 July 2018, approved by the National Assembly on 22 December 2018, and approved by referendum on 24 February 2019 Amendments: proposed by the National Assembly of People’s Power; passage requires approval of at least two-thirds majority of the National Assembly membership; amendments to constitutional articles on the authorities of the National Assembly, Council of State, or any rights and duties in the constitution also require approval in a referendum; constitutional articles on the Cuban political, social, and economic system cannot be amended |
| Independence | 20 May 1902 (from Spain 10 December 1898; administered by the US from 1898 to 1902); not acknowledged by the Cuban Government as a day of independence |
Cuba Video
YouTube: ClubTravelie Cuba, a Sea Paradise Rich in History and Culture
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Cuba Geography
What environmental issues does Cuba have?
| Overview |
With an area of more than 44,000 square miles (114,447 sq. km.), Cuba is the largest island in the West Indies, accounting for more than one-half of the total Caribbean land mass. The island is more than 745 miles (1,200 km.) long and ranges from 20 to 125 miles (35-200 km.) in width. Cuba's coastline is highly uneven and is broken into hundreds of bays, inlets, and narrow, shallow rivers. The Isle of Youth (known as the Isle of Pines in pre-Revolution days), and some 1,600 keys and islets lie offshore. The deep-water harbors of Havana, Guantánamo, and Bahía Honda rank among the world's finest. Topographically, three-fifths of Cuba displays flat or gently rolling fields and wide, fertile valleys--ideal for sugar cane and tobacco that have been the agricultural staples of the Cuban economy. The northern coast is low and somewhat rocky; the southern coast is more marshy. Most of what remains, particularly at the southeastern end of the island, forms steep and at times formidable mountains. Three mountain ranges dominate the Cuban terrain, but by far the best known and most rugged is the eastern Sierra Maestra, where peaks rise to almost 6,000 feet (1,829 m.) above sea level. |
| Climate |
Cuba is bordered on the south by the Caribbean Sea and on the north by the Gulf of Mexico and the Straits of Florida. Prevailing trade winds combine with warm waters of the Gulf Stream to produce a mild and semitropical climate. Cuba's mean temperature is about 77°F (25°C) in winter and only slightly more, perhaps 80°F to 85°F (26°C), in summer. Averages range only between 70°F (21°C) and 82°F (27°C) for the coldest and warmest months. Summer readings as high as 100°F (37°C) have been recorded. Occasional near-freezing temperatures occur only in mountain areas. Relative humidity varies from 60% to 70% in the daytime and from 80% to 90% during the night, regardless of the season, of which there are only two. The dry season lasts from November to April. During the May through October rainy season, Cuba receives up to 75% of its yearly rainfall, which averages 54 inches (137 cm). |
| Border Countries |
United States Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay 29 km Note: Guantanamo Naval Base is leased by the United States and remains part of Cuba |
| Environment - Current Issues | Air and water pollution; biodiversity loss; deforestation |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | Mostly flat to rolling plains, with rugged hills and mountains in the southeast |
Cuba Economy
How big is the Cuba economy?
| Economic Overview |
The government continues to balance the need for loosening its socialist economic system against a desire for firm political control. In April 2011, the government held the first Cuban Communist Party Congress in almost 13 years, during which leaders approved a plan for wide-ranging economic changes. Since then, the government has slowly and incrementally implemented limited economic reforms, including allowing Cubans to buy electronic appliances and cell phones, stay in hotels, and buy and sell used cars. The government has cut state sector jobs as part of the reform process, and it has opened up some retail services to "self-employment," leading to the rise of so-called "cuentapropistas" or entrepreneurs. More than 500,000 Cuban workers are currently registered as self-employed. The Cuban regime has updated its economic model to include permitting the private ownership and sale of real estate and new vehicles, allowing private farmers to sell agricultural goods directly to hotels, allowing the creation of non-agricultural cooperatives, adopting a new foreign investment law, and launching a "Special Development Zone" around the Mariel port. Since 2016, Cuba has attributed slowed economic growth in part to problems with petroleum product deliveries from Venezuela. Since late 2000, Venezuela provided petroleum products to Cuba on preferential terms, supplying at times nearly 100,000 barrels per day. Cuba paid for the oil, in part, with the services of Cuban personnel in Venezuela, including some 30,000 medical professionals. |
| Industries | Petroleum, nickel, cobalt, pharmaceuticals, tobacco, construction, steel, cement, agricultural machinery, sugar |
| Currency Name and Code | Cuban pesos (CUP) |
| Export Partners | Canada 17.7%, Venezuela 13.8%, China 13%, Netherlands 6.4%, Spain 5.4%, Belize 4.7% |
| Import Partners | Venezuela 31.8%, China 17.6%, Spain 10%, Brazil 4.8% |
Cuba News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Cuba?
Source: Google News
Cuba Travel Information
What makes Cuba a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Cuba is an authoritarian state that routinely employs repressive methods against internal dissent and monitors and responds to perceived threats to its authority. These methods include intense physical and electronic surveillance, as well as detention and interrogation of both Cuban citizens and foreign visitors. U.S. citizens visiting Cuba should be aware that any on-island activities could be subject to surveillance, and their contacts with Cuban citizens monitored closely. Human rights conditions in Cuba remain poor, as the Cuban government limits fundamental freedoms, including freedom of expression and peaceful assembly. The United States does not have diplomatic relations with Cuba, but Cuba generally welcomes U.S. citizen travelers, and U.S. citizens are generally well received. The United States Government provides consular and other services through the U.S. Interests Section in Havana (USINT), but U.S. diplomats are not allowed to travel freely outside the capital and may be prevented from providing assistance outside Havana. USINT operates under the legal protection of the Swiss government but is not co-located with the Swiss Embassy.
Crime
Official crime statistics are not published by the Cuban government, but reporting by U.S. citizens and other foreign travelers indicates that the majority of incidents are non-violent and theft-related – e.g., pick-pocketing, purse snatching, or the taking of unattended/valuable items. There is anecdotal evidence that violent crime has increased in Cuba and is generally associated with assaults committed during a burglary or robbery. The U.S. Government cannot confirm this information but rates the threat of crime in Cuba as medium. In the event of a confrontation, travelers should not resist as perpetrators may be armed. Thefts generally occur in crowded areas such as markets, beaches, and other gathering points, including Old Town Havana and the Prado neighborhood. Travelers should exercise basic situational awareness at all times and are advised not to leave belongings unattended, nor to carry purses and bags loosely over one shoulder.Visitors should avoid wearing flashy jewelry or displaying large amounts of cash. When possible, visitors should carry a copy of their passport with them and leave the original at a secure location. U.S. visitors should also beware of Cuban "jineteros" (hustlers) who specialize in swindling tourists. While most jineteros speak English and go out of their way to appear friendly, e.g., by offering to serve as tour guides or to facilitate the purchase of cheap cigars, many are in fact professional criminals who may resort to violence in their efforts to acquire tourists' money and other valuables. When exchanging currency, use state-run offices to convert dollars and avoid independent/street vendors as we have seen a slight increase in the number of persons trying to pass counterfeit bills at the Interests Section.
All travelers should ensure that valuables remain under their personal control at all times and are never put into checked baggage.
Criminal Penalties
While in a foreign country, a U.S. citizen is subject to that country's laws and regulations, which sometimes differ significantly from those in the United States and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Cuba’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Cuba are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Those accused of drug-related and other crimes face long legal proceedings and delayed due process. In one 2009 drug conviction, a U.S. citizen was sentenced to 18 years in prison. In some cases, the Cuban government has not permitted U.S. consular access to Cuban-American prisoners with dual nationality.Criminal penalties are also harsh for foreigners or dual nationals suspected of assisting Cuban migrants who attempt to leave Cuba illegally. Average jail sentences for individuals charged with migrant smuggling range from 10 to 25 years. In a 2007 case, a U.S. citizen was arrested for attempting to facilitate the illegal departure of his Cuban family members via raft. He was charged with migrant smuggling and received a jail sentence of 16 years.
Traffic laws in Cuba differ greatly from those in the United States. U.S. citizen drivers involved in traffic accidents that result in the death or injury of any party may be held criminally liable, regardless of fault. Six U.S. citizens are currently serving prison terms in Cuba for vehicular homicide, including one for a single-car accident that resulted in the death of the driver’s family-member passenger. The U.S. Interests Section recommends extreme caution when driving in Cuba as hazardous road conditions, poor signage, and jaywalking pedestrians may result in accidents. See TRAFFIC SAFETY AND ROAD CONDITIONS for more information.
The Cuban government has strict laws prohibiting the importation of weapons. The Department of State warns all U.S. citizens against taking any type of firearm or ammunition into Cuba. Entering Cuba with a firearm or even a single round of ammunition is illegal, even if the weapon or ammunition is taken into Cuba unintentionally. The Cuban government strictly enforces laws restricting the entry of firearms and ammunition at airports and seaports, and routinely x-rays all incoming luggage. U.S. citizens entering Cuba with a weapon or ammunition (including even a small number of bullets), even accidentally, are subject to fines or possible imprisonment. Travelers are strongly advised to thoroughly inspect all belongings prior to travel to Cuba to avoid the accidental import of ammunition or firearms.
For more information, please contact the U.S. Interests Section's American Citizens Services Unit at:
U.S. Interests Section
American Citizen Services Unit
Calzada, entre L y M
Vedado, Havana, Cuba
Phone: 53-7-839-4100
Fax: 53-7-839-4247
Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime, prosecutable in the United States.
Languages
Spanish (official)
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in Cuba does not meet U.S. standards. While medical professionals are generally competent, many health facilities face shortages of medical supplies and bed space. Many medications are unavailable, so travelers to Cuba should bring with them any prescribed medicine in its original container and in amounts commensurate with personal use. Travelers may also wish to consider bringing small additional amounts of prescribed medicines and over-the-counter remedies in the event that a return to the United States is delayed for unforeseen reasons. A copy of the prescription and a letter from the prescribing physician explaining the need for prescription drugs may facilitate their entry into the country.Travelers to the Havana area should be aware that U.S. and other foreign visitors are generally referred to the “tourist” Cira Garcia Hospital located in the Miramar neighborhood of Havana. Treatment at Cira Garcia and any other medical consultation requires payment in cash (see the section on Medical Insurance), and the Cuban Government disallows the use of U.S. dollars.
Safety and Security
The security environment in Cuba is relatively stable and characterized by a strong military and police presence throughout the country. Demonstrations against the United States are less frequent and smaller than in past years, are always approved and monitored by the Cuban Government, and have been peaceful in nature. The same cannot be said about state-organized demonstrations against domestic opposition groups, which can be violent. American citizens should avoid all demonstrations. Hijackings of vessels to depart Cuba are much less common. The United States Government has publicly and repeatedly announced that any person who hijacks (or attempts to hijack) an aircraft or vessel (whether common carrier or other) will face the maximum penalties pursuant to U.S. law, regardless of that person's nationality.In recent years, the Cuban government has detained U.S. citizens it suspects of engaging in activities perceived to undermine state security. In 2011, it sentenced one such U.S. citizen to a lengthy prison sentence on arbitrary charges after a two-day show trial. U.S. citizens traveling to Cuba should be aware that the Cuban Government may detain anyone at any time for any purpose and should not expect that Cuba’s state security or judicial systems will carry out their responsibilities according to international norms.
Cuban territorial waters are extremely dangerous and difficult to navigate, even for experienced mariners. The potential for running aground is very high and the bottom type is unforgiving. Search and rescue capability in Cuba is limited and running aground will often lead to the complete destruction and loss of the vessel. U.S. boaters who enter Cuban waters (legitimately or illegitimately) have encountered problems that require repairs and/or salvage; costs for both are significantly higher than comparable services in the United States or elsewhere in the Caribbean. In addition, the Government of Cuba does not allow the use of the United States dollar for transactions, and United States credit cards are not accepted in Cuba. Cuban authorities typically hold boats as collateral payment. U.S.-registered/flagged vessels belonging to U.S. citizens have been permanently seized by Cuban authorities. Due to the lack of resources, the quality of repairs in Cuba is inconsistent. Repairs take significantly longer in Cuba than they would in the United States due to a lack of the most basic materials and bureaucratic impediments. Boaters are often confined to their boats while repairs are made. Boaters can be detained while Cuban authorities investigate the circumstances of their entry to Cuba, especially if their travel documents are not in order or they are suspected of illegal activities. Mariners and their passengers should not navigate close to Cuban territorial waters without possessing a valid passport unless seeking a safe port due to emergencies. The ability of the U.S. Interests Section to assist mariners in distress is extremely limited due to Cuban restrictions on travel by U.S. personnel outside of Havana. Notifying the U.S. Interests Section, regardless of legitimately or illegitimately entering Cuban territorial seas is the most reliable way to obtain assistance.
The transfer of funds from the United States to Cuba to pay for boat repair and salvage is subject to restrictions relating to commercial transactions with the Government of Cuba. A Department of the Treasury license is required for such payments and applicants should be prepared to provide documentary evidence demonstrating the emergency nature of the repairs. U.S. credit or debit cards, personal checks, and travelers’ checks cannot be used in Cuba so boaters should be prepared to pay for all transactions in cash, keeping in mind that the Government of Cuba does not allow the use of the U.S. dollar. It is difficult to transfer money to Cuba and travelers have frequently been required to spend several hundred dollars for transportation to Havana to receive transferred funds.
For the latest security information, U.S. citizens traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department of State, at the Bureau of Consular Affairs' website, where the current Travel Warnings and Travel Alerts, as well as the Worldwide Caution, can be found.
Up-to-date information on safety and security can also be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll-free in the U.S. and Canada, or for other callers, a regular toll line at 1-202-501-4444. These numbers are available from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
The Department of State urges U.S. citizens to take responsibility for their own personal security while traveling overseas.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Cuba is provided for general reference only, and may not be necessarily accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Driving is on the right-hand side of the road, as in the United States; speed limits are sometimes posted and generally respected in urban areas. Passengers in automobiles are generally required to wear seatbelts, and all motorcyclists are required to wear helmets.
Unconfirmed reports suggest that accidents involving motor vehicles are now the leading cause of accidental death in Cuba. Many accidents involve motorists striking pedestrians or bicyclists. Drivers found responsible for accidents resulting in serious injury or death are subject to prison terms of up to 10 years, and Cuban authorities may prohibit drivers of rental cars who are involved in accidents from leaving the country until all claims associated with an accident are settled. Witnesses to vehicular accidents may not be permitted to leave Cuba until an investigation into the accident has been completed.
Taxis are available in busy commercial and tourist areas; radio-dispatched taxis are generally clean and reliable. Travelers should be cautious in sharing information with taxi drivers or other strangers. In addition, travelers should not accept rides in unlicensed taxis as they may be used by thieves to rob passengers. Buses designated for tourist travel, both between and within cities, generally meet international standards for both cleanliness and safety. Public buses used by Cubans, known as "guaguas," are crowded and unreliable and are havens for pickpockets. These public buses usually will not offer rides to foreign visitors.
Although popular with tourists, the three-wheeled, yellow-hooded “Co-Co” taxis are highly unsafe and should be avoided. “Co-Co” taxis are modified motorcycles that reach speeds of up to 40 mph but have no seat belts or other safety features.
Drivers should exercise extreme care. Although the main arteries of Havana are generally well-maintained, secondary streets often are not. Many roads and city streets are unlit, making night driving dangerous, especially as some cars and most bicycles lack running lights or reflectors. Street signage tends to be insufficient and confusing. Many Cuban cars are old, in poor condition, and lack turn signals and other standard safety equipment.
The principal Cuban east-west highway is in good condition, but it lacks lights and extends only part of the way from Havana to the eastern tip of the island. Road signage on highways may be lacking or confusing. Night driving should be strictly avoided outside urban areas. Secondary rural roads are narrow, and some are in such bad condition as to be impassable by cars. Due to the rarity of cars on rural roads, pedestrians, bicycles, horse-drawn carts, and farm equipment, operators wander onto the roads without any regard for possible automobile traffic. Unfenced livestock constitute another serious road hazard.
Rental car agencies provide roadside assistance to their clients as a condition of the rental contract. Cuban authorities may prohibit drivers of rental cars who are involved in accidents from leaving the country, even if they are injured and require medical evacuation until all claims associated with an accident are settled.
Travelers should not permit unauthorized persons to drive the rental vehicle. Automobile renters are provided telephone numbers to call in Havana or in other places where they might be motoring; agencies generally respond as needed with tow trucks and/or mechanics. A similar service is available to foreign residents of Cuba who insure cars with the National Insurance Company.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
