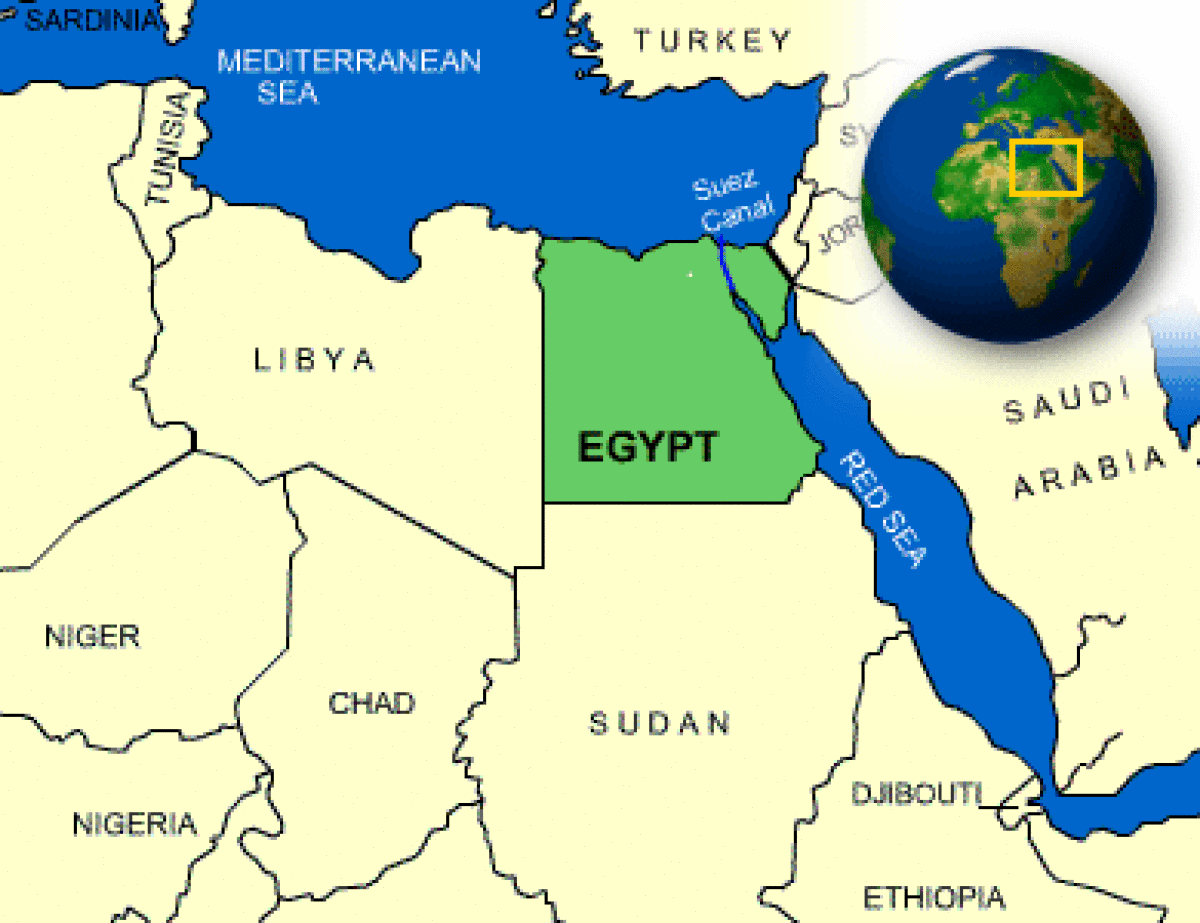
Where is Egypt located?
What countries border Egypt?
Egypt Weather
What is the current weather in Egypt?
Egypt Facts and Culture
What is Egypt famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Part of Egyptian humor is a love for riddles (especially during the month of Ramadan), jokes, sarcasm, and wordplays. Egyptians... More
- Family: In most homes, a girl is protected by her brothers and may even be accompanied by them in public. Traditionally,... More
- Personal Apperance: Dress standards in Egypt are modest and traditional. Traditional women completely cover their hair and bodies, except their faces and... More
- Recreation: The main form of recreation in cities and villages is socializing. People enjoy going to the bazaar, an outdoor market,... More
- Diet: Egyptians eat rice, bread, fish, lamb, chicken, turkey, and stuffed vegetables. Tahina (sesame seed paste), tomatoes, yogurt, and cucumbers are... More
- Food and Recipes: In restaurants, food is left behind as a sign of wealth. Bread, usually unleavened, is eaten with every meal. Tahina... More
- Visiting: Not visiting for a long period is a sign of the relationship’s insignificance. If a gift is given, it is... More
- Dating: Although attitudes toward dating are changing, dating is not widespread. Moral purity is highly valued in a woman and is... More
Egypt Facts
What is the capital of Egypt?
| Capital | Cairo |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Egyptian pounds (EGP) |
| Total Area |
386,660 Square Miles 1,001,450 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Libya and the Gaza Strip, and the Red Sea north of Sudan, and includes the Asian Sinai Peninsula |
| Language | Arabic (official), English and French widely understood by educated classes |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $12,100.00 (USD) |
Egypt Demographics
What is the population of Egypt?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent respondents by nationality |
| Ethnic Groups | Egyptian 99.7%, other 0.3% |
| Language - note | Arabic is the official language in Egypt, although English and French are used in business and education. The written language differs from the spoken Egyptian dialect used in daily life. The Cairene dialect is the standard for spoken Egyptian; the people are extremely proud of it. They like to use it for wordplays, jokes, clichés, and riddles. Cairene is therefore both the spoken language and an integral part of Egyptian culture. |
| Languages | Arabic (official), English, and French widely understood by educated classes |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Egyptian(s) adjective: Egyptian |
| Population | 111,247,248 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.49% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 22.183 million CAIRO (capital), 5.588 million Alexandria, 778,000 Bur Sa'id |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 43.1% of total population rate of urbanization: 1.9% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 57,142,484 female: 54,104,764 |
Egypt Government
What type of government does Egypt have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Abdelfattah ELSISI (since 8 June 2014) head of government: Prime Minister Mostafa MADBOULY (since 7 June 2018) cabinet: Cabinet ministers nominated by the executive branch and approved by the House of Representatives elections/appointments: president elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 6-year term (eligible for 3 consecutive terms); election last held on 26 to 28 March 2018 (next to be held 10 to 12 December 2023); prime minister appointed by the president, approved by the House of Representatives; note - following a constitutional amendment approved by referendum in April 2019, the presidential term was extended from 4 to 6 years and eligibility extended to 3 consecutive terms election results: Abdelfattah ELSISI reelected president in first round; percent of valid votes cast - Abdelfattah ELSISI (independent) 97.1%, Moussa Mostafa MOUSSA (El Ghad Party) 2.9%; note - more than 7% of ballots cast were deemed invalid |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: if the father was born in Egypt dual citizenship recognized: only with prior permission from the government residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Revolution Day, 23 July (1952) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest approved by a constitutional committee in December 2013, approved by referendum held on 14-15 January 2014, ratified by interim president on 19 January 2014 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or by one fifth of the House of Representatives members; a decision to accept the proposal requires majority vote by House members; passage of amendment requires a two-thirds majority vote by House members and passage by majority vote in a referendum; articles of reelection of the president and principles of freedom are not amendable unless the amendment "brings more guarantees;" amended 2019 |
| Independence | 28 February 1922 (from UK protectorate status; the military-led revolution that began on 23 July 1952 led to a republic being declared on 18 June 1953 and all British troops withdrawn on 18 June 1956); note - it was ca. 3200 B.C. that the Two Lands of Upper (southern) and Lower (northern) Egypt were first united politically |
Egypt Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Egypt Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Egypt Geography
What environmental issues does Egypt have?
| Overview |
The Arab Republic of Egypt is located in northeast Africa and, with the Sinai Peninsula, extends into southwest Asia. It consists of 1,002,000 square kilometers of land. There are three land borders: Israel, Libya, and the Sudan, as well as four water barriers: the Mediterranean Sea, Gulf of Suez, Gulf of Aqaba, and the Red Sea. Most of the country is part of the band of desert stretching from the Atlantic Coast of Africa to the Middle East. Geological changes have produced four distinct physical regions: the Nile River's Valley and Delta, where 95% of the population lives: the Western Desert, with two-thirds of the country's total land area in barren limestone plateaus and depressions; the Eastern Desert, scored by gullies in rugged hills; and the Sinai Peninsula, geographically a barren part of the Asian Continent, separating slowly from Africa. Only the Nile Valley, Delta, and a few desert oases can support productive agriculture. The date palm is the most prevalent indigenous tree, though frequently eucalyptus, acacia, sycamore, juniper, jacaranda, and tamarind are seen. Papyrus, once prevalent throughout Egypt, exists now only in botanical gardens. According to reports written in the first century A.D., seven branches of the Nile ran through the Delta to the Mediterranean. Since then, nature and man have closed all but two outlets: the Damietta and the Rosetta. A network of canals, salt marshes, and lakes now supplement these channels. Lower Egypt is the area north of the 30th parallel of latitude, which passes through Cairo and Suez. Upper Egypt is everything south. The highest point in the country, Jebel Katrinah (Mount St. Catherine), is 8,600 feet above sea level--a part of the red-colored Sinai terrain that gave the Red Sea its name. Nearby is Jebel Musa (Mount Sinai), the legendary site where Moses received the Ten Commandments. The lowest point, the Qattarah Depression in the Western Desert, drops at places to 132 meters below sea level. Alexandria receives the majority of Egypt's limited rainfall, with 19cm (about 7 ½ inches) being the yearly average. Two cm (about ½ inch) is the usual annual total in Cairo. |
| Climate | From November to April, temperatures range in Cairo from 40° to 65°F, and during the hot period, May to October, from 70° to 110°F. The Mediterranean coast is usually 10° cooler, while Upper Egypt is 10° to 20° warmer. Extreme temperatures during both seasons are moderated by the prevailing northerly winds. The exception is the hot, dry southerly Khamaseen, named for the number 50 because it occurs in a 50-day timeframe from April to June. With winds up to 90 miles an hour, the resulting sandstorms close down airports and roads. |
| Border Countries | Gaza Strip 11 km, Israel 266 km, Libya 1,115 km, Sudan 1,273 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | agricultural land being lost to urbanization and windblown sands; increasing soil salination below Aswan High Dam; desertification; oil pollution threatening coral reefs, beaches, and marine habitats; other water pollution from agricultural pesticides, raw sewage, and industrial effluents; limited natural freshwater resources away from the Nile, which is the only perennial water source; rapid growth in population overstraining the Nile and natural resources |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Vast desert plateau interrupted by the Nile Valley and delta |
Egypt Economy
How big is the Egypt economy?
| Economic Overview |
Occupying the northeast corner of the African continent, Egypt is bisected by the highly fertile Nile valley where most economic activity takes place. Egypt's economy was highly centralized during the rule of former President Gamal Abdel NASSER but opened up considerably under former Presidents Anwar EL-SADAT and Mohamed Hosni MUBARAK. Agriculture, hydrocarbons, manufacturing, tourism, and other service sectors drove the country’s relatively diverse economic activity. Despite Egypt’s mixed record for attracting foreign investment over the past two decades, poor living conditions and limited job opportunities have contributed to public discontent. These socioeconomic pressures were a major factor leading to the January 2011 revolution that ousted MUBARAK. The uncertain political, security, and policy environment since 2011 has restricted economic growth and failed to alleviate persistent unemployment, especially among the young. In late 2016, persistent dollar shortages and waning aid from its Gulf allies led Cairo to turn to the IMF for a 3-year, $12 billion loan program. To secure the deal, Cairo floated its currency, introduced new taxes, and cut energy subsidies - all of which pushed inflation above 30% for most of 2017, a high that had not been seen in a generation. Since the currency float, foreign investment in Egypt’s high-interest treasury bills has risen exponentially, boosting both dollar availability and central bank reserves. Cairo will be challenged to obtain foreign and local investment in manufacturing and other sectors without a sustained effort to implement a range of business reforms. |
| Industries | Textiles, food processing, tourism, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, hydrocarbons, construction, cement, metals, light manufactures |
| Currency Name and Code | Egyptian pounds (EGP) |
| Export Partners | Saudi Arabia 9.1%, Italy 7.5%, Turkey 5.8%, UAE 5.1%, United States 5.1%, UK 4.4%, India 4.1% |
| Import Partners | China 13%, Germany 7.7%, United States 5.9%, Turkey 4.5%, Russia 4.4%, Italy 4.4%, Saudi Arabia 4.1% |
Egypt News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Egypt?
Source: Google News
Egypt Travel Information
What makes Egypt a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Egypt is a republic with a developing economy. It has extensive facilities for tourists.
Crime
Following the Revolution in January 2011, the incidence of crime, including attacks on foreigners, increased throughout the country. Travelers should apply common sense personal security measures when moving about, particularly in urban areas after dark, to avoid becoming a victim. While the majority of incidents reported are crimes of opportunity, such as purse snatching and theft, there is growing and serious concern of incidents that involve weapons, including car-jackings. There have been multiple reports of men on motorcycles or in cars grabbing purses or other valuables in drive-by assaults. U.S. citizens are advised to carry mobile phones in pockets rather than on belts or in purses. Avoid wearing headphones, which make the wearer more vulnerable and readily advertise the presence of a valuable item. Limit or avoid display of jewelry as it attracts attention and could prompt a robbery attempt. Limit cash and credit cards carried on your person. Be sure to store valuables, wallet items, and passports in a safe place. Travelers are strongly cautioned not to leave valuables such as cash, jewelry, and electronic items unsecured in hotel rooms or unattended in public places. Women are vulnerable to sexual harassment and verbal abuse; the Embassy has received numerous reports of foreigners being groped in taxis and while in public places. Travelers are cautioned to be aware of their surroundings and to be cautious going anywhere with a stranger alone.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Egypt, you are subject to its laws. The Egyptian legal system is different from the legal system in the United States. If you break Egyptian laws, your U.S. passport will not prevent arrest or prosecution. Punishments often are harsher in Egypt for comparable crimes than they are in the United States. You may be detained and taken in for questioning if you do not have proper identification, such as a passport. Although the enforcement of traffic laws generally is lax, foreigners are subject to extra scrutiny and driving under the influence could result in arrest or detainment.Be aware that you can also be prosecuted for violating U.S. laws while in Egypt. Do not purchase counterfeit or pirated goods, such as DVDs. They are illegal in Egypt and in the United States. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.
While some countries routinely notify the U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested, others do not. If you are arrested or detained in Egypt, you should immediately ask authorities to notify the U.S. Embassy in Cairo.
Languages
Arabic (official), English, and French widely understood by educated classes
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care in Egypt falls short of U.S. standards. The U.S. Embassy in Cairo can provide a list of local hospitals and English-speaking physicians. Emergency and intensive care facilities are limited. Most Nile cruise boats do not have a ship's doctor, but some employ a medical practitioner of uncertain qualification. Hospital facilities in Luxor and Aswan are inadequate, and they are nonexistent at most other ports-of-call. The Egyptian ambulance service hotline is 123, but Egyptian ambulance service is not reliable.Beaches on the Mediterranean and Red Sea coasts are generally unpolluted. However, persons who swim in the Nile or its canals, walk barefoot in stagnant water, or drink untreated water are at risk of exposure to bacterial and other infections and the parasitic disease schistosomiasis (bilharzia).
It is generally safe to eat freshly prepared cooked food in hotels, on Nile cruise boats, and in mainstream restaurants. When selecting a restaurant, select a clean and reputable place,eat only freshly prepared, cooked foods, avoid all uncooked food including raw fruits and vegetables. Tap water in many locations is not potable. It is best to drink bottled water or water that has been boiled and filtered. Well-known brands of bottled beverages are generally considered to be safe if the seal is intact.
Safety and Security
Political protests occur often throughout Egypt. We remind U.S. citizens that even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and possibly escalate into violence. Demonstrations have led to frequent violent clashes between police and protesters, resulting in deaths, injuries, and property damage. In some areas, protesters have blocked major streets and bridges, burned tires and debris, established unofficial checkpoints, and thrown rocks and Molotov cocktails. Security forces have responded with tear gas, crowd-control measures, and firearms to disperse demonstrations. Protests can occur with little to no warning in any area, but Cairo's Tahrir Square; Nasr City near Rabaa Aladawiya; Dokki near Cairo University; and Salah Salem Road, as well as the AlQaed Ibrahim, Sidi Gaber and Sidi Beshr areas of Alexandria have been favored locations for rallies and demonstrations, particularly on Fridays. Protests and incidents of political violence have occurred with greater frequency at universities. Although the state of emergency and curfew imposed in August 2013 were rescinded in November, armed security forces remain heavily deployed in many areas.On June 28, 2013, a U.S. citizen was killed during a demonstration in Alexandria. Women in particular are advised to avoid demonstrations as there have been multiple reports of gender-based violence and sexual assaults against both foreign and Egyptian women. U.S. citizens are advised that it is illegal to photograph certain facilities in Egypt, and enforcement of this law is particularly strict at demonstrations. U.S. citizens have been detained, questioned and in some cases deported for taking pictures or videos of protests or military and police personnel, facilities and equipment.
Protests and public disorder are not confined to Cairo and Alexandria. Sohag, Suez, Port Said, Fayoum, Minya, Qena, Asyut, and the Sinai Peninsula have also witnessed incidents of political violence. U.S. Embassy personnel traveling to these areas require advance approval. Egyptian authorities also restrict the travel of foreigners to certain locales. U.S. citizens planning to travel beyond Cairo and Alexandria should contact the Embassy prior to travel. Large gatherings in Egypt, including sporting events such as soccer matches, can cause major traffic disruptions and sometimes turn violent. U.S. citizens should exercise extreme caution if attending soccer matches in Egypt, be aware of the potential for snarled traffic and agitated crowds after sporting events, and avoid venues--such as bars and coffee houses--where large numbers of people gather to watch sporting events on television. We strongly urge you to avoid crowds, to exercise extreme caution if within the vicinity of any large public gatherings, and to stay well away from demonstrations.
U.S. citizens are urged to remain alert to local security developments and to be vigilant regarding their personal security by knowing the locations of police and fire stations, hospitals, and other places to relocate to feel secure. If you are concerned for your security, you should exercise personal responsibility, remove yourself from the situation, and relocate to an area where you feel secure. U.S. citizens are advised to avoid urban areas after dark. U.S. citizens should also carry identification and a cell phone or other means of communication that works in Egypt. U.S. citizens are encouraged to make common sense plans to deal with security situations and to investigate alternate means of communication in country, evacuation insurance, and alternative destinations both within and outside the country in case of emergency.
Terrorism: Egypt witnessed several terrorist incidents in 2013. A large number of these incidents specifically targeted Egyptian security forces and infrastructure, including the attempted assassination of the Minister of Interior, attacks on police stations, and the discoveries of explosive devices in Cairo and elsewhere. The authorities have made several arrests and responded with heavy police and military presence throughout the country. Responsibility for these attacks has been attributed primarily to jihadist elements operating out of the Sinai Peninsula, which remains a particularly restive region. Foreign tourists, including U.S. citizens, were kidnapped in the Sinai in 2012 and 2013. U.S. citizens who plan to visit there in spite of the persistent threat of kidnapping and terrorist attacks should exercise extreme caution. U.S. citizens should be especially vigilant in crowded tourist areas, practice good personal security measures, and be alert to their surroundings. Travelers should avoid resorts and hotels that lack significant physical setback from roads and adequate security procedures. U.S. citizens are encouraged to visit the U.S. Embassy in Cairo website for the most up-to-date security information.
Alexandria: The State Department lifted ordered departure status for employees of the U.S. Consulate General Alexandria and their family members on December 16, 2013. Even though ordered departure status has been lifted, security upgrades required for U.S. government facilities in Alexandria mean that U.S. Consulate General personnel will be based out of the U.S. Embassy in Cairo while these upgrades are made.
Restricted Areas: The U.S. Embassy restricts its employees and their family members from traveling to specific areas and advises all U.S. citizens to do the same. U.S. Embassy personnel in Egypt are currently prohibited from traveling to the Sinai, except by air to Sharm El Sheikh. Overland personal travel by U.S. government employees anywhere in the Sinai outside of Sharm El Sheikh is prohibited. In addition, travel by road by U.S. government employees west of Marsa Matruh on the north coast is prohibited. Travel between Fayoum, Asyut, Sohag, and Qena is only approved on a case-by-case basis. Reports indicate that the security situation in the northern Sinai area, which is generally defined as the area north of the Cairo-Nekhl-Taba and Sheikh Zeid road, remains difficult due to the continuing potential for violence. Travelers should be aware of the possible dangers of overland travel.
Safari travelers must obtain permission and a travel route from the Egyptian Military Intelligence and the Tourist Police Headquarters via a local or overseas travel agency to access Egypt's frontiers, including the borders with Libya, Sudan, Israel, and parts of the Sinai off paved roads. Police escorts are assigned to accompany foreigners during their tour.
Travelers should be aware that landmines have caused many casualties in Egypt, including deaths of U.S. citizens. All travelers should check with local authorities before embarking on off-road travel. Known minefields are not reliably marked by signs, but are sometimes enclosed by barbed wire. Heavy rains can cause flooding and move landmines, and travelers should be exercise caution when encountering sand drifts on roadways. Though mines are found in other parts of Egypt, the highest concentrations are in World War II battlefields along the Mediterranean coast west of Alexandria, the Eastern Desert between Cairo and the Suez Canal, and much of the Sinai Peninsula. Travelers are urged to be especially prudent in these areas.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Egypt, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Egypt is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Driving in Egypt, a country with one of the world’s highest rates of road fatalities per mile driven, is a challenge. Even seasoned residents of Cairo must use extraordinary care and situational awareness to navigate the hectic streets of the capital. Traffic rules routinely are ignored. Any visiting U.S. citizens thinking about driving in Cairo should carefully consider their options, take the utmost precautions, and drive defensively. Drivers should be prepared for motorists not using their headlights at night; few, if any, road markings; vehicles traveling at high speeds; vehicles traveling the wrong way on one-way streets; divided highways and connecting ramps; pedestrians dodging in and out of traffic; and a variety of animals on the roads. Traffic lights in Cairo are not functional. Instead, major intersections are staffed by police who gesture to indicate which cars may move. Pedestrians should exercise extreme caution when traversing roadways, especially in high-volume/high-velocity streets such as Cairo's Corniche, which follows the east bank of the Nile River. Motorists in Egypt should be especially cautious during the rare winter rains, which can cause extremely slippery road surfaces or localized flooding.
Accidents involving public mini- and microbuses are frequent, including serious incidents involving fatalities. Riders also are subject to pick-pocketing and other crimes. For these reasons, the Embassy strongly recommends that its personnel not use them. Intercity roads are generally in good condition, but unmarked surfaces, stray animals, and vehicles that halt or turn without warning are among the many hazards that can be encountered on highways. Disabled vehicles or motorists who do not use their lights after dark pose additional dangers. U.S. Embassy personnel in Egypt are prohibited from traveling by road outside Cairo after sunset. In addition, some roads, especially in the Sinai and southeastern part of the country, are off-limits to foreigners. Traffic warning signs should be respected. Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of Egypt’s national tourist office and national authority for road safety.
Trains are usually a safe means of transportation in Egypt. However, there have been several collisions of trains and traffic accidents on railway tracks between 2009-2013 in the greater Cairo and Upper Egypt areas where a number of Egyptian nationals were killed or injured.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
