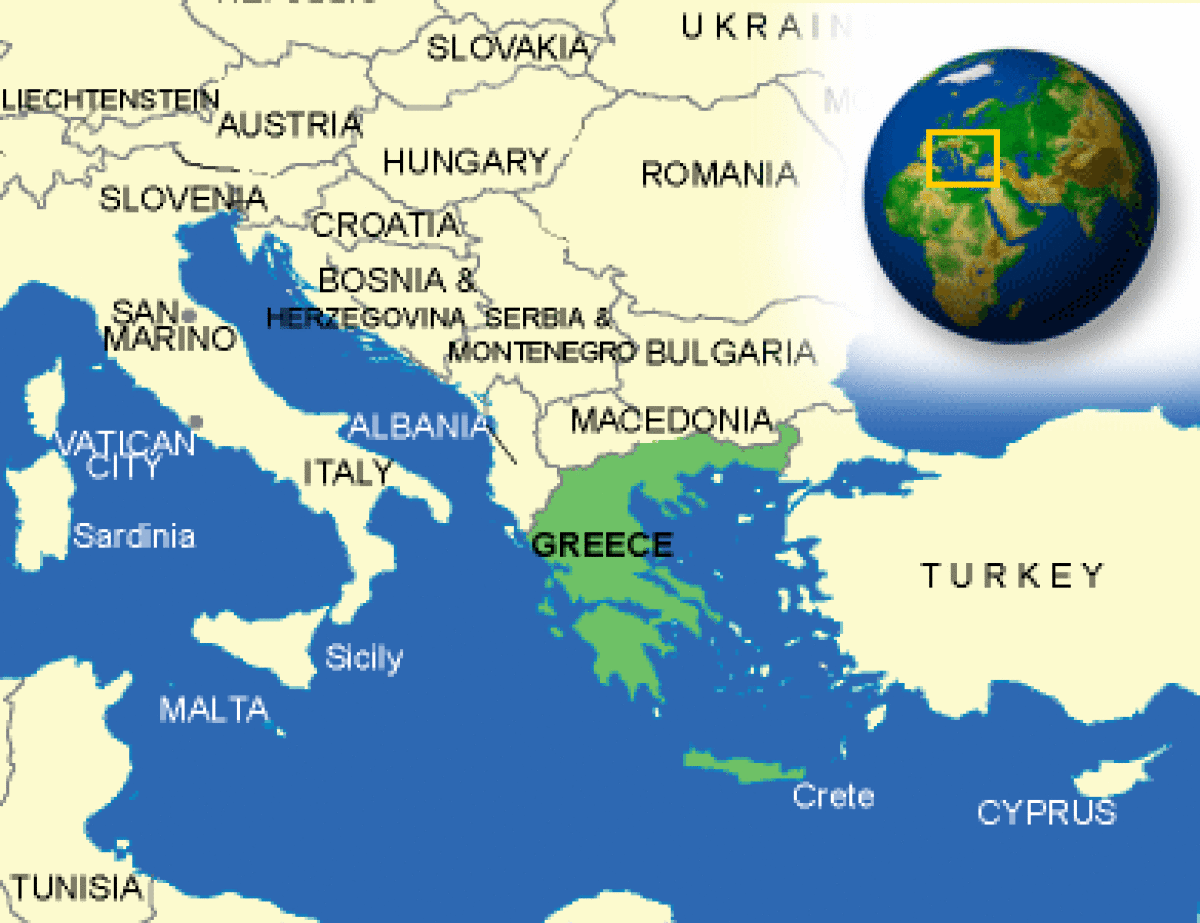
Where is Greece located?
What countries border Greece?
Greece Weather
What is the current weather in Greece?
Greece Facts and Culture
What is Greece famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: While women have gained greater prominence and rights in the last generation, Greek society is still male-dominated. Men may attribute... More
- Family: The elderly are respected, and have much authority in society. They are addressed by courteous titles and are served... More
- Personal Apperance: People in Greece typically dress in a blend of modern Western styles and traditional elements, depending on the occasion and... More
- Recreation: Ancient Greeks were proud of their athletic skills and held the first Olympic Games in 776 B.C. These games were... More
- Diet: While tastes vary between urban and rural dwellers, certain foods are common to all Greeks, such as lamb, seafood, olives... More
- Food and Recipes: The main meal of the day is lunch, served in the early afternoon. However, lunch is becoming less important as... More
- Visiting: It is very common for friends and relatives to drop by unannounced in rural towns. Unnanounced visits occur less often... More
- Dating: Young men and women socialize like the rest of Europe. They enjoy dancing, visting clubs and eating out. More
Greece Facts
What is the capital of Greece?
| Capital | Athens |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
50,949 Square Miles 131,957 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Europe, bordering the Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea, between Albania and Turkey |
| Language | Greek (official) 99%, |
| GDP - real growth rate | -2.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $25,600.00 (USD) |
Greece Demographics
What is the population of Greece?
| Ethnic Group - note | note: data represent citizenship; Greece does not collect data on ethnicity |
| Ethnic Groups | Greek 91.6%, Albanian 4.4%, other 4% |
| Languages | Greek (official) 99%, other (includes English and French) 1% |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Greek(s) adjective: Greek |
| Population | 10,461,091 |
| Population Growth Rate | -0.35% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 3.154 million ATHENS (capital), 815,000 Thessaloniki |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 80.7% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.11% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 5,117,862 female: 5,343,229 |
Greece Government
What type of government does Greece have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Ekaterini SAKELLAROPOULOU (since 13 March 2020) head of government: Prime Minister Kyriakos MITSOTAKIS (since 26 June 2023) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister elections/appointments: president elected by Hellenic Parliament for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 January 2020 (next to be held by February 2025); president appoints as prime minister the leader of the majority party or coalition in the Hellenic Parliament election results: 2020: Katerina SAKELLAROPOULOU (independent) elected president by Parliament - 261 of 300 votes; note - SAKELLAROPOULOU is Greece's first woman president 2015: Prokopis PAVLOPOULOS (ND) elected president by Parliament - 233 of 300 votes |
| Suffrage | 17 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Greece dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 25 March (1821) |
| Constitution |
history: many previous; latest entered into force 11 June 1975 amendments: proposed by at least 50 members of Parliament and agreed by three-fifths majority vote in two separate ballots at least 30 days apart; passage requires absolute majority vote by the next elected Parliament; entry into force finalized through a "special parliamentary resolution"; articles on human rights and freedoms and the form of government cannot be amended; amended 1986, 2001, 2008, 2019 |
| Independence | 3 February 1830 (from the Ottoman Empire); note - 25 March 1821, outbreak of the national revolt against the Ottomans; 3 February 1830, signing of the London Protocol recognizing Greek independence by Great Britain, France, and Russia |
Greece Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Greece Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Greece Geography
What environmental issues does Greece have?
| Overview | Greece, a rugged country of mountains and islands. The land area, including the islands, is 50,270 square miles (about the size of Alabama). Only 25% of the land is arable, and much of that is dry and rocky. |
| Climate |
Greece has mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Athens daytime summer temperature averages 90°F and often exceeds 100°F for periods in July-August. Humidity is low and the heat is tempered by sea breezes. Summer evenings are comfortable outdoors. Spring and fall temperatures are pleasant, and winter temperatures are 30°-55°F. Snow flurries occur, particularly in the northern suburbs, but seldom accumulate. Air pollution is a major problem in Athens throughout the year, but the climate is otherwise healthy. Thessaloniki, in northern Greece, experiences high temperatures and humidity from the end of May until the end of September. Summer heat is sometimes tempered by late morning and early evening breezes. July and August nights can be uncomfortably warm. In winter, periods of mild, sunny, and spring-like weather are interspersed with uncomfortable cold periods. Thessaloniki has periods of chilly and damp weather, with considerable rainfall and occasional snow. Temperatures often fall below freezing in winter. Although snow does not linger, the city has been struck by blizzards. One feature of Thessaloniki’s climate is the vardari, a strong northwesterly wind that appears suddenly and irregularly from the area of the Axios (Vardar) River Valley. |
| Border Countries | Albania 282 km, Bulgaria 494 km, Turkey 206 km, Macedonia 246 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution; water pollution |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds |
| Terrain | mostly mountains with ranges extending into the sea as peninsulas or chains of islands |
Greece Economy
How big is the Greece economy?
| Economic Overview |
Greece's economy has shown signs of recovery and growth after a prolonged period of financial crisis that began in 2009. The crisis was characterized by high levels of public debt, a significant budget deficit, and structural weaknesses in the economy, leading to severe austerity measures and international bailouts. Key Points of Greece's Economy: Economic Growth: Greece has experienced moderate economic growth in recent years. The tourism sector, a vital part of the economy, has been a significant driver of this growth, alongside a resurgence in exports and increased foreign investment. Unemployment: Unemployment rates, which soared during the crisis, have been gradually declining but remain high compared to the European Union average. Youth unemployment is particularly concerning, although it has improved somewhat. Public Debt: Greece's public debt remains one of the highest in the world relative to its GDP. Debt relief measures and restructuring by the EU and IMF have provided some relief, but managing this debt continues to be a major challenge. Reforms and Austerity: The government has implemented numerous economic reforms and austerity measures aimed at stabilizing the economy. These include pension cuts, tax hikes, and privatizations, which have been necessary for securing international financial assistance but have also led to social and political unrest. Banking Sector: The Greek banking sector has undergone significant restructuring, with banks recapitalized and efforts made to address the high levels of non-performing loans. Confidence in the banking system is slowly being restored. Investment and Business Climate: Efforts to improve the business climate have been ongoing, with initiatives to reduce bureaucracy, enhance digital infrastructure, and attract foreign direct investment. These measures aim to foster entrepreneurship and innovation. Challenges and Outlook: Despite positive signs, challenges remain. These include the need for further structural reforms, reducing unemployment, managing public debt, and addressing social inequalities. The geopolitical situation in the region and global economic trends also impact Greece's economic outlook. |
| Industries | tourism, food and tobacco processing, textiles, chemicals, metal products; mining, petroleum |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Italy 9.5%, Turkey 7.9%, Germany 7.9%, Cyprus 6.1%, Bulgaria 5.5%, US 5.2% |
| Import Partners | Germany 10.6%, Russia 9.4%, Italy 9.2%, China 5.7%, Netherlands 5.5%, France 5%, Iran 4.5% |
Greece News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Greece?
Source: Google News
Greece Travel Information
What makes Greece a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Greece is a developed and stable democracy with a modern economy. Tourist facilities are widely available.
Crime
You should take the usual safety precautions you would in any urban or tourist area during a visit to Greece. Crimes against tourists (such as pick-pocketing and purse-snatching) occur at popular tourist sites and on public transportation - especially the Metro - and in some shopping areas in and around Thessaloniki. If you travel by Metro, keep track of your purse/backpack/wallet at all times. Thieves will often try to create a diversion to draw your attention away from your immediate surroundings. These diversions can include accidentally sneezing or spilling something on you and loudly accusing you of having bumped into them. Thieves ride the trains in from the Athens Airport, so be especially careful when you first arrive. You may be tired and a bit disoriented and you may have just visited the ATM or exchanged money. Be discreet when discussing plans and organizing your belongings upon your initial arrival. Always keep a close eye on your suitcase. Try to avoid standing near the doors, as thieves will often wait to strike just as the train/bus doors open and then dash onto the platform and disappear into the crowd. Omonia, Vathi, and Kolokotroni Squares in Athens, while very close to the tourist sites, are areas with high crime rates; Glyfada Square has a significant organized-crime network associated with its clubs, which should be avoided if you get a hard-sell pitch for business. Never agree to go to a bar or club with someone you have just met on the street. Sexual assaults of U.S. citizens, including date or acquaintance rape, are not uncommon. Drink alcohol in moderation and stay in control. Never leave your drink unattended in a bar or club. Some bars and clubs serve counterfeit or homemade spirits of unknown potency.Dont buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even those widely available, along the sidewalks in Central Athens or Thessaloniki. Not only are these goods illegal to bring back into the United States, the purchase of bootlegs and knock-offs in Greece violates Greek law.
Due to an increase of card skimming at ATMs throughout Greece it is recommended that you use one located inside a bank or hotel. Do not use ATMs located in dark or isolated areas. Before using an ATM, check to see if anything is stuck to the machine and/or if it looks unusual in any way. When using an ATM, always stay focused on what you are doing, and cover the keypad with your free hand to prevent anyone from seeing your PIN.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Greece, you are subject to its laws, even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Greek laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Greece are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.Mace or pepper-spray canisters, though legal in the U.S., are illegal in Greece. Such items will be confiscated and may result in detention and arrest.
If you are arrested in Greece, the authorities are required to notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate on your behalf.
Languages
Greek (official) 99%, other (includes English and French) 1%
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are adequate, and some, particularly the private clinics and hospitals in Athens and Thessaloniki, are quite good. Some private hospitals have affiliations with U.S. facilities, and generally their staff doctors have been trained in the United States or Europe.Public medical clinics, especially on the islands, may lack resources; care can be inadequate by U.S. standards, and often, little English is spoken. Many patients-- Greeks and visitors alike-- are transferred from the provinces and islands to Athens hospitals for more sophisticated care. Others may choose to transfer from a public to a private hospital within Athens or Thessaloniki. U.S. citizens choosing to do so would arrange for an ambulance belonging to the private hospital to transport them from the public hospital to the private one. The cost of the ambulance for this transfer, as well as all expenses in a private hospital, must be borne by the patient. Private hospitals will usually demand proof of adequate insurance or cash before admitting a patient.
Nursing care, particularly in public hospitals, may be less than adequate. For special or through-the-night nursing care, it is suggested that a private nurse be hired or a family member or friend be available to assist. One parent or a private nurse should always plan to stay with a hospitalized child on a 24-hour basis, as even the best hospitals generally maintain only a minimal nursing staff from midnight to dawn on non-emergency floors or wards.
Please insure that you have an adequate supply of your prescription medications when travelling to Greece as you may not be able to find a local equivalent in the pharmacies.
Safety and Security
The U.S. Government remains deeply concerned about the heightened threat of terrorist attacks against U.S. citizens and interests abroad. Like other countries that are members of the Schengen Agreement for free cross-border movement, Greece's open borders with other members of the Schengen zone allow for the possibility of terrorist groups entering/exiting the country with anonymity. As the first entry point into Schengen from points south and east, Greece's long coastline and many islands increase the possibility that foreign-based terrorists might try to enter Europe through its borders.Greece continues to experience sporadic violence attributed to terrorist organizations. In 2012, a previously unknown domestic group placed an improvised explosive device (IED) that failed to detonate in a metro train car, and another group crashed a stolen van into the lobby of a corporate headquarters in Athens before activating an attached improvised incendiary device (IID, also known as a Molotov cocktail). In 2013, unknown individuals conducted attacks on the homes of journalists and judges, as well as several political party offices, in Athens and Thessaloniki; a previously unknown domestic group claimed responsibility for planting a small bomb in a prominent shopping mall in a northern suburb of Athens, causing minor injuries to two people; and alleged members of the domestic terrorist group Conspiracy of Fire Nuclei were arrested for armed bank robbery in northern Greece.
Strikes and demonstrations are a regular occurrence. As a result of austerity measures imposed by the government and the ongoing economic recession, labor unions, certain professions, and other groups affected by the current financial crisis hold frequent demonstrations, work stoppages, and marches throughout the center of Athens. Strikes in the transportation sector often affect traffic and public transportation, to include taxis, ports, and airports; most are of short duration, but you should always reconfirm domestic and international flights before heading to the airport. Demonstrations also occur annually on November 17, the anniversary of the 1973 student uprising against the military regime in power at the time.
University campuses are exploited as refuges by anarchists and criminals. Demonstrators frequently congregate in the Polytechnic University area; Exarchia, Omonia, and Syntagma Squares in Athens; and at Aristotle Square, Aristotle University, and the Kamara area in Thessaloniki. U.S. citizens should be aware of demonstrations and avoid areas where demonstrations are underway.
While most demonstrations and strikes are peaceful, on occasion violent anarchist groups have joined these demonstrations to clash with police and vandalize public and private property. Riot-control procedures often include the use of tear gas and/or water cannons. Visitors should stay informed about demonstrations from local news sources and hotel security.
There has been a rise in unprovoked harassment and violent attacks against persons who, because of their complexion, are perceived to be foreign migrants. U.S. citizens most at risk are those of African, Asian, Hispanic, or Middle Eastern descent. Travelers are urged to exercise caution, especially in the immediate vicinity of Omonia Square from sunset to sunrise. Travelers should avoid Exarchia Square and its immediate vicinity at all times. The U.S. Embassy has confirmed reports of U.S. African-American citizens detained by police authorities conducting sweeps for illegal immigrants in Athens.
U.S. citizens are strongly urged to carry a copy of their passport or some form of photo identification with them at all times when traveling in Greece.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Greece, you will encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. Drivers and pedestrians alike should exercise extreme caution when operating motor vehicles or when walking along roadways or crossing streets, mindful that Greece's traffic fatality rates are the fourth-highest of the 27 nations that make up the European Union. Visitors to Greece must be prepared to drive defensively. Heavy traffic, poor roads, and high speeds pose hazards, especially at night or in inclement weather. Be especially careful if you are riding a motorbike. The law in Greece requires motorcyclists to wear a helmet. You may see many wearing theirs on the arm, but do not be tempted to follow their example. When driving, be sure to double-check rear and side mirrors, as motorbikes will often ride between lanes and pass on both the left and right. On many two-lane highways, slower traffic will drive on the shoulder and cars will pass straddling the center, double yellow line. Talking on a cell phone while driving is illegal in Greece; the police check cell phone call records when investigating accidents. Driving while under the influence of an alcoholic substance is illegal. A breath-alcohol test (BrAC) showing 250-400 carries a fine of 200; from 400-600, it is 700 and a three-month suspension from driving; if your BrAC is more than 600 the case is remanded to the local court of misdemeanors. Additionally, the blood-alcohol content limit is 0.05% (mg/L), lower than the U.S. limit of 0.08%. For motorcyclists, professional drivers, and those holding a license less than two years the limit is 0.01%. Exceeding the limit may result in arrest, heavy fines, and/or license confiscation. There are a number of nationwide auto-service clubs and plans, similar to those in the United States, providing towing and roadside service, which a tourist can call and pay for per service; the largest, quite similar to AAA, is ELPA, whose nationwide phone number is 10400.Tourists and temporary residents who will stay in Greece for fewer than 185 days, and plan to drive, must carry a valid U.S. license as well as an international driver's permit (IDP). Failure to have both documents may result in police detention or other problems. The U.S. Department of State has designated two organizations to issue IDPs to those who hold valid U.S. driver's licenses: AAA and the American Automobile Touring Alliance. Issuance of an IDP is quick and inexpensive, but must generally be done before a traveler leaves the United States. Vehicles may not properly be rented without the IDP, although sometimes they are. A driver without one, however, will be cited for failure to have one in the event of an accident, and may be open to civil suit as well. Fines are high. Small motorbike rental firms frequently do not insure their vehicles; customers are responsible for damages and should review their coverage before renting. Individuals who expect to spend more than 185 days in Greece should either obtain a Greek license or convert their valid U.S. license for use in Greece through their local Nomarchy Office of Transportation and Communications.
